Vestibular Apparatus and Equilibrium
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Hearing and balance are provided by the structures of ?
The Inner Ear
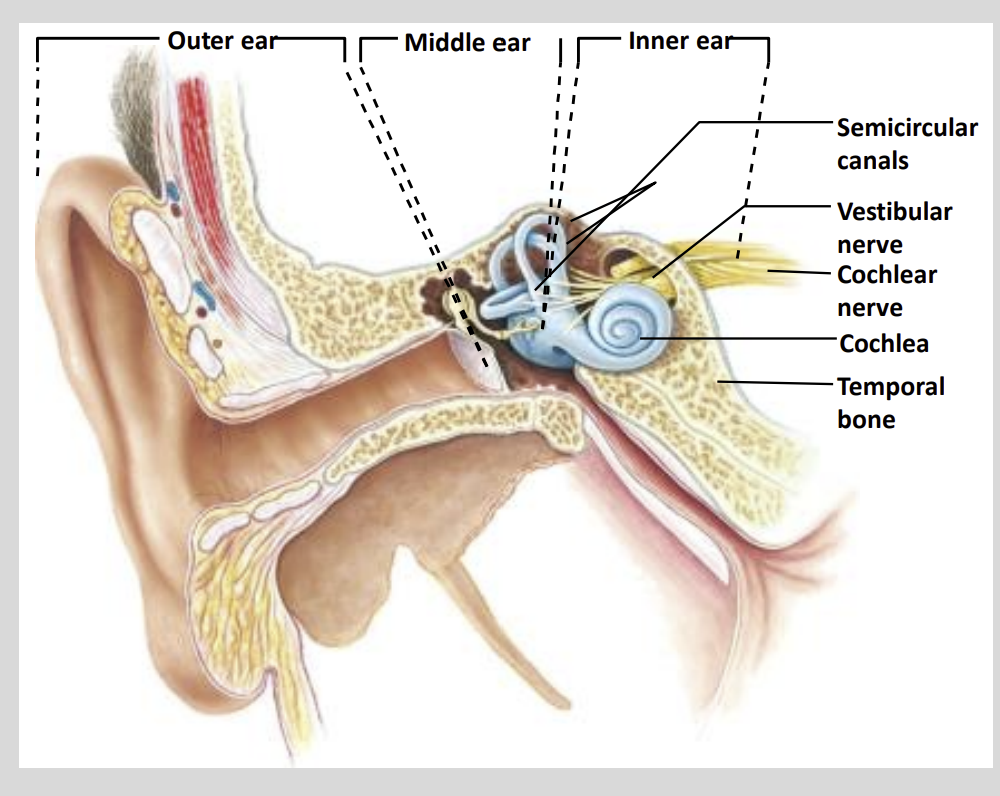
Ear Structure Diagram
Equilibrium is a sense of ?
Balance & Orientation
In respect to gravity
provided by the Vestibular Apparatus
Static Equilibrium is sensed when?
