( 7f ) Chemoreceptors Continued
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
There are 2 Types of Chemoreceptors that respond to something different
Peripheral Chemoreceptors
what’s the other type?
Central Chemoreceptors
“Central”
because they’re located in the
Central Nervous System
specifically in the
Medulla Oblongata (BRAIN)
( NOT IN SPINAL CORD )
remember
Medulla Oblongata is where basic vital signs are controlled
★ Central Chemoreceptors in the Medulla Oblongata monitors a chemical and sends a signal to the DRG to adjust our breathing
Do Central Chemoreceptors respond to
a DROP in PO2 ( ⭣PO2 )
NO

Again, that would ONLY happen in a
life threatening emergency
what DO Central Chemoreceptors respond to?
CO2 in the BLOOD

what’s the DOMINATE CONTROL over ventilation?
( movement of air in/out lungs )?
CO2 levels
what’s the DOMINATE CONTROL over breathing?
CO2 levels
sidenote
former students said
TEAS exam asks question of “which of these is most important for controlling breathing?”
oxygen?
CO2?
the answer is
CO2

example
Competitive Swimmers before they dive in will
hyperventilate ( breathing out as much CO2 as they can )
why?
So they can hold their breath for LONGER underwater!!
how?
if CO2 accumulates that FORCES us to
BREATHE
→ causing us to not hold our breath anymore
what receptor tracks the CO2 accumulation to trigger breathing?
Central Chemoreceptors
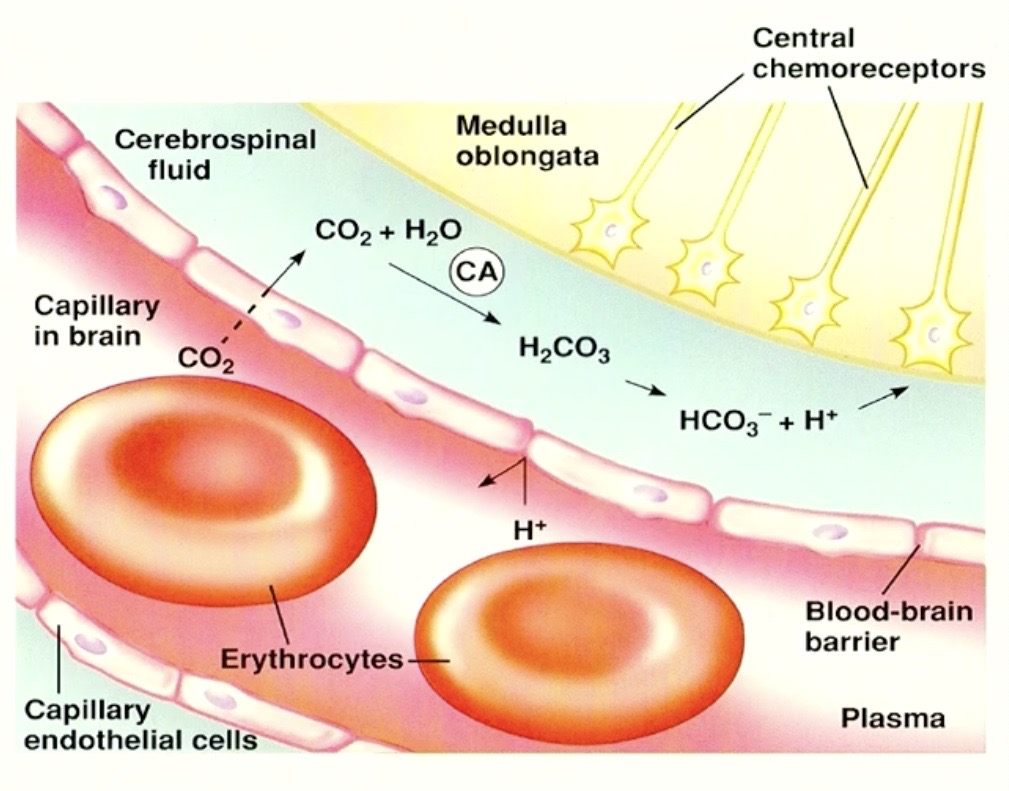
Blood Brain Barrier Capillary next to Medulla Oblongata
( where central chemoreceptors are! )
Scenario Shown
Increased PCO2 in the blood
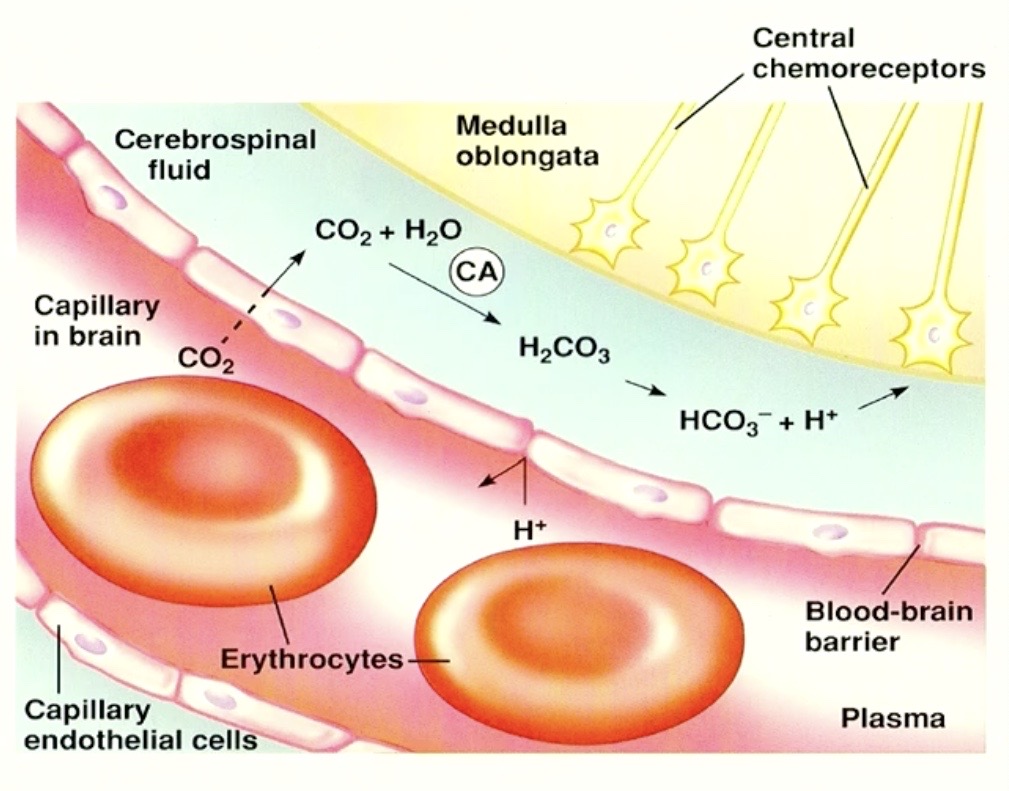
can CO2 cross the blood brain barrier?
