Arteries --> conceptual (exam three)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
organization of blood vessels
heart --> artery --> arteriole --> capillary --> venule --> vein --> heart
where is blood going during systole
pushed out of the ventricles and either sent to the body or to the lungs for exchange of O2 and CO2
where is blood going during diastole
blood enters the ventricles, leaving the atria
when and where is pressure highest
within the arteries, during systole
- arterioles start to lower pressure as they reach the capillaries and then veins
when and where is pressure lowest
within veins, during diastole
layers of the blood vessels (arteries and veins) and their function
Three layers, or tunics:
- tunica intima: endothelium continuous with heart lining
- tunica media: smooth muscle under autonomic regulation
- tunica externa: outermost connective tissue layer
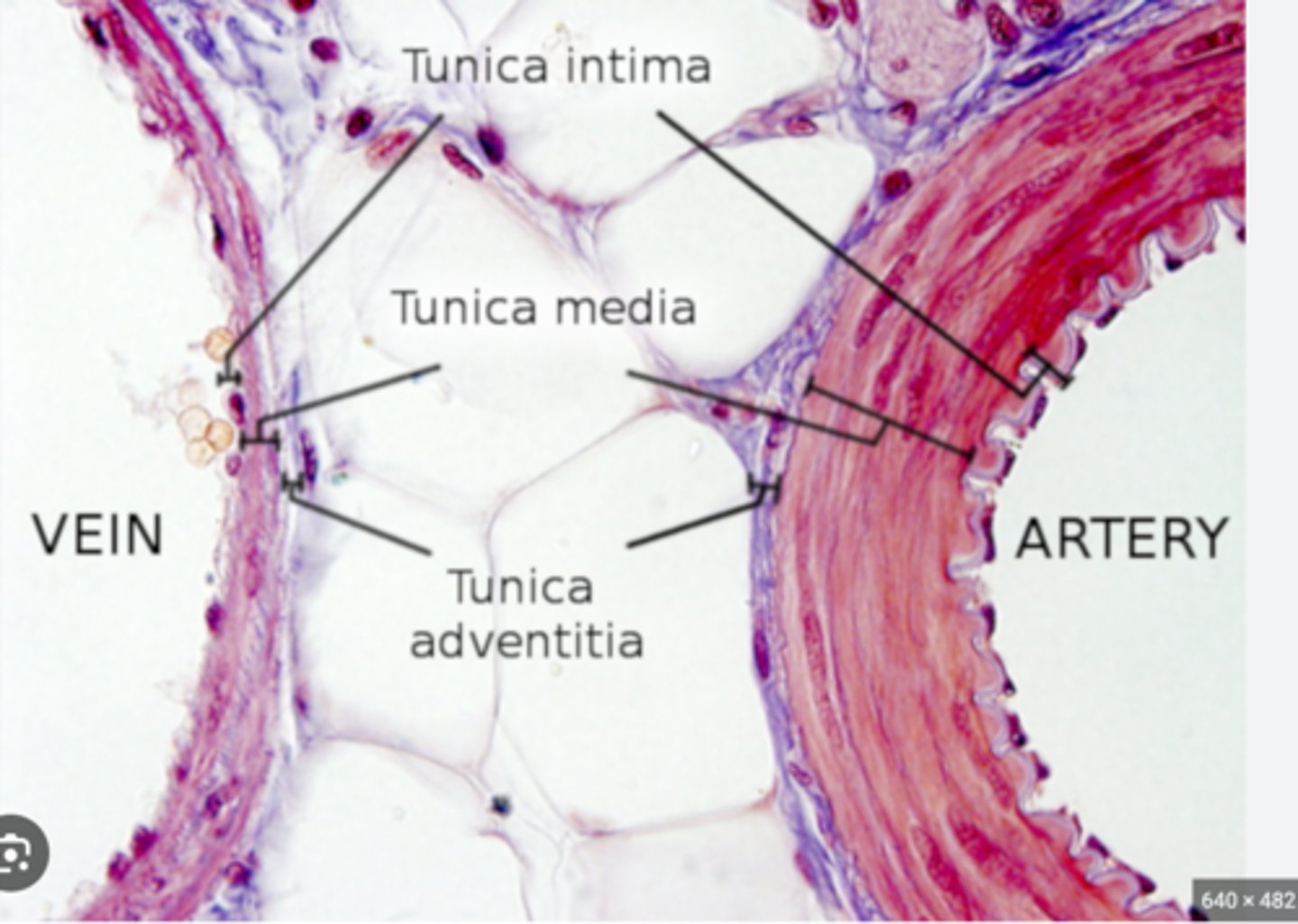
what extra layers are only apart of arteries?
The internal and external elastic lamina, which both provide the ability to expand and recoil
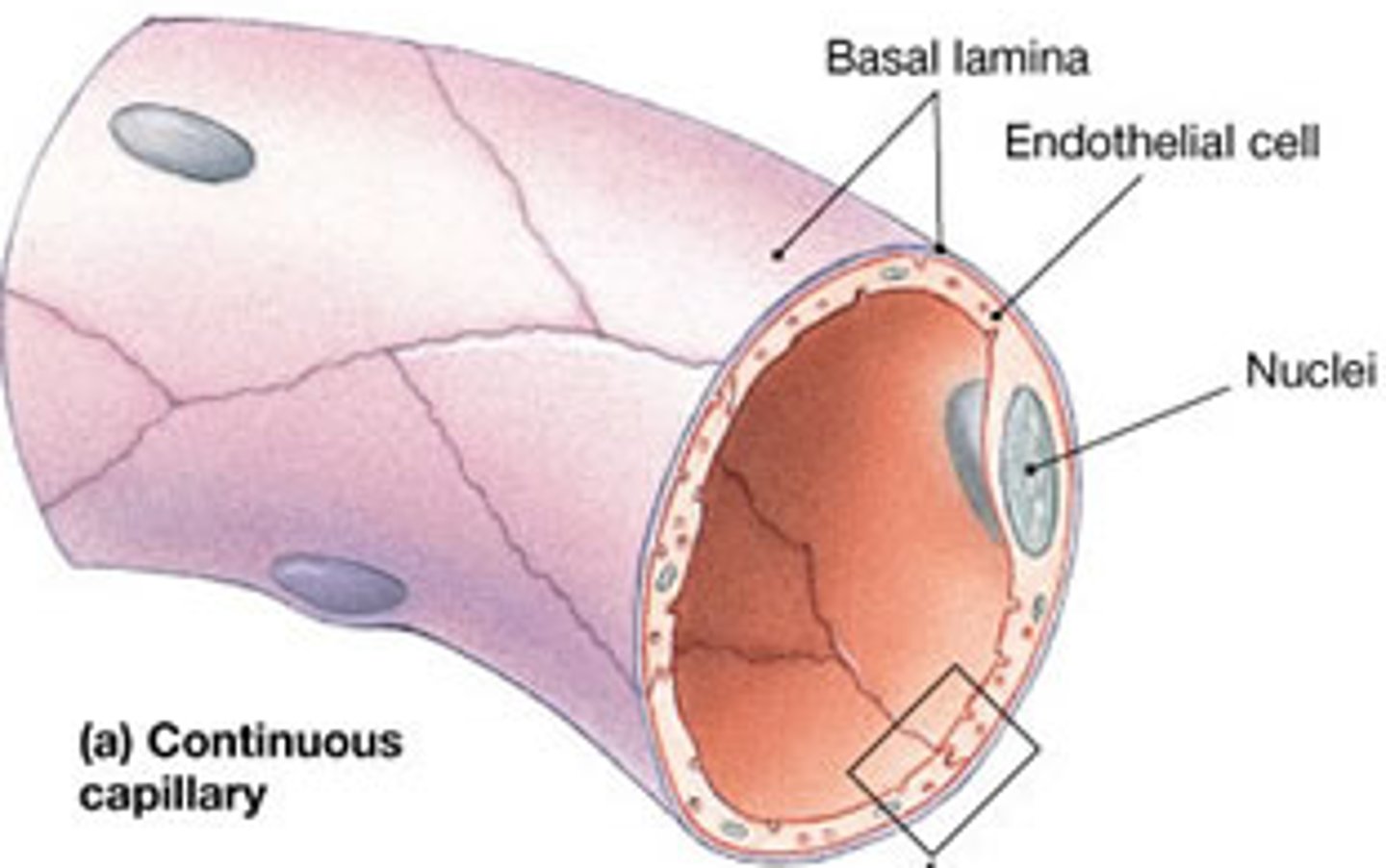
what are capillaries made of?