The Head is still.
Dynamic Equilibrium is sensed when ?
The head is moving.
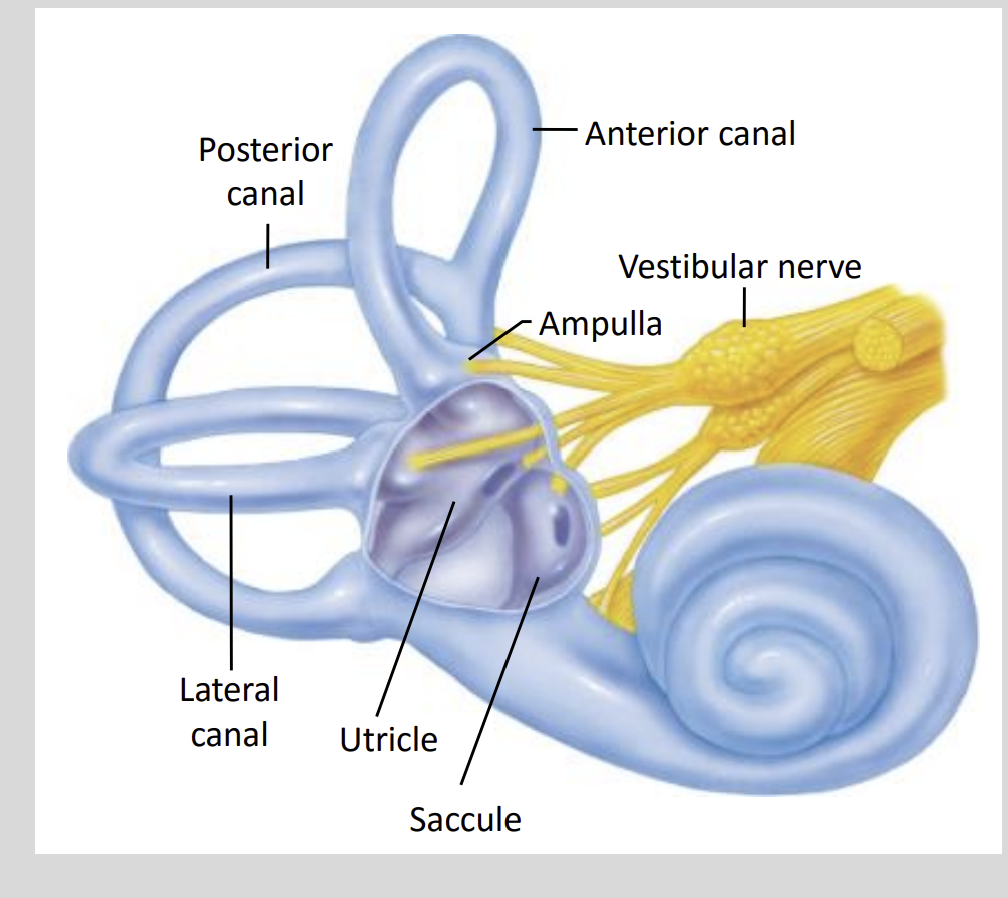
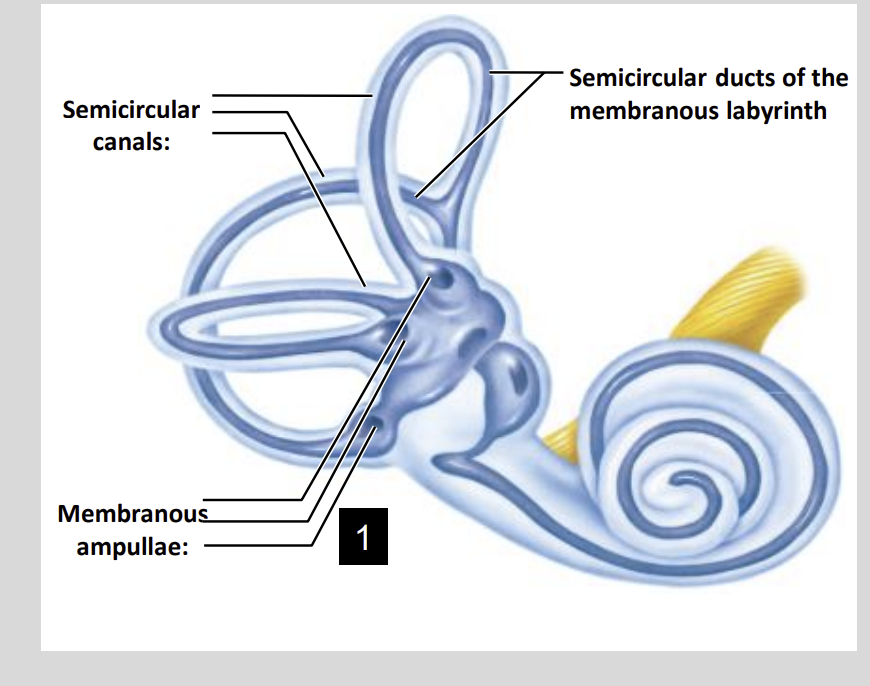
Vestibular Apparatus Diagram Structure?
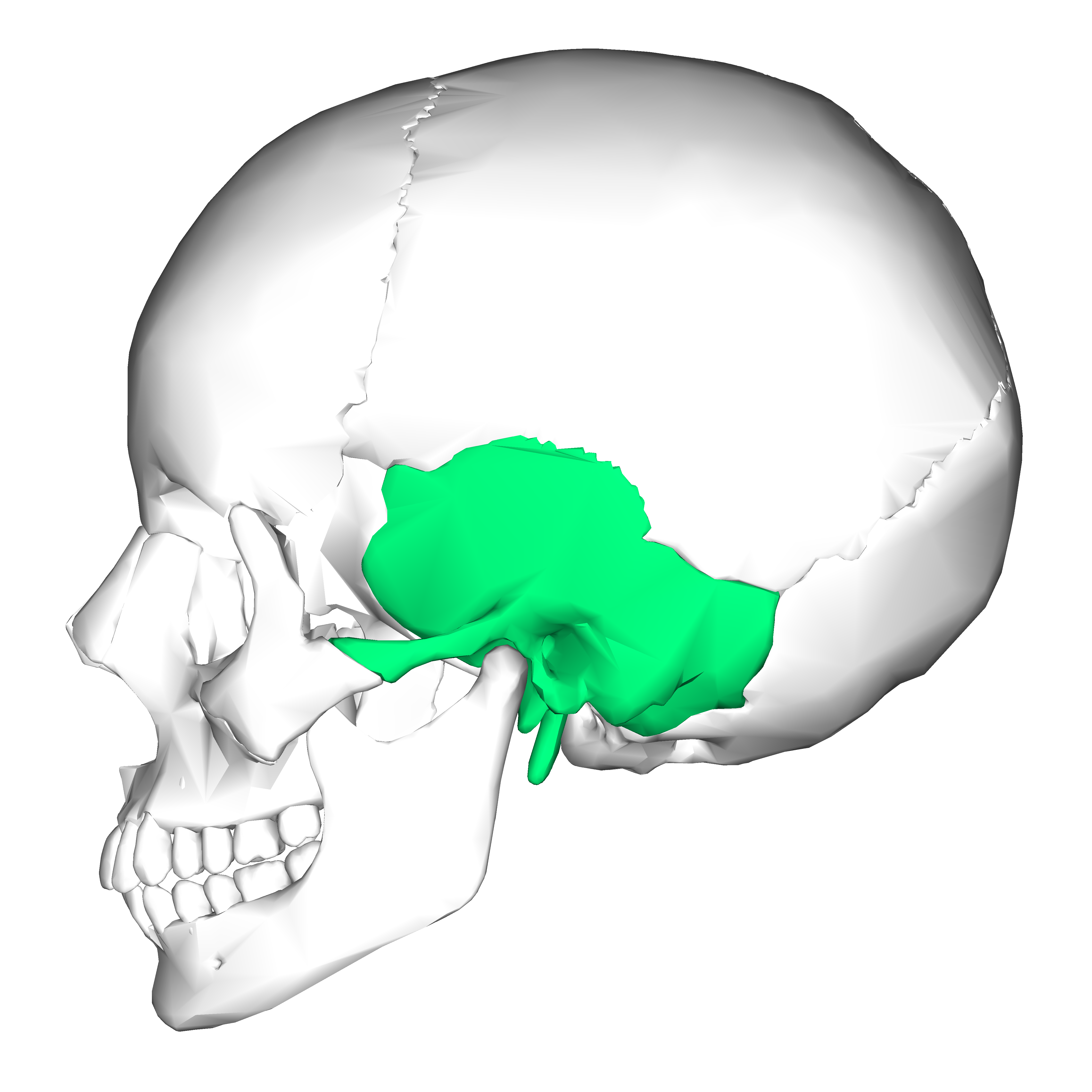
Vestibular Apparatus is located within what bones of the Skull?
Temporal Bones
What does the Vestibular Appartus consist of?
