Pathogenic Eukaryotes and Viruses Overview
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
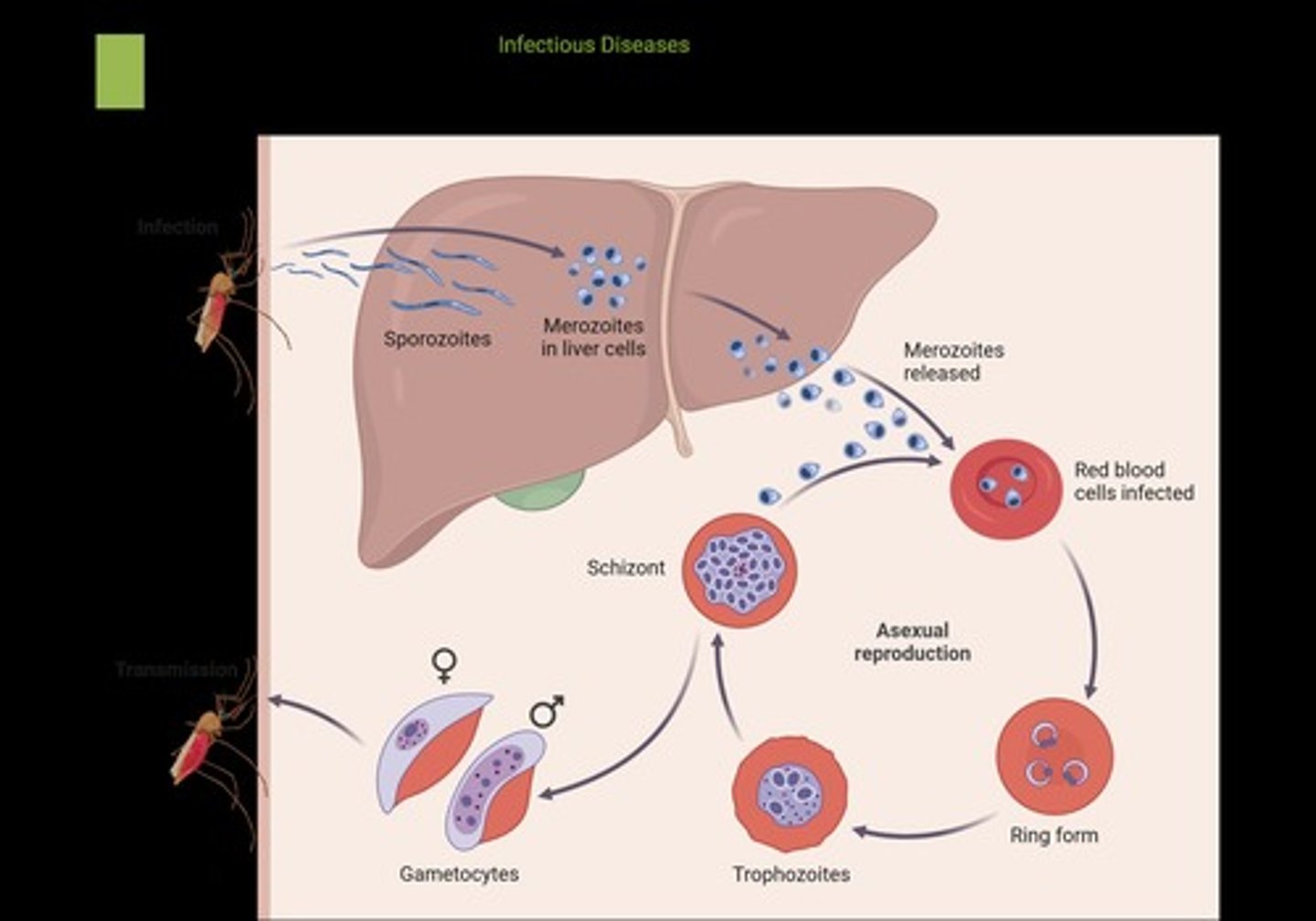
What protozoan causes malaria?
Plasmodium spp.
What disease is caused by Trypanosoma brucei?
African sleeping sickness.
What gastrointestinal infection is caused by Giardia lamblia?
Giardiasis.