An endothelial and sub-endothelial layer, made up of single squamous cells
- only tunica intima
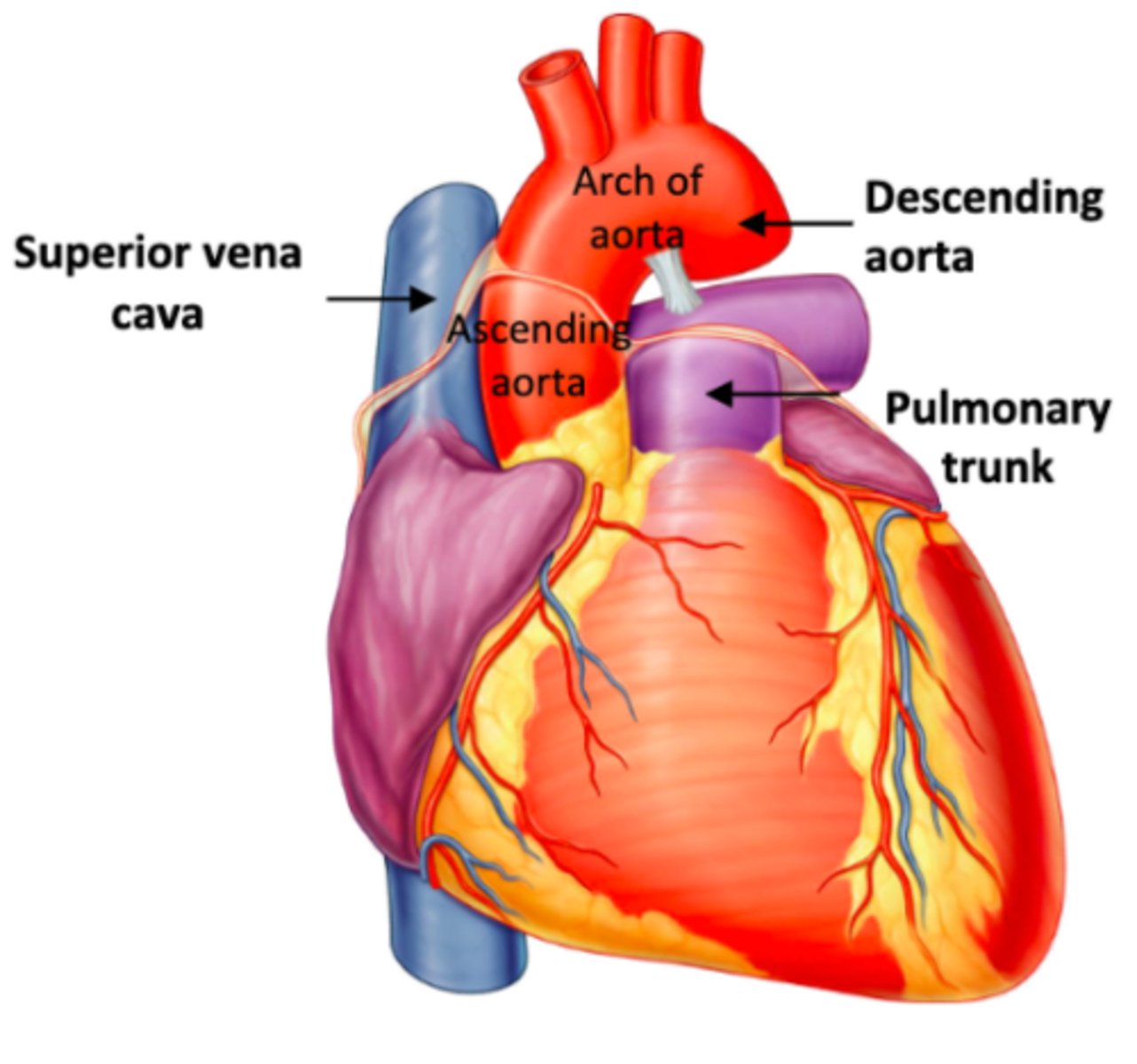
components of the aorta
ascending aorta, aortic arch, descending aorta (which becomes abdominal aorta once out of the thorax)
What are the three branches off the aorta
brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian artery
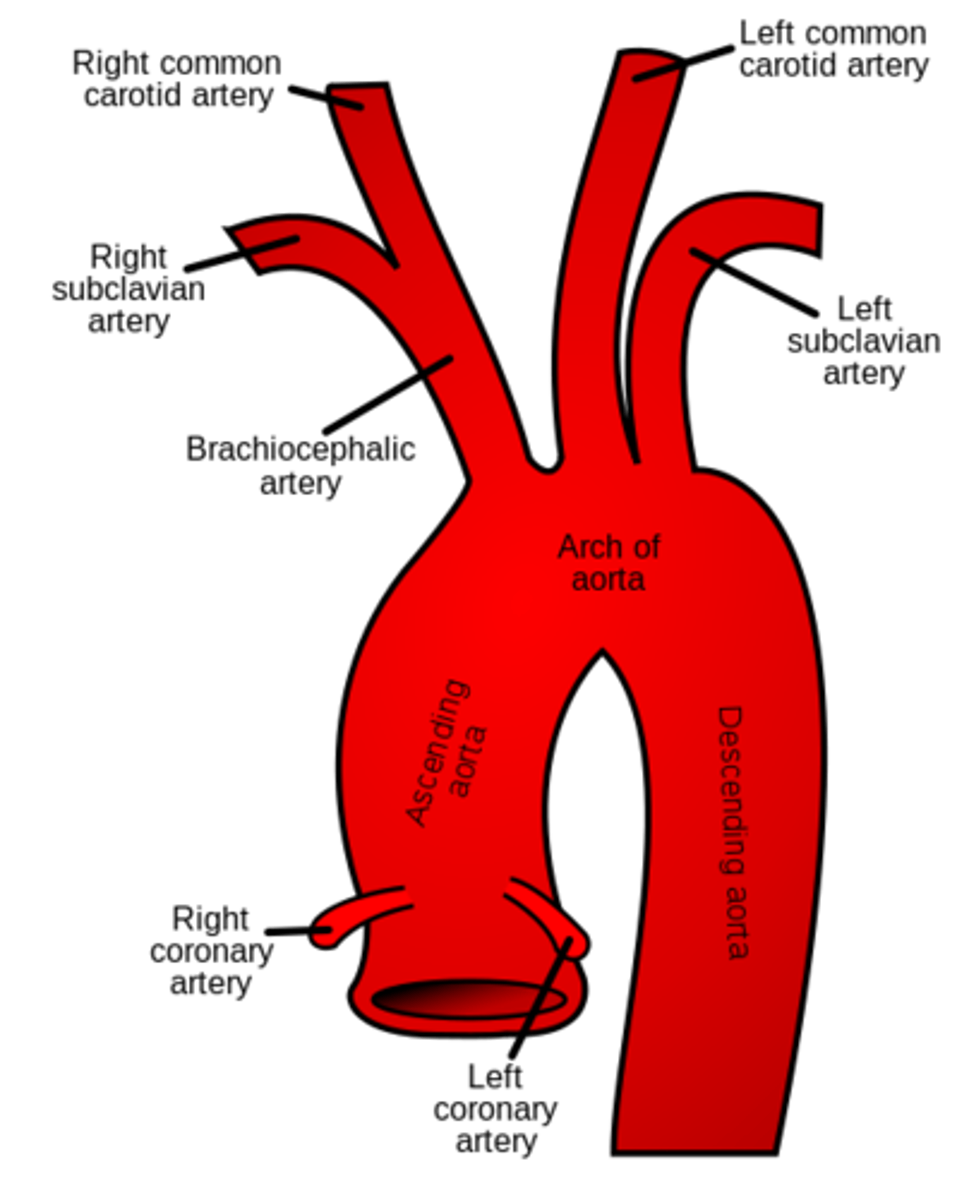
comonents of the brachiocephalic trunk