YES
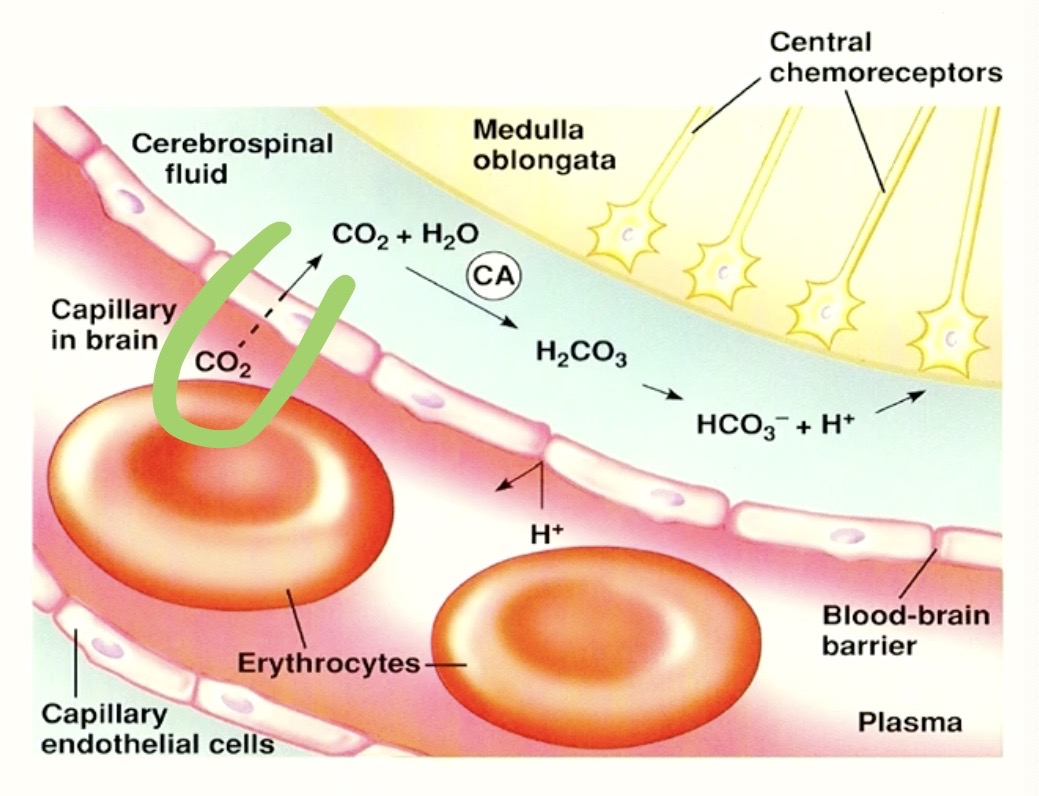
why
CO2 is
Lipid Soluble
Small
CO2 CAN go into the
BRAIN
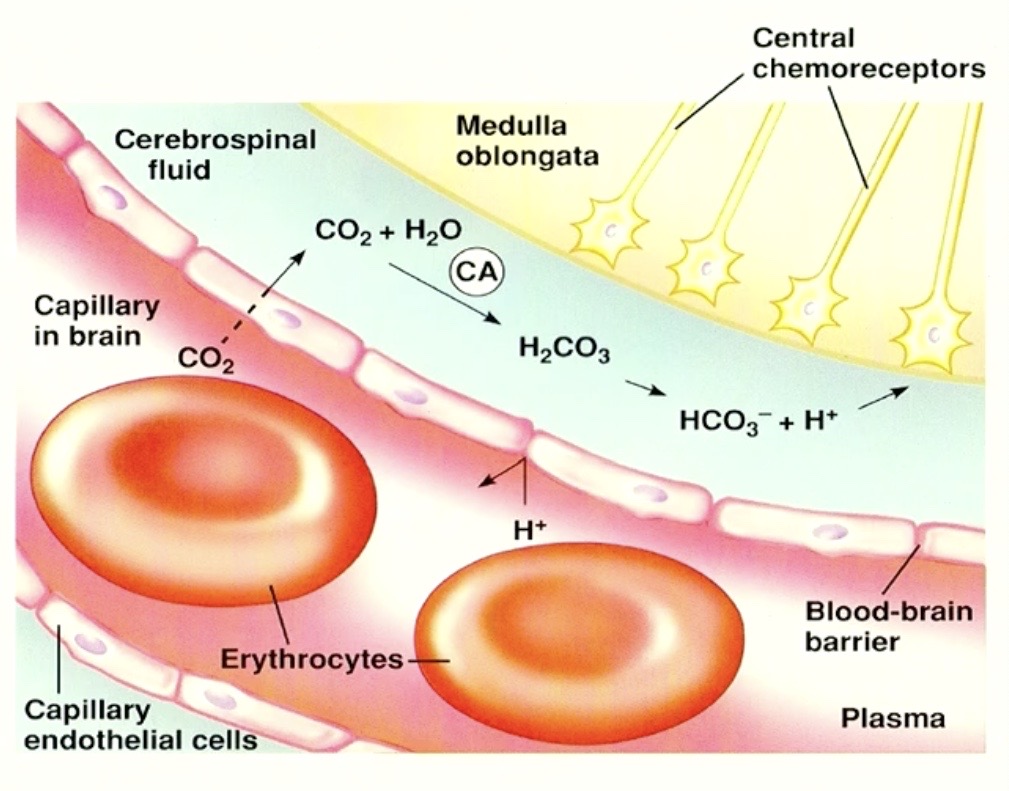
so far CO2 crosses out of blood into brain
what happens to CO2 in the brain?
the chemical reaction!!
→ cerebral spinal fluid has water ( H2O ) that CO2 can react with!
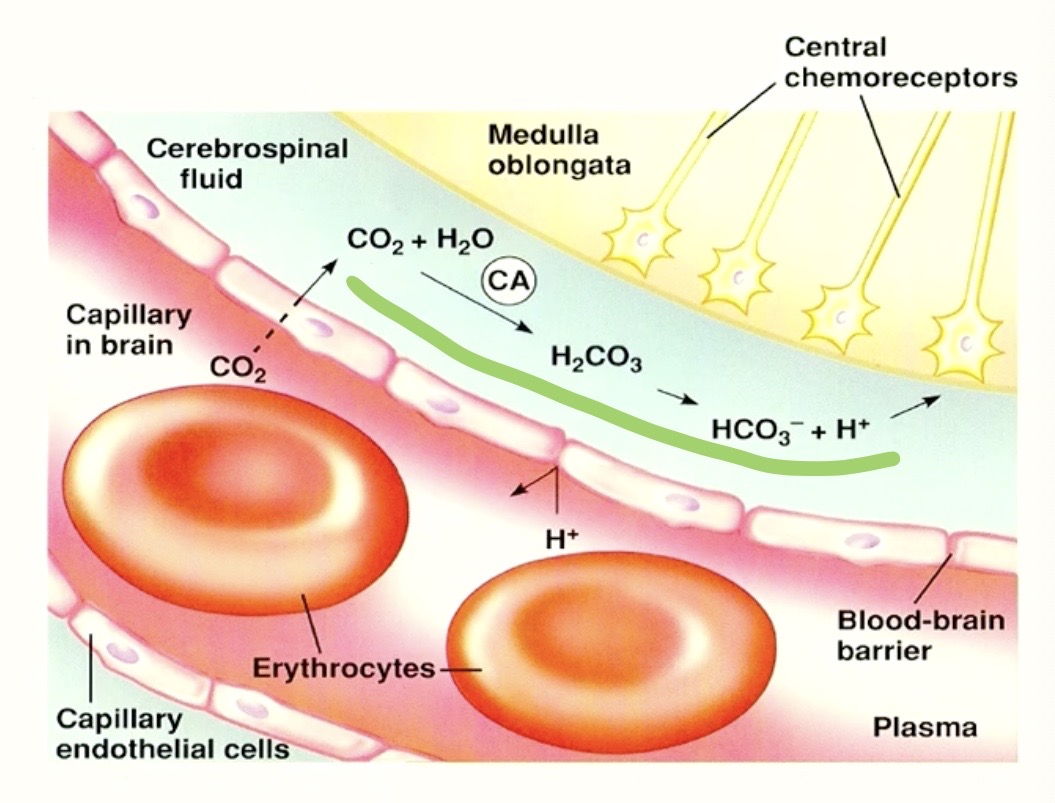
what do the Central Chemoreceptors ACTUALLY respond to?
