AP Human Geography Unit 6
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Human Geography Unit 6- Origin, Distribution, and Systems of Cities
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Ecumene
The permanently inhabited portion of the Earth’s surface
Settlement
A place with a permanent human population
Urbanization
The process of developing towns and cities, this does not end once a city is formed.
Site
The characteristics at the immediate location
Situation
The location of a place relative to its surroundings and its connectivity to other places.
City-State
Consists of an urban center and its surrounding territory and agricultural villages. It has its own political system, and is independent.
Urban Area
A central city plus land developed for commercial, industrial, or residential purposes.
City
A higher density area with territory inside officially recognized political boundaries.
Metropolitan Area
A collection of adjacent cities economically connected, across which population density is high and continuous.
Metropolitan Statistical Area
Another way to define a city. Must have at least 5,000 people, and the county its in + adjacent counties must have a high degree of social and economic integration with the urban core.
Social Heterogeneity
A greater variety of people
Borchert’s Transportation Model
A model that describes urban growth based on transportation technology
Sail Wagon Epoch
An epoch between 1790 and 1830 in which water ports became very important. Cities are most powerful along the coast, because boats are the main and fastest mode of transportation.
Iron Horse Epoch
An epoch between 1830 and 1870 in which steam engines powered boats. River cities are now the most important cities.
Steel Rail Epoch
An epoch between 1870 and 1920 in which trains are now the most important mode of transportation, making railway cities the most important cities.
Auto Air Amenity Epoch
An epoch between 1920 and 1970 in which cars emerged. Airport hubs also emerged, and cities became more interconnected. This made it so that cities could emerge and thrive virtually anywhere.
High Technology Epoch
An epoch between 1970 and the present, whose defining tech is the Internet. The Internet allowed for anyone to communicate with anyone anywhere, further interconnecting the world.
Streetcar Suburbs
Communities grew along rail lines, often creating a pinwheel shaped city.
Suburbanization
The process of people moving, usually from cities, to residential areas on the outskirts of cities.
White Flight
As more ethnicities move to the city, white americans moved to the suburbs.
Transportation, demographics, and the economy
After WWII, what changed how cities developed?
Boomburgs
Rapidly growing communities (over 10% per 10 years), have a total population of over 100,000 people, and are not the largest city in the metro area.
Edge Cities
Found along transportation routes, have mini downtowns, hotels, malls, restaurants, etc.
Counter Urbanization
The counter flow of urban residents leaving cities.
Reurbanization
When suburbanites return to live in the city.
Megacity
A city that has a population of more than 10 million people
Metacity
A city that has a population greater than 20 million people, and has attributes of a network of urban areas that have grown together into one larger interconnected urban system.
Tokyo
The world’s first and largest metacity
Megalopolis
A chain of connected cities.
Concurbation
When cities continuously grow and merge into an uninterrupted area
World Cities
The most influential cities in the world. They don’t have to necessarily be the largest cities!
Nodal Cities
Command centers on a regional and occasionally national level.
Urban System
An interdependent set of cities that interact on the regional, national, and global scale.
Rank-Size Rule
One way in which the sizes of cities within a region may develop. The nth largest city of any region is 1/n the size of the largest city.
The nth largest city of any region is 1/n the size of the largest city.
Rank Size Formula
Primate City
When the largest city in an urban system is more than twice as large as the 2nd largest city.
Gravity Model
Larger and closer places will have more interactions than places that are smaller and farther from each other.
Christaller’s Central Place Theory
A model used to describe distribution of governments based on consumers and goods. Uses hexagons and assumes an isotropic plane.
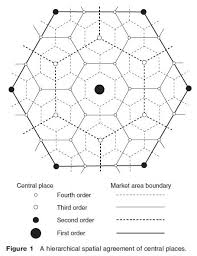
Market Area
A zone that contains people who will purchase goods or services. These surround each central place.
Threshold
The size of the population necessary for any particular service to exist and remain profitable.
Range
The distance people will travel to obtain specific goods or services.
Functional Zonation
The idea that portions of an urban area have specific and distinct purposes.
Central Business District
The commercial heart of a city, it is the most dense and the most expensive land.
Industrial/Commercial Zone
Just outside of the CBD is dedicated to…
Commensal Relationship
When commercial interests benefit each other.
Chicago
These classic North American city models were based on the city of…
Concentric Zone Model
Describes a city as a series of rings that surrounds a central business district.
