A&P LECTURE EXAM #1
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
Anatomy
study of structure
Physiology
Study of function
Stages of mitosis
1. Interphase
2. Prophase
3. Metaphase
4. Anaphase
5. Telophase
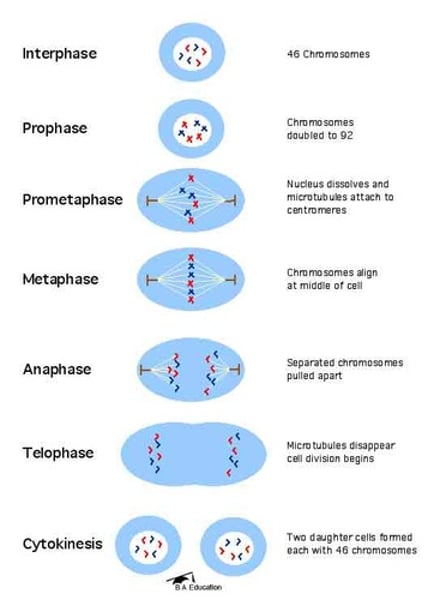
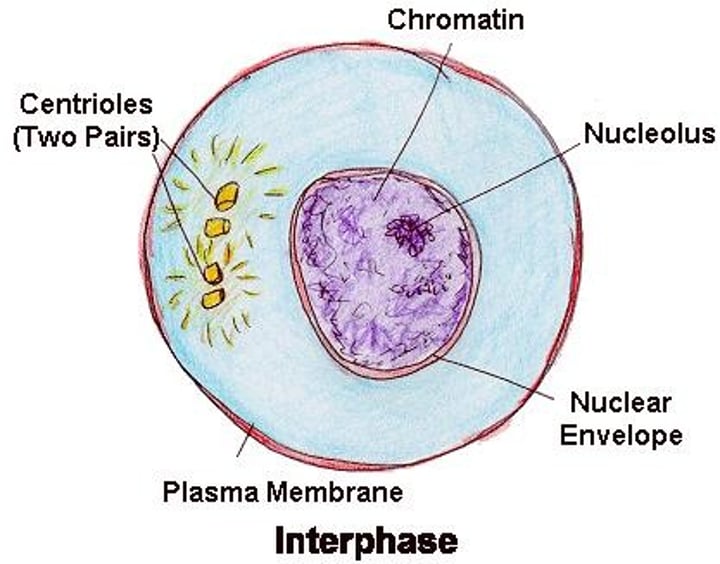
Interphase
•Longest stage of a cell's life
•Time spent between divisions
•Produces all materials required for growth
•Preparation for division (CHROMOTANIN)
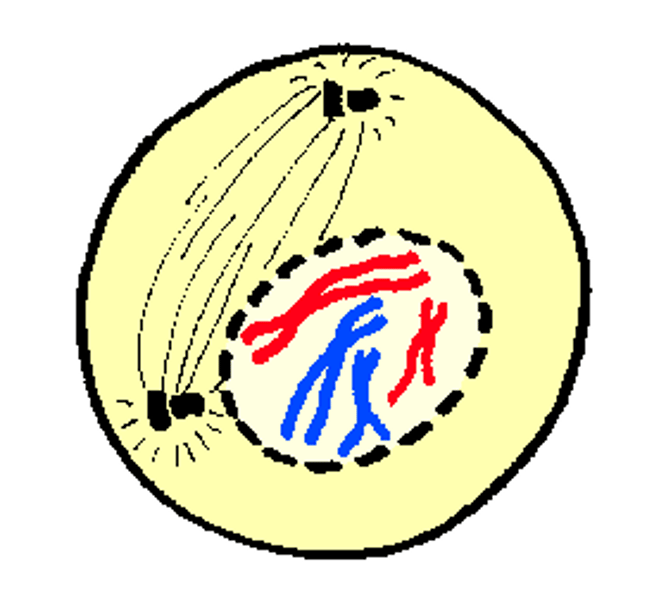
Prophase
- Nucleus disappears
- Nuclear membrane breaks down
- Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
- Spindle fibers form from centrosomes. (CHROMOTANIN)
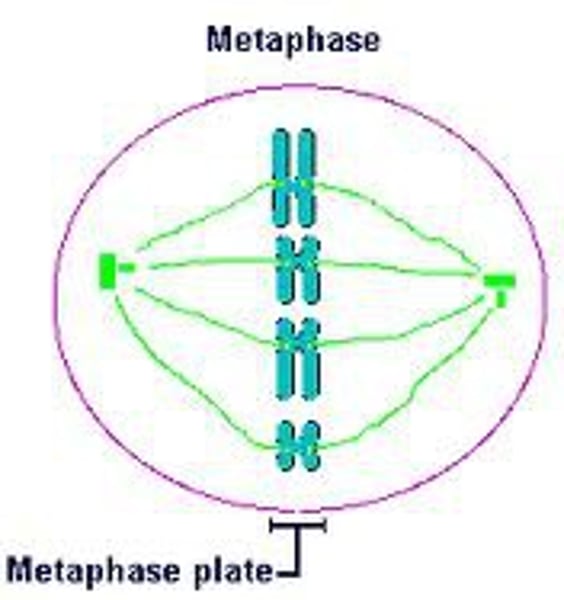
Metaphase
- 2nd phase of mitosis
- Chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
- Each chromatid is attached to the spindle with a centromere (CHROMATID)
ANAPHASE
- Sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell.
- Each chromatid is now considered as a separate chromosome (DAUGHTER CHROMOSOMES)
TELOPHASE
- Final phase of cell division
- 2 nuclear envelopes form & chromosomes begin to uncoil back to form chromatin (DAUGHTER CHROMOSOMES)