Hydrogen Ions ( H+ )
BUT WHERE did the Hydrogen Ions ( H+ ) COME FROM?
the REACTION represented by CO2 that entered the brain!
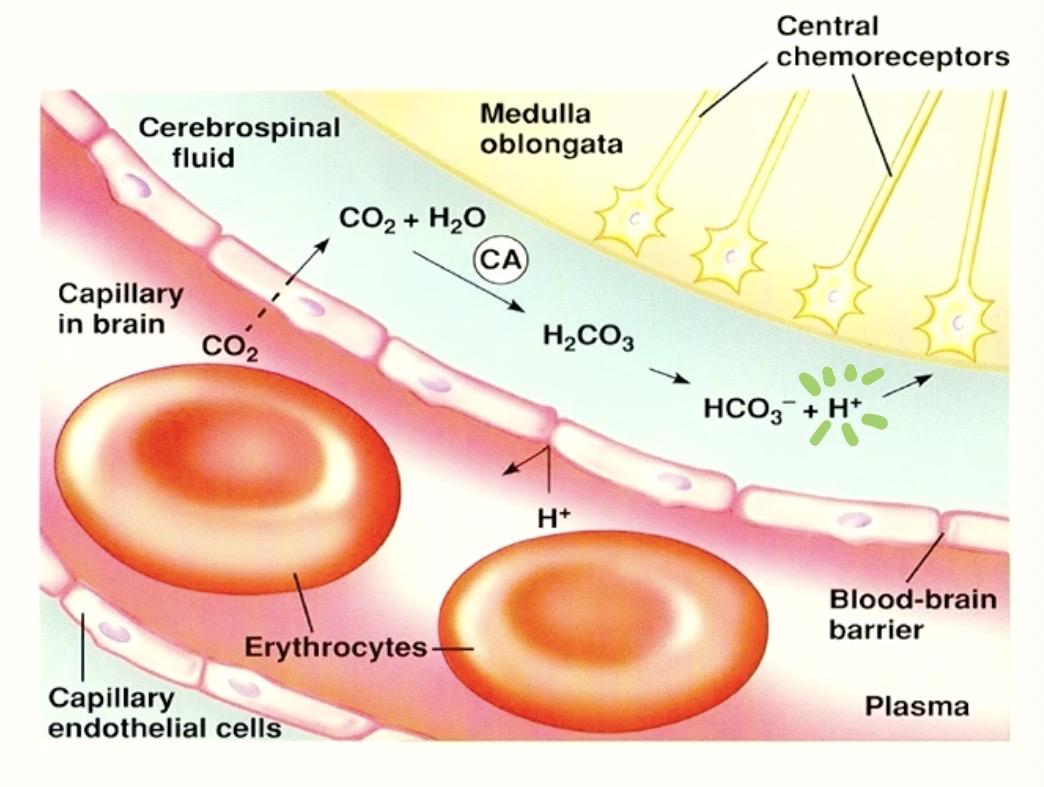

notice in chart
underneath
(⭡PCO2 )
it says
( ⭡H+ ) Increase of Hydrogen in the BRAIN
which is from this reaction!
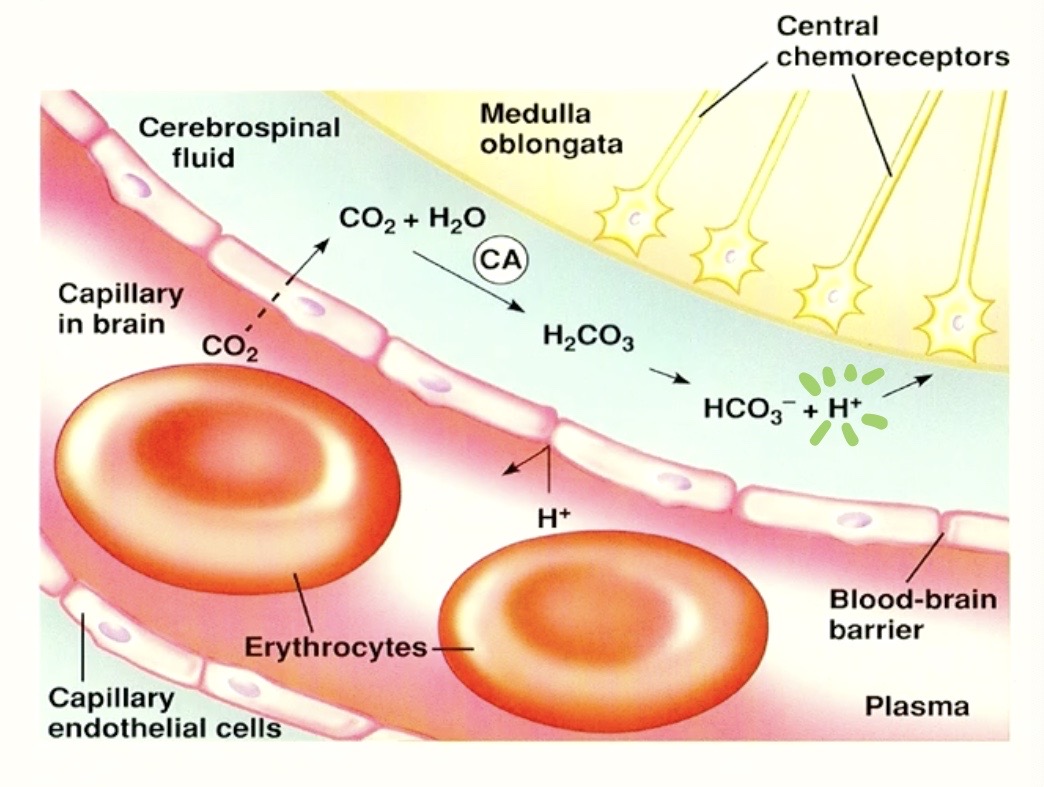
when we have HIGH CO2 in the BLOOD
that leads to
Hydrogen ( H+ ) in the BRAIN
→ from CO2 crossing into brain and causing reaction
Hydrogen ( H+ ) in the BRAIN
Central Chemoreceptors respond to
Do Central Chemoreceptors respond to Hydrogen ( H+ )
IN BLOOD THAT’S NOT IN THE BRAIN?