Branches off into the right subclavian artery and right common carotid artery
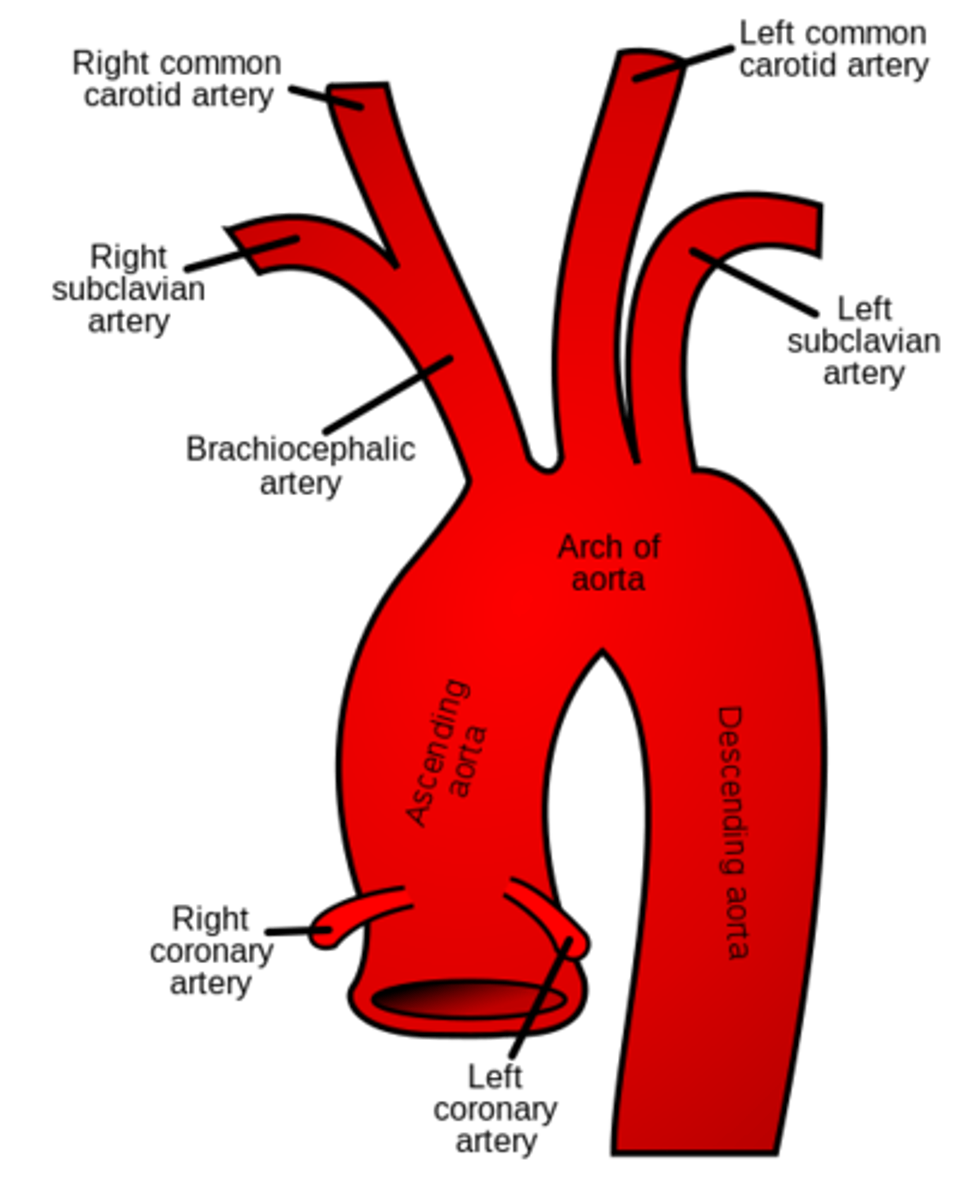
what are the terms "common" and "trunk" indicating
indicates that the artery will split into smaller vessels or bifurcate in some way
what does the descending aorta become?
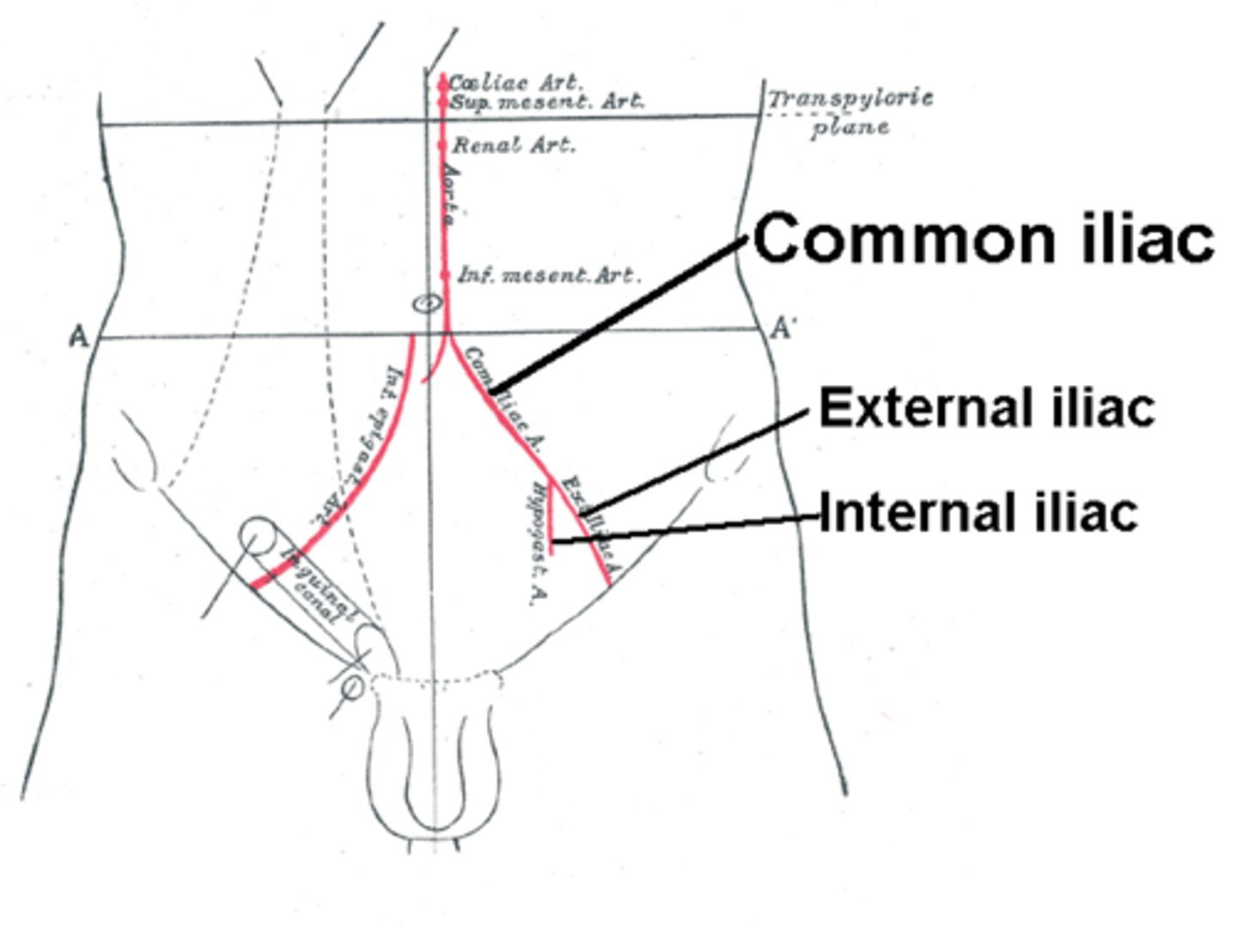
Once out of the thorax it becomes the abdominal artery become bifurcating and becoming the right and left common iliac artery
what does the common iliac artery bifurcate into?