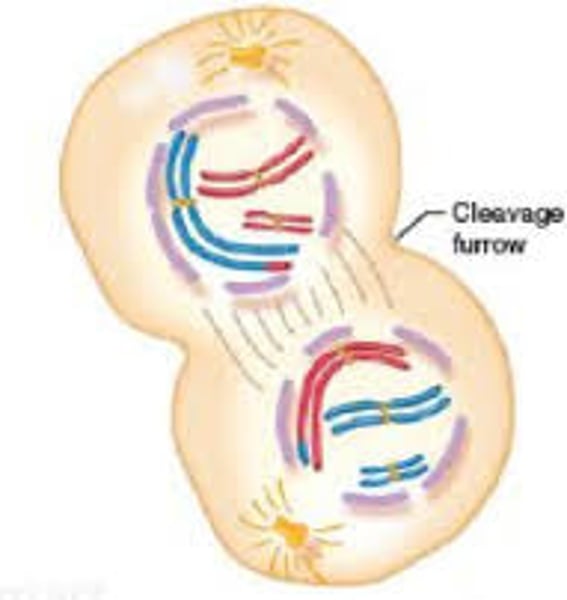
CYTOKINESIS
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
Functions of human life
maintaining boundaries, movement, responsiveness, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, growth, digestion
Levels of organization
chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
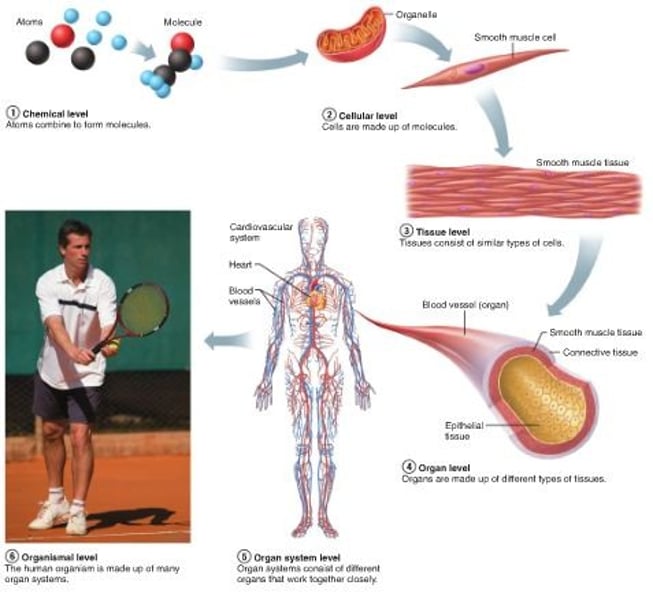
CHEMICAL LEVEL
atoms, molecules, and organelles
CELLULAR LEVEL
molecules combine to form cells
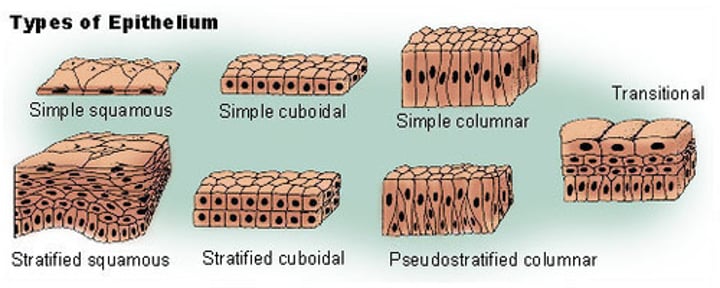
TISSUE LEVEL
groups of similar cells that have a common function
- Epithelial tissue (skin, protects), Connective Tissue (adipose, blood, bones), Muscle Tissue (cardiac, skeletal), Nervous Tissue (brain, spinal cord)
ORGAN LEVEL
one or more tissues functioning together
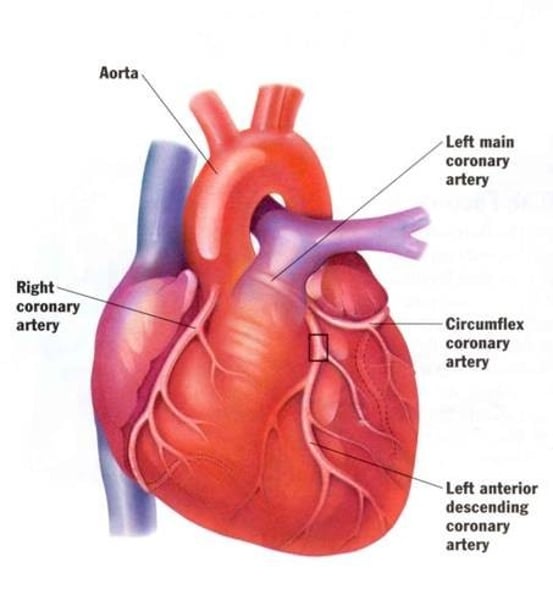
ORGAN SYSTEM LEVEL
Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely
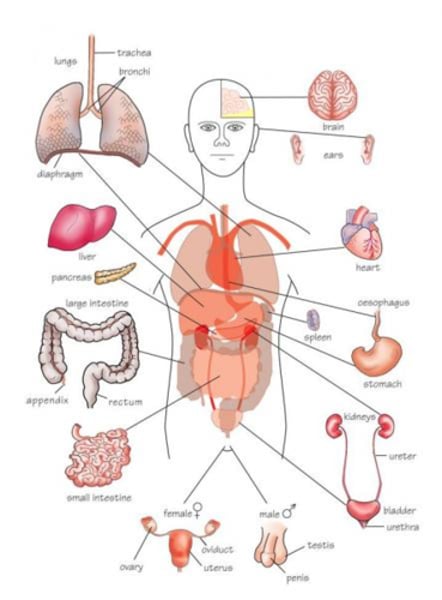
ORGANISM
all of the components interact to allow the human to survive & flourish
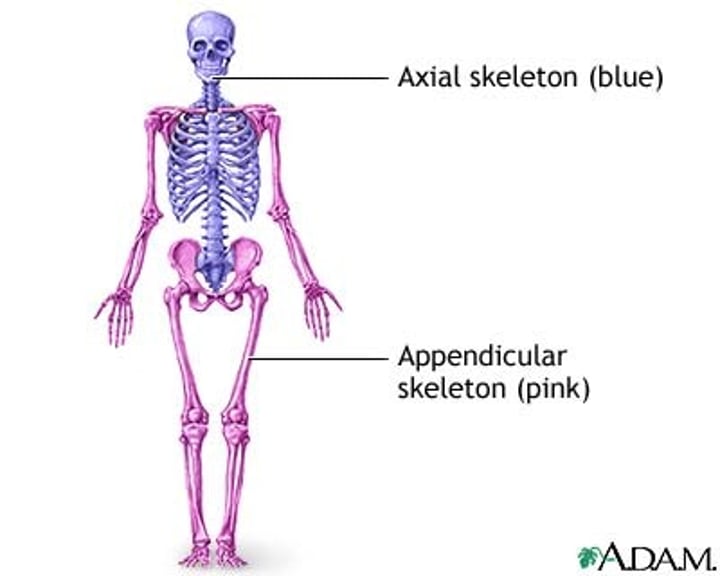
Axial Subdivision
- head
- neck
- torso, or trunk, its subdivisions
- everything but arms and legs
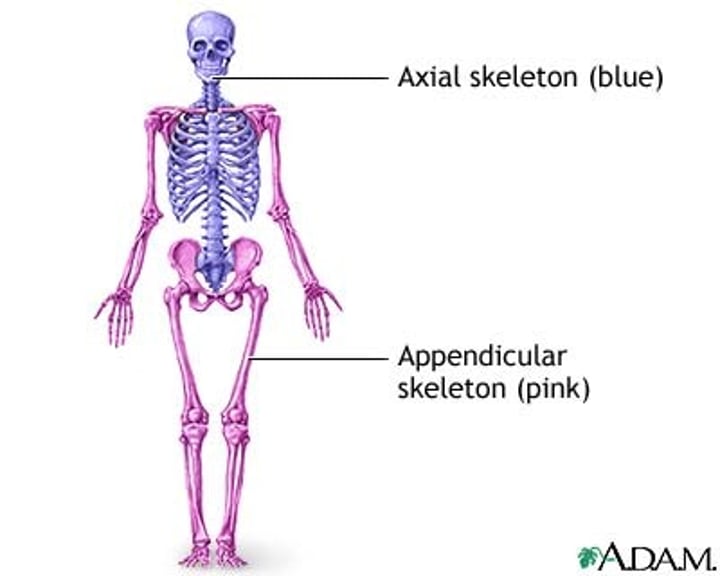