3 Semicircular Canals
- Posterior, Anterior & LateralOtolith Organs
- Utricle & Saccule
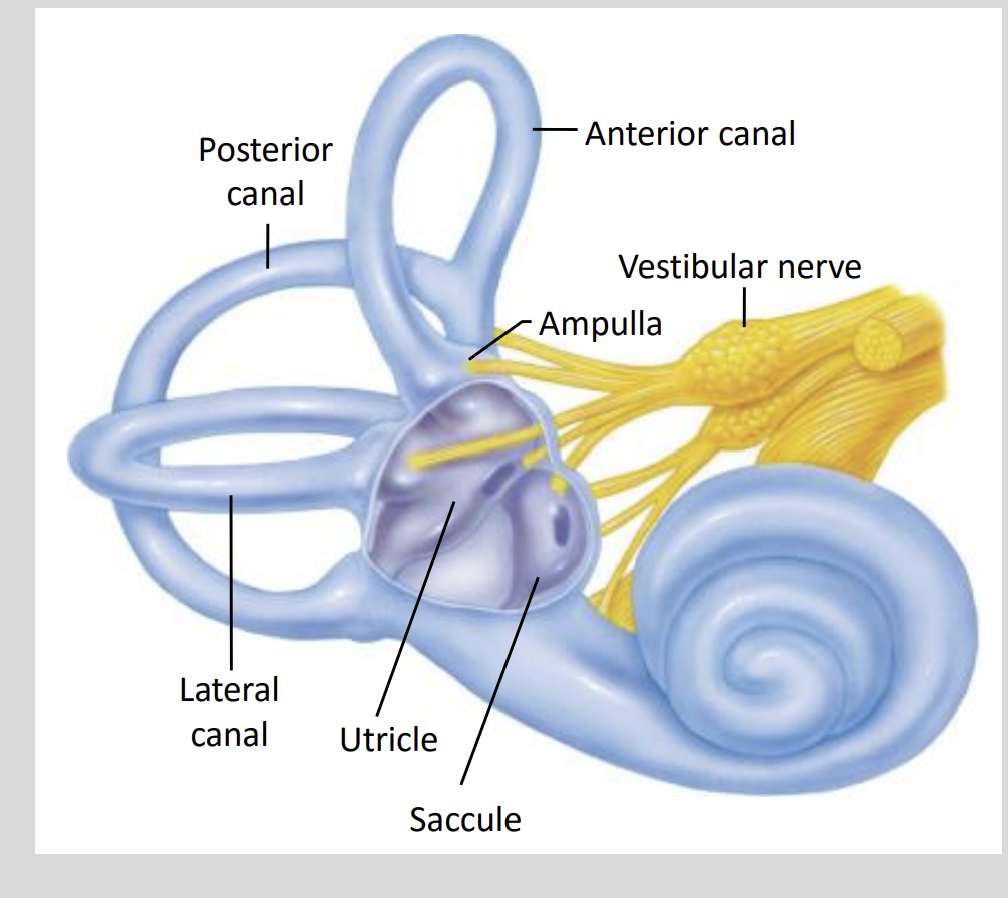
The Semi CC detect?
Rotational and Angular Forces
The anterior, posterior and lateral canals are set at?
90 Degree Angles
To Detect Rotational Forces
Movement of the head results the disturbance of a fluid called?
Endolymph
How many Otolith organs are there?
2
Saccule & Utricle
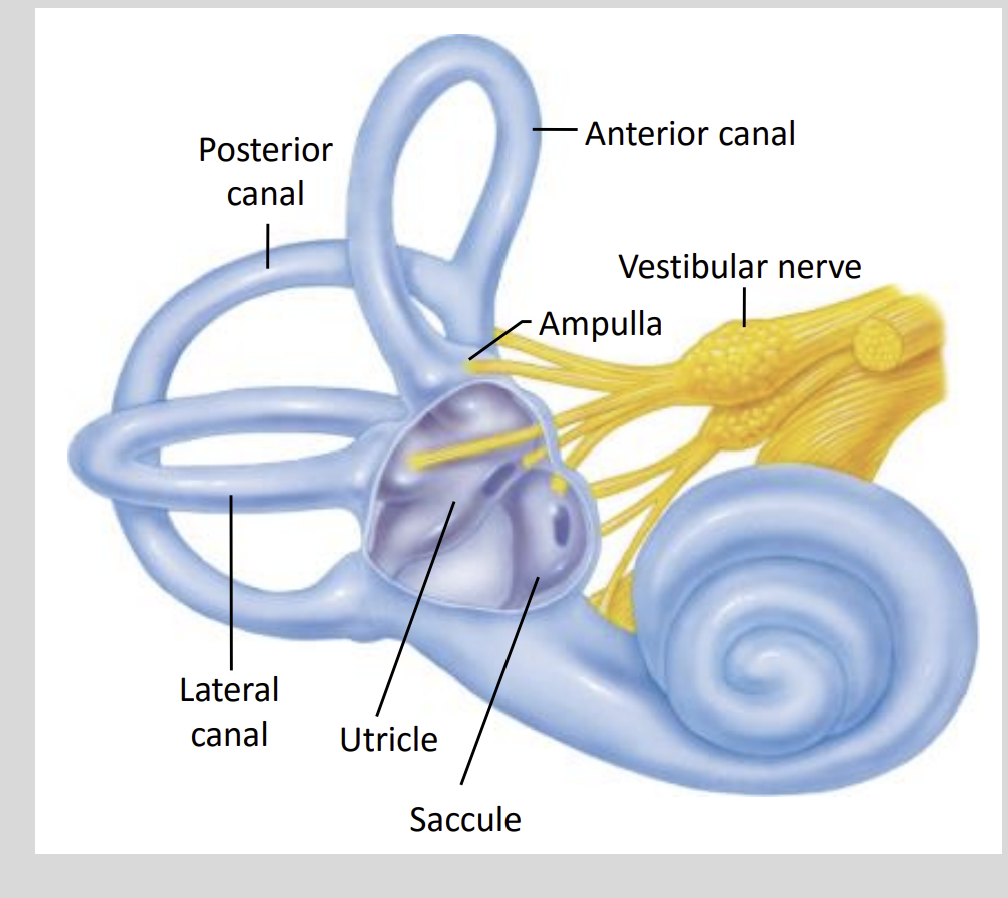
What is the role of the 2 Otolith Organs?