the right and left internal and external arteries
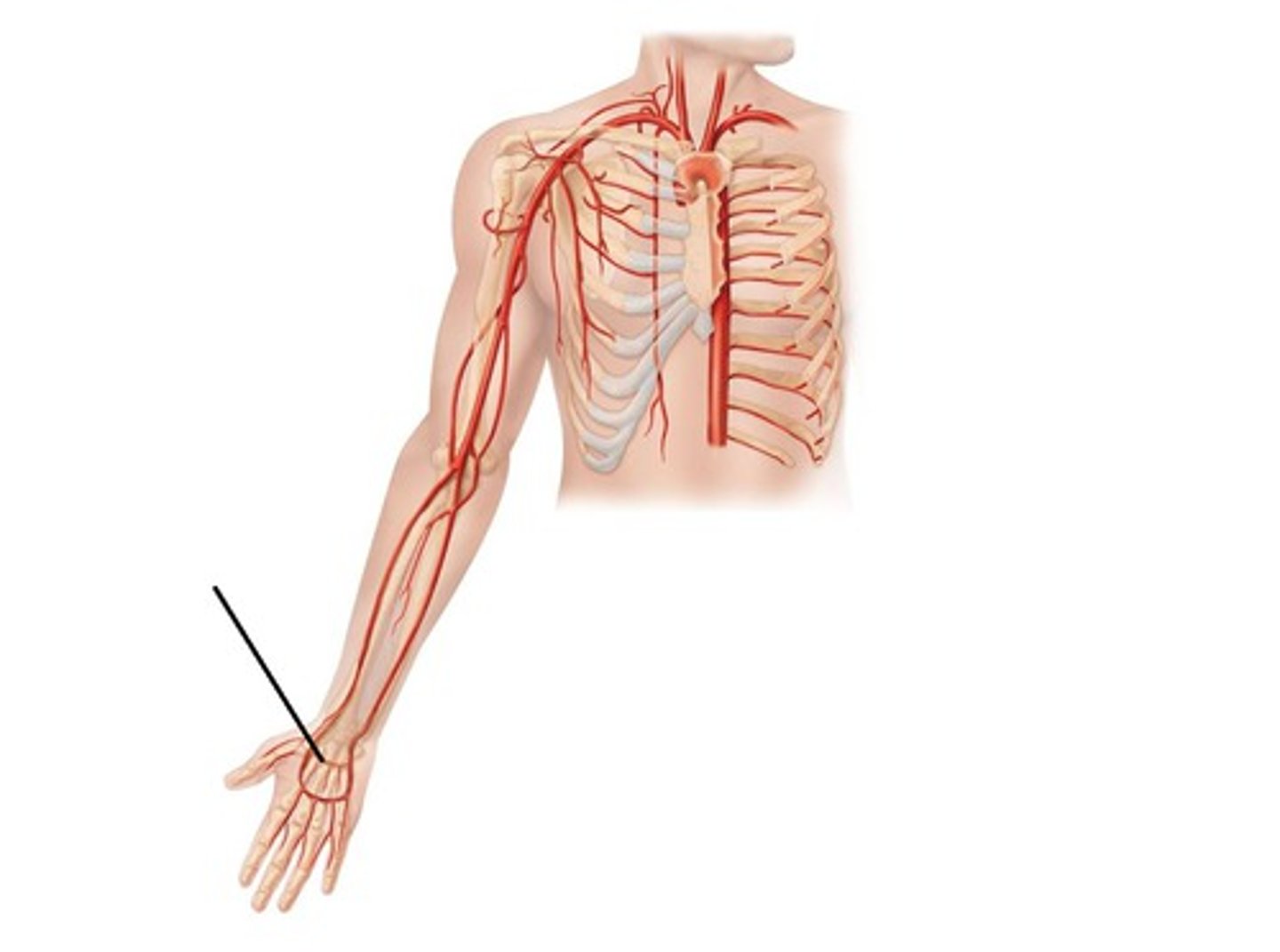
what does the subclavian artery become as it courses down the upper arm?