Appendicular subdivision
Includes the upper extremities and lower extremities and their subdivisions
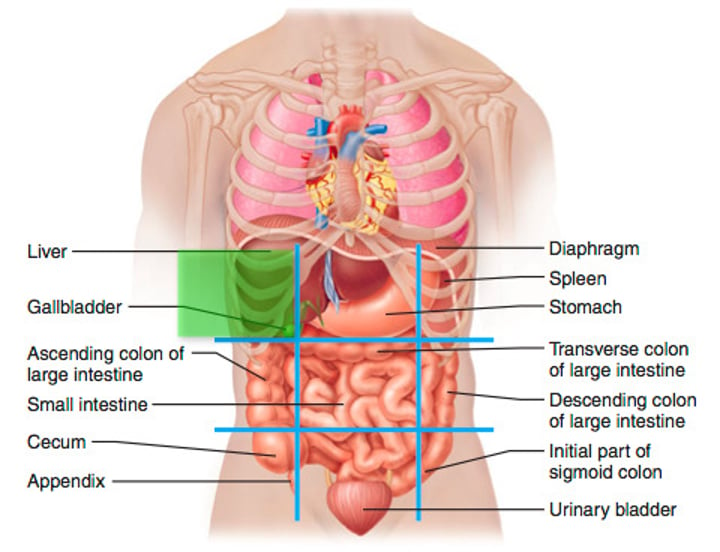
right hypochondriac region (1)
Liver, Gallbladder, Right Kidney, Small Intestine
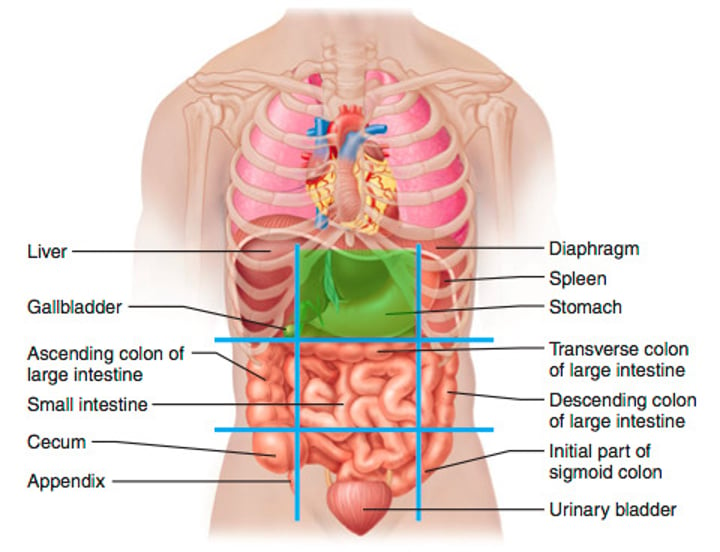
epigastric region (2)
located above the stomach, superior to the umbilical region (majority of stomach, part of liver, pancreas, duodenum, spleen & the adrenal glands)
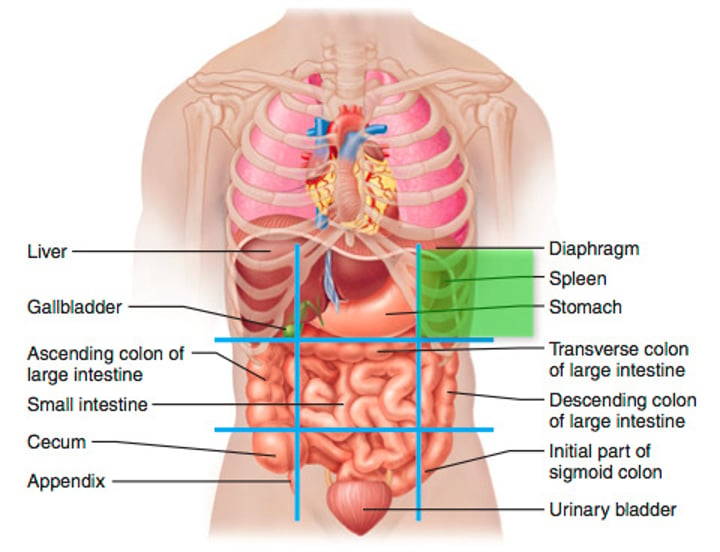
left hypochondriac region (3)
left upper region below the rib cartilage; diaphragm, spleen
right lumbar region (4)
right middle region near the waist
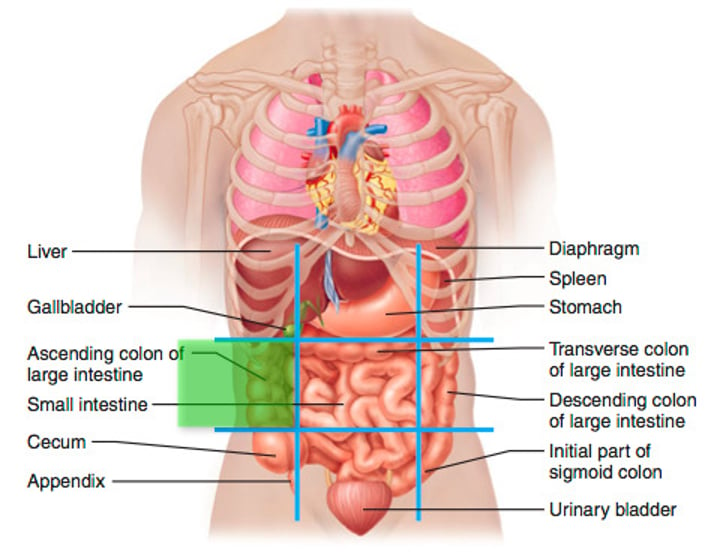
umblical region (5)
refers to the middle portion
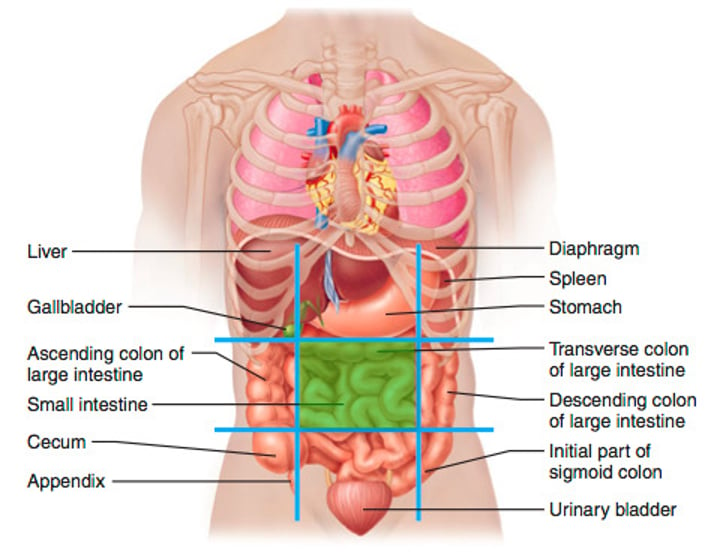
left lumbar region (6)
left middle region near the waist
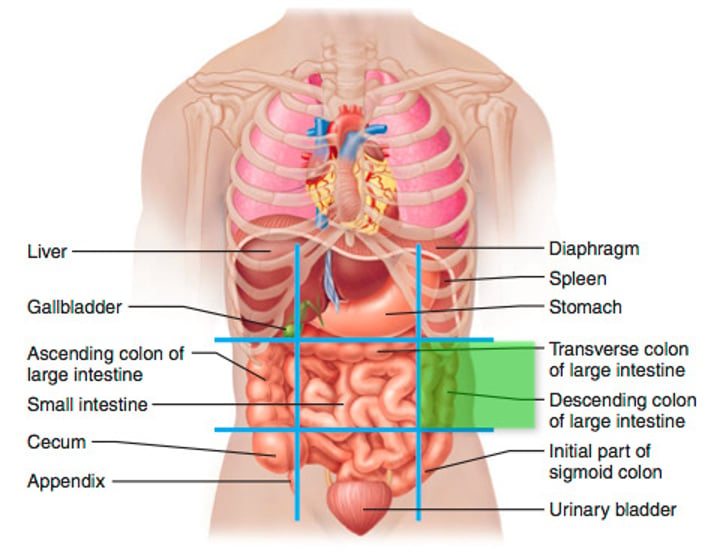
Right lilac (inguinal) region (7)
under the right lumbar region
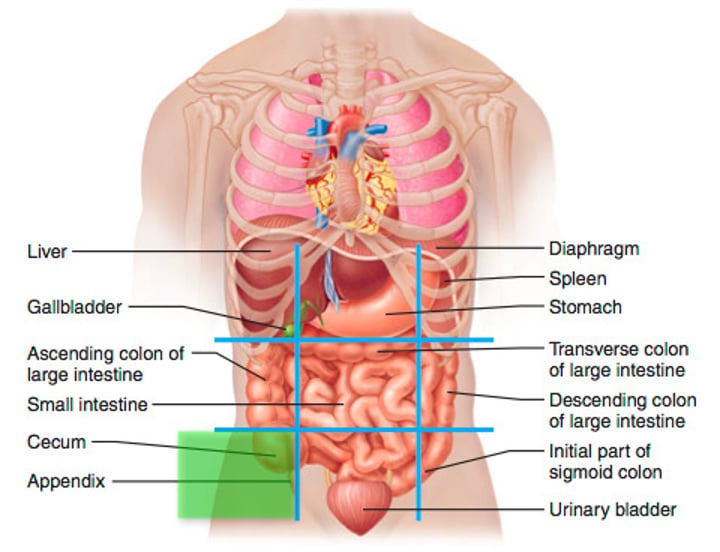
hypogastric region (8)
lower middle portion
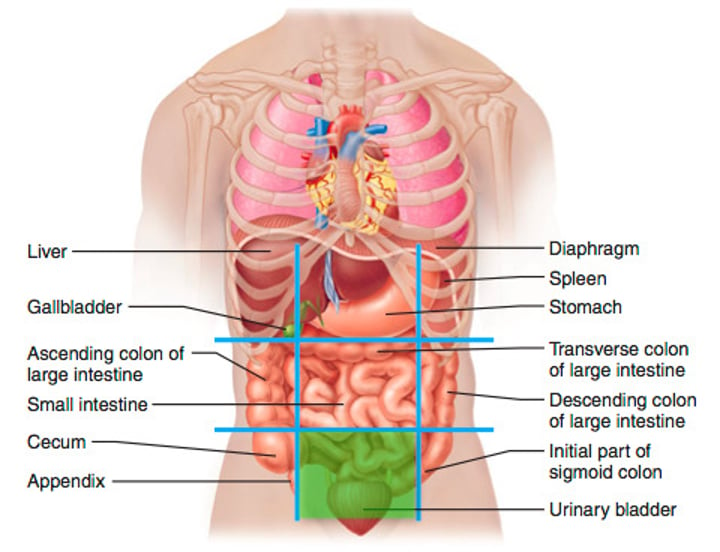
left lilac (inguinal) region (9)
- lateral left-hand side of the hypogastric region
- last one
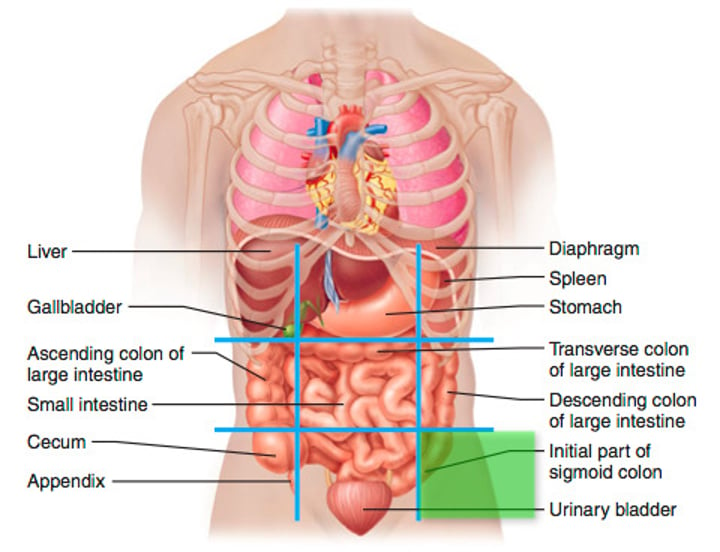