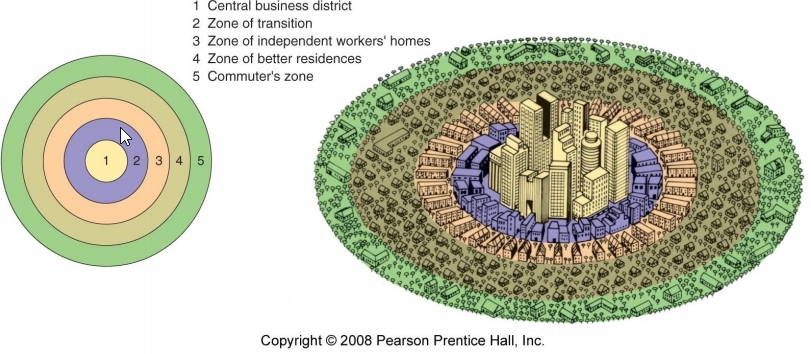
Burgess Model
The Concentric Zone Model is also known as the…
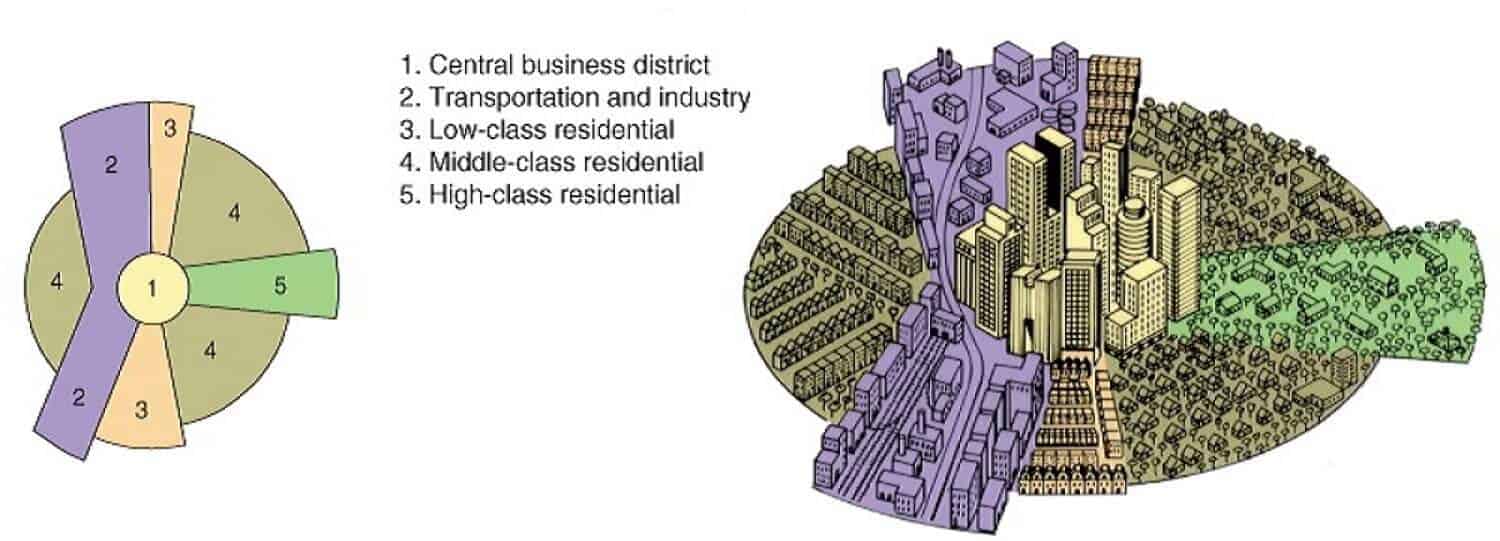
Sector Model
Developed by Homer Hoyt, this model grew out from the center.
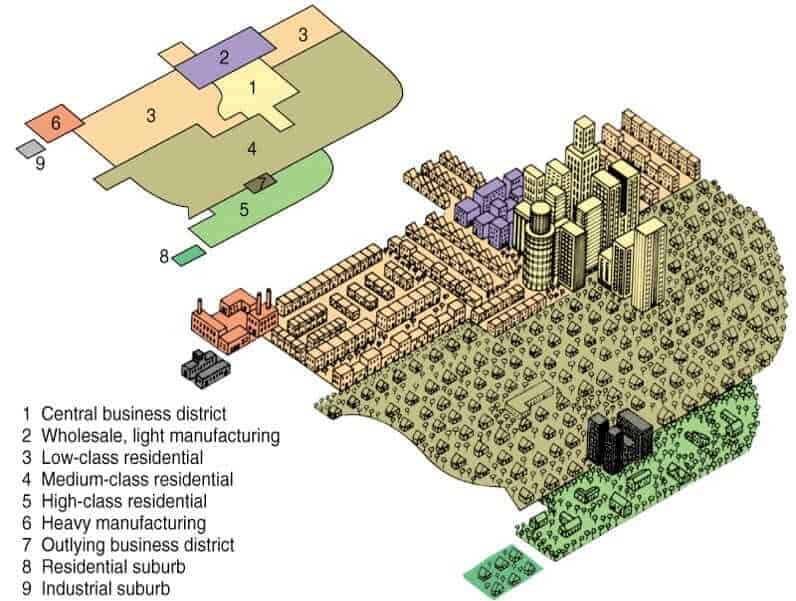
Multiple Nuclei Model
Multiple CBDs, but still has a main CBD.