( from lactic acid, fatty acids, etc )
NO
that’s what peripheral chemoreceptors do!
it can’t because of the
Blood Brain Barrier
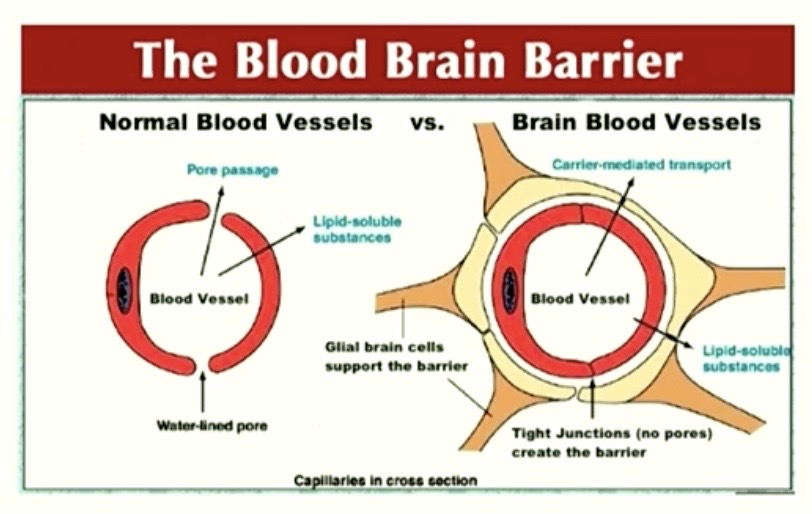
reminder
Capillary Cells in the brain are FUSED together by TIGHT JUNCTIONS
= no pores!
the ONLY way something can go in/out is
ACROSS the CELL MEMBRANE
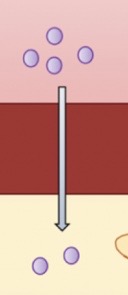
Can Hydrogen ( H+ ) cross the cell membrane?
NO
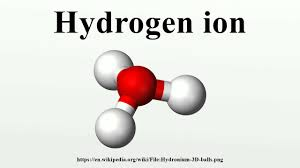
why?
it’s a CHARGED PARTICLE ( + POLAR )