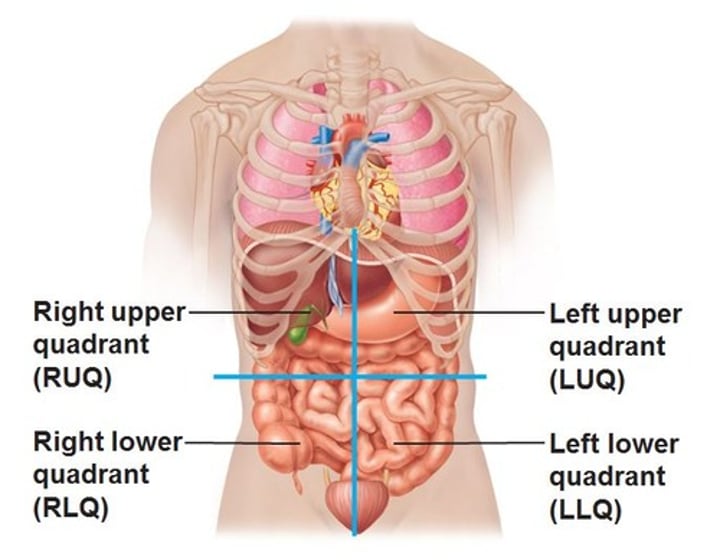
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
right upper quadrant, left upper quadrant, right lower quadrant, left lower quadrant
Superior
Higher on the body, nearer to the head
inferior
Lower on the body, farther from the head
Anterior (ventral)
front of the body
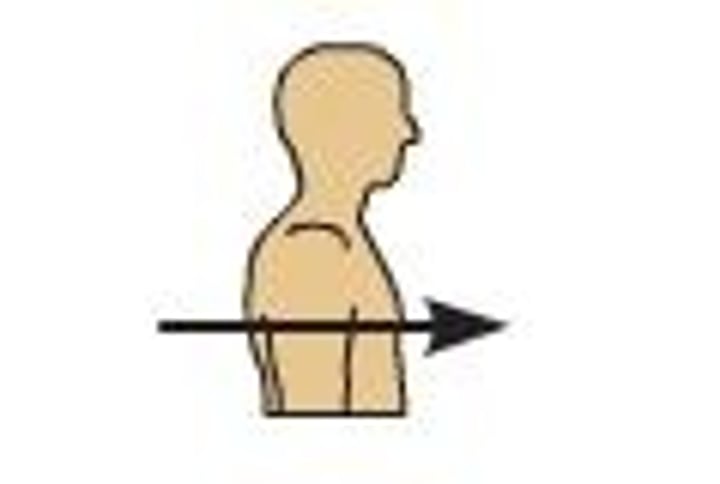
Posterior (dorsal)
back of body
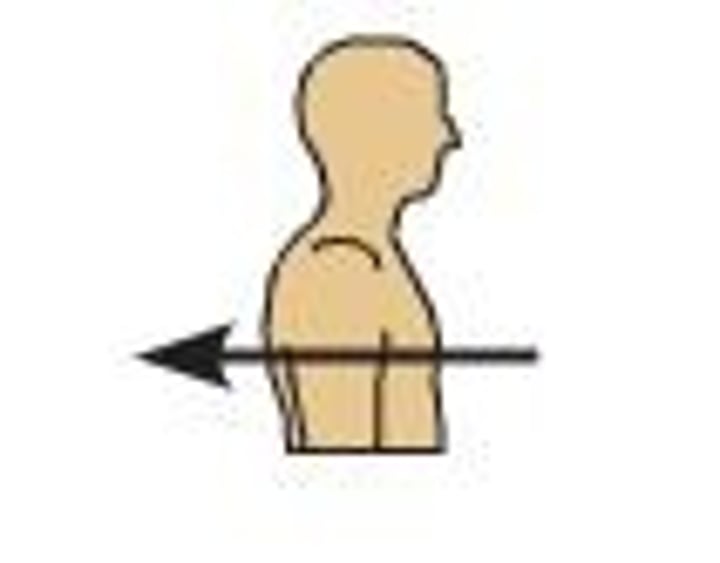
medial (not middle)
near the midline of the body
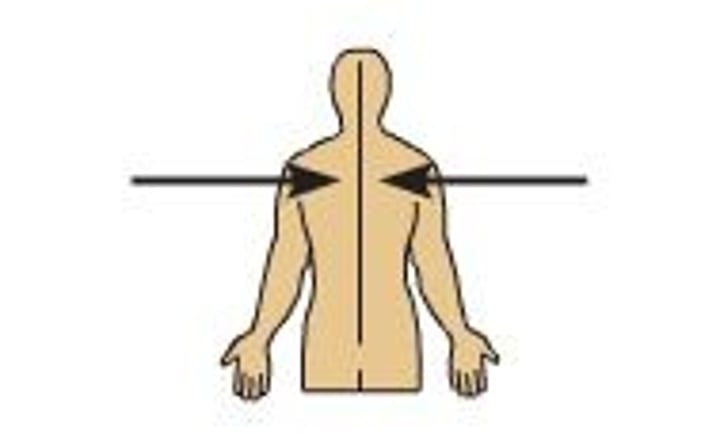
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body (up and down)
Proximal
Nearer to the trunk of the body
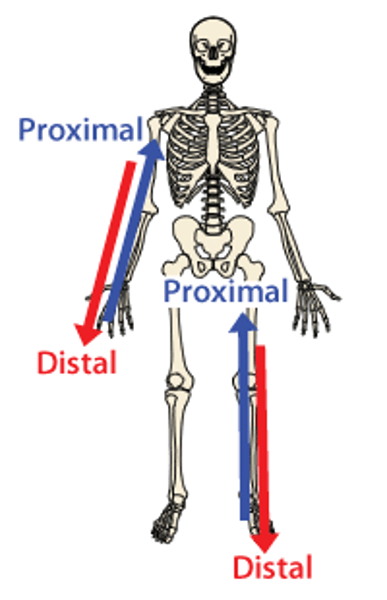
Distal
Farther from the trunk of the body
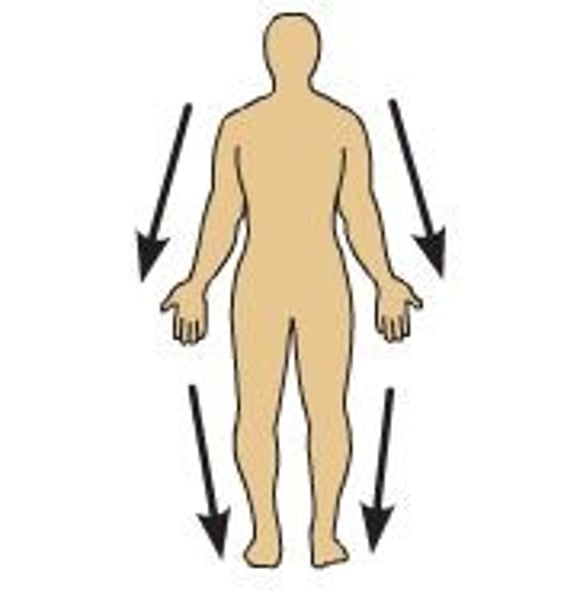
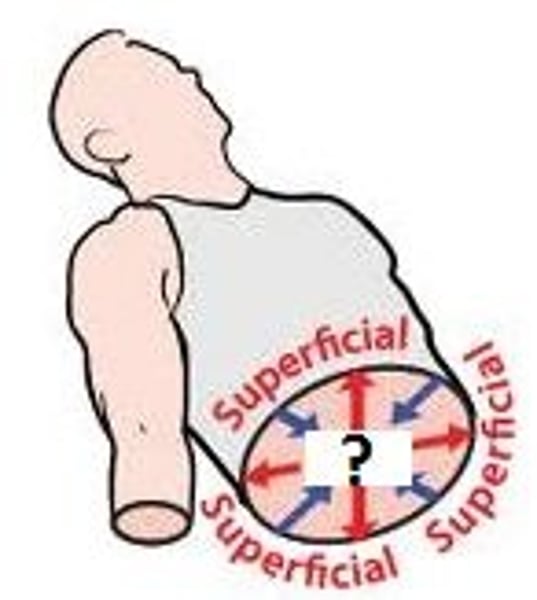
superficial
near the surface, more on the outside (ex: skin, eyes)
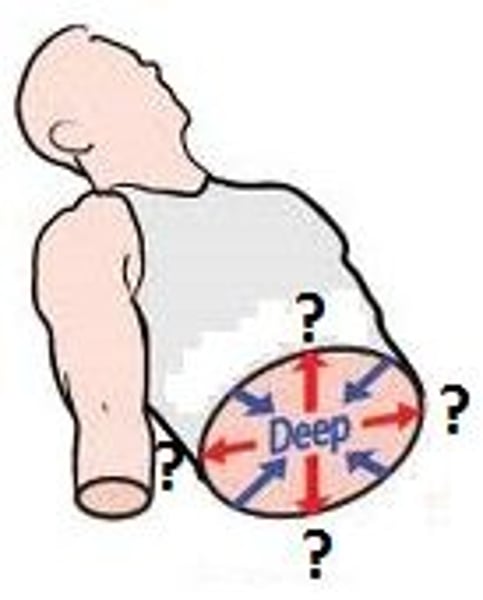
deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
lumen (luminal)
space inside digestive, respiratory, and urogenital organs or vessels of the body
peripheral
away from the center
cortical (cortex)
outer region of an organ
basal (base)
Base or widest part of an organ
central
