Chapter 2: Algebraic Properties
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is a review of basic algebraic properties in Pre-Algebra and A1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
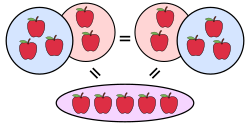
Commutative Property of Addition
The algebraic property, which states that when we add two or more numbers, the order of the addition does not matter.
a + b = b + a
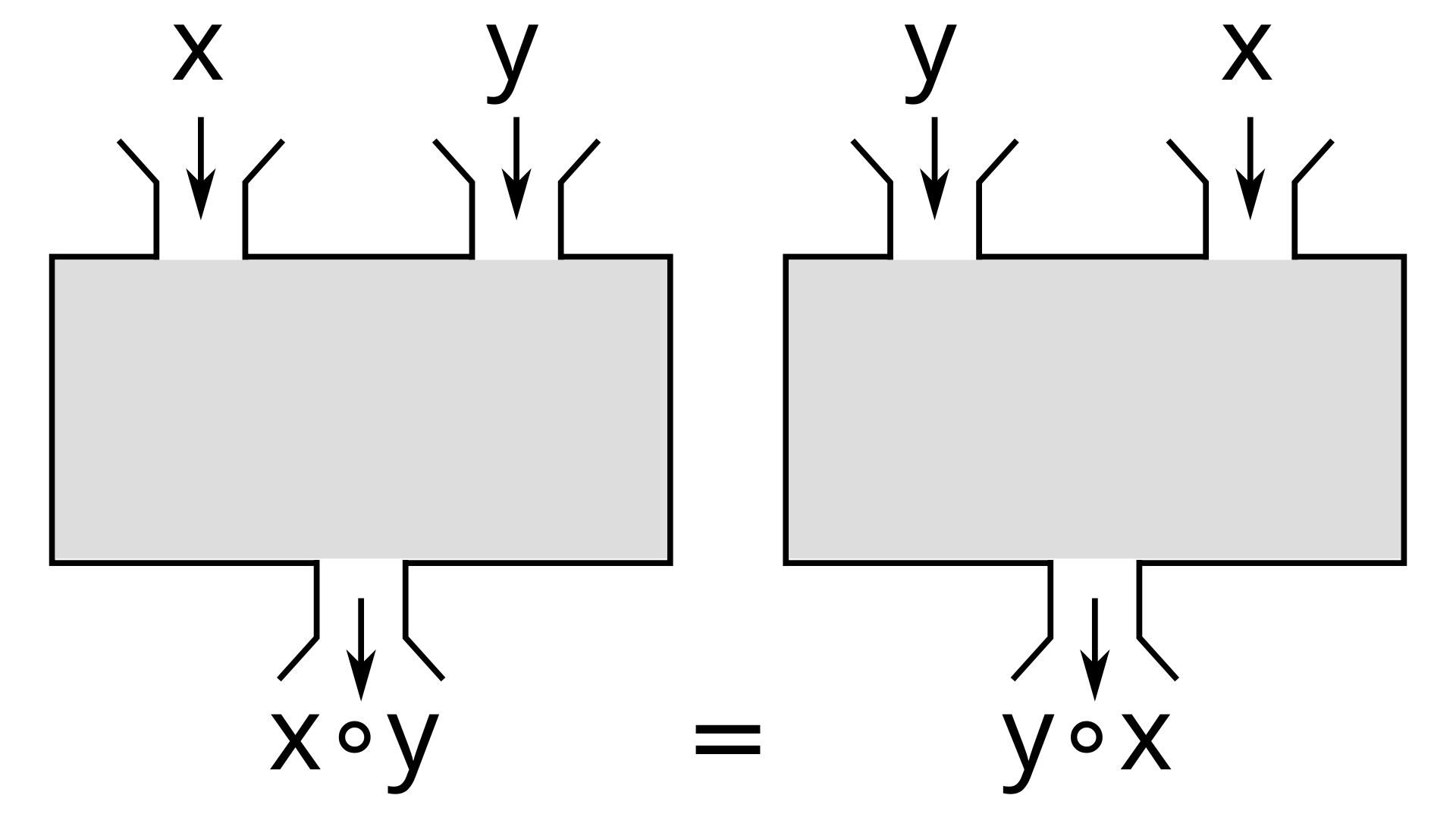
Commutative Property of Multiplication
The algebraic property that states that for any two numbers, a and b, their order of multiplication does not matter.
