Things to note: acid-base equilibria
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Devise an experiment to determine the acid dissociation constant, Ka, for a solution of ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, of unknown concentration.
Assume that you have access to a pH meter and a solution of sodium hydroxide of similar concentration to the acid.
Include how to determine the Ka from your results.
titrate ethanoic acid with sodium hydroxide
use phenolphthalein indicator to find end-point
then add same volume of acid to mixture at end point
measure pH of resultant mixture (with pH meter)
at half neutralisation, pH=pKa so Ka=10-pH
Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH is a monobasic acid.
CH3COOH + H2O ⇌ CH3COO- + H3O+
Give a reason why only the proton from the carboxylic acid group, and not the methyl group, is donated to the water molecule.
the loss of the hydrogen from the O-H group is made possible by the delocalisation of charge / stabilisation on the carboxylate ion
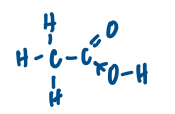
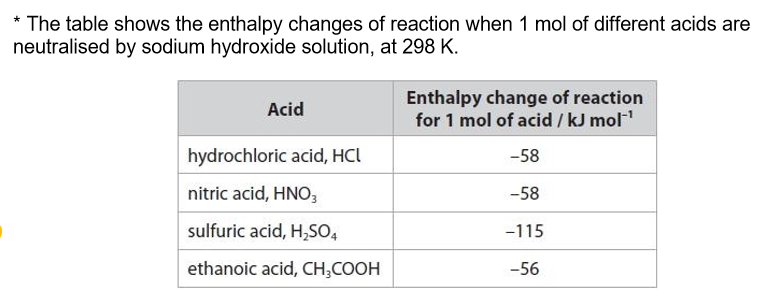
In acid-base neutralisation reactions, there is a temperature change.
Comment on the relative enthalpy changes of reaction, using the data from the table and including any relevant equations.
Hydrochloric acid and nitric acid:
same value for hydrochloric acid and nitric acid as they are strong and completely dissociate into ions in solutions
Sulfuric acid:
sulfuric acid is diprotic
so value is almost twice that of hydrochloric acid / nitric acid
Ethanoic acid:
ethanoic acid is weak / partially dissociated into ions in solution
some energy is needed to break the O-H bond to release H+ ions so enthalpy change of neutralisation is less for a weak acid than a strong acid
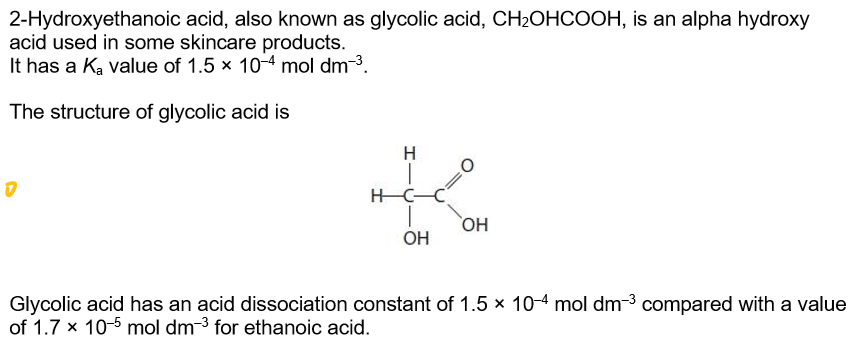
Give a possible explanation as to why the value of Ka for glycolic acid is approximately ten times larger than that of ethanoic acid.
the O of the extra O-H in the 2 position withdraws electrons
so stabilises the anion (CH2OHCOO- ion) and weakens the O-H bond in the acid so the hydrogen ion is more easily lost
Predict, with a reason, whether water is acidic, alkaline or neutral at 310K.