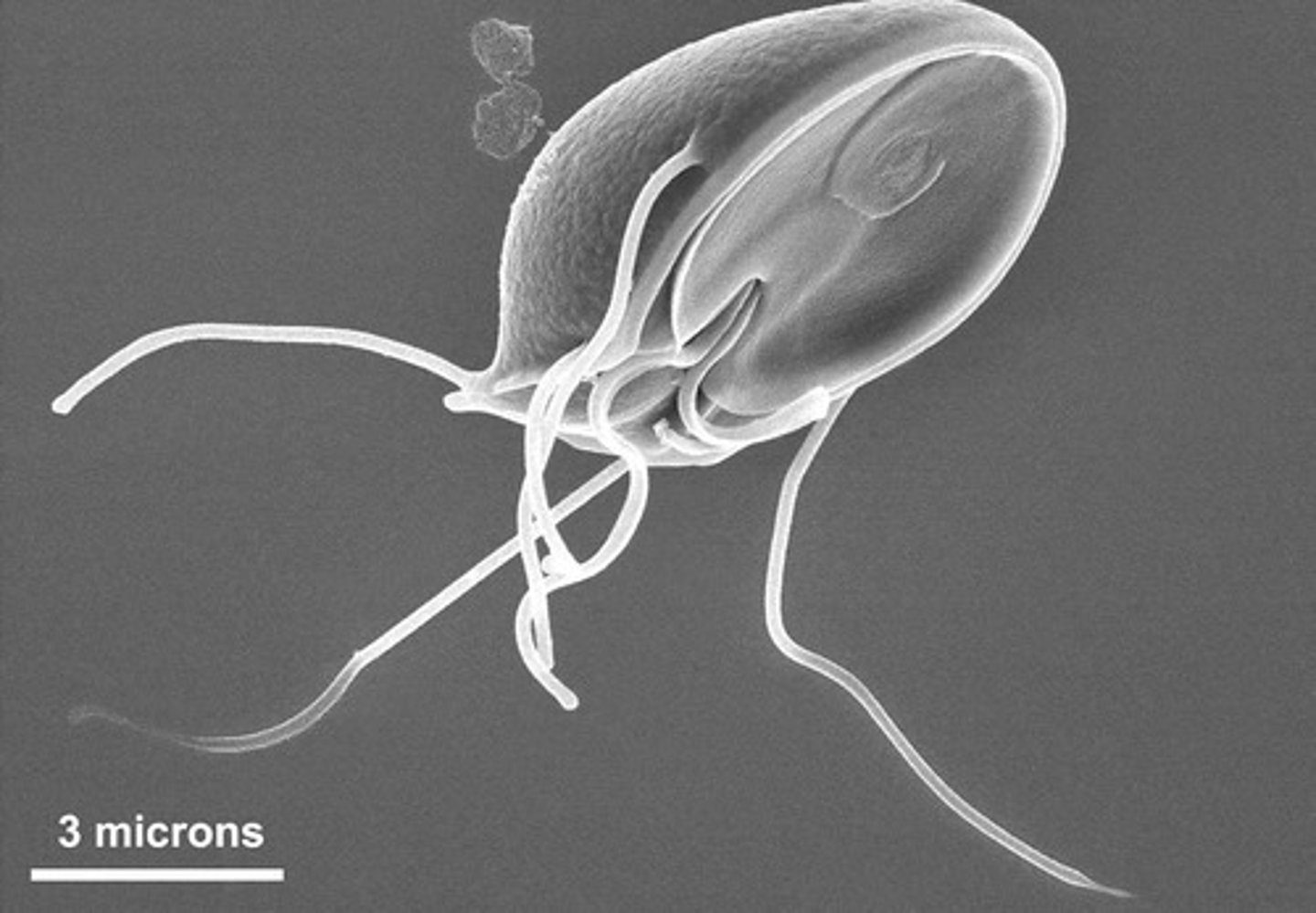
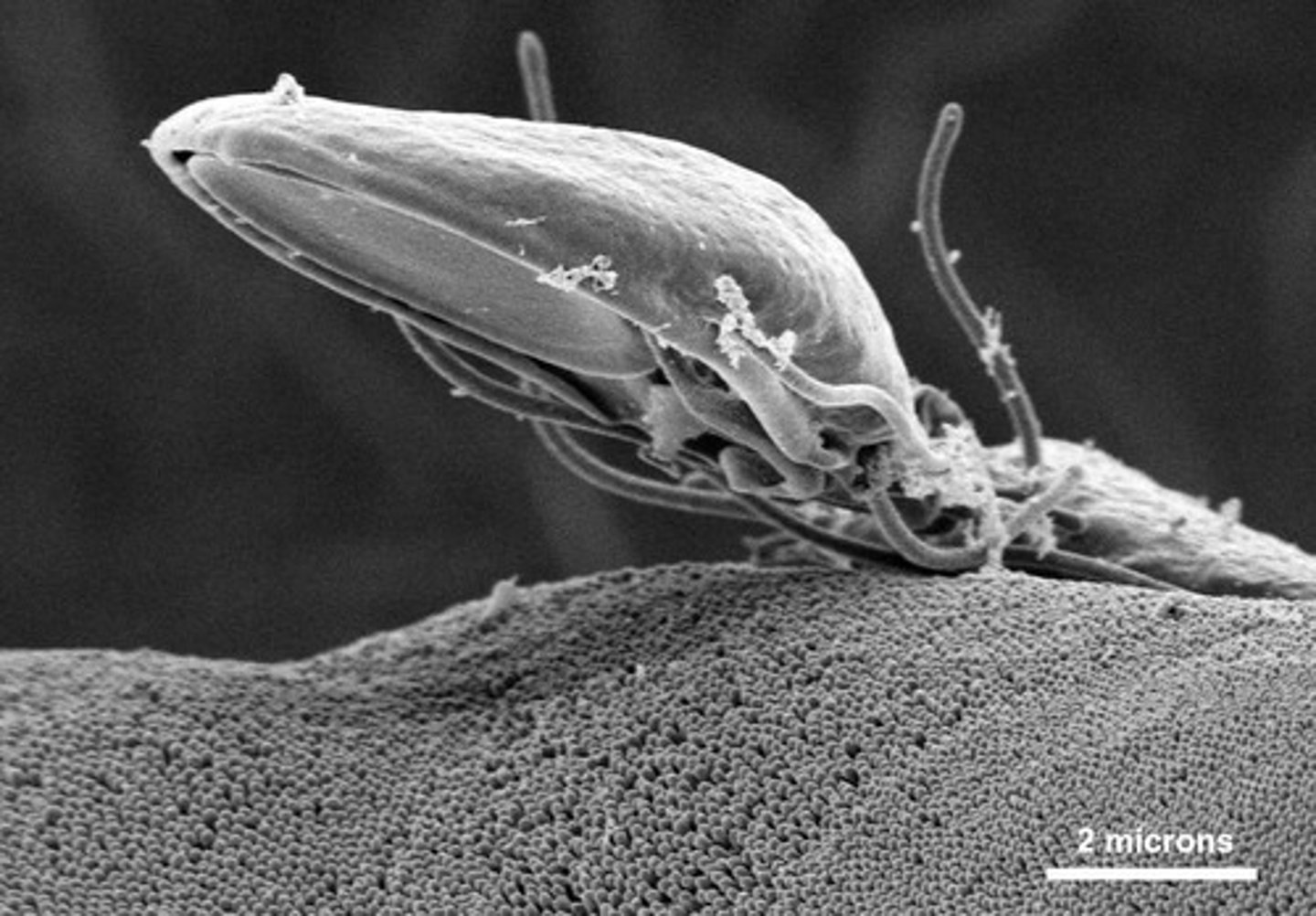
What are the characteristics of Giardia lamblia?
It is a flagellated anaerobic parasite that survives in contaminated water.
How is Giardia lamblia transmitted?
Through the fecal/oral route via contaminated food, water, or surfaces.