Saccule
- Detect Vertical AccelerationUtricle
- Detects Horizontal Acceleration
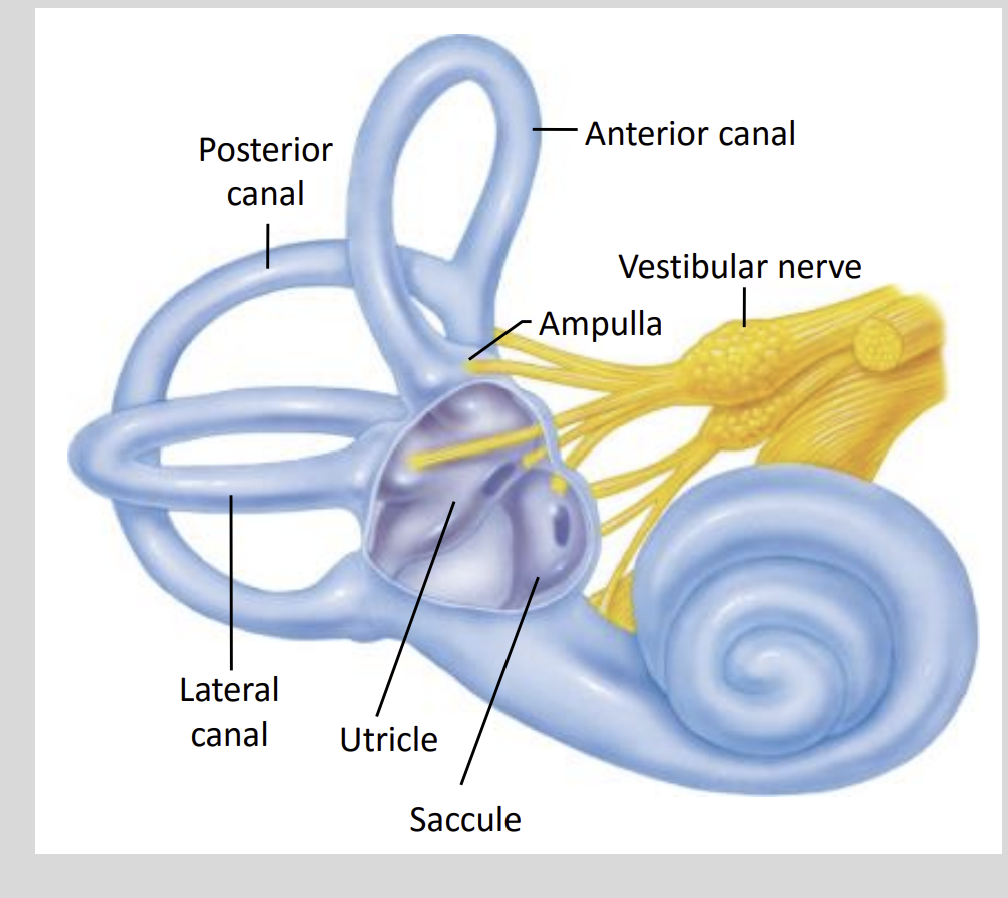
The sense of equilibrium is transduced by specialised?
Neuroepithelial Cells called ‘Hair Cells’.
The Hair cells excite the dendrites of Sensory nerves which form what nerve?
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VII)
Vestibular Apparatus Cross Section
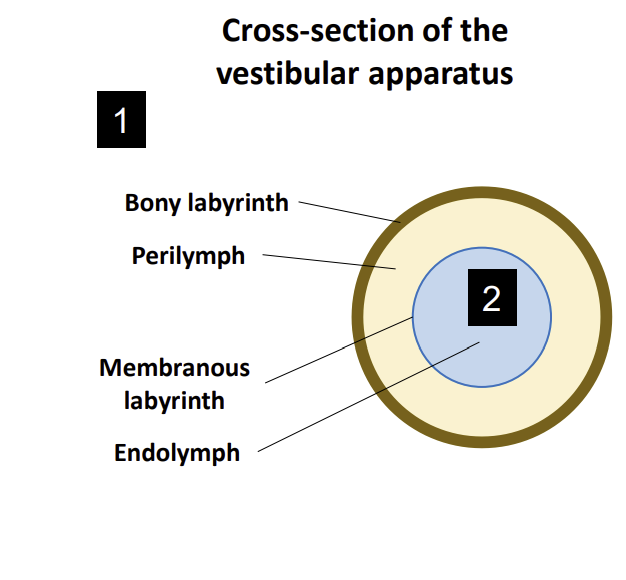
Labyrinth Diagram
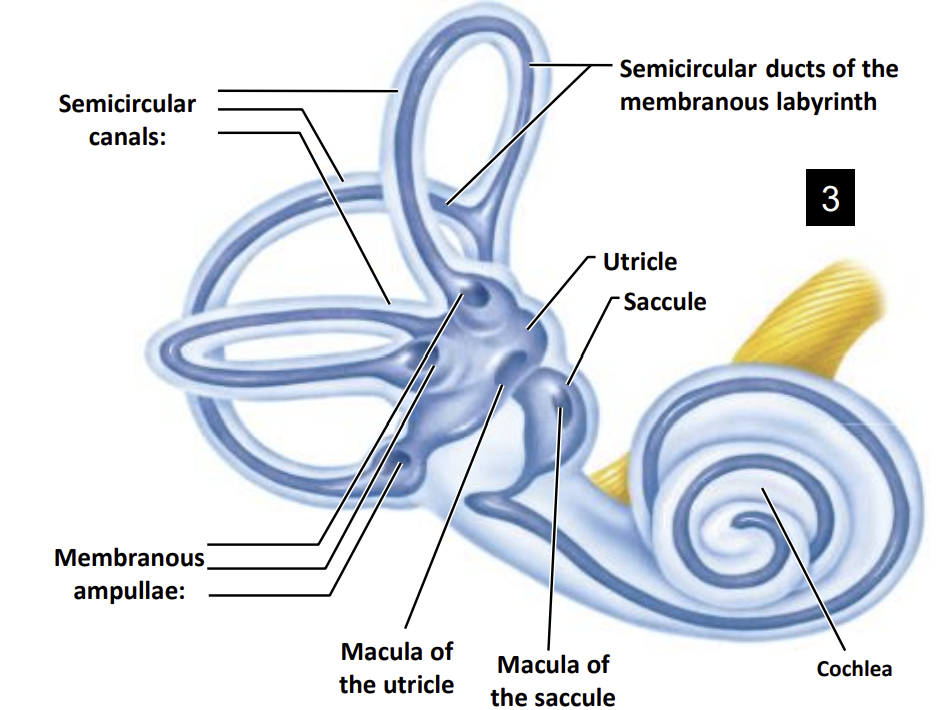
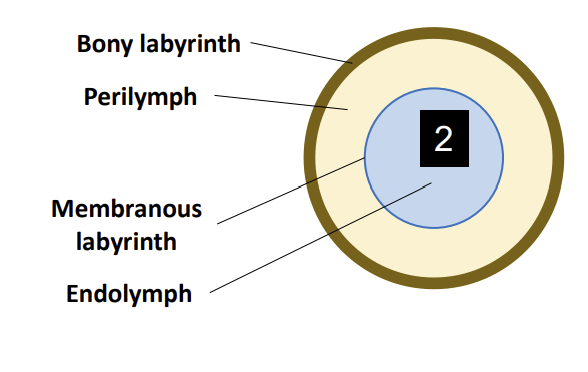
Internal Structure of the Vestibular Apparatus:
Within the temporal bone, there is a hollow structure known as the?