brain and spinal cord
Medullary (medulla)
inner region of an organ
Apical (apex)
narrow tip of an organ
Transcytosis
Transport into, across, and then out of cell; combination of endocytosis and exocytosis
Exocytosis
release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane.
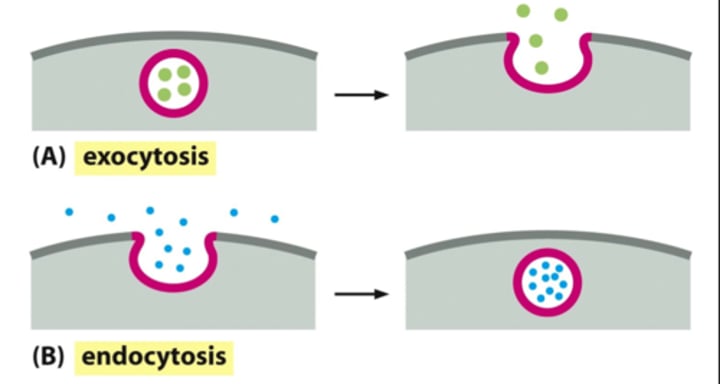
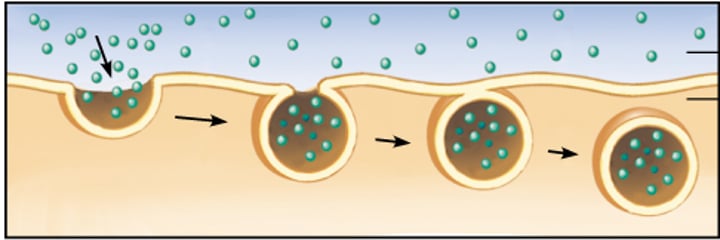
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
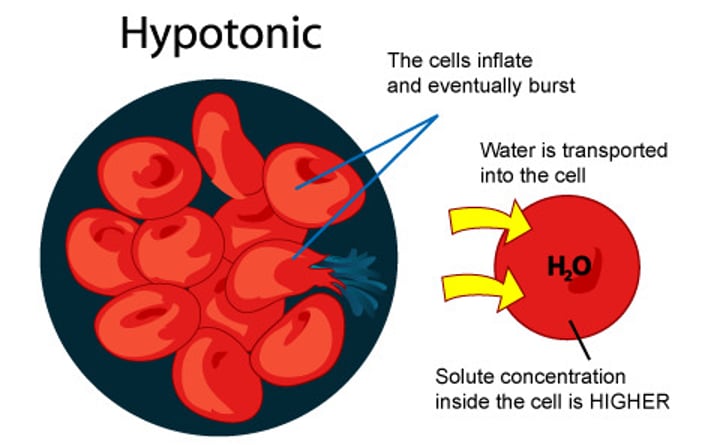
Hypotonic solution
- Solution has MORE water than cells
- Water flows from L to H concentration
- Cells swell and burst (osmosis)
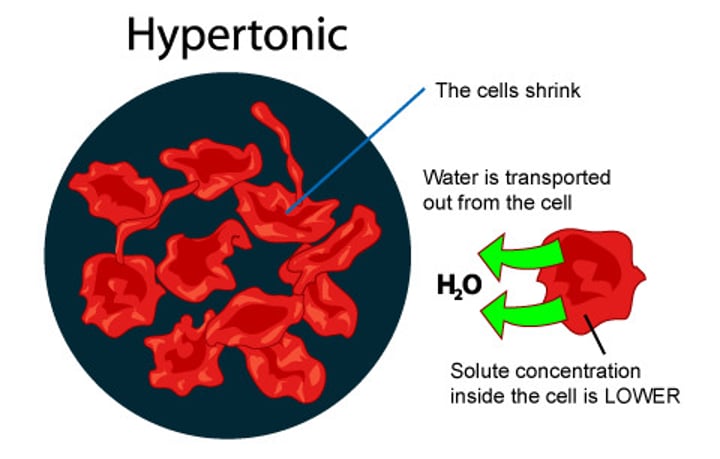
hypertonic solution
Solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell; cell loses water
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference (L --> H)
primary active transport
Active transport that relies directly on the hydrolysis of ATP.
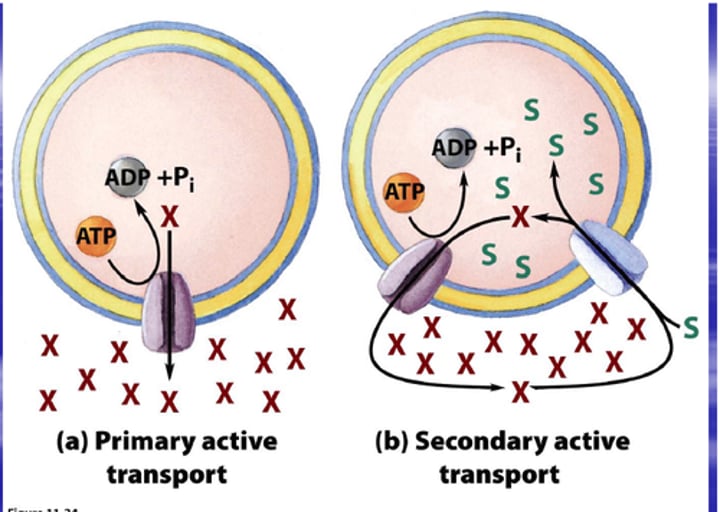
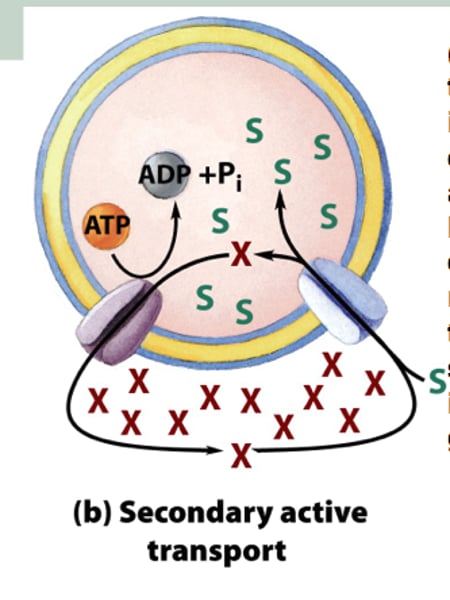
secondary active transport
Form of active transport that does not use ATP as an energy source; rather, transport is coupled to ion diffusion down a concentration gradient established by primary active transport.