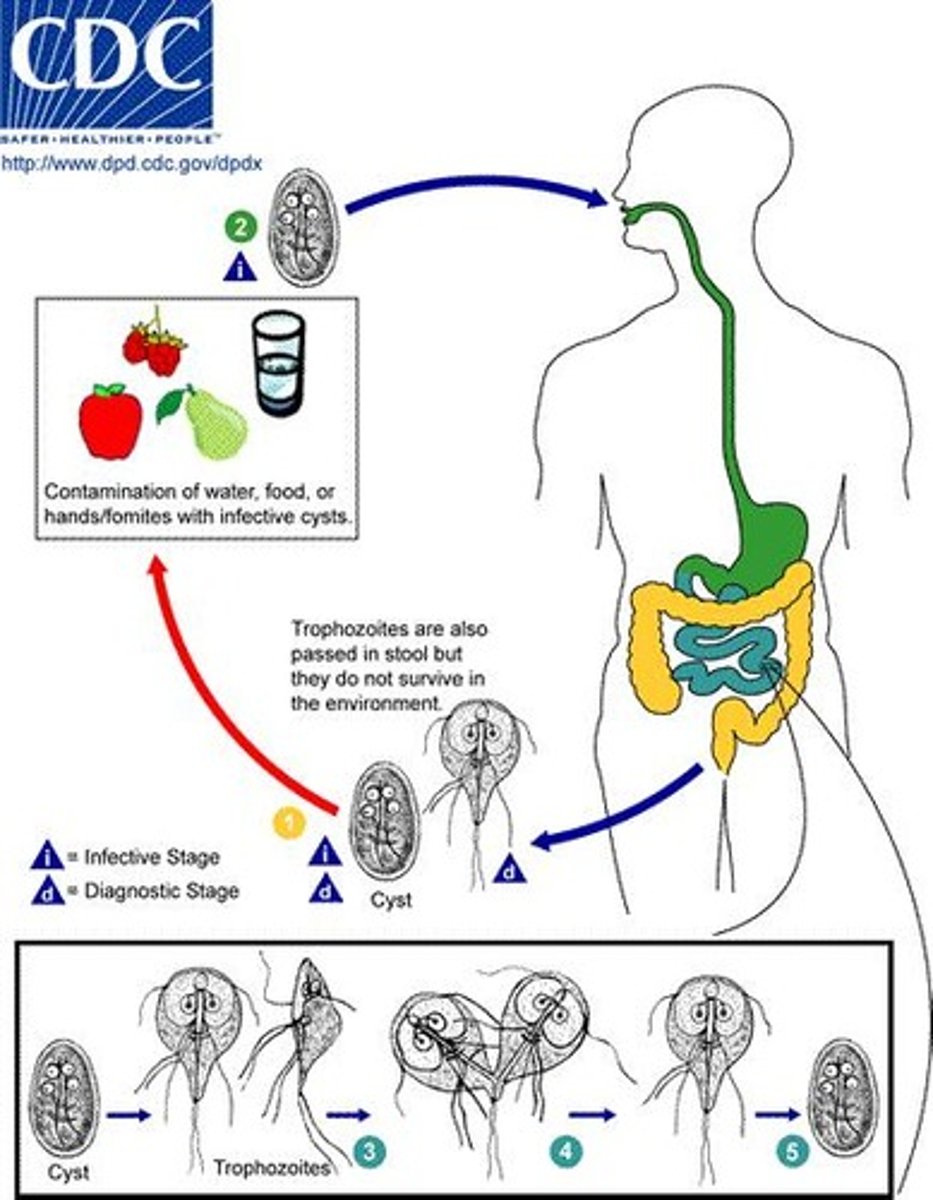
What is the infectious dose of Giardia lamblia?
10-100 cysts.
What is the target tissue for Giardia lamblia?
The small intestine.
What is the incubation period for giardiasis?
1-3 weeks.
What are common signs and symptoms of giardiasis?