Bony labyrinth
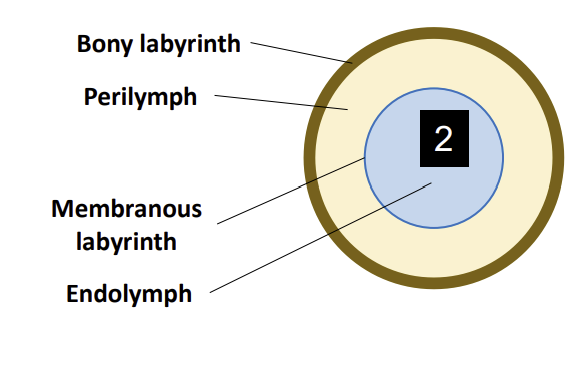
Internal Structure of the Vestibular Apparatus:
Within this bony labyrinth sits another structure called the?
Membranous Labyrinth
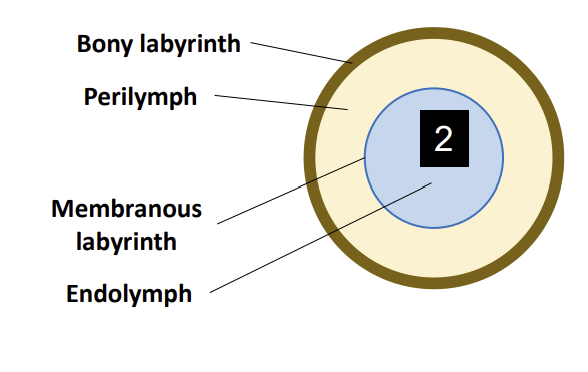
Internal Structure of the Vestibular Apparatus:
the membranous labyrinth which is suspended in place by a solution called?
Perilymph
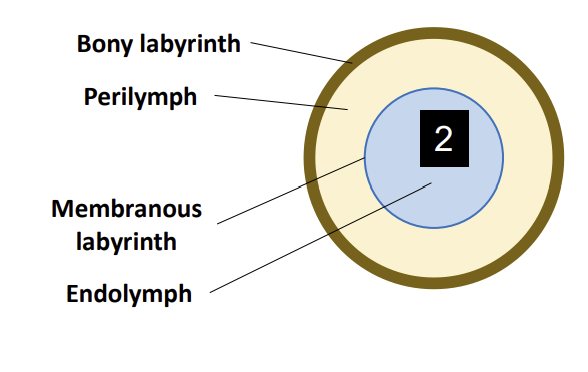
Internal Structure of the Vestibular Apparatus:
The perilymph sits between the bony labyrinth and the?
Membranous Labyrinth
Internal Structure of the Vestibular Apparatus:
The membranous labyrinth itself is filled with an extracellular solution called?
Endolymph
also contains the sensory structures of equilibrium.
Endolymph is the only Extracellular solution that?
That has a very high K+ concentration (greater than that of the intracellular fluid)
And much lower concentrations of Na+ and Ca2+ than other extracellular solutions.
depolarisation of hair cells occurs as the result of inflow of ….. ? into the cell as it moves down its concentration and electrical gradient.
K+
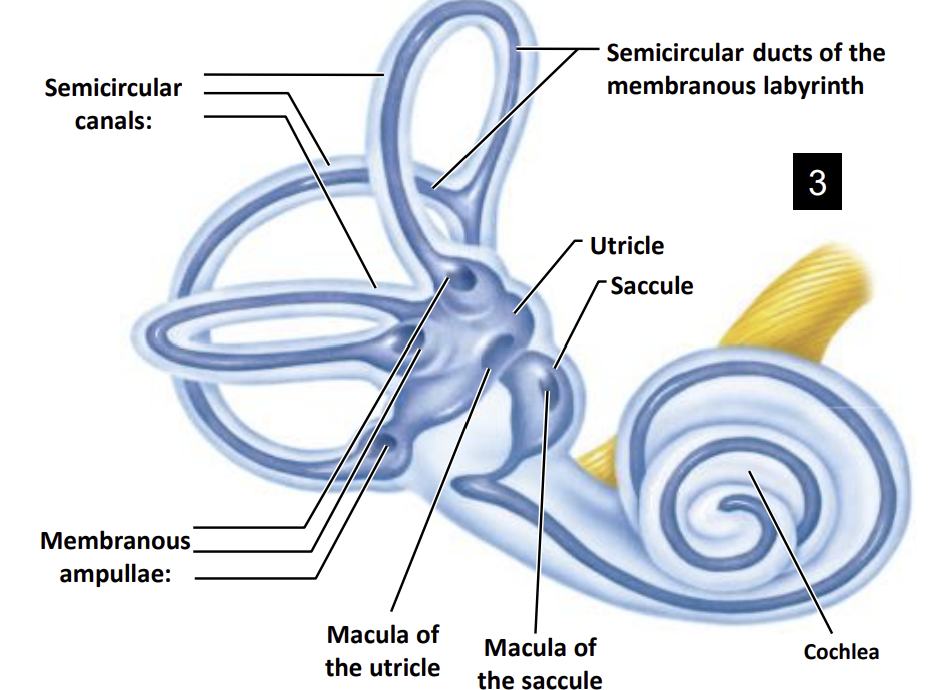
Location of the Sensory Cells:
Within the membranous labyrinth the sensory cells are bundled together at specific locations called?