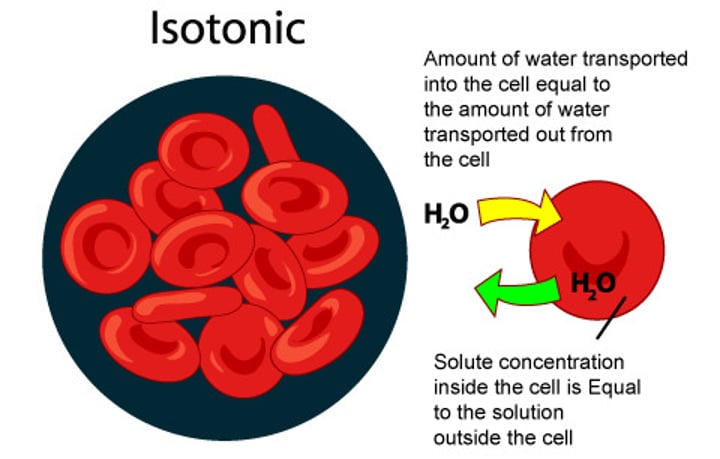
Isotonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell
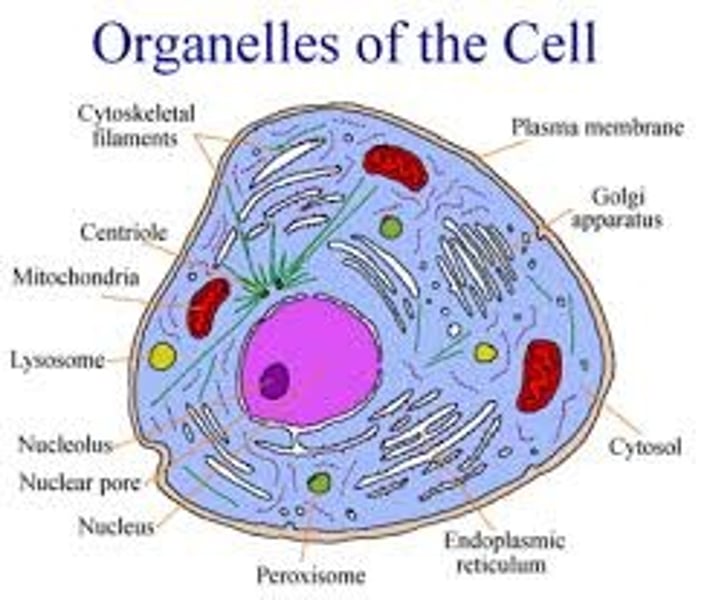
Ribosomes
Makes proteins
eccrine glands
glands that produce sweat; found over most of the body
sebaceous glands
oil glands
Epidermis
outermost layer of skin
Dermis
middle layer of skin
Hypodermis
loose connective tissue layer of skin below the dermis
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
osmsis
When a cell has emerged in water, the water molecules pass through the cell membrane from low solute (outside) to high solute (inside) (diffusion of water)
simple diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
tranverse plane
a horizontal plane that divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions
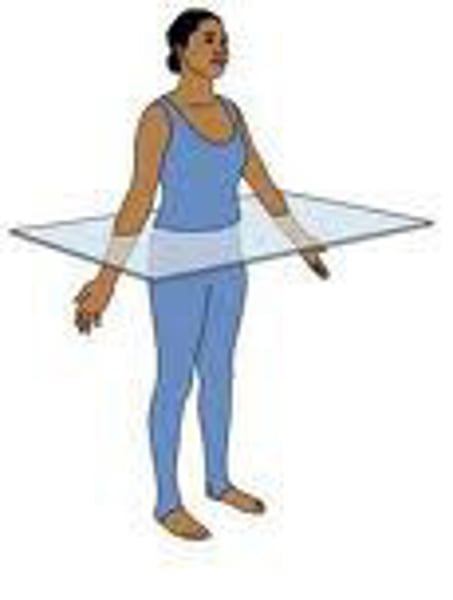
frontal plane (coronal plane)
Divides the body into front and back portions.
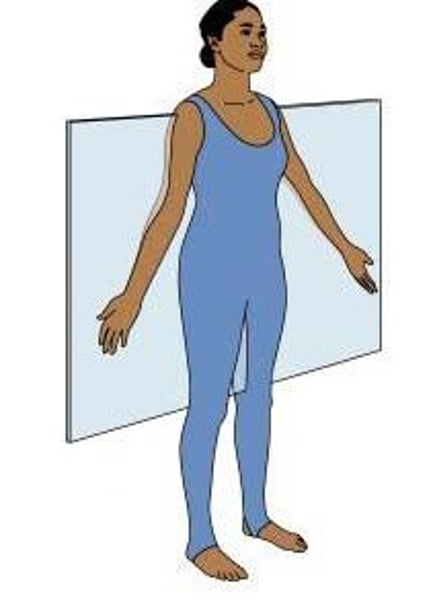
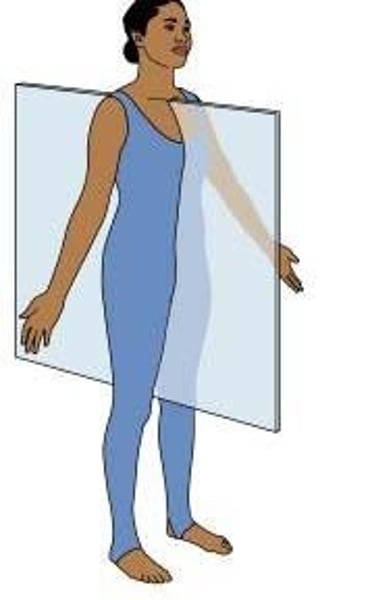
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
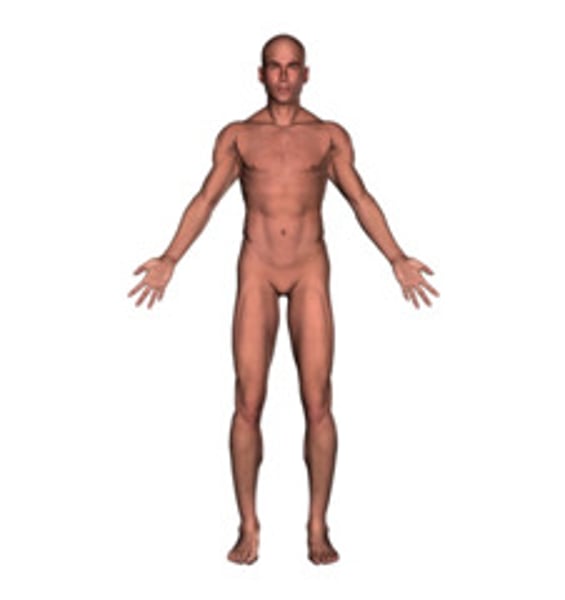
anatomical position
erect, feet forward, arms at side with palms facing forward, head facing forward
Metabolism
sum of all anabolic and catabolic reactions that break and build food, respectively.