water is neutral at 310K
because [H+ (aq)]=[OH- (aq)]
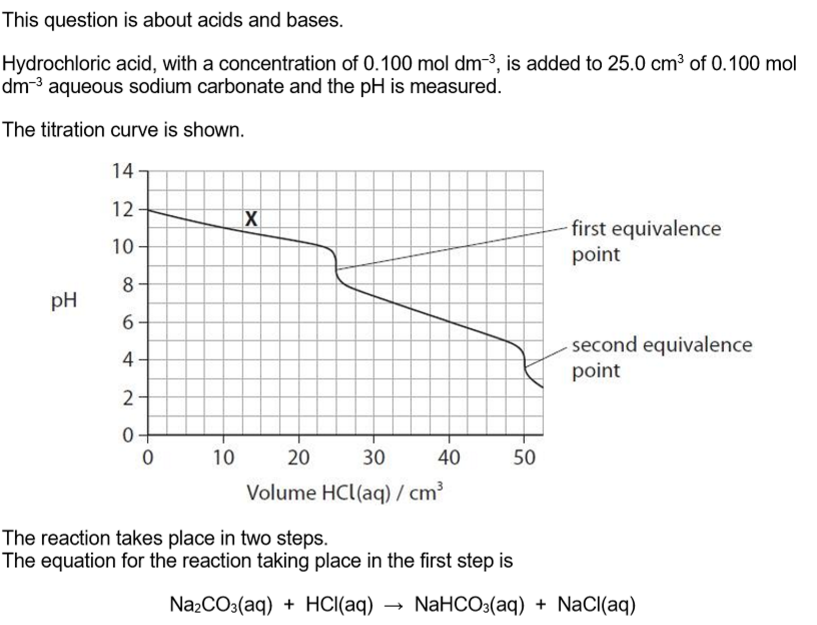
Write the equation for the reaction taking place at the second equivalence point. State symbols are not required.
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + CO2 + H2O
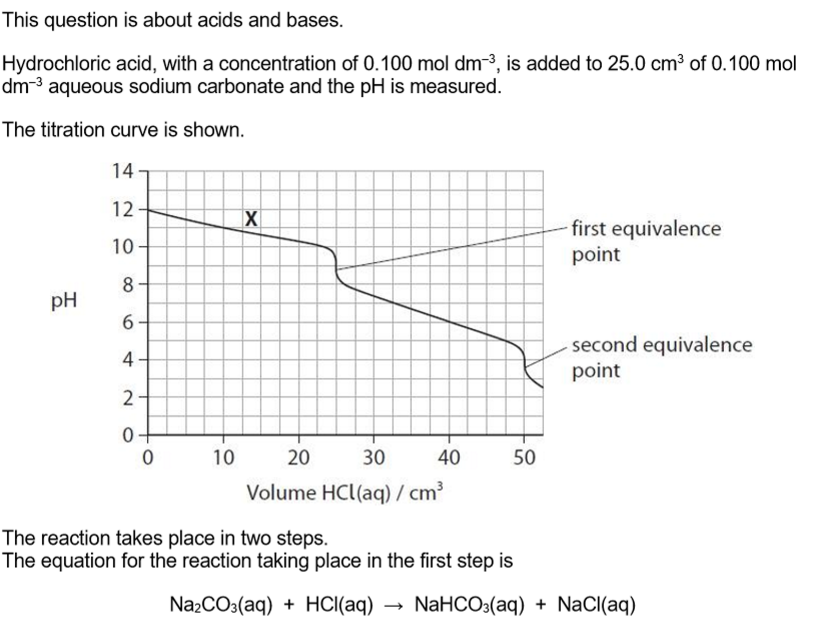
Explain how the solution at point X on the graph can act as a buffer solution.
(solution at X) contains a large amount / reservoir of carbonate ions and hydrogencarbonate ions
carbonate ions react with added hydrogen ions
hydrogencarbonate ions react with added hydroxide ions
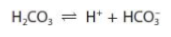
One of the systems controlling the pH of the blood is the carbonic acid-hydrogencarbonate buffer system.
Explain how this buffer system helps to control the pH of blood when extra carbon dioxide is present due to strenuous exercise.
carbon dioxide dissolved in blood forms carbonic acid (and so this concentration increases)
the equilibrium will shift to the right and produce more H+
the high concentration of hydrogencarbonate ions suppress the ionisation of carbonic acid (to help control the pH) or the large reservoir of hydrogencarbonate ions combine with the H+ ions (to help control the blood pH)
the ratio of [HCO3-]:[H2CO3] remains essentially constant so the pH does not change
![<ul><li><p>carbon dioxide dissolved in blood forms carbonic acid (and so this concentration increases)</p></li><li><p>the equilibrium will shift to the right and produce more H+ </p></li><li><p>the high concentration of hydrogencarbonate ions suppress the ionisation of carbonic acid (to help control the pH) or the large reservoir of hydrogencarbonate ions combine with the H+ ions (to help control the blood pH)</p></li><li><p>the ratio of [HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>]:[H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub>] remains essentially constant so the pH does not change </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e72e48ed-e78b-4b10-bb6d-8dc3b6959d85.png)