a × b = b × a
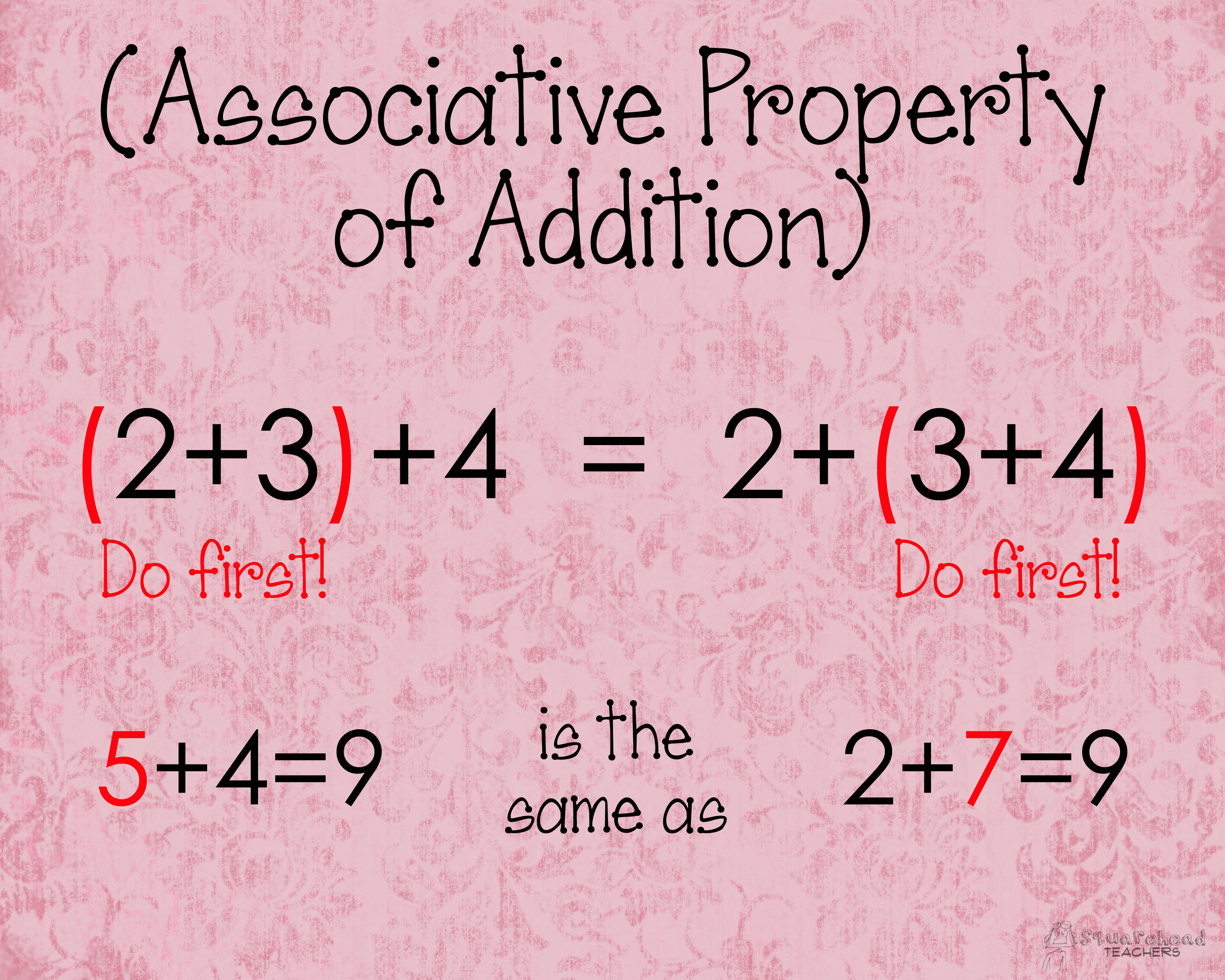
Associative Property of Addition
The property which states that for any case of addition with three numbers, a, b, and c, the order of grouping does not matter.