Diarrhea, bloating, flatulence, greasy stools, fatigue.
How does Giardia lamblia affect the gut microbiome?
It has a negative effect on gut microbiome diversity, leading to dysbiosis.
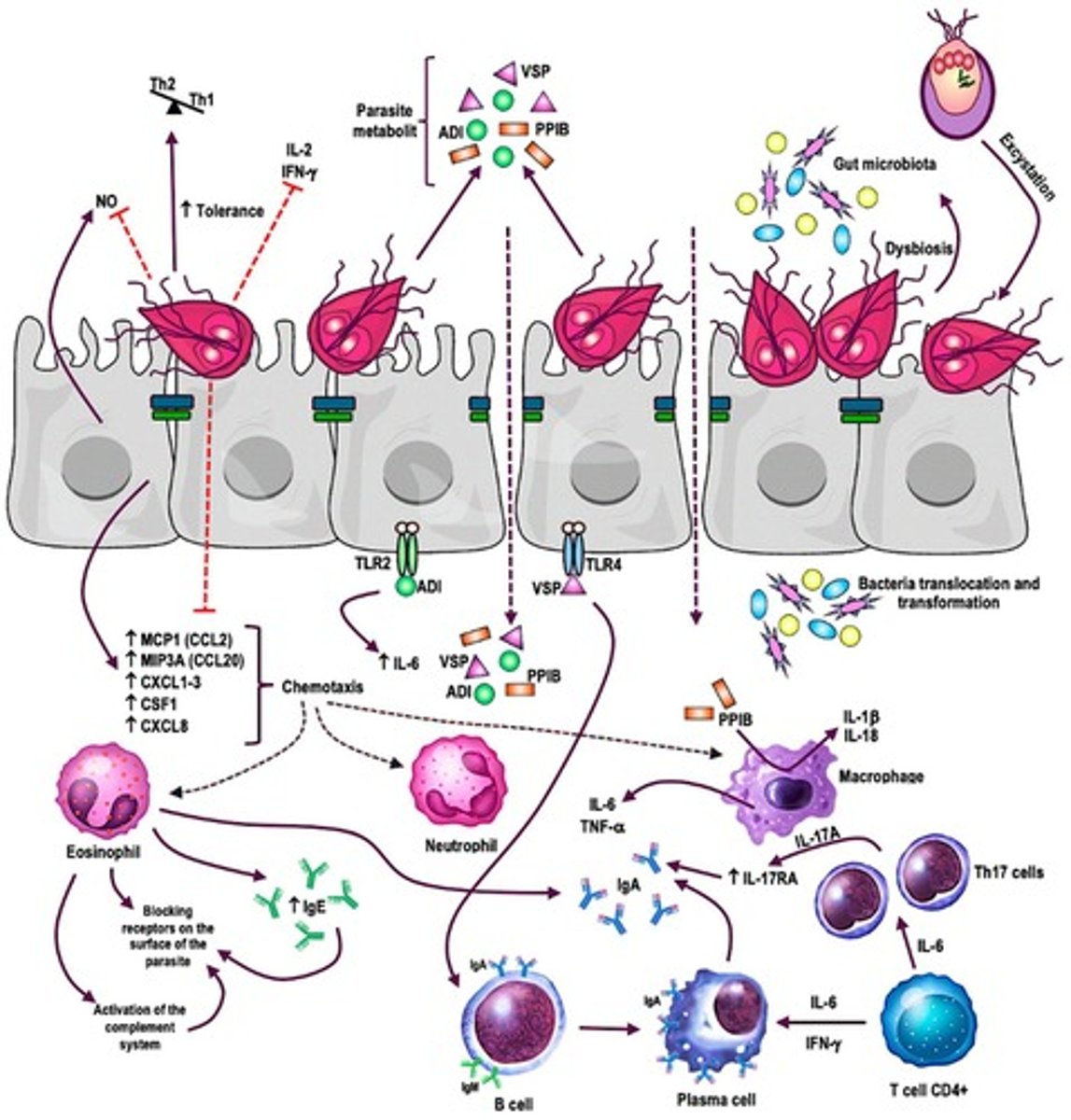
What is the disease caused by Candida albicans?