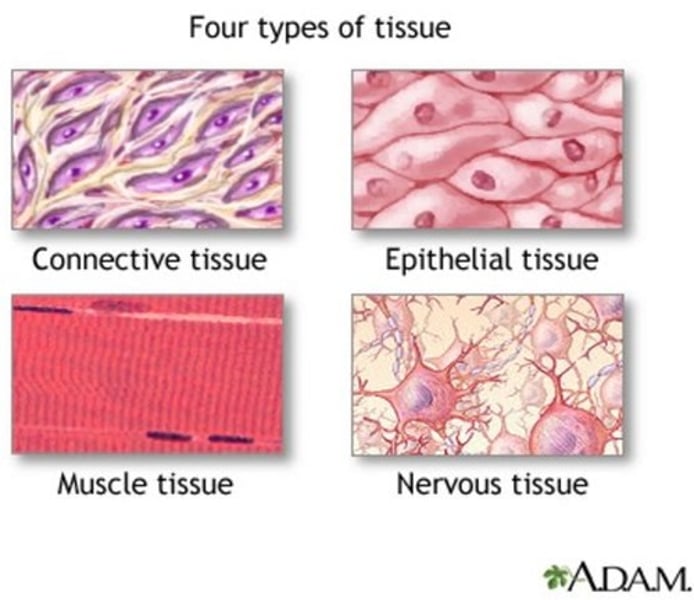
4 types of tissue
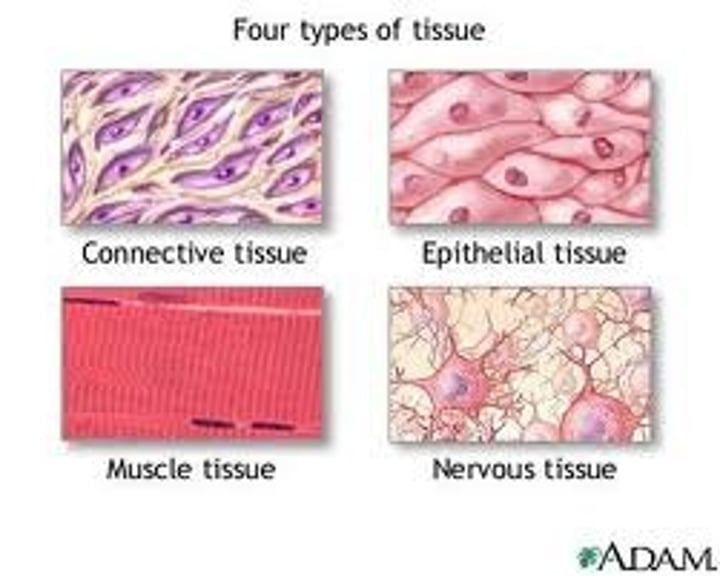
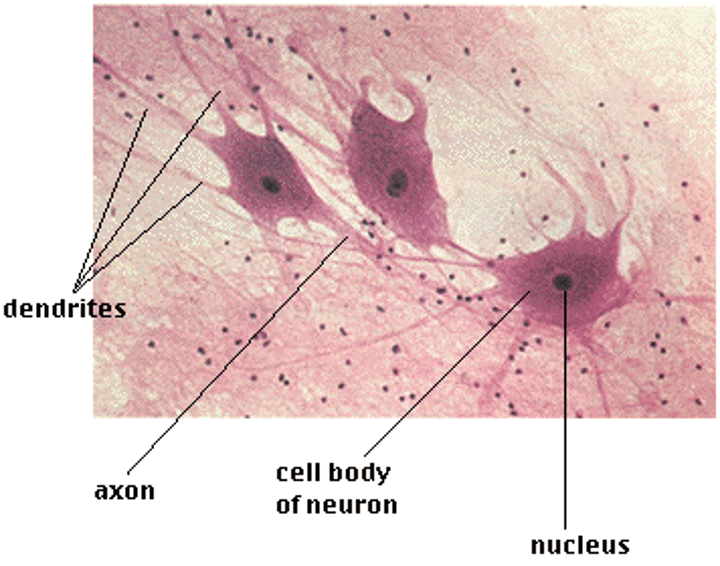
nervous tissue
A body tissue that carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and every other part of the body.
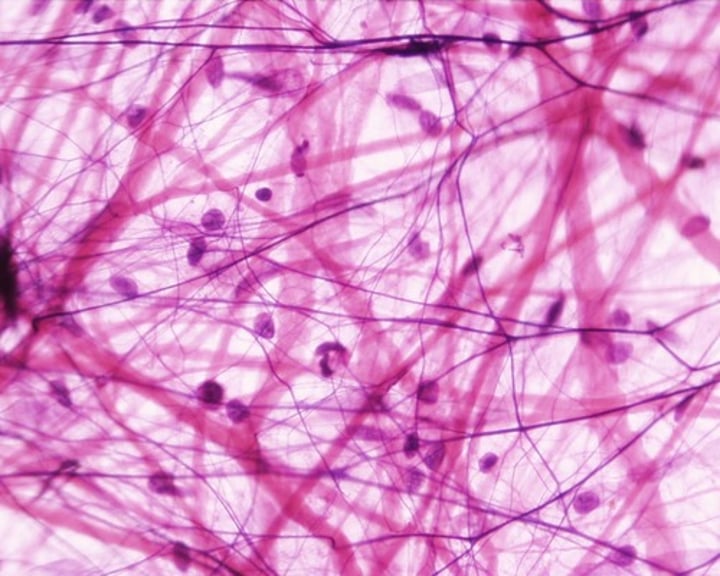
connective tissue
provides support for your body and connects all its parts
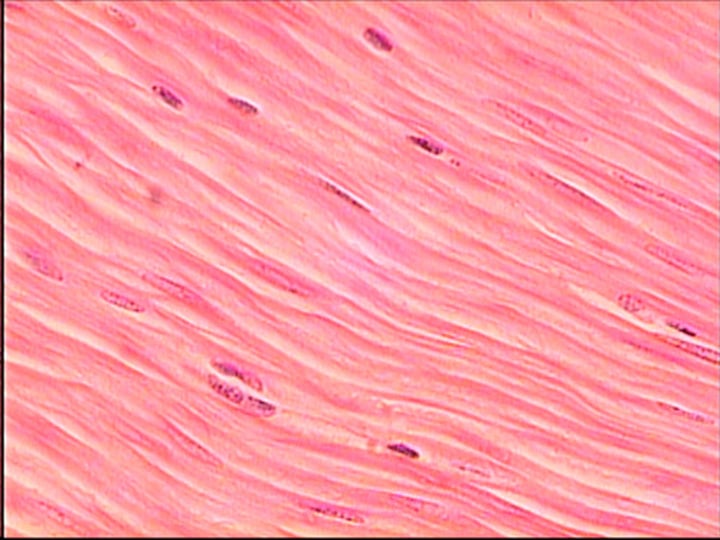
muscle tissue
A body tissue that contracts or shortens, making body parts move.
Epethelial tissue
covers the surface of the body and is the main tissue in the skin
Organelle
specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell
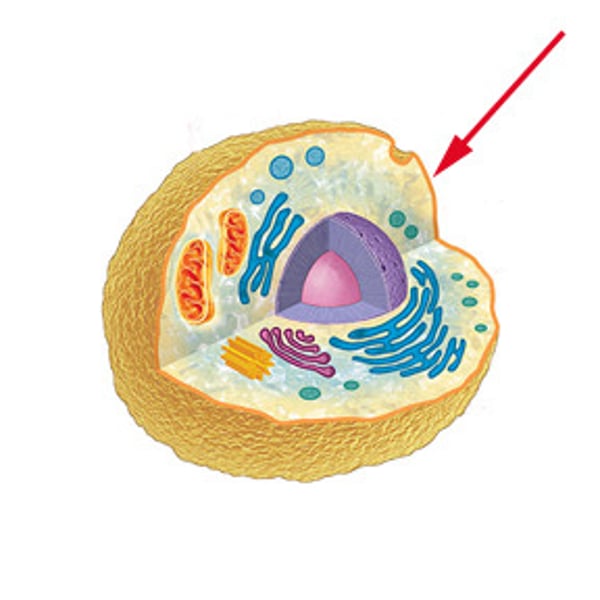
cell membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
Which of the following is isotonic to red blood cells?
0.9% NaCl solution
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy.
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that construct molecules, requiring energy.