which can’t go through phospholipid bilayer ( + NON-POLAR )
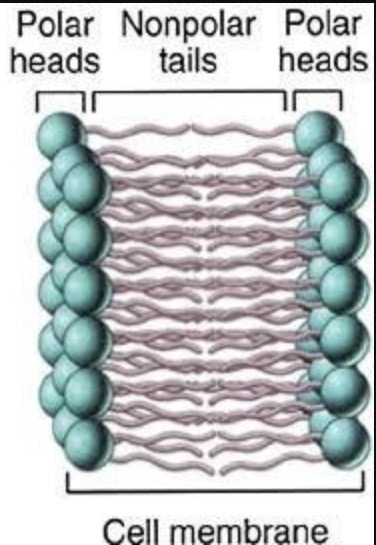
meaning
Hydrogen ( H+ ) CANNOT cross the
Blood Brain Barrier
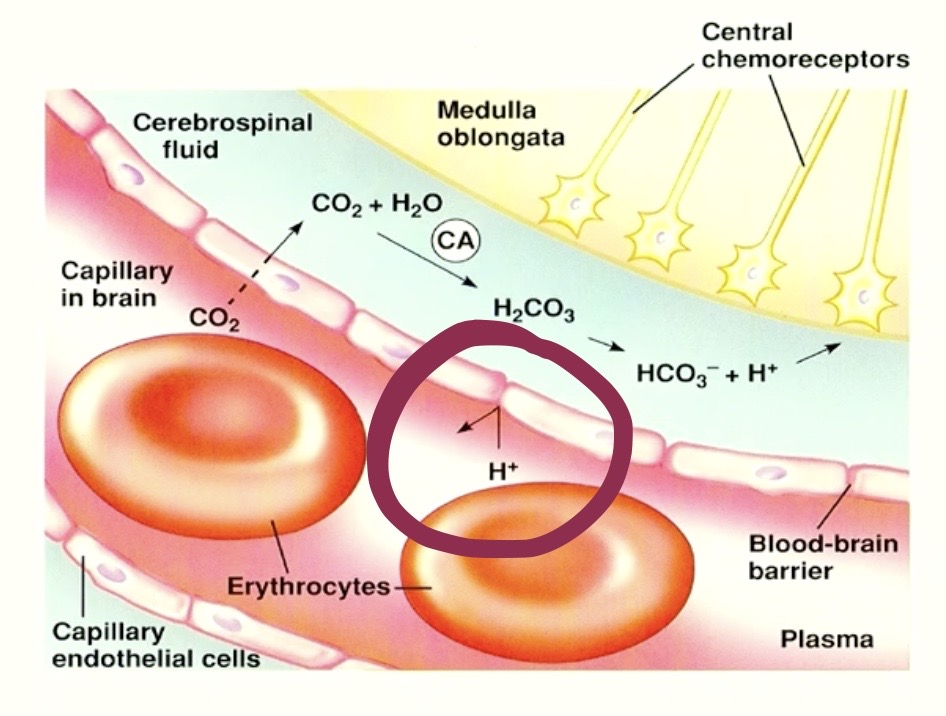
Meaning
Hydrogen ( H+ ) coming DIRECTLY FROM THE BLOODSTREAM
( ex. lactic acid )
CANNOT
Stimulate the Central Chemoreceptors in the BRAIN !!
H+ can ONLY REACH Central Chemoreceptors through CO2 reaction !!
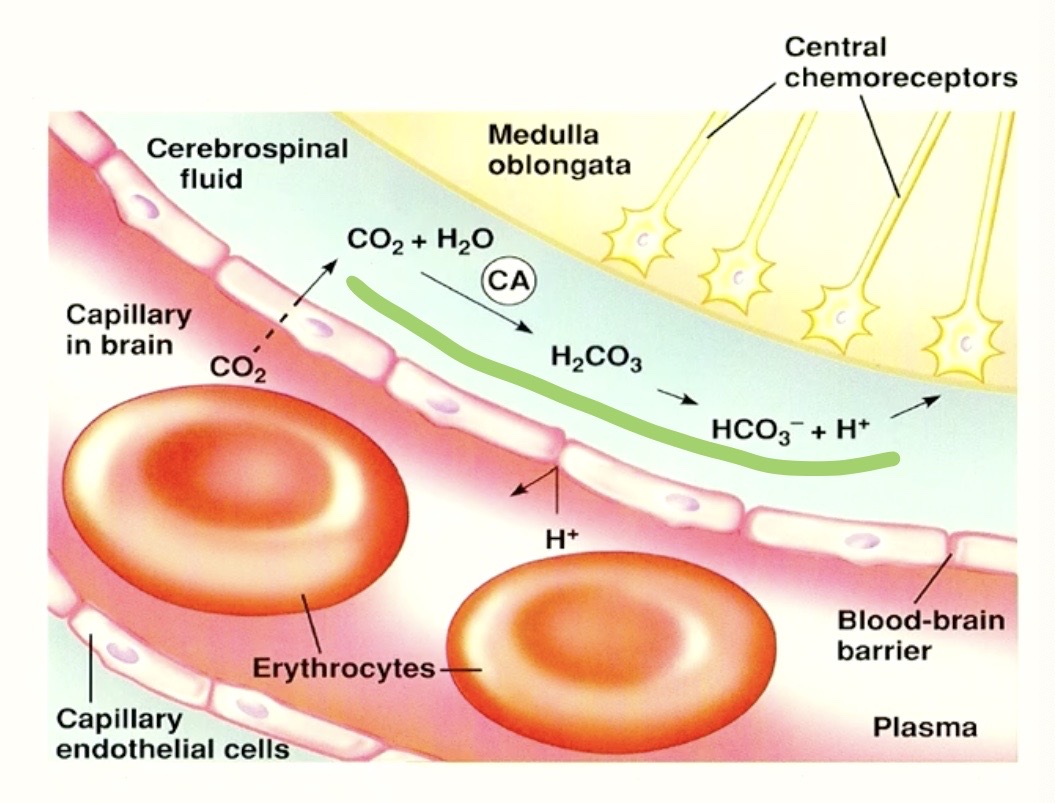

why in chart it says
⭡H+ in blood does not effect central chemoreceptors