The ampullae at the base of each semicircular canal
The maculae within the utricle and saccule.
Hell Cells are capable of?
Depolarization & Hyperpolarization
And Releasing Neurot at Basolateral membrane.
Sensing Motion Diagram
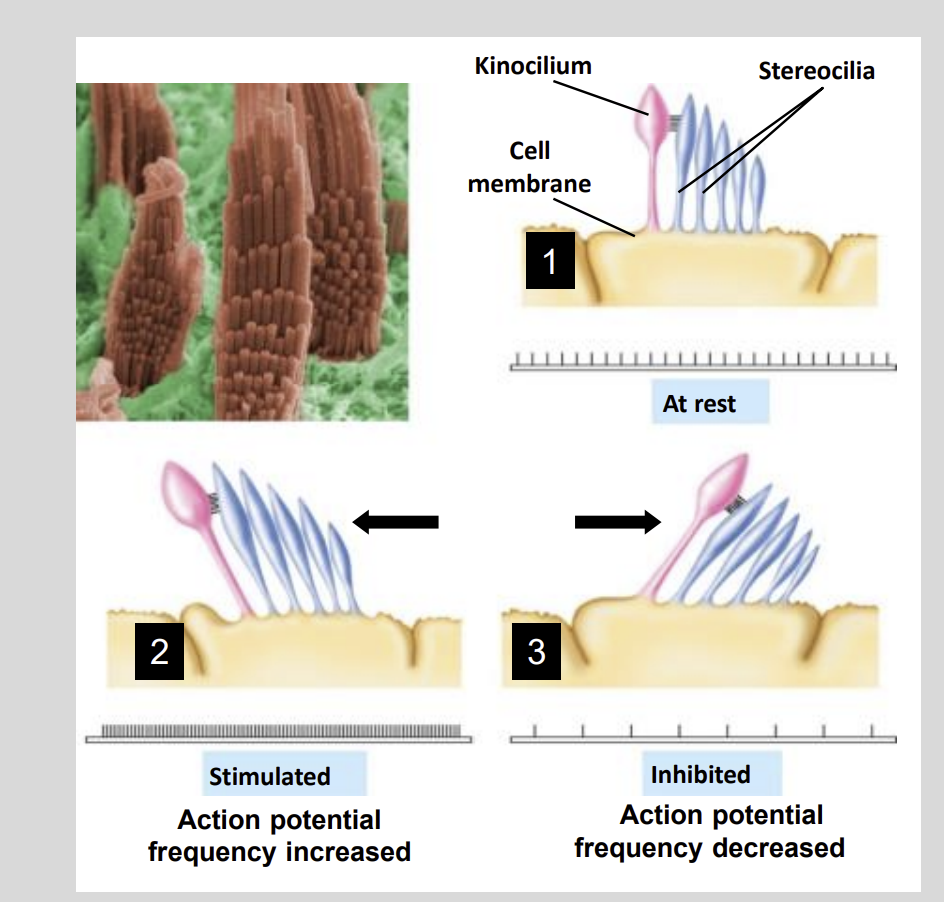
Each hair cell has ? stereocilia on its apical surface
20 -50Each hair cell has 20-50 stereocilia on its apical surface
Movement of the Largest Cilla called … causes?
Kinocilium causes Depolarization or Hyperpolarization of the cell.
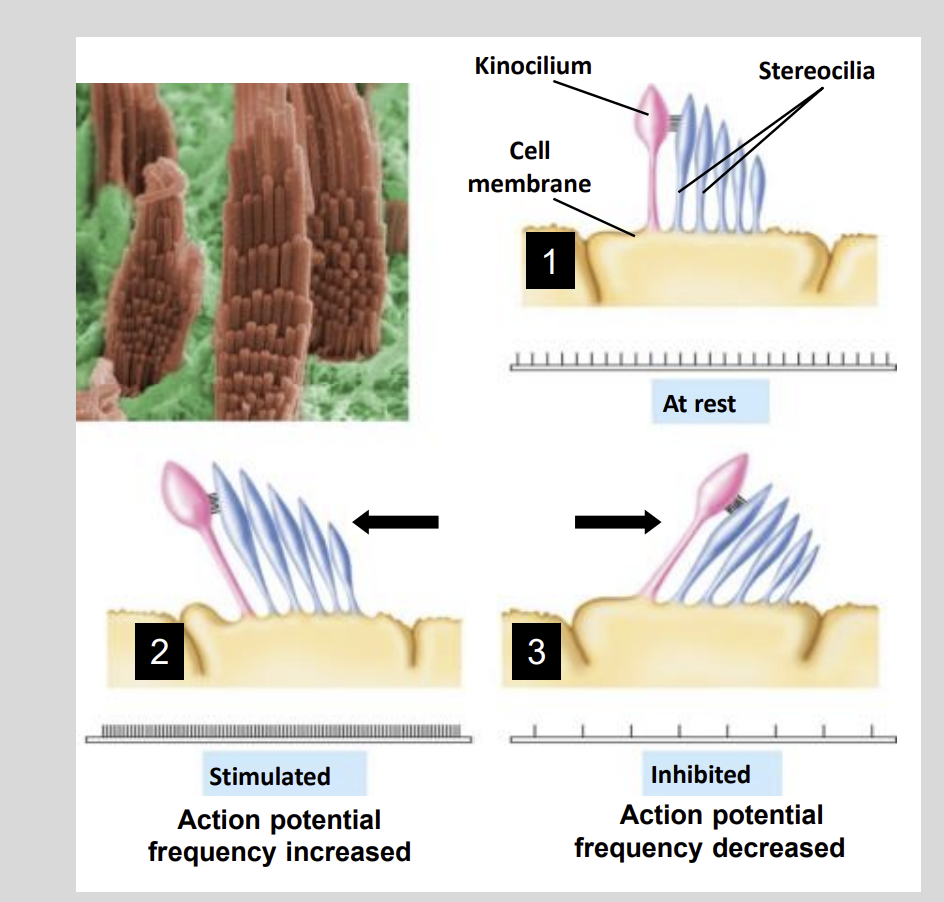
Sensing Motion:
At rest cilla?