The axillary artery as it passes the first rib, then turns into the brachial artery as it passes teres major
- both supplying the anterior upper arm
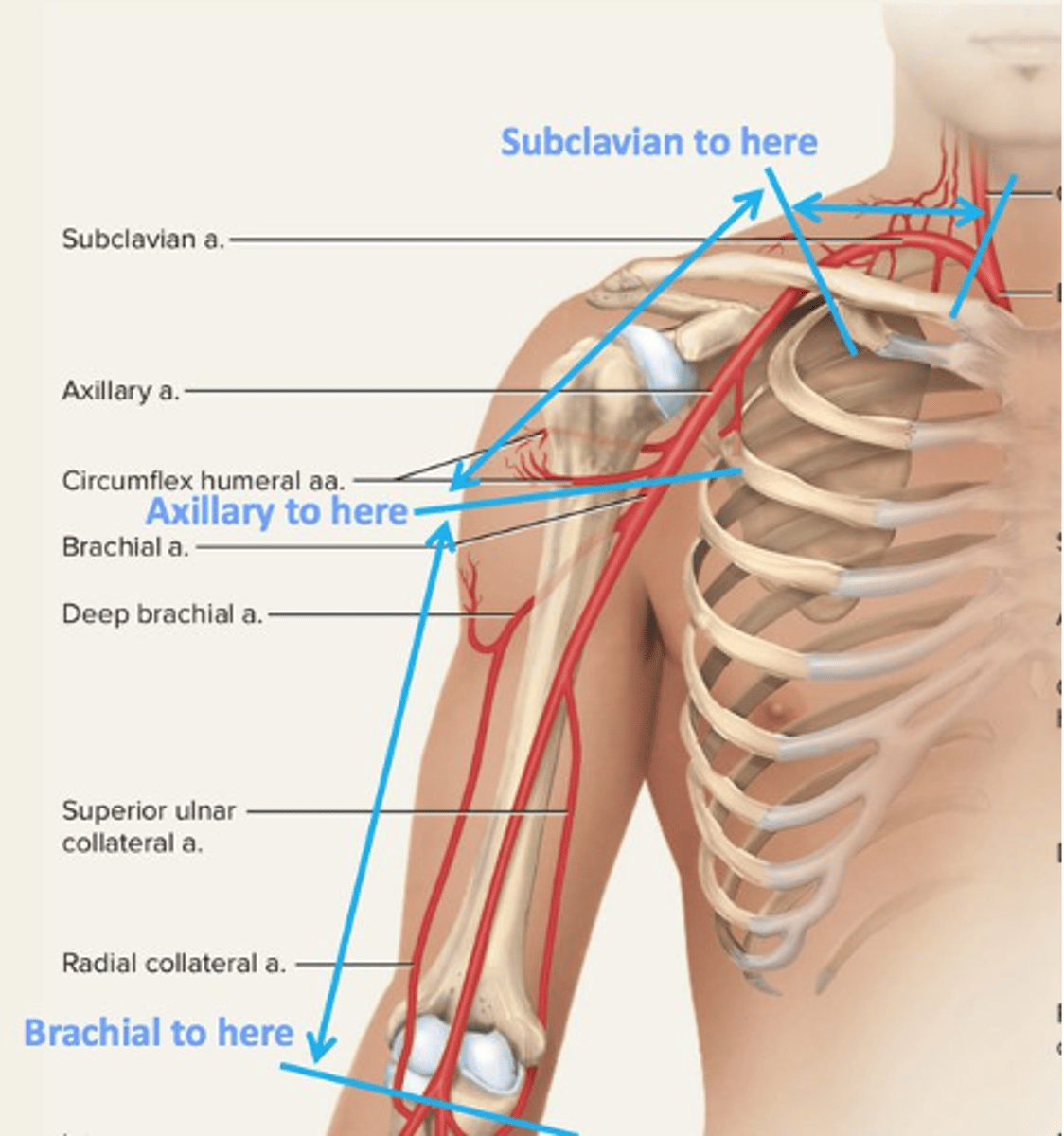
what branches off the brachial artery near teres major?
the deep brachial artery, which courses posteriorly to the humerus to supply triceps
what does the brachial artery bifurcate into as it reaches the elbow?
the radial and ulnar artery, which follow their respective bones downward
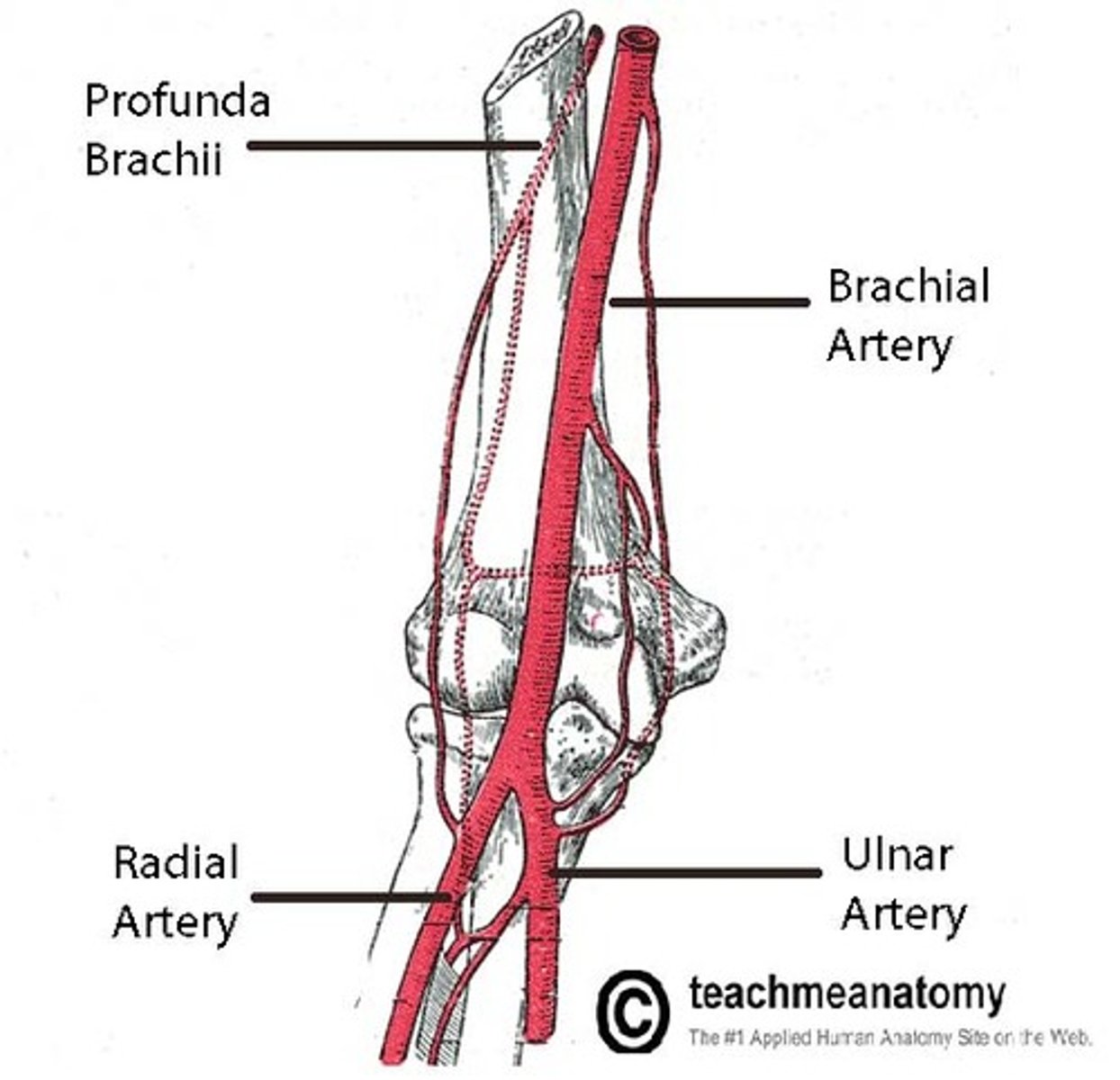
what branches off the ulnar artery?
