Q2 Environmental Science Exam Study Guide
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
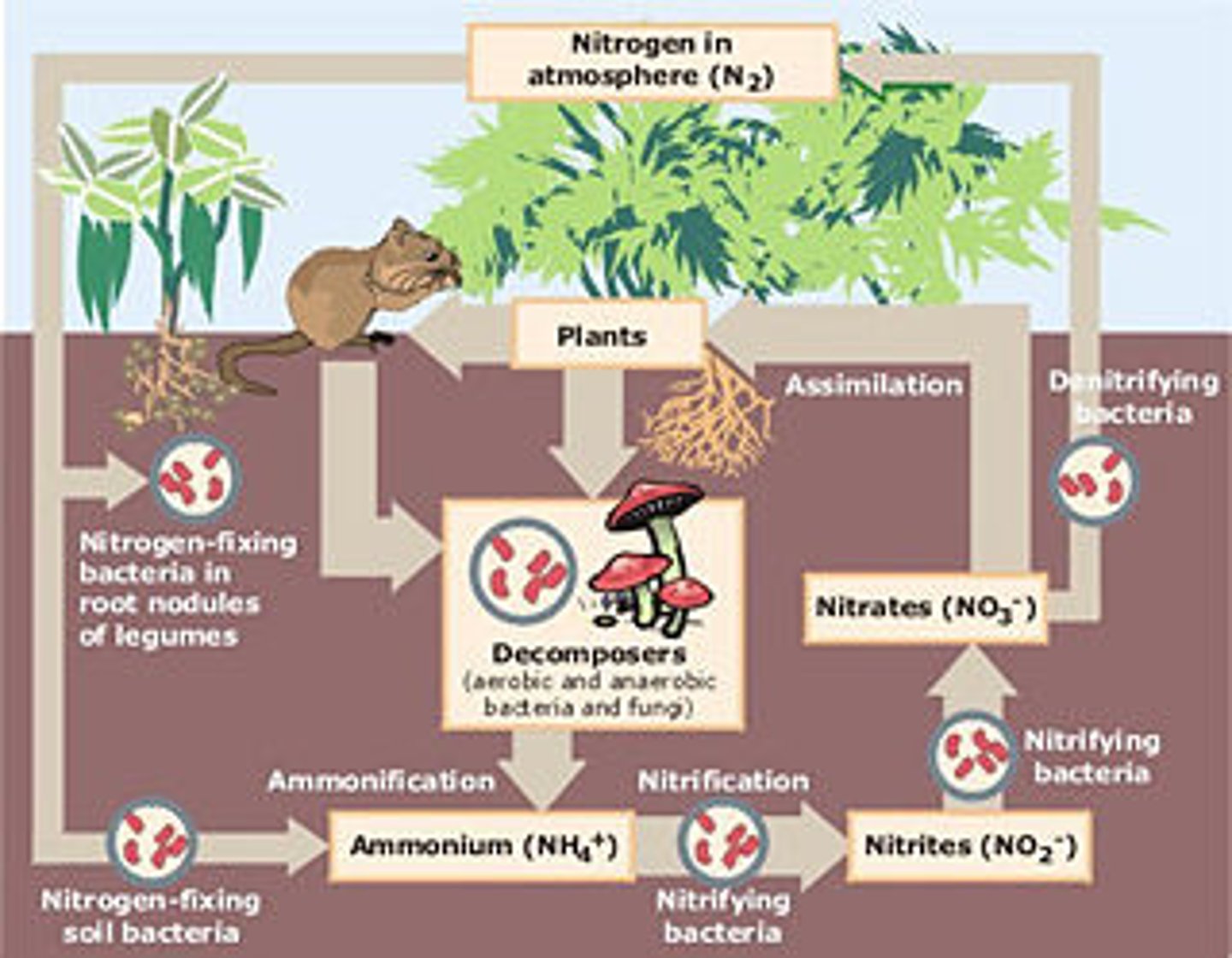
nitrogen cycle
Key processes include nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation ammonification, and dentrification