Candidiasis (yeast infections).
What disease is associated with Aspergillus spp.?
Aspergillosis, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
What lung infection is caused by Histoplasma capsulatum?
Histoplasmosis.
What are the characteristics of opportunistic pathogens like fungi?
They can form biofilms and are often dimorphic.
What is the transmission route for fungal infections?
Endogenous, direct contact, or mother to child.
What is the target tissue for Candida infections?
Mucosal surfaces (oral, vaginal, GI) and the bloodstream.
What are common signs and symptoms of candidiasis?
Oral thrush, difficulty swallowing, vaginal yeast infection, fever, sepsis, organ failure.
What disease is caused by Schistosoma spp.?
Schistosomiasis.
What infection is caused by Taenia solium?
Taeniasis (tapeworm infection).
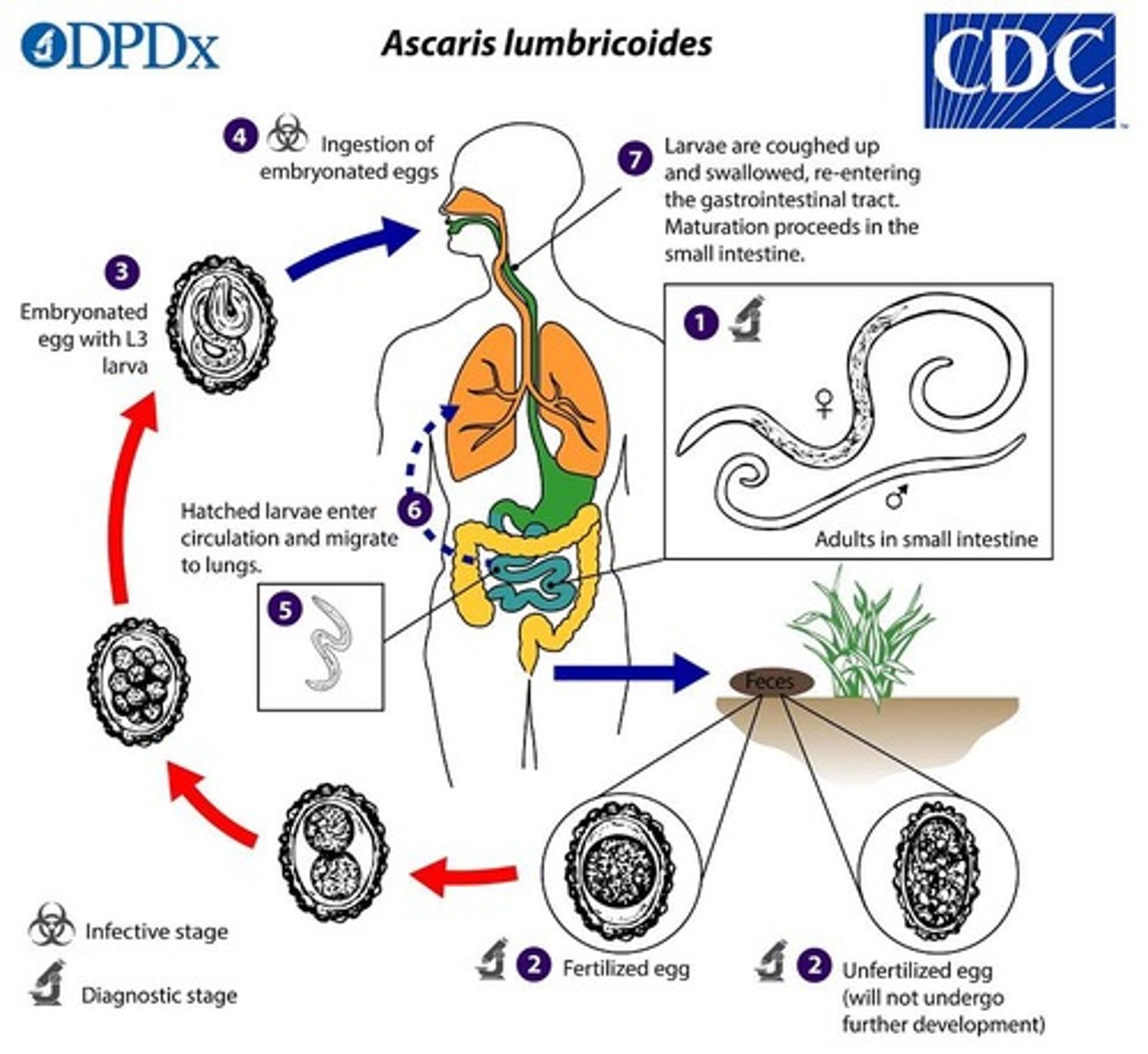
What type of infection is caused by Ascaris lumbricoides?