“cannot penetrate the blood brain barrier”
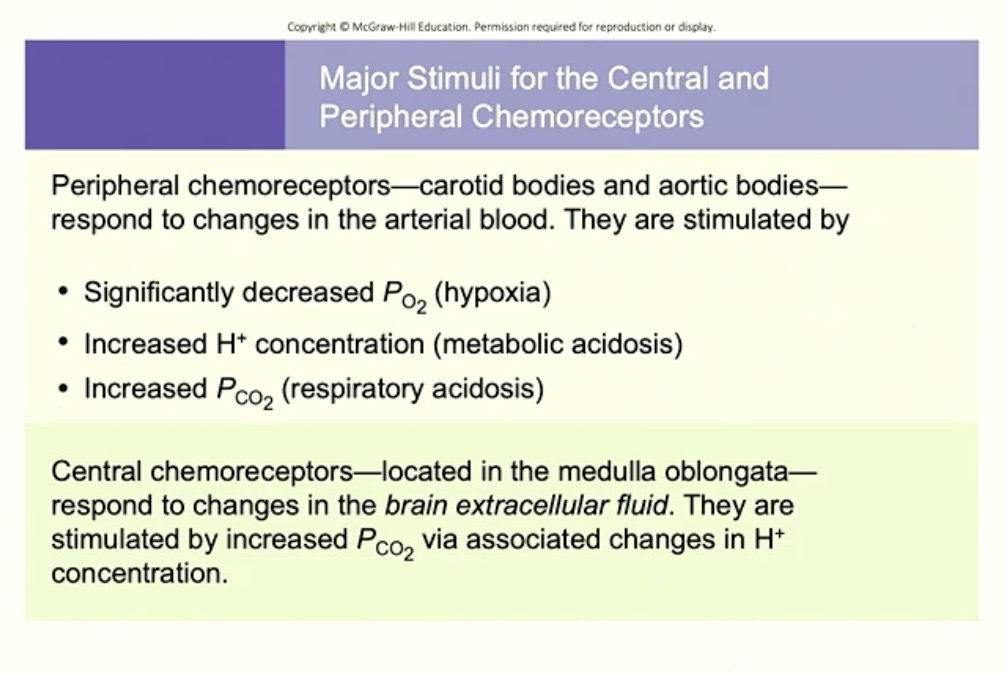
Summary Chart of Chemoreceptors
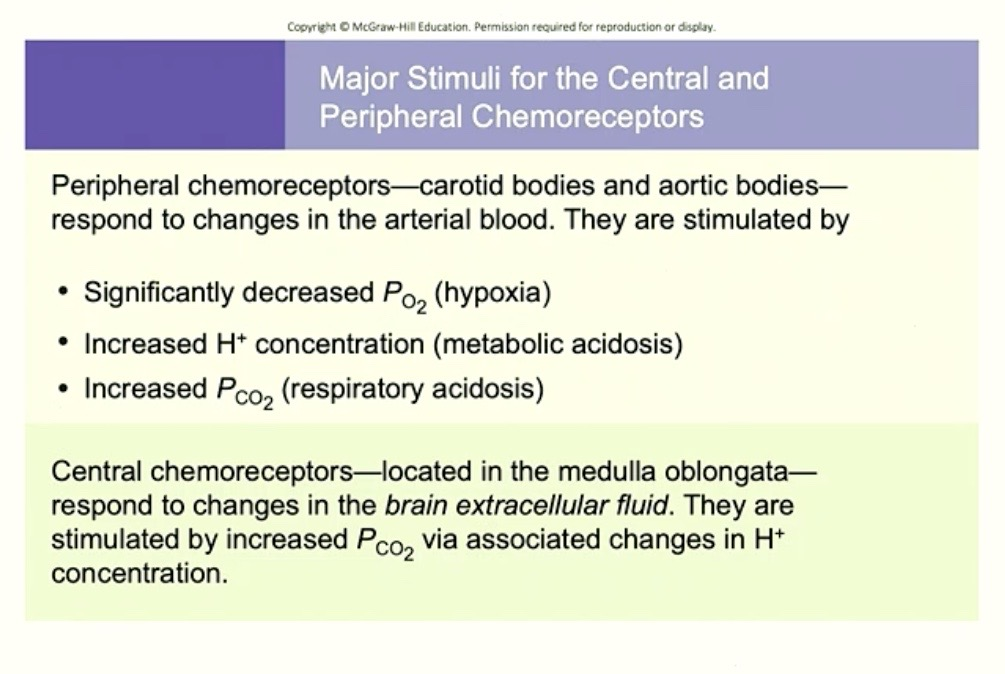
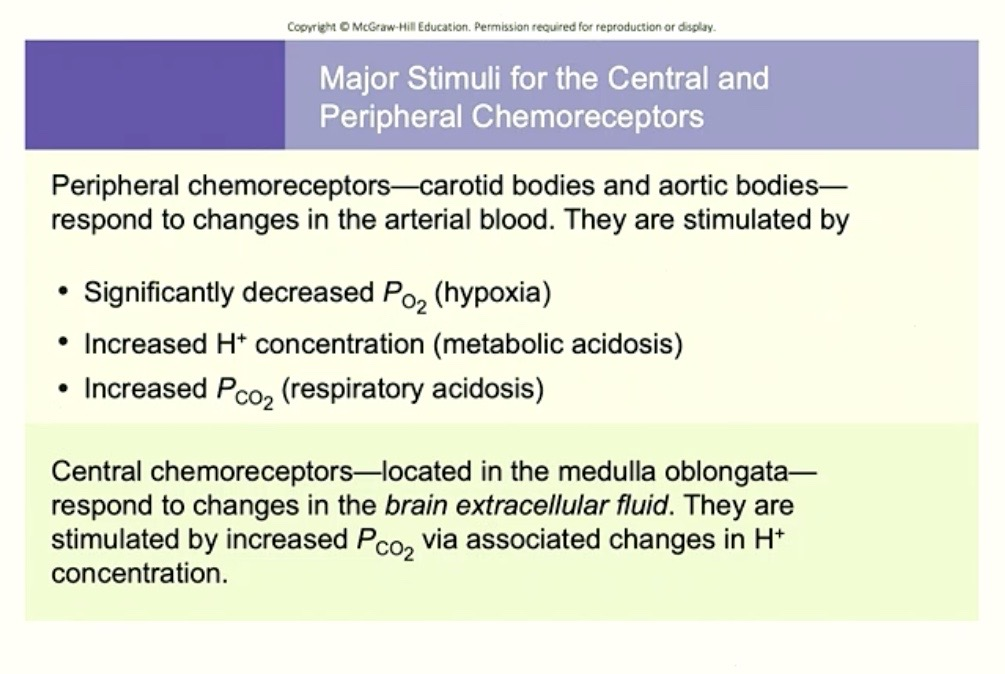
Peripheral Chemoreceptors
Located : Carotid Bodies + Aortic Bodies
Do NOT respond to: PO2 ( unless its super dramatic )
DOES responds to: Increased Hydrogen ( H+ ) in BLOOD
→ from metabolic acidosis mostly
→ also responds a LITTLE BIT to increased PCO2
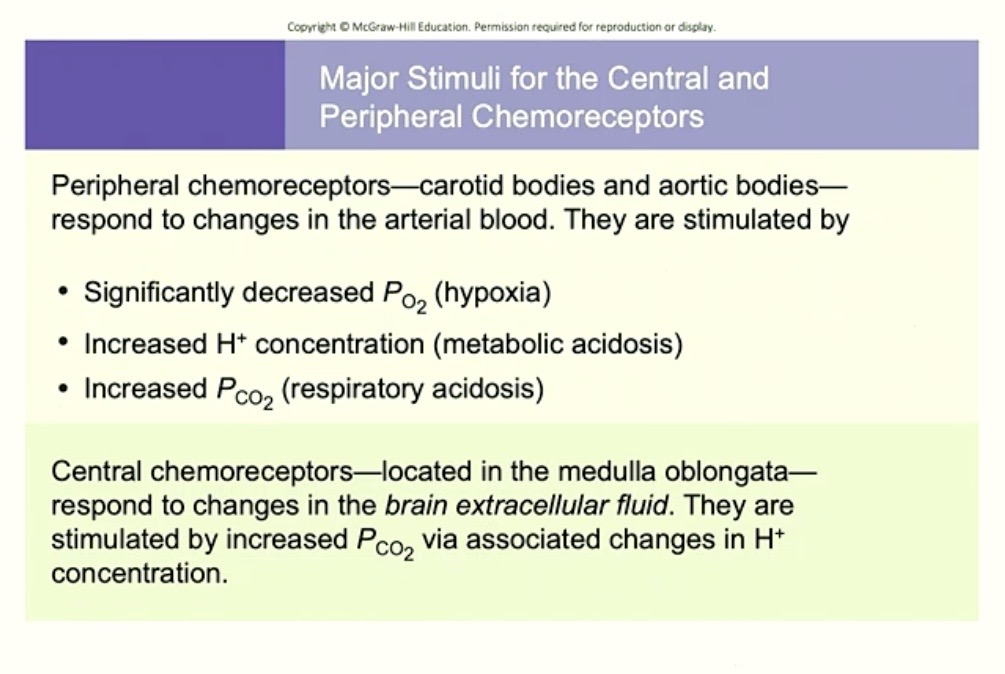