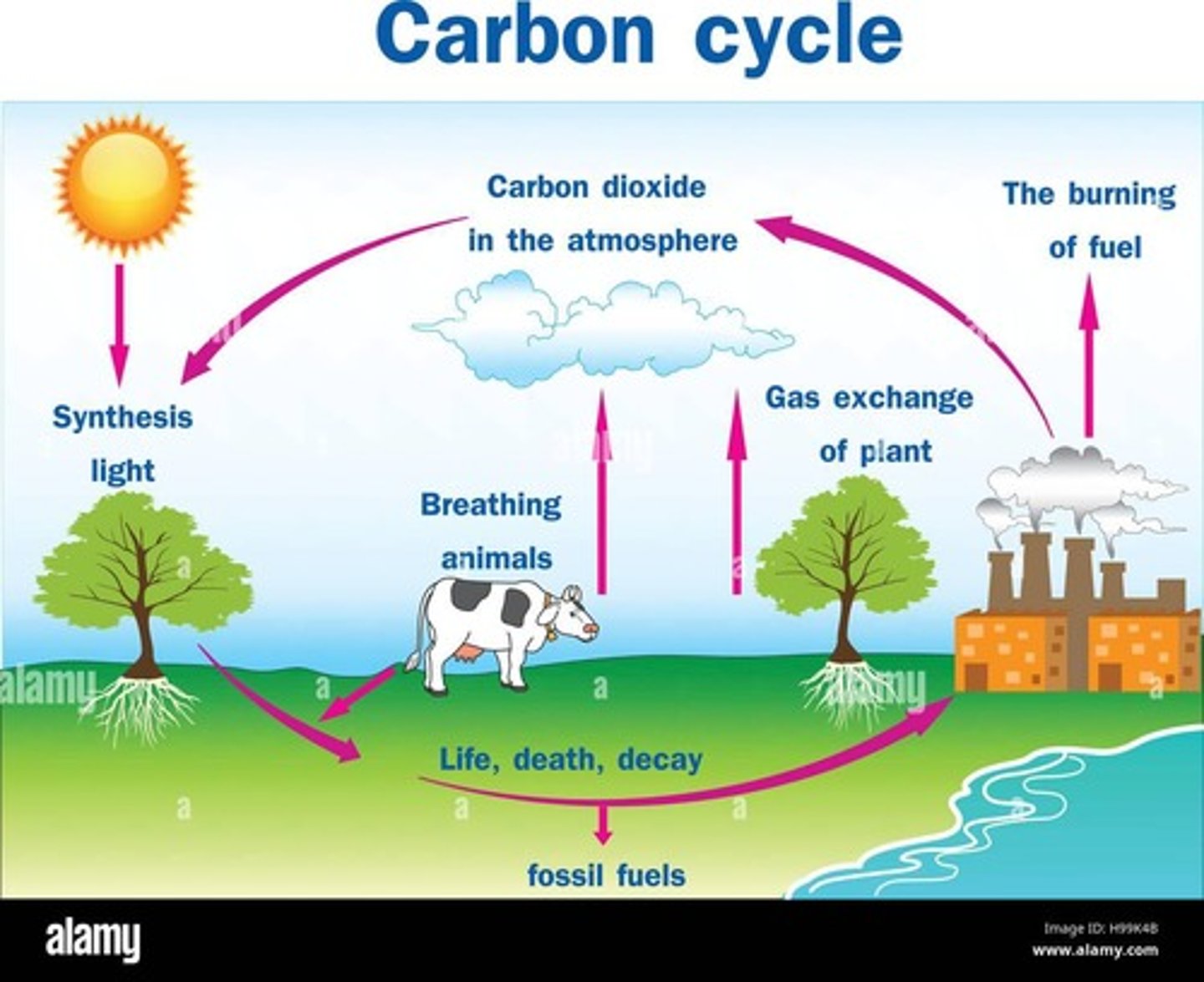
Carbon Cycles
Emphasis on biological (photosynthesis/respiration), geological (sedimentation, fossil fuels), and anthropogenic (burning fossil fuels) processes.