Ascariasis, a type of roundworm infection.
What type of disease is caused by Ascaris lumbricoides?
Ascariasis.
What is the primary mode of transmission for Ascaris lumbricoides?
Respiratory droplets.
What is the infectious dose of Ascaris lumbricoides?
Low.
What is the target tissue or cell for Ascaris lumbricoides?
Respiratory epithelium.
What is the incubation period for Ascaris lumbricoides?
Weeks to months.
What are the signs and symptoms of Ascariasis?
Abdominal pain, intestinal obstruction, cough, wheezing.
What precautions should be taken to prevent Ascaris lumbricoides infection?
Standard precautions, deworming, hygiene education.
What are the two main life cycles of bacteriophages?
Lytic cycle and lysogenic cycle.
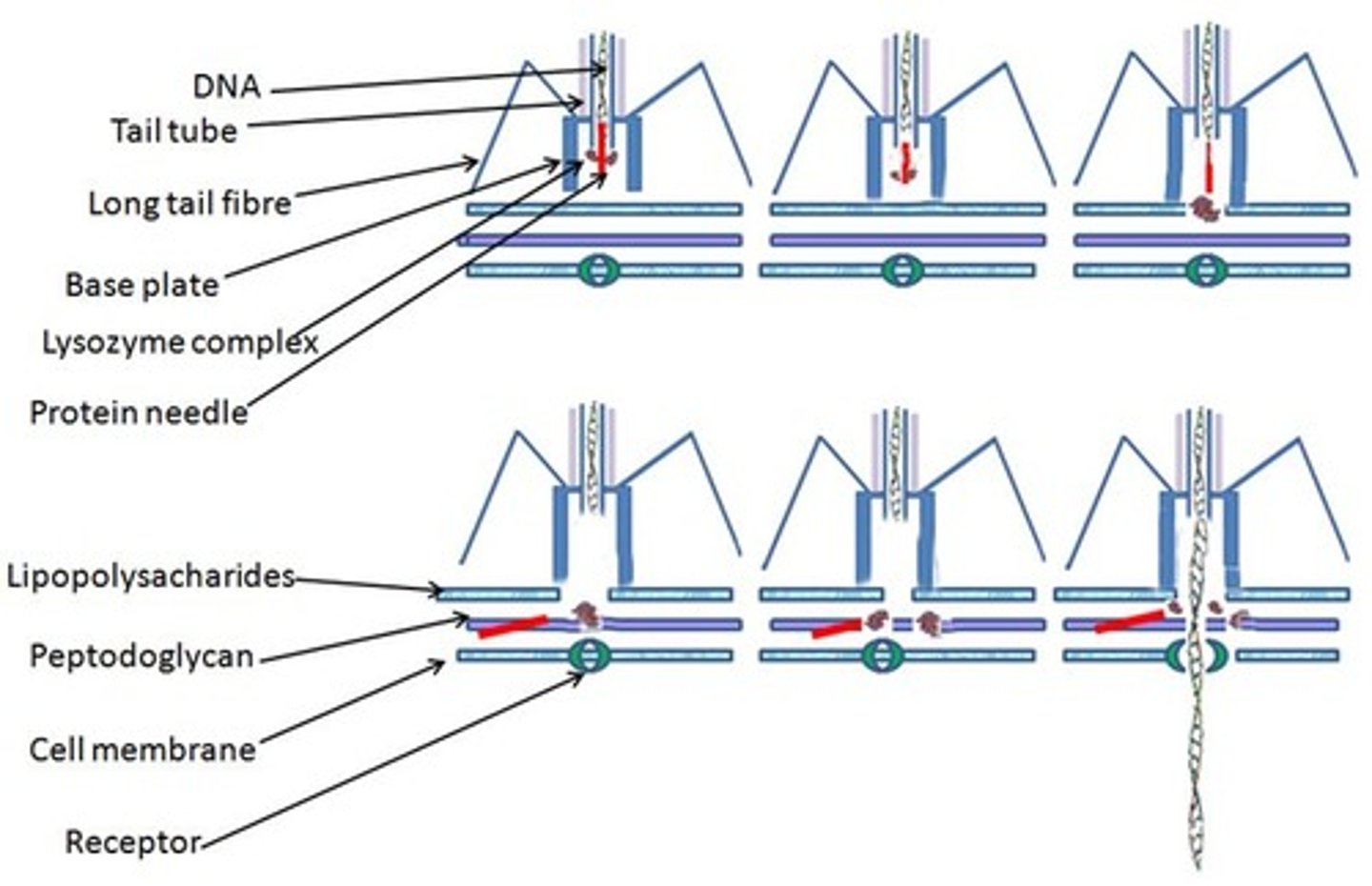
What happens during the lytic cycle of a bacteriophage?
