Biology- Photosynthesis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Overall symbol equation for ps
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12o6 + 6O2
What form of energy is captured?
What form of energy is a flow of electrons?
What form of energy are ATP and glucose?
Light (photons)
Electrical
Chemical
What are the main stages of ps
Light dependant reaction LDR
Light independent reaction LIR
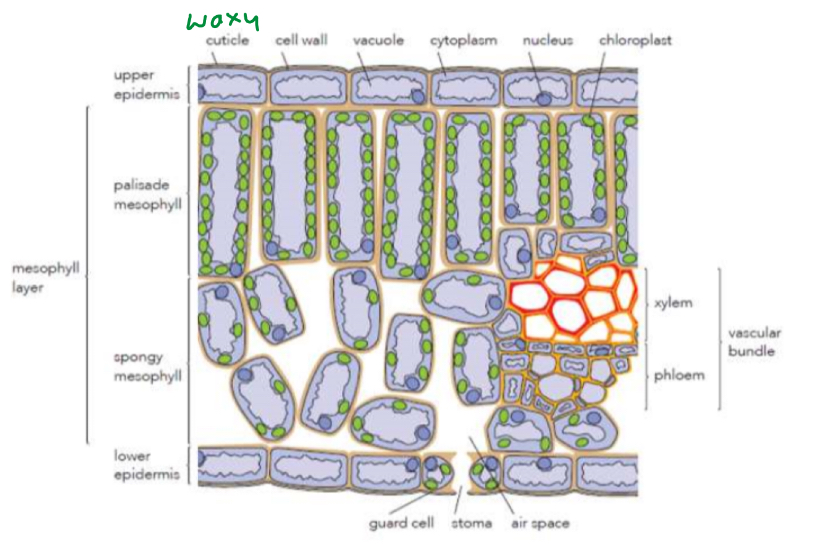
3 ways which leaf structure is adapted for ps
Link structure to function
Waxy cuticle/guard cells → reduce water loss
Palisade mesophyll→ stacked (closely packed) lots of them in small space for max light absorption