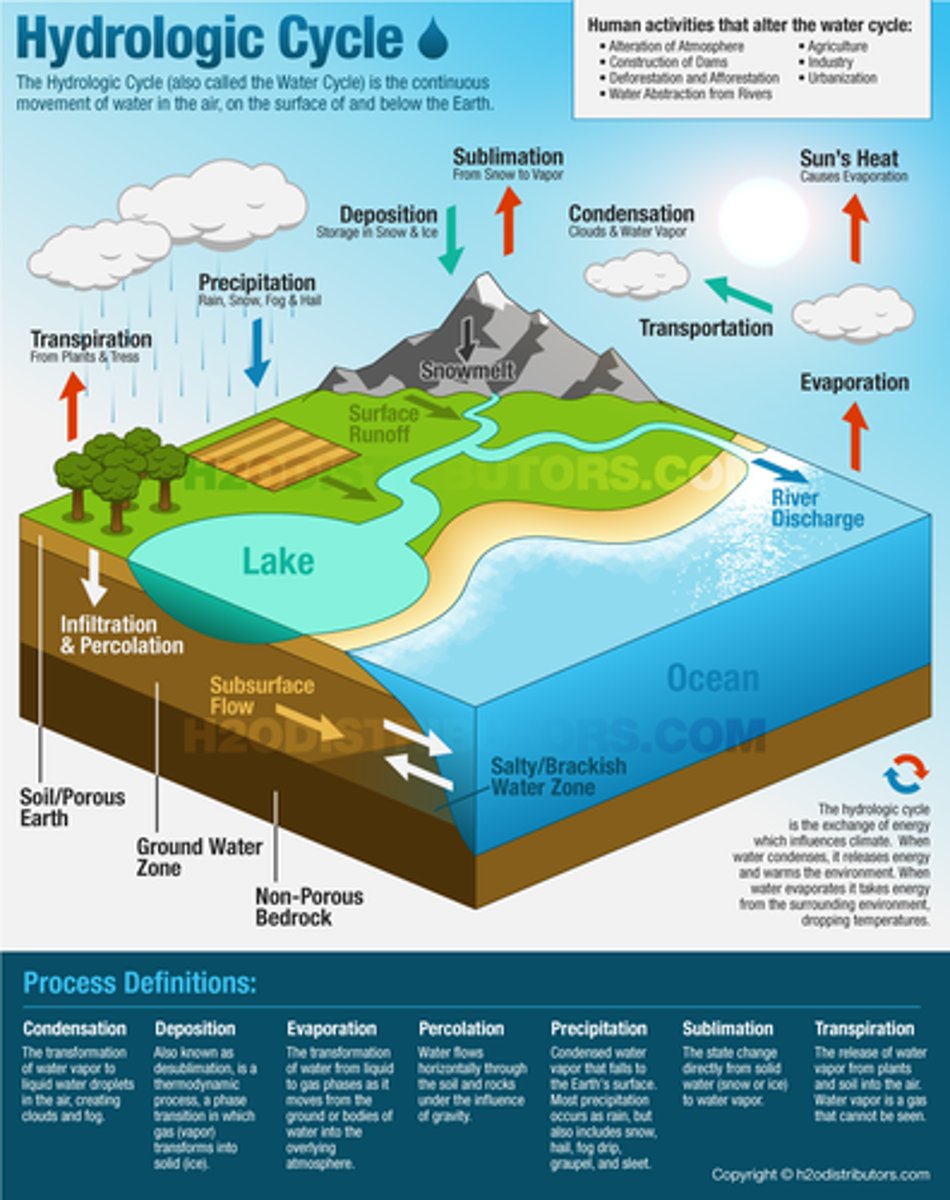
Water (Hydrologic) Cycle
Processes include evaporation, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, runoff
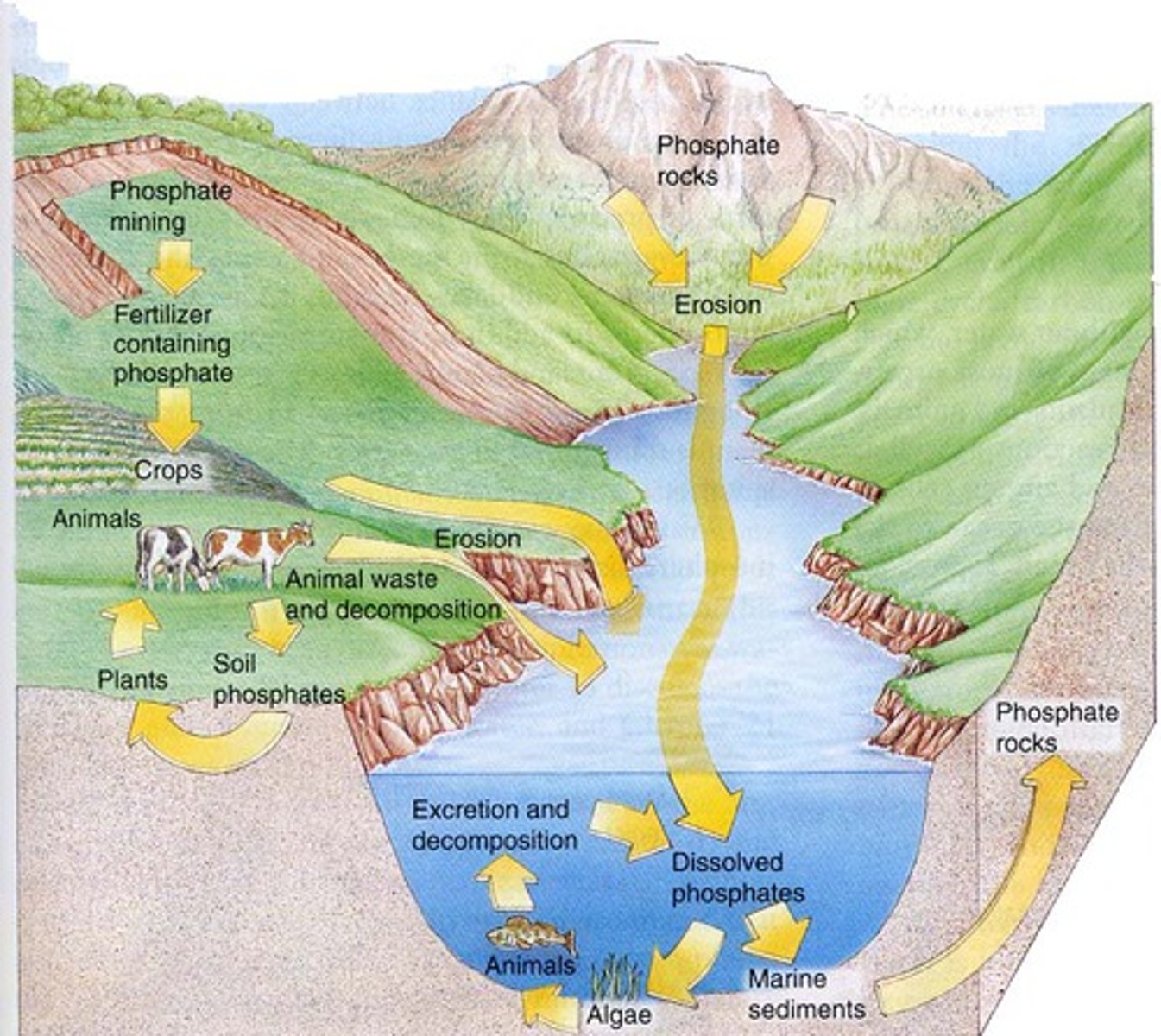
Phosphorus Cycle
Unique in that it doesn't typically have an atmospheric component.
Carbon Sequestration
The process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide, such as in forests, soils, or geological formations
Producers
Organisms that make their own food usually through photosynthesis (mostly plants/ algae)
Consumers
Organisms that eat other organisms (Herbivores/Carnivores)
Herbivores
Primary consumers that eat producers.