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
atomic weight
protons + neutrons
How to calculate the number of neutrons
atomic mass - atomic number
how to calculate the number of electrons
equals the number of protons
carbohydrates
Monomers = monosaccharides (Glucose, Fructose.Galactose)
Polymer = Disaccharides, Polysaccharides (starch, and glycogen)
Main Use = an immediate energy source
lipids
Monomer = glycerol and free fatty acids
Polymers = triglycerides, steroids, eicosanoids, phospholipids, prostaglandins
Main use = energy reserve, hormones, insulation, structural component of cell membrane
Proteins
Monomer = amino acids
Polymers = polypeptides or proteins
Main use = movement, transport of substances, immunity, support, catalysts for chemical reactions
nucleic acids
Monomers = nucleotides, made from sugars , a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base
Polymers = DNA and RNA
Main use = storage of genetic information and protein synthesis
cranial cavity
houses the brain
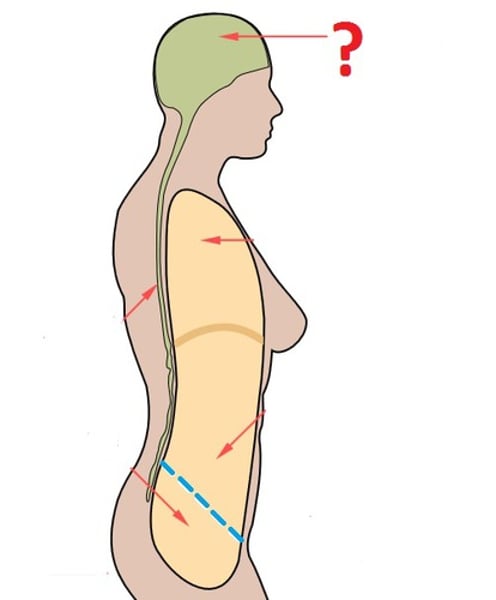
spinal cavity
contains the spinal cord
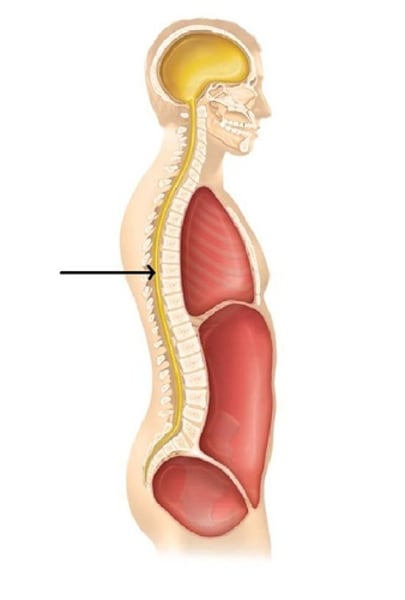
thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs
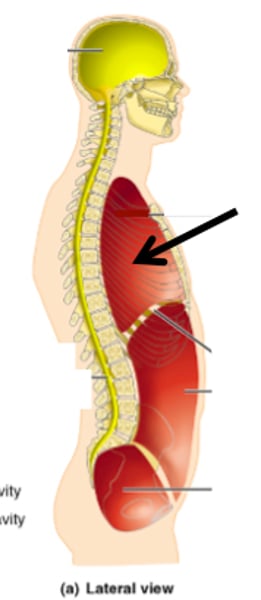
pleural cavity
contains the lungs
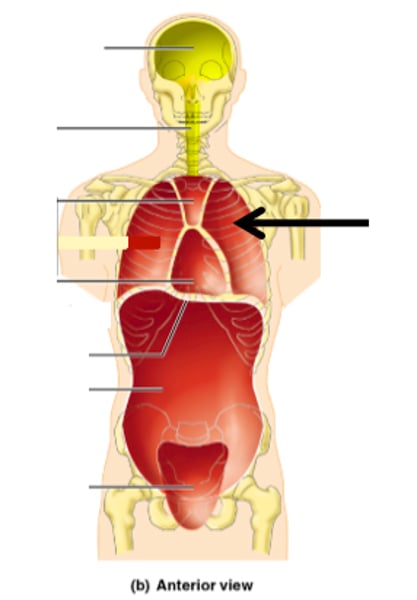
Mediastinum
space between the lungs. It contains the heart, esophagus, trachea, great blood vessels, and other structures.
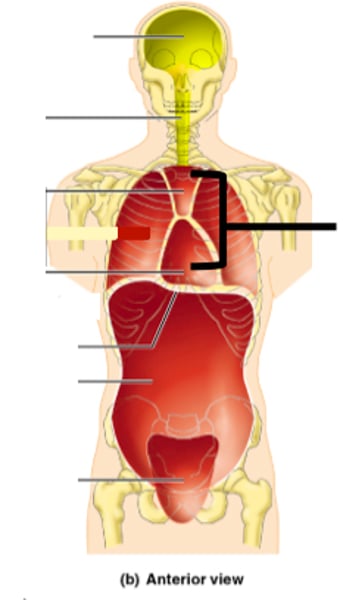
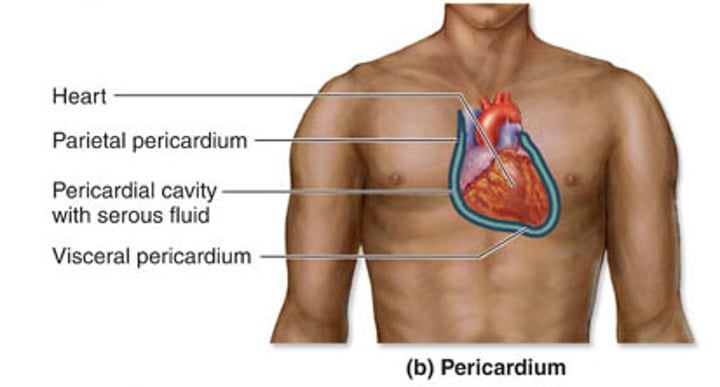
pericardial cavity
contains the heart
amphipathic
have a hydrophilic portion (water-loving), and hydrophobic portion (water-hating)
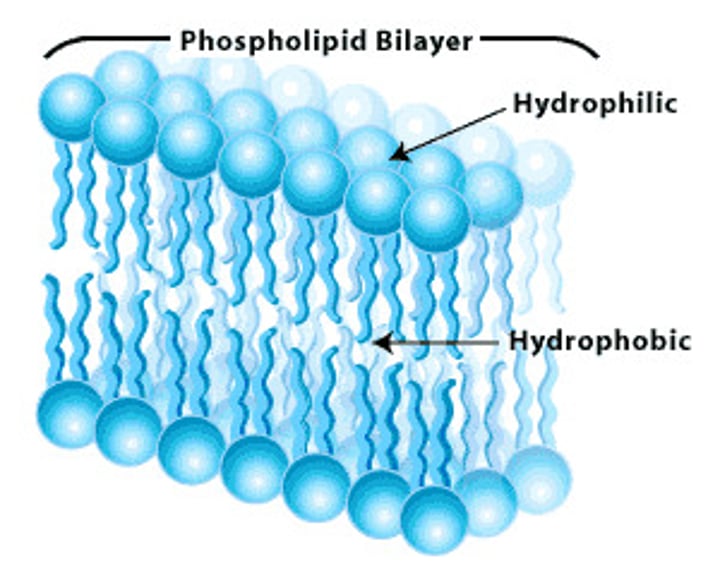
hydrohilic
water loving... requires help to pass through membrane
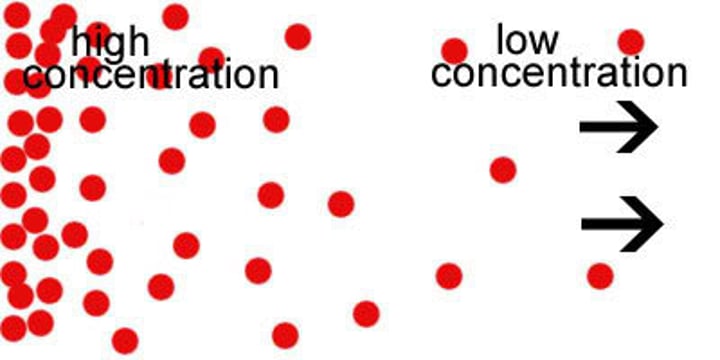
concentration gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance.
how much water does our body contain?
60%
Intracellular fluid (ICF)
fluid inside cells
Extracelular fluid
fluid outside the cell