common interosseous artery, which will bifurcate further into the posterior and anterior interosseous artery
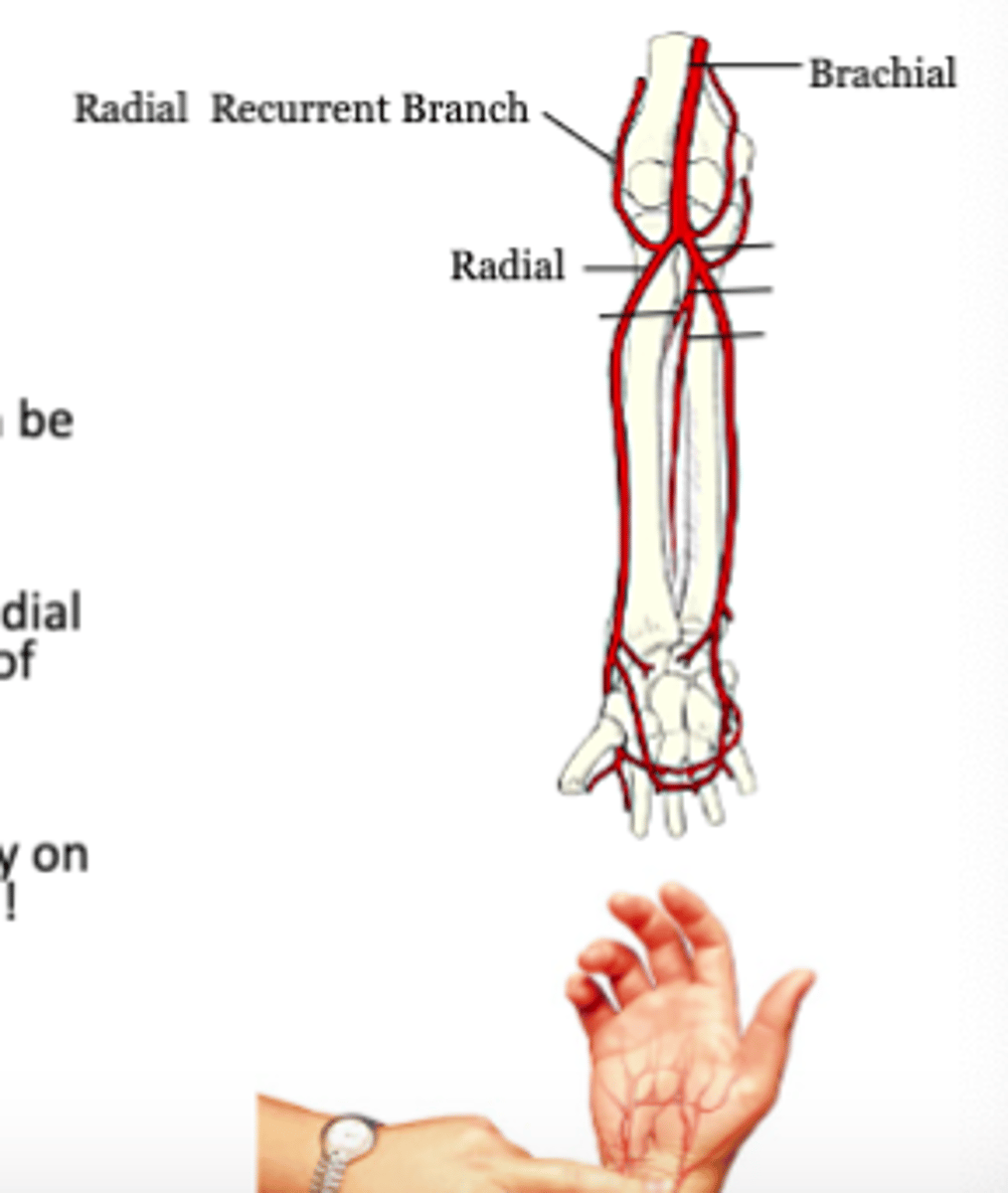
How is blood flow still maintained in forearm if both the radial and ulnar artery underwent occlusion?
because smaller arteries that branch off the brachial artery, called collateral arteries, and arteries coming off of the radial and ulnar arteries, called recurrent arteries, anastomoses to form collateral circulation, which would be maintained, even after occlusion
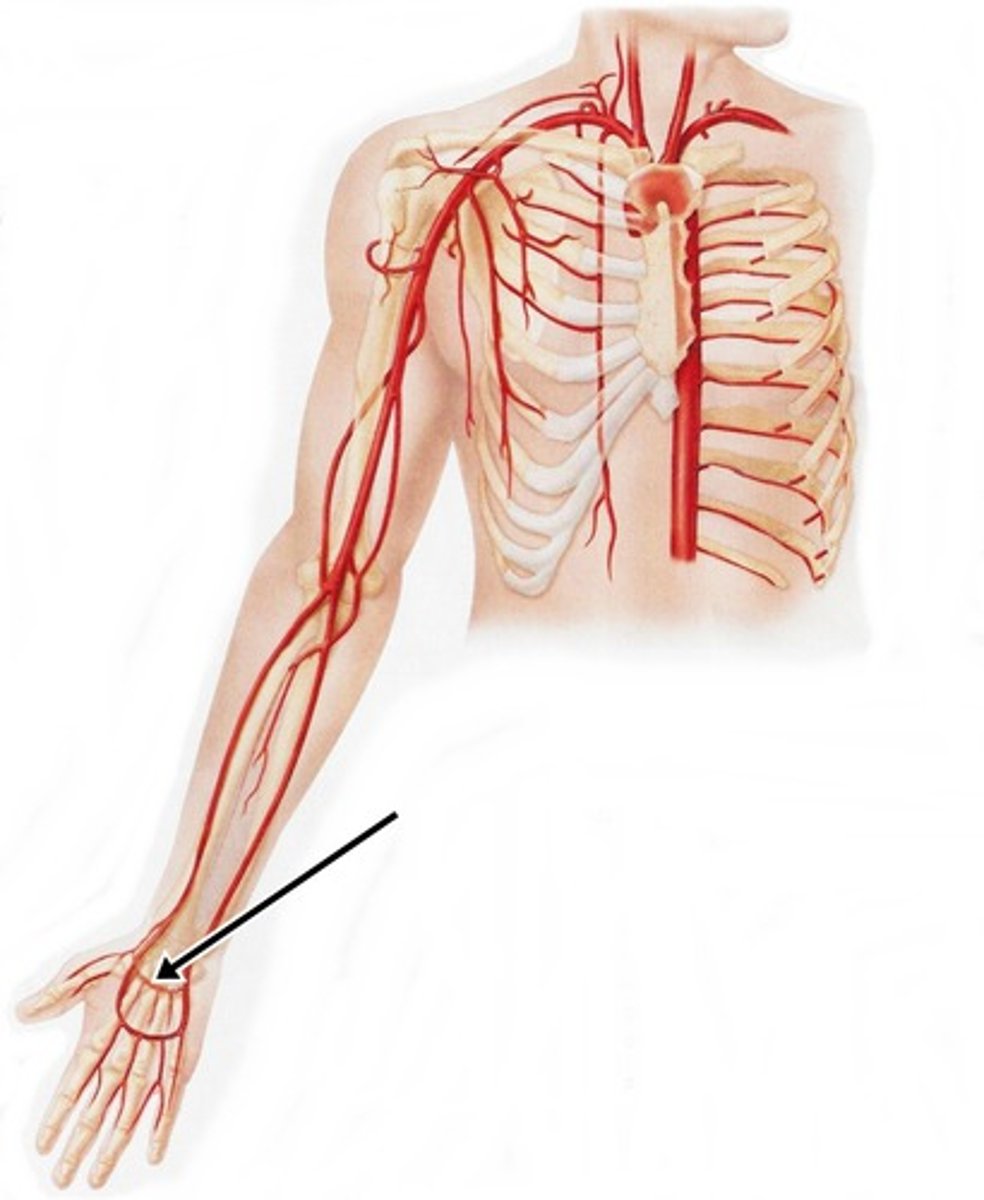
palmer arches
Arch shaped arteries
- anastomoses of the radial and ulnar arteries at wrist, via collateral circulation of forearm and hand
what do the common carotid arteries bifurcate into?