Stand up straight.
Sensing Motion:
This tonic activity of firing provides the brain with?
Static Equilibrium
Sensing Motion:
The frequency of discharge is altered if the?
The Stereocilia move
Sensing Motion: If the stereocilia move towards the kinocilium the hair cell?
Depolarizes
Exciting the Sensory neuron and generates a greater frequency of action potentials.
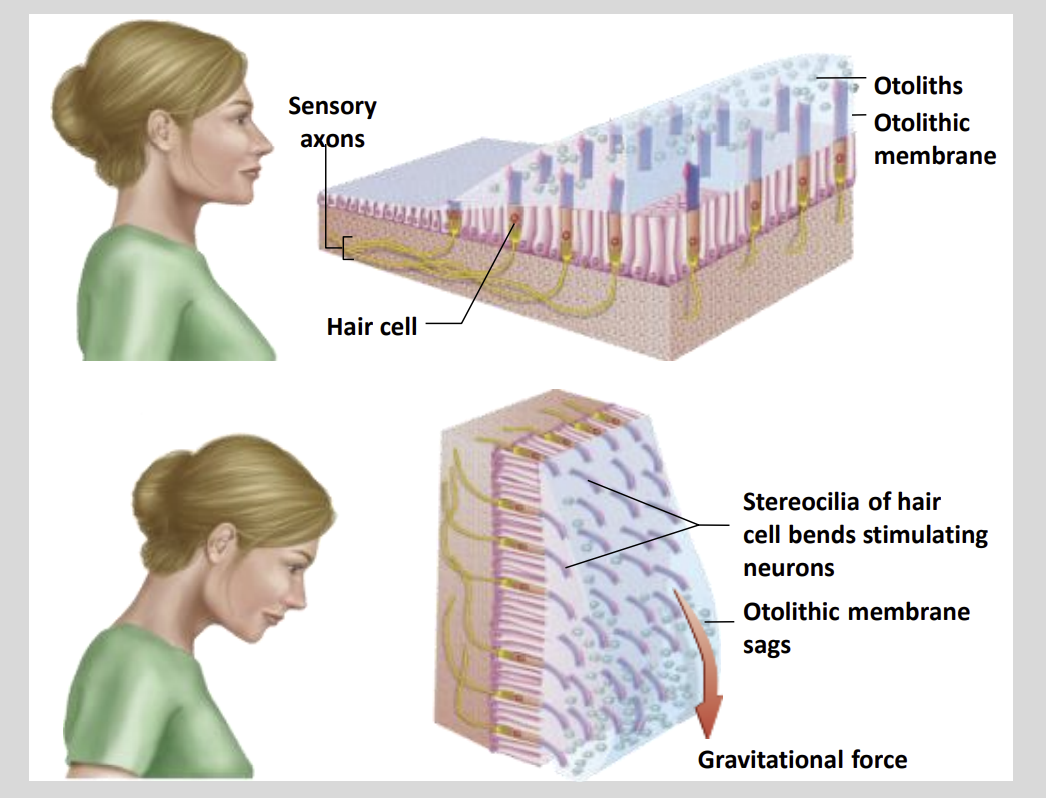
Otolith Organs:
The macula is the site where hair cells are found within ?
The utricle and saccule.
Otolith Membrane:
the cilia of these hair cells are embedded in a ?
Gelatinous otolithic membrane.
Otolith Membrane:
The otolithic membrane contains
Otoliths
Which increase the Mass of the Cell.
Provides more Inertia
Otolith Organs:
What are Otoliths?
Microscopic calcium carbonate crystals
When the head is tilted up or down, gravitational force pulls on the?
Otoliths & Otolithic Membrane
Results in Depolarization or Hyperpolarization
Semi CC Diagram
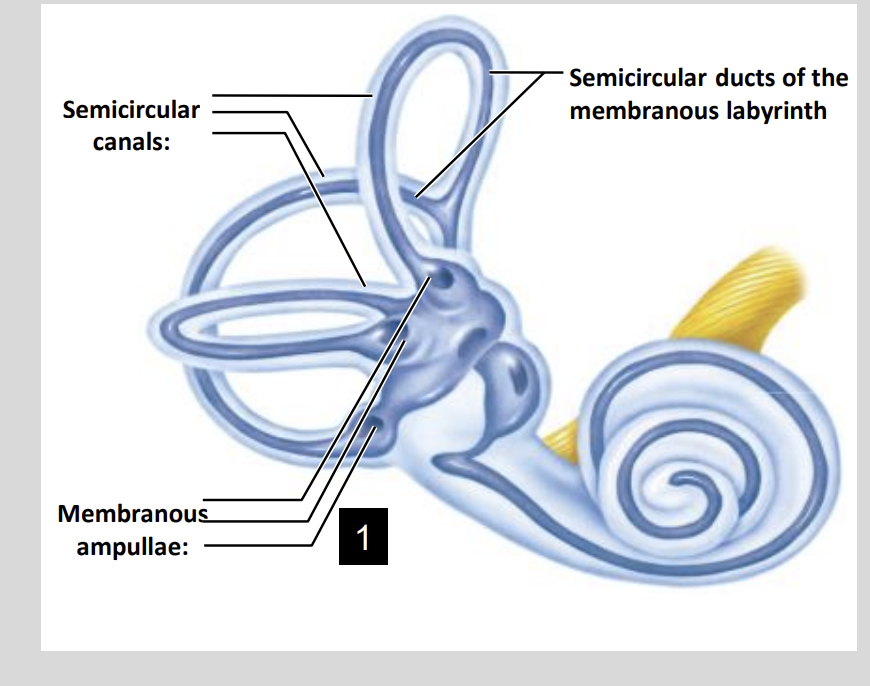
Rotational Acceleration Diagram
Semi Circular Canals:
The hair cells of each semicircular canal structure are located at the?