Spongy mesophyll→ air spaces provide a quicker diffusion pathway
Chloroplast structure (diagram labelled)
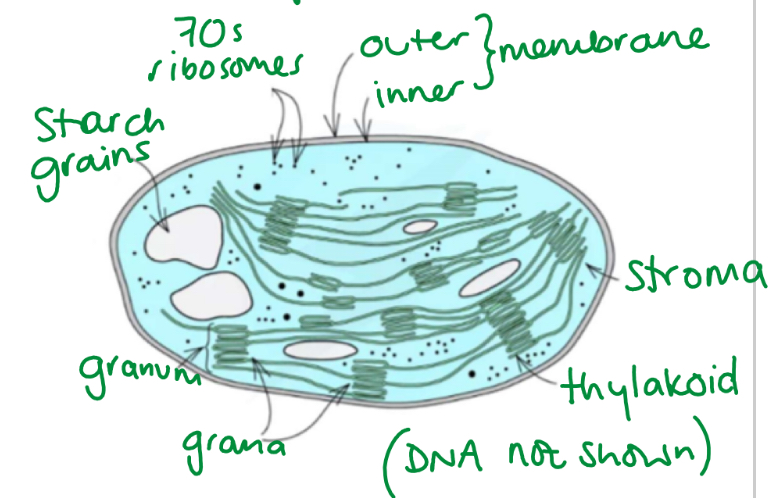
How is a chloroplast adapted for ps
Contain DNA and ribosomes- to quickly manufacture some proteins needed for the LDR
Thylakoids have large surface area- for attachment of many chlorophyll molecules, electron carreirs and ATP synthase enzymes
ATP synthase molecules are found in thylakoid membrane to catalyse production of ATP in the LDR
Proteins in the thylakoid membrane hold chlorophyll in a specific orientation to allow it to absorb more light
How does chromatography of leaf pigments work
Sample is placed on to chromatography paper, the bottom of which is placed into a solvent