The phage quickly replicates and kills the host cell.
What occurs during the lysogenic cycle of a bacteriophage?
The phage integrates into the host cell's chromosome as a prophage and can reactivate to become lytic.
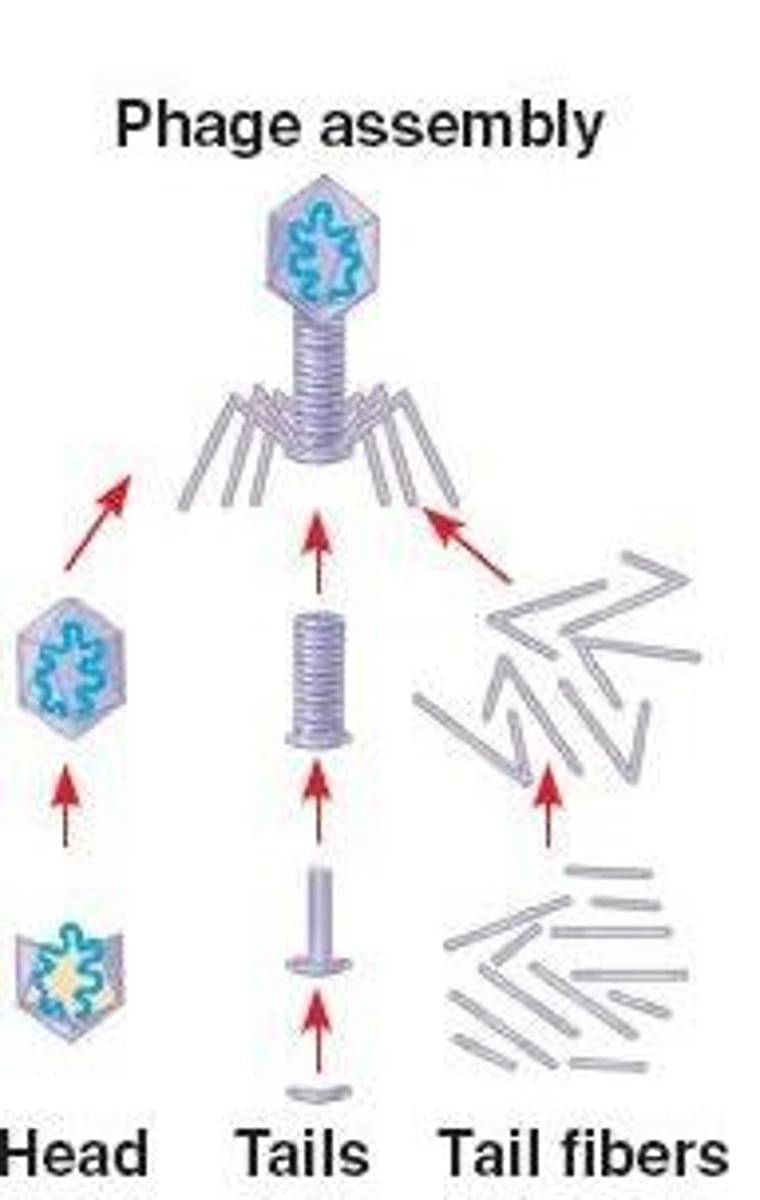
What are the five stages of the lytic cycle?
1. Host recognition and attachment, 2. Genome entry, 3. Synthesis, 4. Assembly of virion, 5. Exit and transmission.
What is the role of tail fibers in the lytic cycle?
They attach to structures on the cell envelope of the host.
What is released during genome entry in the lytic cycle?