Beltway
A road in a huge ring around the city.
Galactic City Model
A CBD that has become surrounded by a system of smaller nodes (in suburbs) that mimic its function.
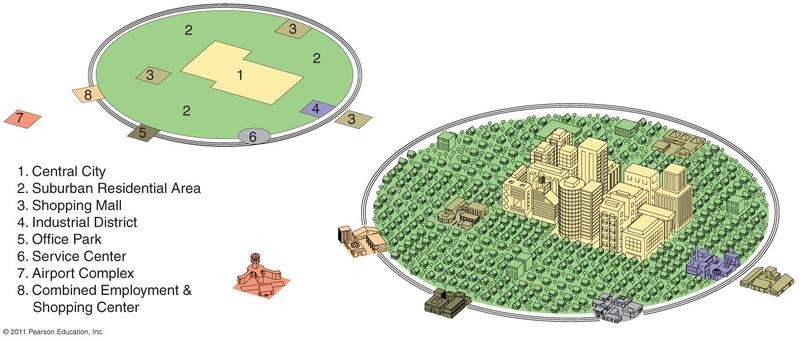
Middle Eastern City Model
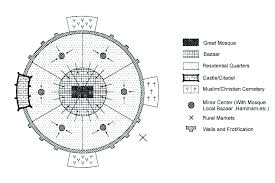
Latin American City Model
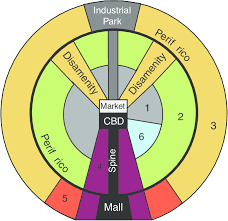
Griffin Ford Model
The Latin American City Model is also known as…
African City Model
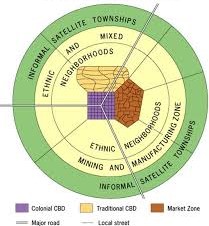
Informal Satellite Townships
Another word for slums
Southeast Asian Model
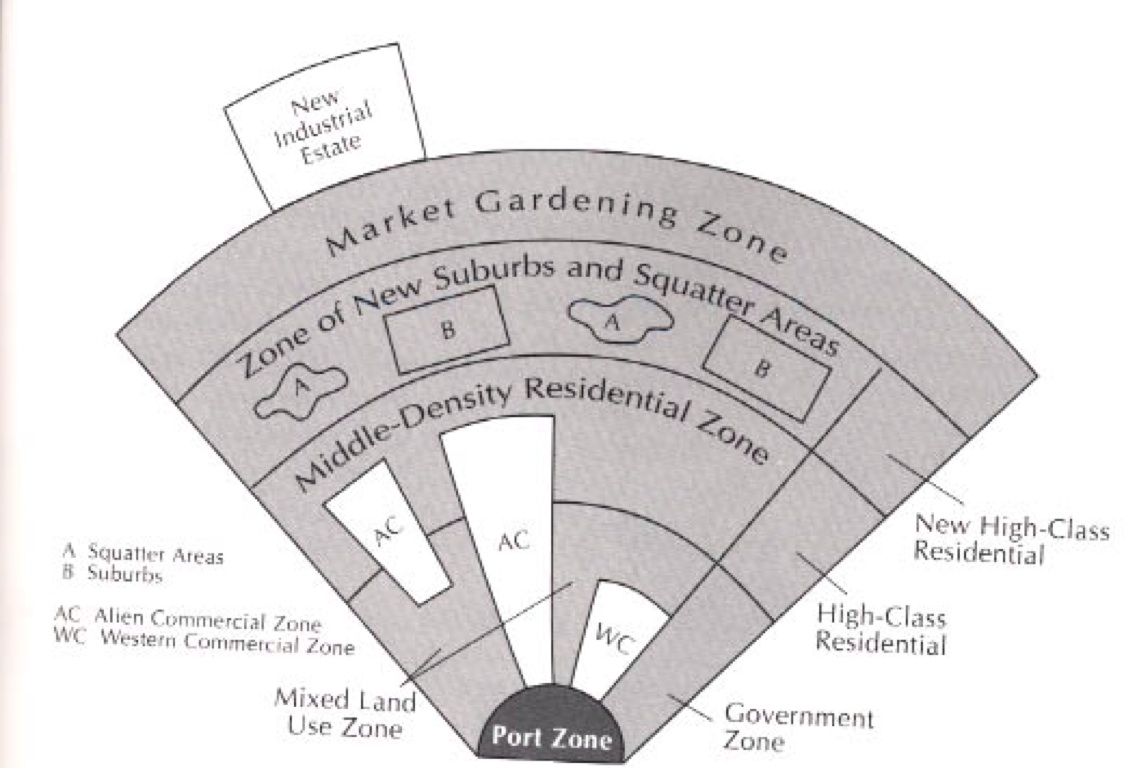
McGee Model
Another name for the Southeast Asian Model is…
Zoning Ordinances
Regulations that define how property in specific geographic regions may be used.