The solvent travels up the chromatography paper, taking any pigments (which are soluble in the solvent) with it
Different pigments will be carried different distances by the solvent due to their solubility, and so the pigments are separated out

Formula for Rf value
What does it allow us to do
Allows for comparison between samples between different leaves

Rf values of pigments (carotenoids, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b)
High → low
Carotenoids have the highest Rf values (close to 1)
Chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll b
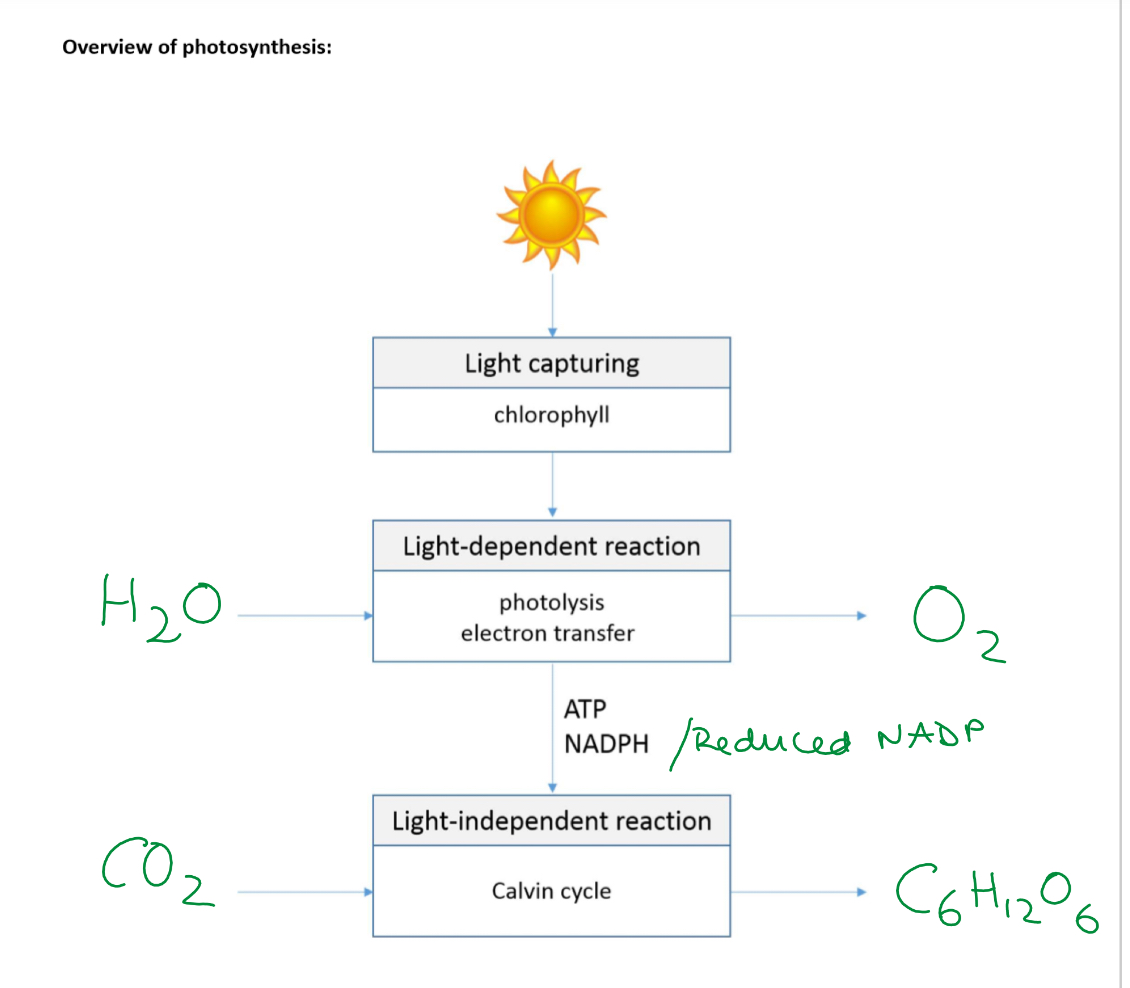
Processes in LDR Light energy is used to power