internal and external carotid arteries
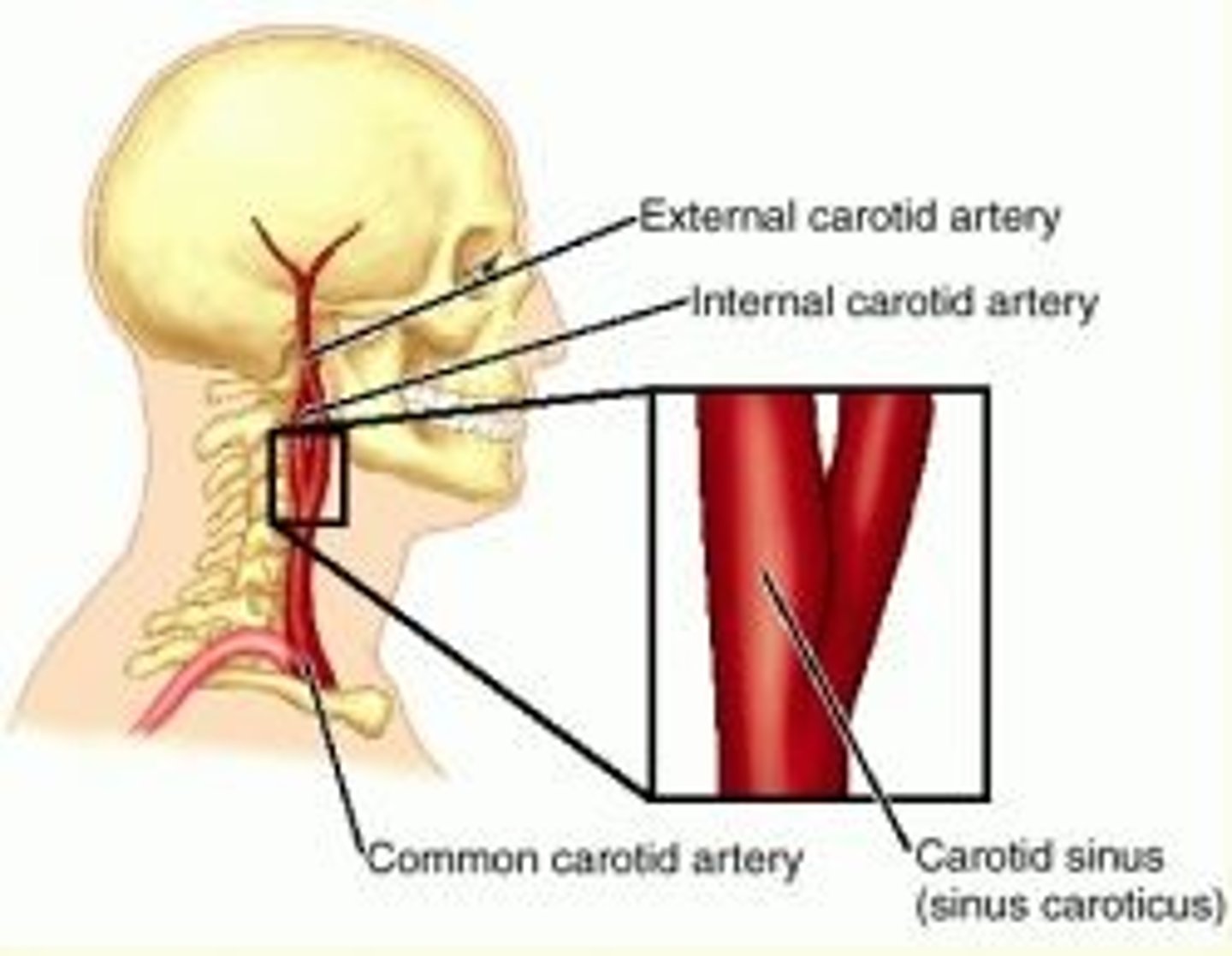
External carotid artery blood supply
forms many branches to supply the external head
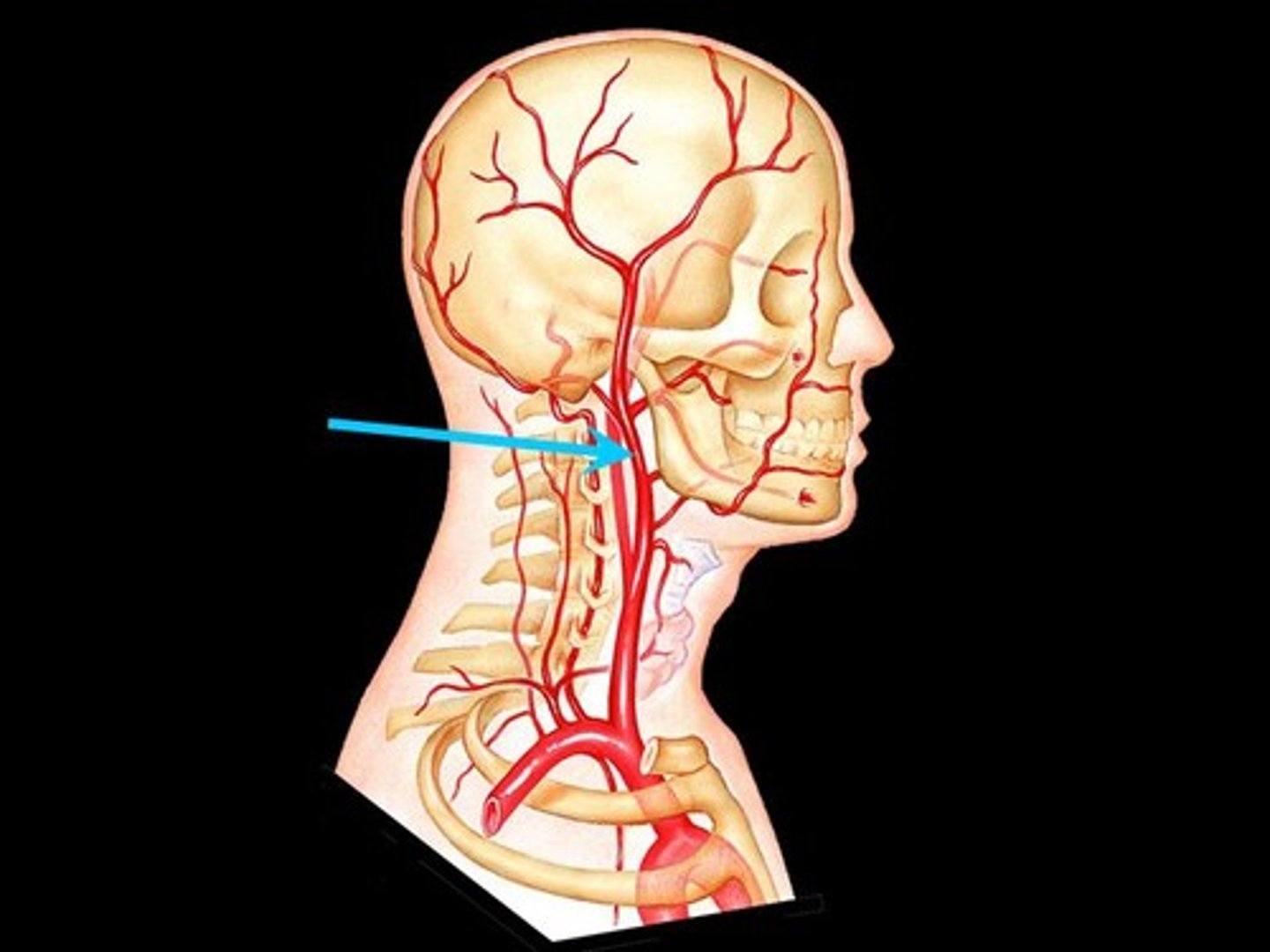
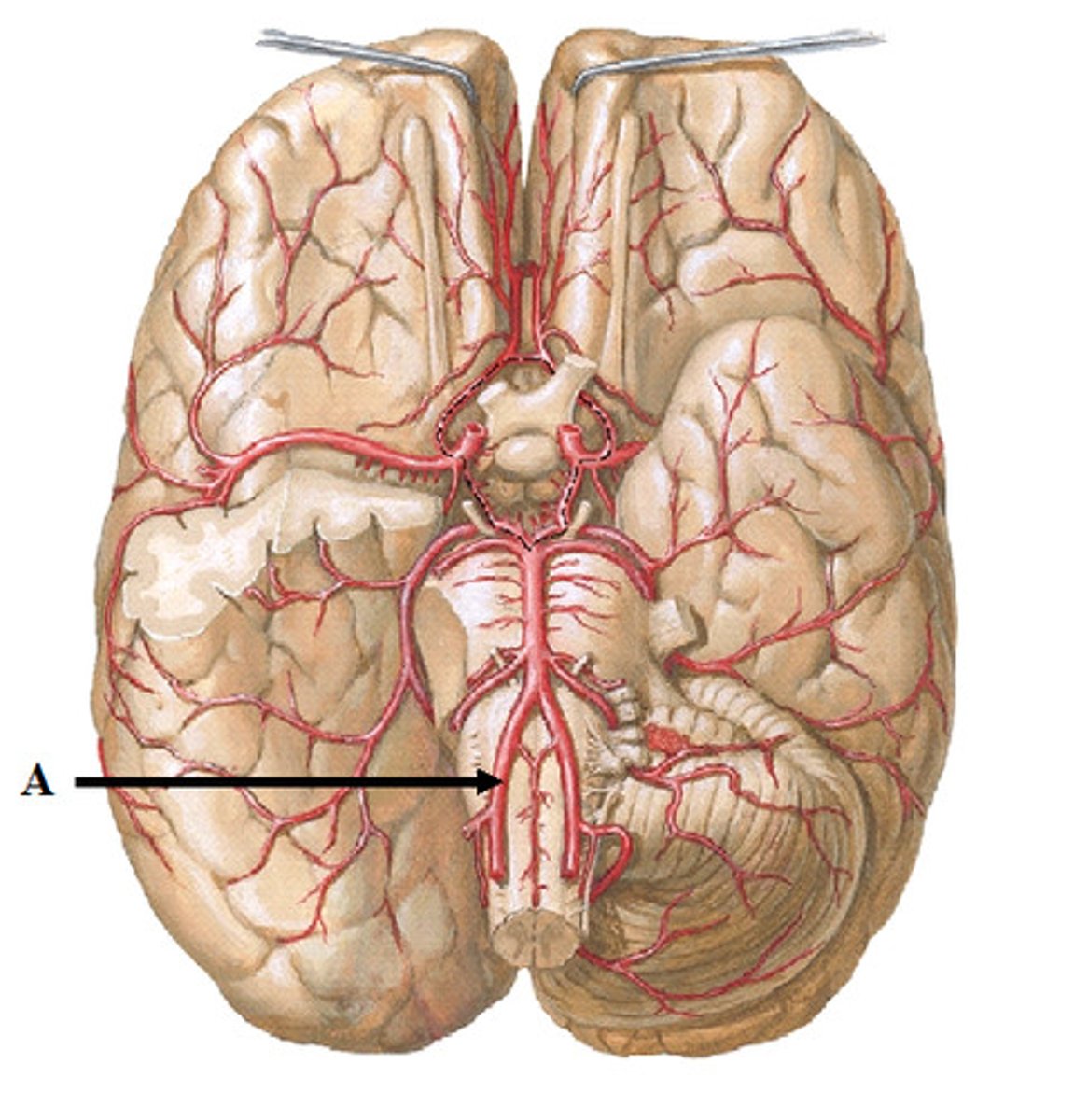
path of internal carotid artery
enters the skull through carotid canal after branching off the common carotid --> entering the skull through the foramen lacerum --> forms the middle and anterior cerebral arteries