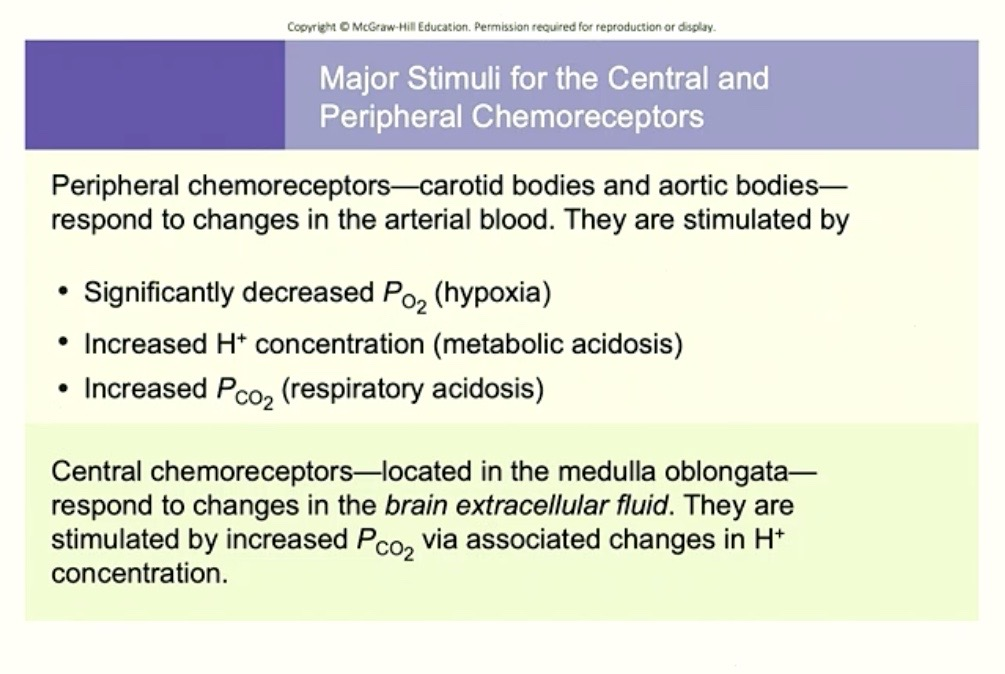
Central Chemoreceptors
Located : Medulla Oblongata
Responds to: Changes to Extracellular Fluid ( ECF ) in Brain
Stimulated by: PCO2 via ( through the means of ) Hydrogen ( H+ ) in BRAIN
→ because of the chemical reaction!
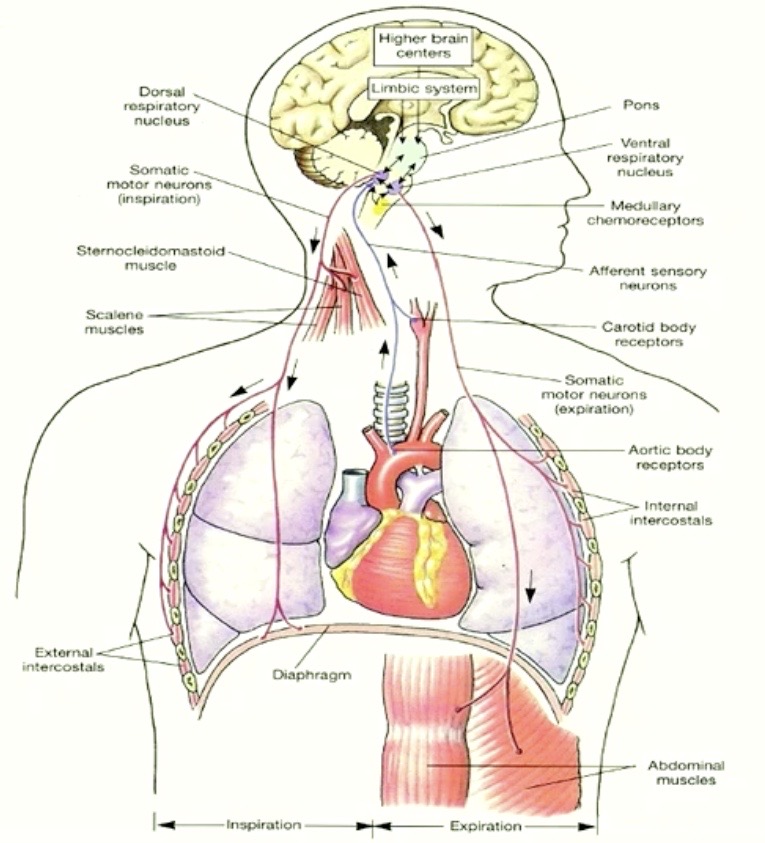
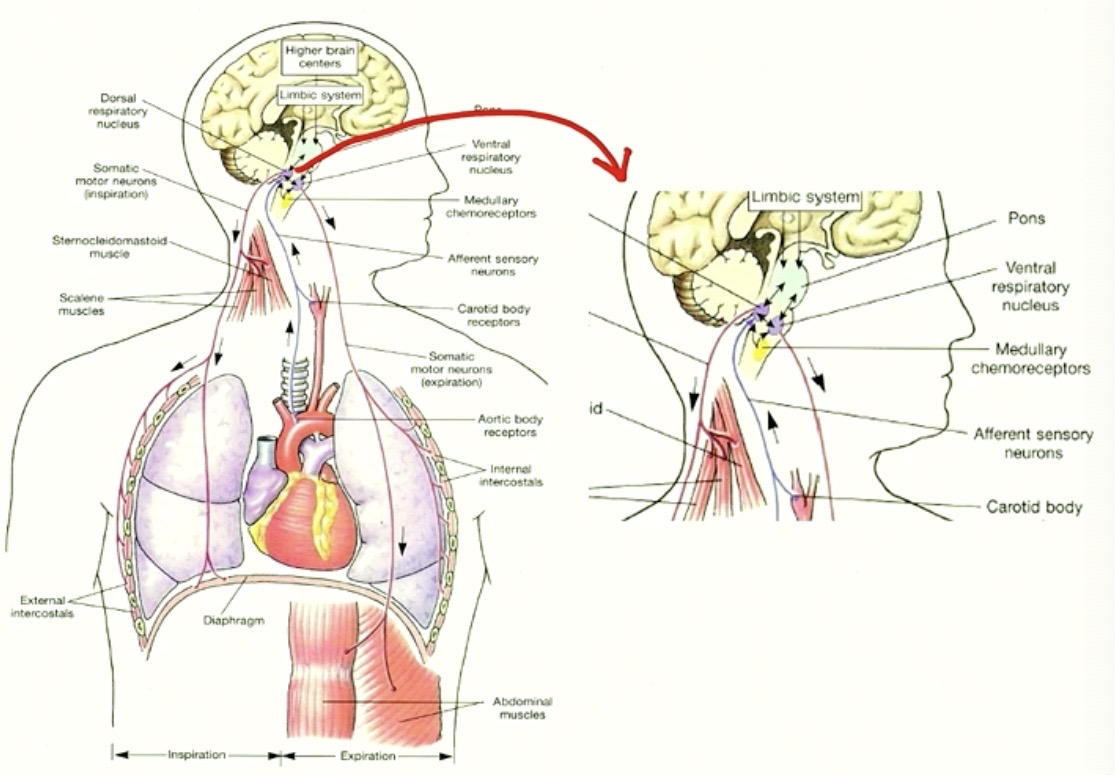
figure that puts it all together
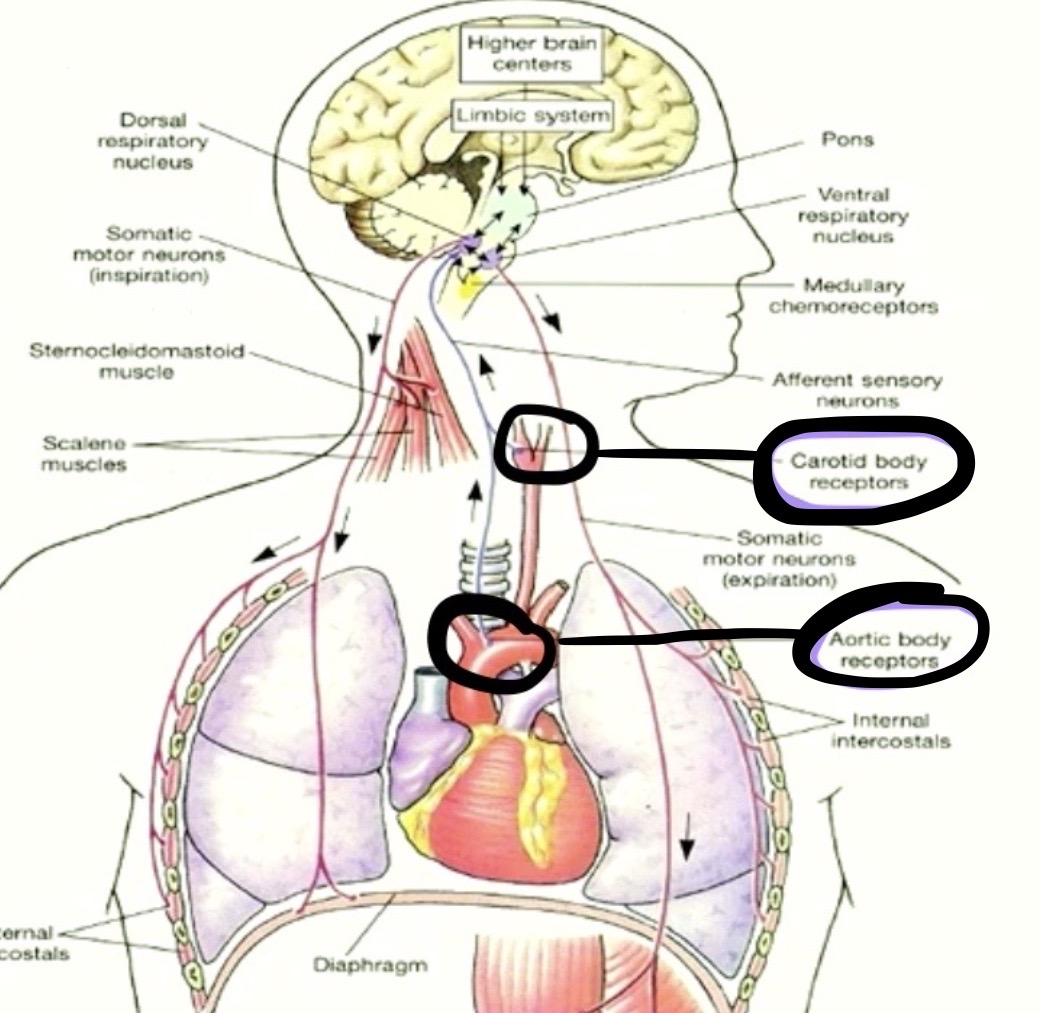
Aortic Bodies + Carotid Bodies
brings information where?