Carnivores
secondary/tertiary consumers that eat other consumers
Decomposers
Organisms (bacteria, fungi) that break down dead organic matter and waste, recycling nutrients.
Detritivores
Organisms (worms, insects) that feed on detritus (dead organic material)
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis creates glucose and oxygen from CO2, water, and sunlight
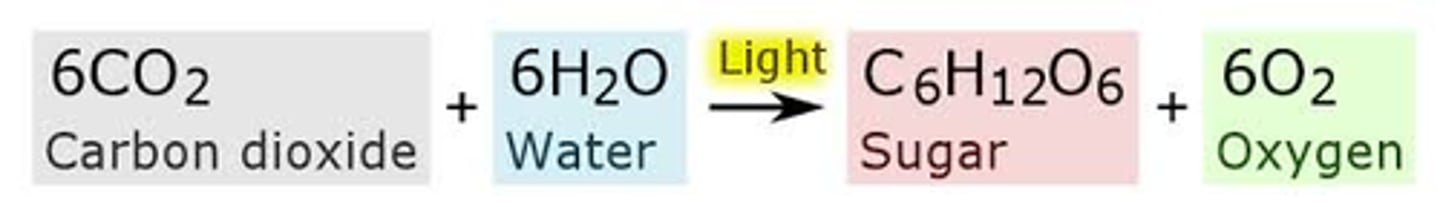
Cellular respiration
Uses glucose and oxygen to release energy, producing CO2 and water
Biosphere
Zone of Earth where life exists (all living things)
Geosphere
Solid earth (rocks, mineral, land)
Atmosphere
Gaseous envelope surrounding earth
Hydrosphere
All water on earth (liquid, solid, gas)
Biotic
Living components of an ecosystem
Abiotic
Non-living components (e.g. , sunlight, water, soil, temperature)
Positive feedback
Loop that amplifies or strengthens an initial change (e.g., melting ice -> less reflection -> more warming -> more melting)
Negative feedback
Loop that counteracts or dampens an initial change, stabilizing the system (e.g., predator-prey cycles, body temperature regulation).
Hydrologic and Nutrient Cycling
The continuous movement of water and nutrients through the environment
Terrestrial Ecosystem vs Aquatic Ecosystems
Review the fundamentals differences in how energy flows, habitats are structured, and challenges faced by organisms in land vs water environments.
Tragedy of the Commons
This principle, discussed by Garrett Hardin, describes hoe shared, finite resources (commons) are often overused and depleted because individuals act in their own self-interest, rather than for the collective good. The inevitable result is the destruction of resources for everyone.
Principle of Sustainability
Focuses on meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves living within the limits of Earth's natural system.
Ecology
The study of the relationships between living organisms and their environment.
Natural capital
This refers to the world's stock of natural resources (geology, soils, air, water, living organisms) that provide essential good and ecosystem services underpinning the economy and society
Renewable Resources
Resources that can replenish naturally on a human timescale, such as timber, fresh water, and solar, wind, and geothermal energy
Inexhaustible Resources
Resources that are perpetually available like solar energy
Nonrenewable Resources
Resources that exist in a fixed amount or are depleted faster that they can be replaced by natural processes (e.g., fossil fuels. minerals, metal ores)
Point Sources
Single, identifiable sources of pollution, such as a factory smokestack, a sewage treatment plant discharge pipe, or an oil spill from and specific tank
Non-point Sources
Diffuse contamination from large areas, difficult to trace to a single origin (e.g., agricultural runoff, urban stormwater runoff, wind-borne pollutants)
Ecological Footprint
A measure of the total area of a functionally productive land a marine ecosystem required to produce the resources a population consumes and to assimilate the waste that population generates
Water Pollution
Contamination of water bodies, typically by human activities, which negatively affects their uses.
Causes of Environmental Problems
Factors such as population growth, unsustainable resource consumption (affluence), poverty, undervaluing natural capital, and the isolation from nature are common underlying causes