Lysozyme, holins, and spanins degrade membranes and peptidoglycan.
What happens during the synthesis phase of the lytic cycle?
Host DNA is slowly degraded, and late proteins are produced.
How are virions assembled in the lytic cycle?
Parts of the virion are assembled separately, with nucleic acid inserted into the icosahedral head.
What is released at the end of the lytic cycle?
Approximately 200 T4 phages.
What is the purpose of lytic phage therapy?
To treat multidrug- or pandrug-resistant infections in human patients.
Where is phage therapy being explored for human patients?
In Georgia (the country).
How do eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells in terms of viral complexity?
Eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure, leading to greater complexity and diversity of viral replication cycles.
What is the symptomatic phase duration for Ascariasis?
6-8 weeks.
What is the estimated number of phages in the biosphere?
10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000.
What is the first postulate of microbial pathogenesis regarding microbes and disease?
Microbe must be present during the disease.
What are some examples of opportunistic pathogens?
Opportunistic pathogens, asymptomatic carriers, and latent infections.
What does the second postulate of microbial pathogenesis state?
Microbe must be grown in a pure culture.
What are some limitations of growing microbes in pure culture?
Obligate intracellular pathogens and fastidious microbes.
What is the third postulate of microbial pathogenesis?
Microbe must cause the same disease in a new host.
What factors can affect the third postulate of microbial pathogenesis?
Opportunistic pathogens, mutations, host variations, and immunology.
What does the fourth postulate of microbial pathogenesis entail?
Isolate the same microbe from the new host.
What factors can complicate the fourth postulate of microbial pathogenesis?
Mutations, immunology, and persistent infections.
What are the primary systems affected by microbial infections?
Respiratory, gastrointestinal (GI), and circulatory & lymph system infections.
What are the components of the upper respiratory system?
Includes structures like bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli.
What is the role of the mucociliary escalator in the respiratory system?
It helps to clear pathogens and debris from the respiratory tract.
How do pathogens bypass the mucociliary escalator?
By employing infection strategies that impair its function.
What is the significance of inflammation in infections?
Signs and symptoms of infection are often due to inflammation.
What is the naming convention for infections in the upper respiratory system?
Name = location + 'itis', e.g., rhinitis and tonsillitis.
What is streptococcal pharyngitis commonly known as?
Strep throat.
What organism causes strep throat?
Streptococcus pyogenes.
What are the characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Gram-positive diplococci, facultative anaerobic, and chemoheterotrophic.
What are some main agents that cause pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
What resistance is growing among Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Growing resistance to B-lactams.
What virulence factors does Streptococcus pneumoniae produce?
Capsule for protection, Lyt A to degrade its own cell wall, and pneumolysin O.
What is the role of streptolysin toxins in Streptococcus pyogenes?
They destroy red blood cells for nutrients.
What are the implications of mutations in microbial pathogenesis?
They can affect the ability of pathogens to cause disease and evade the immune system.
What is the primary transmission method for pneumococcal disease?
Respiratory droplets.
What is the incubation period for pneumococcal disease?
1-3 days.
What are the common signs and symptoms of pneumococcal disease?
Bloody wet coughs, fever, chills, and chest pain.
What diseases are caused by pneumococcus?
Pneumococcal disease, including pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis.
What is the infectious dose for pneumococcal disease?
Low; easily transmissible.
What are the main components of a tooth?
Enamel, dentin, pulp, and gingiva.
What is the hardest material in the body?
Enamel.
What is the role of pulp in a tooth?
Filled with blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves.
What factors control microbial communities in the oral cavity?
Chewing, saliva, and gum fluids.
What is the major opportunistic anaerobe associated with dental caries?
Streptococcus mutans.
How does Streptococcus mutans damage teeth?
It produces lactic acid that may dissolve tooth minerals, enamel, and dentin.
What is periodontal disease?
Gum disease that starts with gingivitis and can lead to tissue damage.
What are Peyer's patches?
Lymphoid tissues that have immune cells and detect pathogens.
What pathogen causes shigellosis?
Shigella.
What is the portal of entry for Shigella?
Mouth.
What is the function of Shiga toxin?
Targets endothelial cells of vessels and binds to the 60s ribosomal subunit.
What is the primary lymphoid tissue?
Bone marrow and thymus.
What is the secondary lymphoid tissue?
Spleen and lymph nodes.
What is the causative agent of cat-scratch disease?
Bartonella henselae.
What is the incubation period for bubonic plague?
2-6 days.
What is the mortality rate of pneumonic plague if untreated?
100%.
What is the mortality rate of bubonic plague with antibiotics?
10%.
What type of bacteria causes the plague?
Yersinia pestis.
What is the primary method of diagnosis for cat-scratch disease?
Immunofluorescence after lymph node ultrasound and biopsy.