UP to the DRG
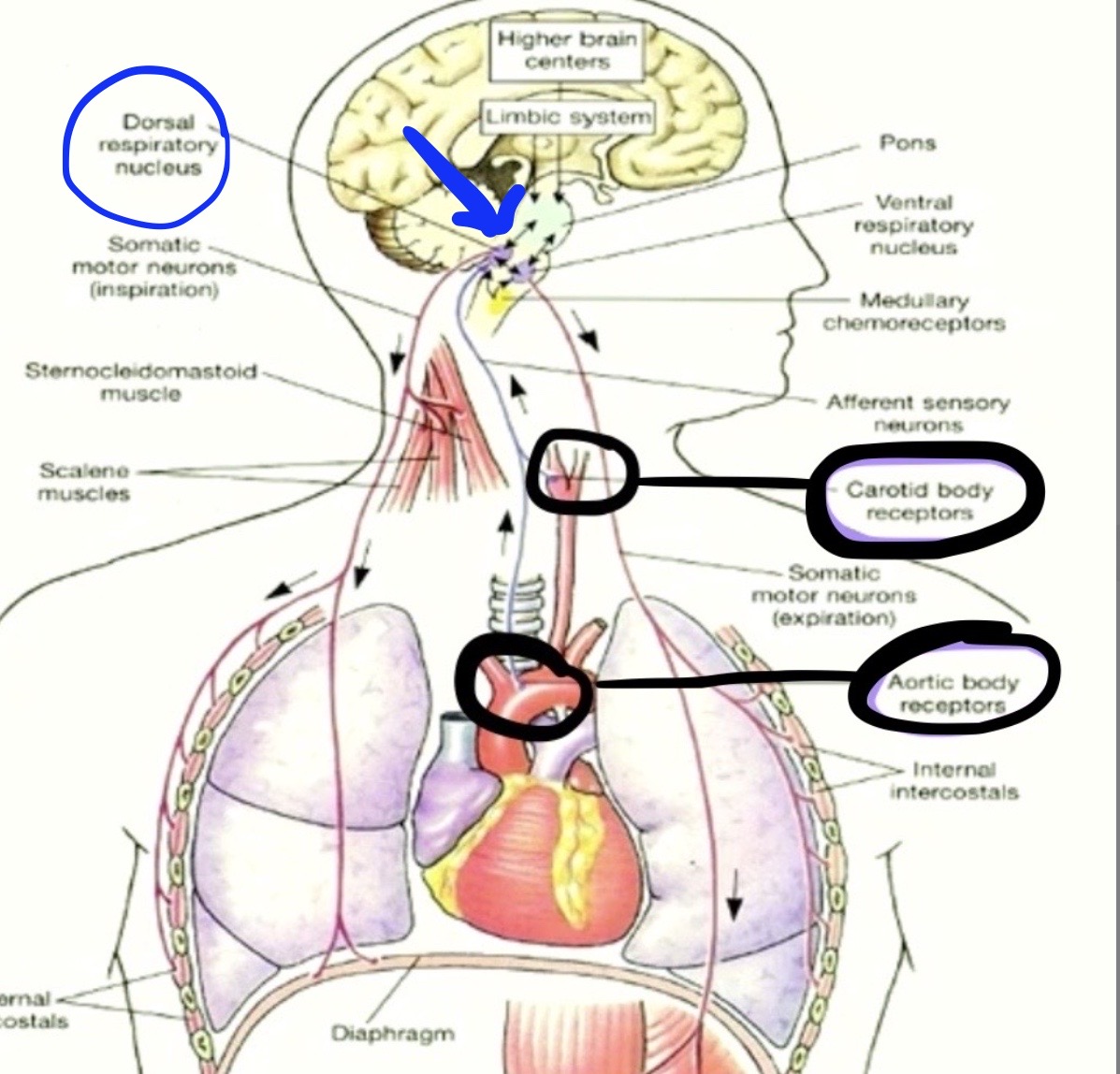
DRG will send it’s adjusting signals out to the
Diaphragm
External Intercostal Muscles
which will adjust breathing accordingly
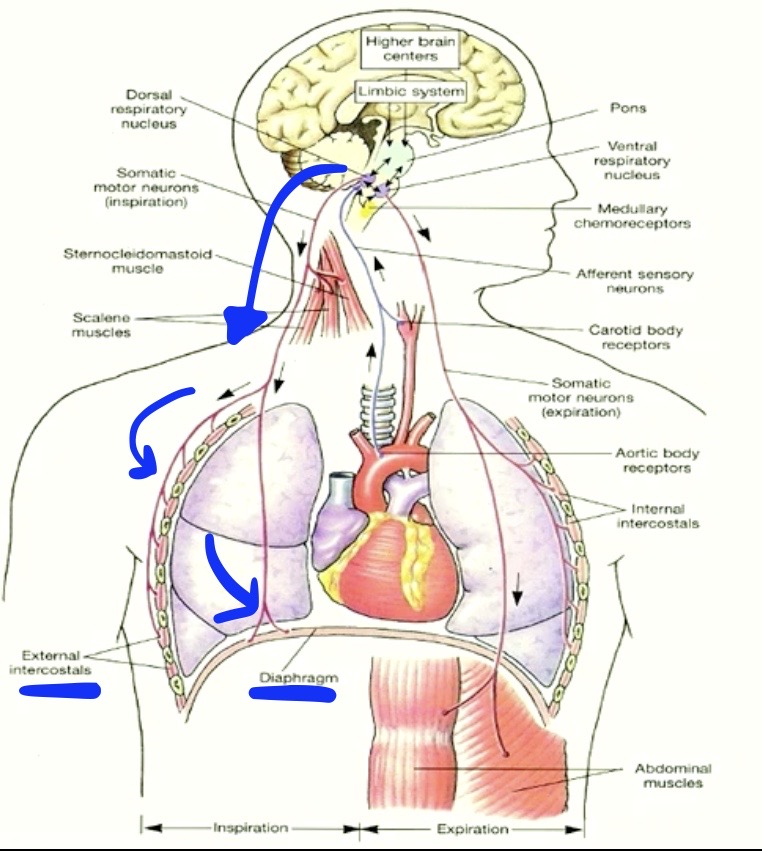
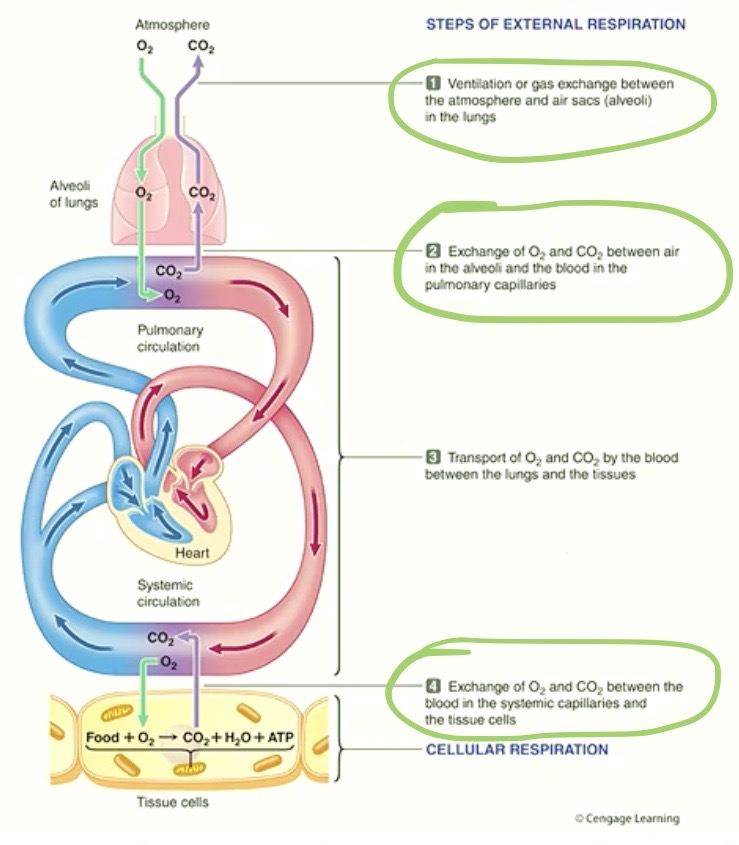
So we’ve covered:
How we get air in and out
How we exchange the gases
there’s one more piece to talk about!
Transportation of Gases