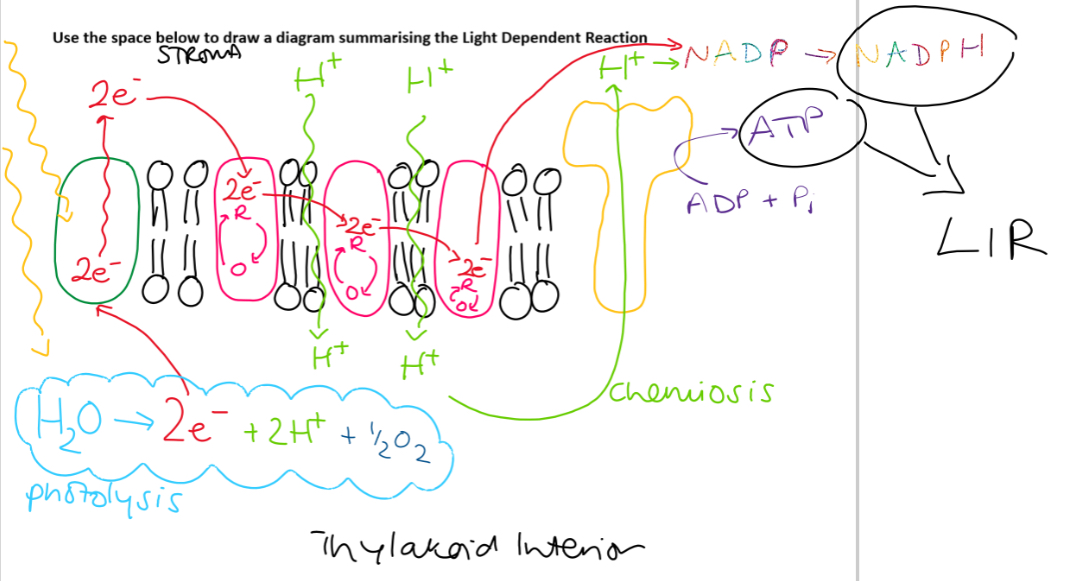
LDR
Summary: The LDR provides a source of reducing power (NADPH) and energy (ATP) for the LIR
O2 from photolysis is used in respiration or lost via the stomata

Why cant plants use ATP produced in LDR as only source of ATP
LDR only occurs in the light
Produces little ATP
Absorption spectrum table for chlorophyll a, b, carotenoid
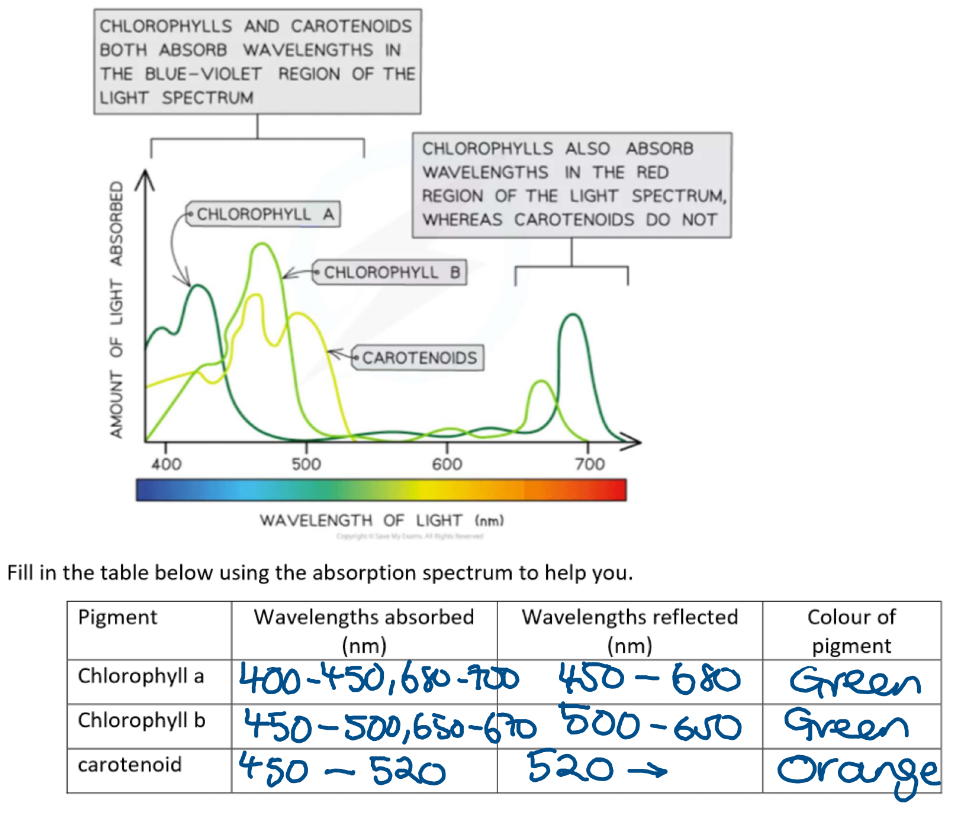
Why is LIR needed
as light energy from the sun is only available during the day, LDR is limited to when it can proceed
A long term store of energy is produced in LIR using energy from ATP and reducing power from NADPH
Can LIR take place in the dark
Yes
But nor indefinitely as relies on the products of the LDR