Urban Planning
A process of promoting growth and controlling change in land use
Filtering
Houses pass from one social group to another.
Invasion and Succession
The process by which one social or ethnic group gradually replaces another through filtering.
Urban Infill
The process of increasing the residential density of an area by replacing open space and vacant housing with residences.
Suburbanization of Business
The movement of commerce out of cities to suburbs where rents are cheaper and commutes for employees are shorter.
Gated Communities
A neighborhood or community closed off to the rest of the world with a gate and security.
Infrastructure
The facilities and systems that serve the population
Municipal
The local government of a city or town and the services it provides.
Municipality
A local entity that is all under the same jurisdiction
Incorporation
The act of legally joining together to form a new city.
Unincorporated Areas
Populated regions that do not fall within the legal boundary of any city or municipality.
Infrastructure
Improvements in ___ dramatically improve the living conditions in the poorest areas of the world.
Public Transportation
Buses, Subways, Trains
Sustainability
Using the Earth’s resources while not causing permanent damage to the environment.
Smart-Growth Policies
Policies that combat urban sprawl and create more sustainable and equitable cities. Focus on city planning and transportation.
Goals of smart growth
Create attractive residential neighborhoods that are walkable, meaning they provide amenities that people can walk to easily.
Develop a strong sense of place among residetns
Increase livability by making the community easy and safe to navigate.
Involve residents and stakeholders in decisions that impact the community.
Greenbelt
Areas of undeveloped land around an urban area. Often used as a barrier to urban sprawl.
Slow-growth cities
Cities that adapt policies to slow the outward spread of urban areas and place limits on building permits in order to encourage a denser, more compact city.
New Urbanism
A set of strategies to put smart growth into action within communities.
Mixed-use neighborhoods
Neighborhoods that have a mix of homes and businesses as opposed to the clear separation of residential and commercial in most cities.
Urban Infill
The process of building up underused lands within a city.
The opposite of leapfrog development and sprawl.
Transit Oriented Development
A concept which locates mixed-use residential or business communities near mass transit stops, resulting in a series of compact communities, which decreases the need for automobiles.
Livability
A set of principles that supports sustainable urban designs. Affordable and equitable housing, access to employment community services, multiple accessible transportation models, social and civic engagement.
Jobs and Services
Why do people live in cities?
Quantitative Data
Information that can be counted, measured, or sequenced by numeric value.
10
The census is every _ years.
Census tract
Contiguous geographic regions that function as the foundation of a census.
Qualitative Data
Based primarily on surveys, field studies, photos, video, and interviews from people who provide personal perception and meaningful descriptions.
Redlining
The process by which banks refuse loans to those who want to purchase and improve properties in certain urban areas. This was often extremely racist and they would refuse loans to certain minorities or ethnicities. This is now illegal!
1968 Fair Housing Act
Made redlining illegal
Segregation
When people live in separate neighborhoods based on their ethnicity or race.
Blockbusting
When people sold their homes/were encouraged to sell their homes upon learning that members of another ethnic group were moving into the neighborhood.
Inclusionary Zoning
Practices that offer incentives for developers to set aside a percentage of housing for low-income renters or buyers. It’s just zoned this way, so anyone who builds on that land has to include houses for that group.
Urban Renewal
A policy which allowed governments to clear out inner-city slums (this displaced the residents to low-income government housing complexes)
Eminent Domain
Allows the government to claim private property from individuals, pay them for the property, and use the land for public good.
Gentrification
When higher-income people come in and buy buildings in poor areas of the city and revamp them. This is done by individuals, not the government. House flipping by rich people of poor properties.
Informal Settlements
Densely populated areas built without coordinated planning and without sufficient services for electricity, water, and sewage. Slums.
Disamenity Zone
An area of land difficult to build on that nobody wants, so slums are often located there. Often hazardous.
Brownfield
An abandoned area created when factories leave an area. Consists of dilapidated buildings and polluted or contaminated soils.
Environmental Injustice
The disproportionate exposure of minorities and the poor to pollution and its impacts, plus the unequal protection of their rights under the law.