a + (b+c) = b + (a+c)
↓
3 + (2+5) = 2 + (3+5)
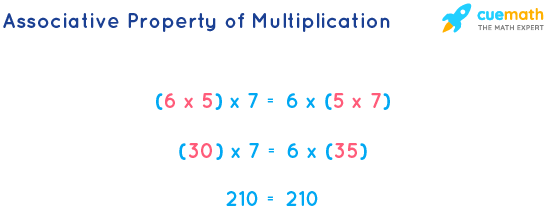
Associative Property of Multiplication
The property which states that for any three digits, when multiplied, the group does not matter.
a * (b*c) = b * (a*c)
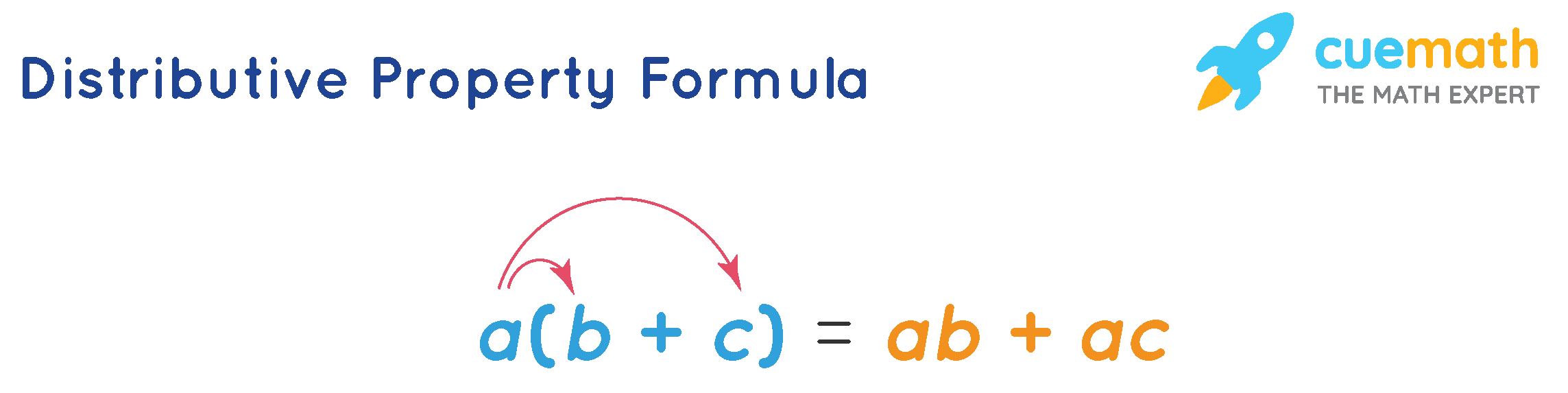
The Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addiction
The property which states that when we multiply a group of numbers by a number, that is equivalent to if we were to multiply and then add.
a(b+c)=a*b+a*c
Suppose we had
3(5+2)
According to the Distributive Property, 3(7) is the same as 15 + 6
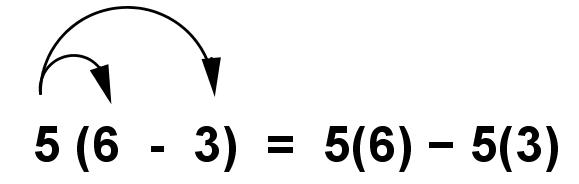
Distributive Property Over Subtraction
The property which states that it is equivalent to multiply the outside number to the sum of the parenthesis.
Example:
3(5-2) = 15-10