How does CO2 for LIR enter leaf
What is this process called
Diffuses into leaf via stomata and dissolves in water around the walls of the mesophyll cells
It then diffuses through the plasma membrane, cytoplasm and chloroplast membranes where the carbon is used to produce organic molecules
This process is called carbon fixation and takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts
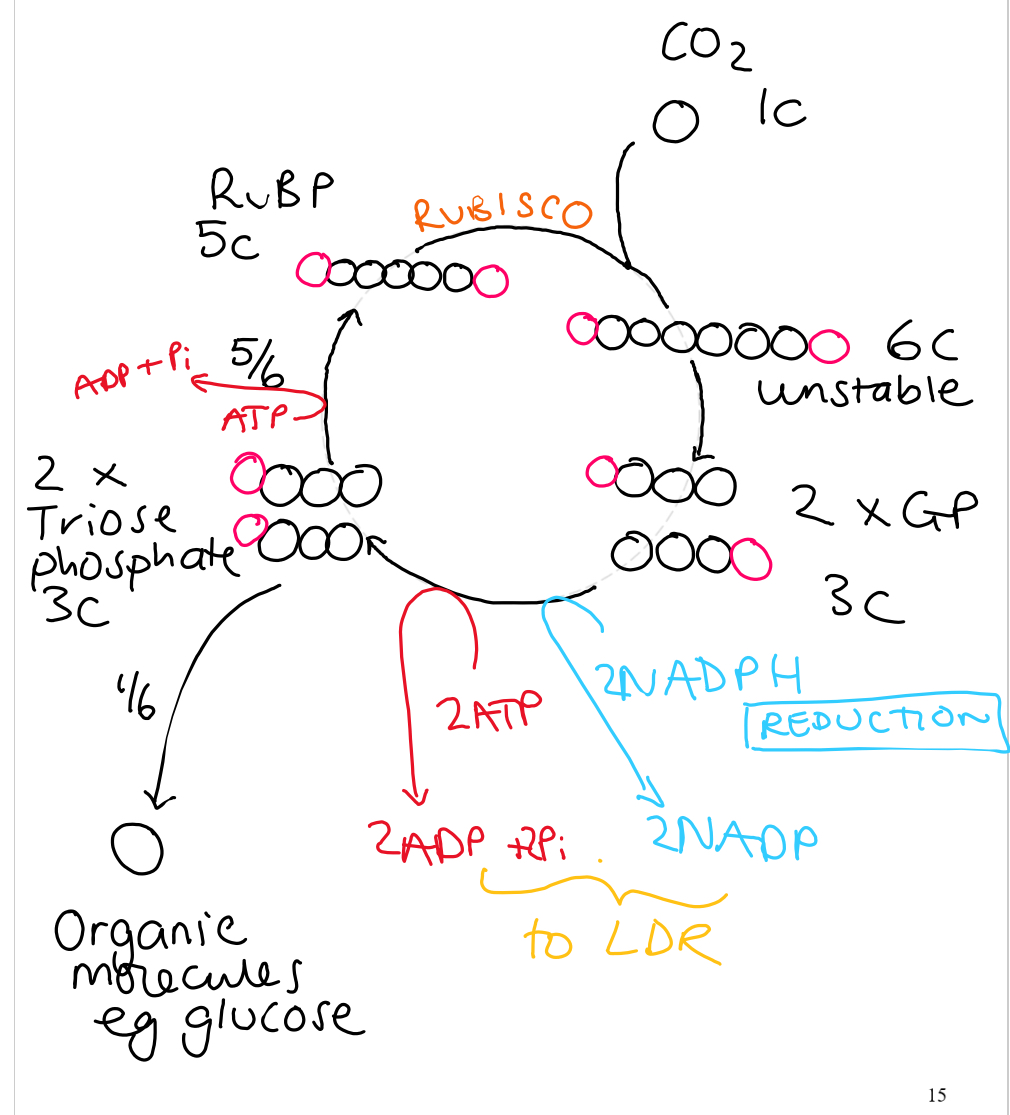
LIR (Calvin cycle)

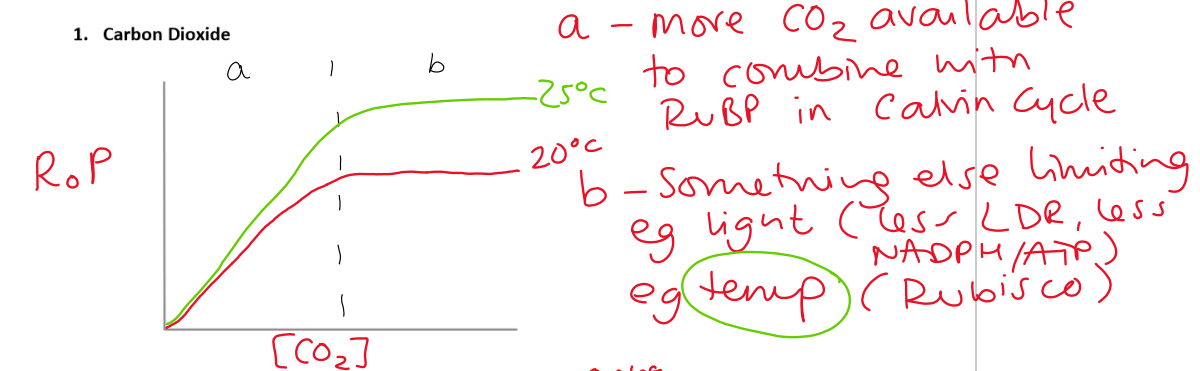
3 factors which affect rate of ps
What is a limiting factor
The factor which is at its least favourable value
Graph to show effect of CO2 on ps
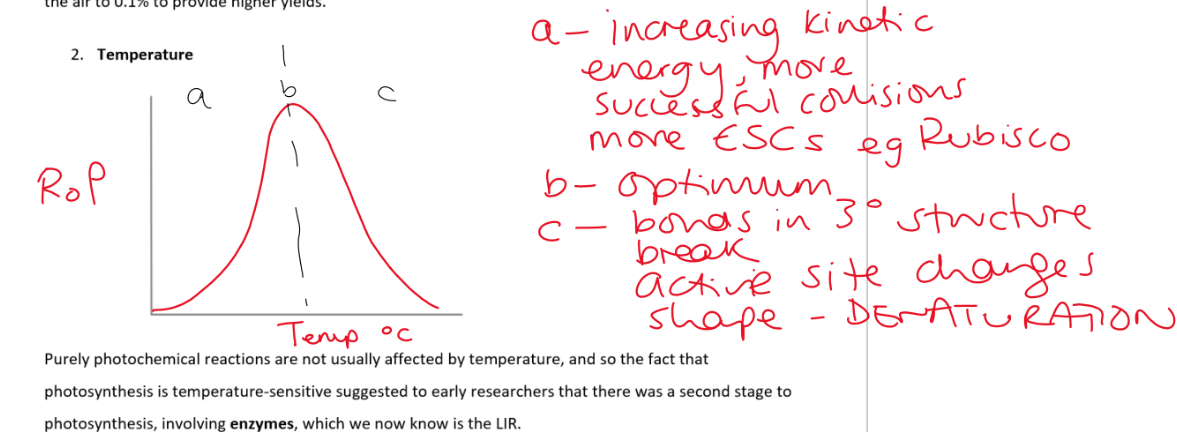