Membranous Ampullae
At the Base of the Semicircular Canal
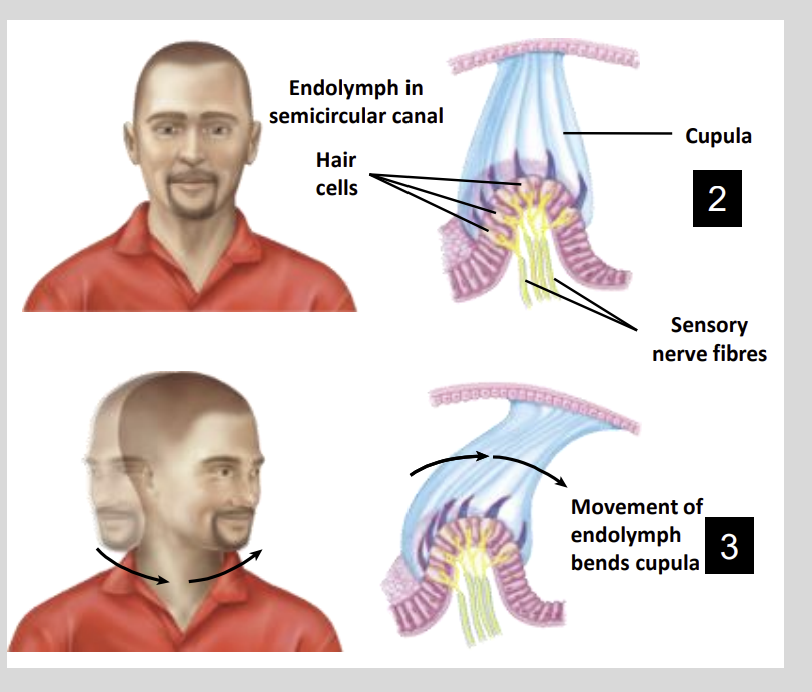
Semicircular Canals:
The cilia of these hair cells emanate out and are embedded in a ?
Gelatinous Membrane
Called the Cupula
Semicircular Canals: The Cupula is found where?
Inside the ampulla of each semicircular canal
Semi Circular Canals:
When the head moves the Endolymph?
Lags Behind
Semi Circular Canals:
What is the result if the Endolymph lagging behind as the head moves?
The endolymph is pushed up against the cupula which results in bending of the cupulas as well as the embedded cilia of the hair cells
This results in stimulation/inhibition the hair cells
Neural Pathways Diagram:
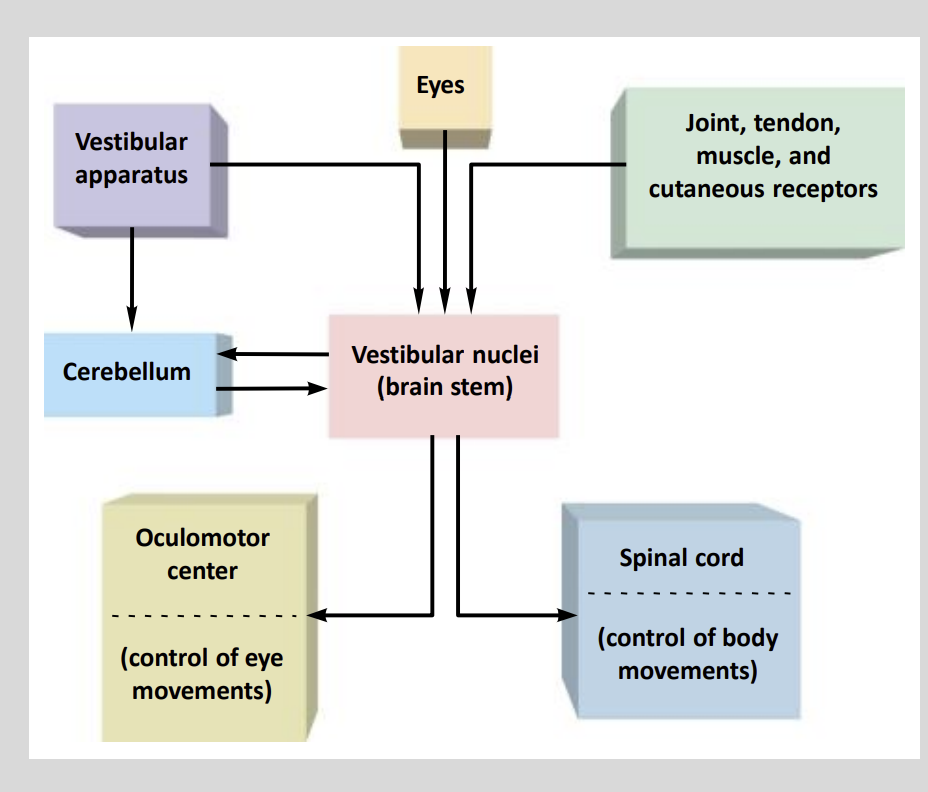
VIII nerve is the ?
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VII)
From the vestibular nuclei, signals can be sent to many different areas of the?
CNS
Axons are projected from the Vestiublar Nuclei to the ?
Oculomotor Centre of the Brainstem
Control of Eye Movements
Spinal Cord
- Body movements.
Motion sickness occurs due to ?
Imbalance between Visual & Equilibrium Senses.
Vertigo is caused by anything that effects the firing mode of the ?
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VII)
Most common cause is a Viral Infection
What is Menieres Disease?
Chronic Inner Ear Disorder
Leading to Recurrent Vertigo.
What Causes Menieres Disease?
Excessive endolymph within the membranous labyrinth
which can produce excessive dilatation, damage or rupture of the membranous labyrinth.