Present in atmosphere at 0.04% conc therefore often the limiting factor
Growers of greenhouse crops enrich the carbon dioxide conc of the air to 0.1% to provide higher yields
Graph to show how temp affects ps
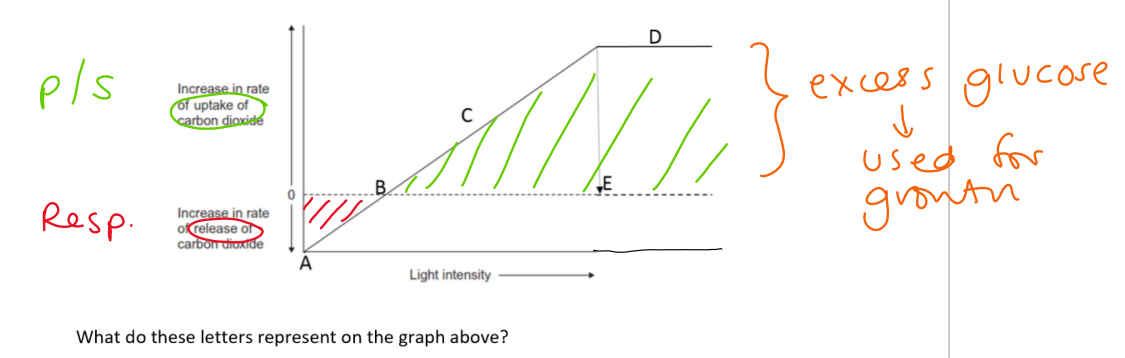
Graph to show how light intensity affects ps
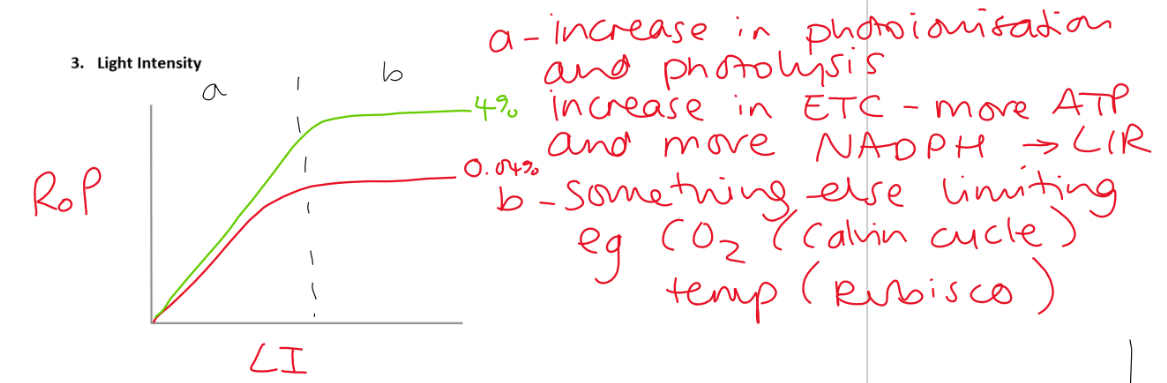
What is light compensation point
What affect will increasing LI above the compensation point
The light intensity at which rate of ps is = to rate of respiration
will increase rate of ps but have no affect on respiration
So increasing vol of oxygen will be given of and CO2 taken up until the light saturation point when another factor becomes limiting