internal carotid artery blood supply
enters the cranium to supply the anterior and and middle of cerebral hemispheres via forming into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries
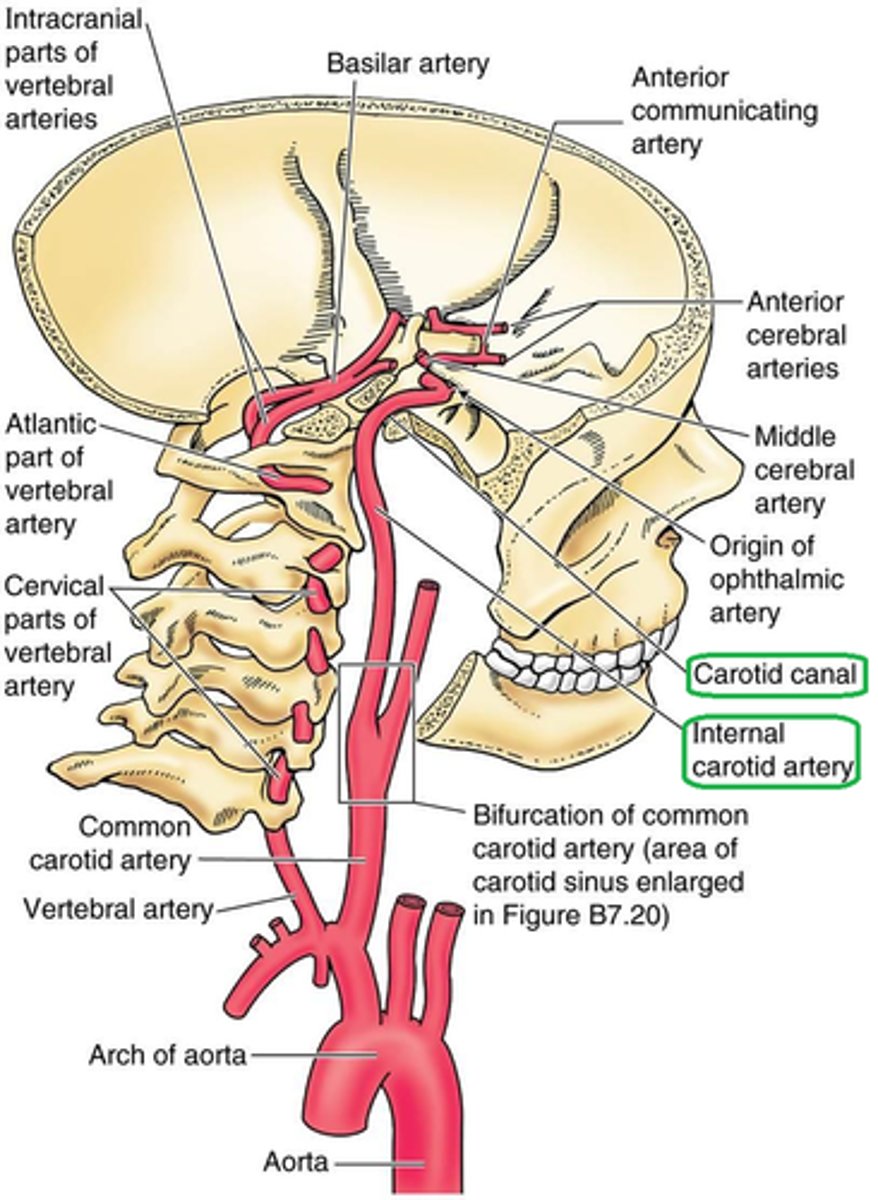
path of vertebral artery
branches of the subclavian --> runs through the transverse foramen of the cervical vertebra --> enters the skull through the foramen magnum --> forms basilar artery which bifurcates into the posterior cerebral arteries
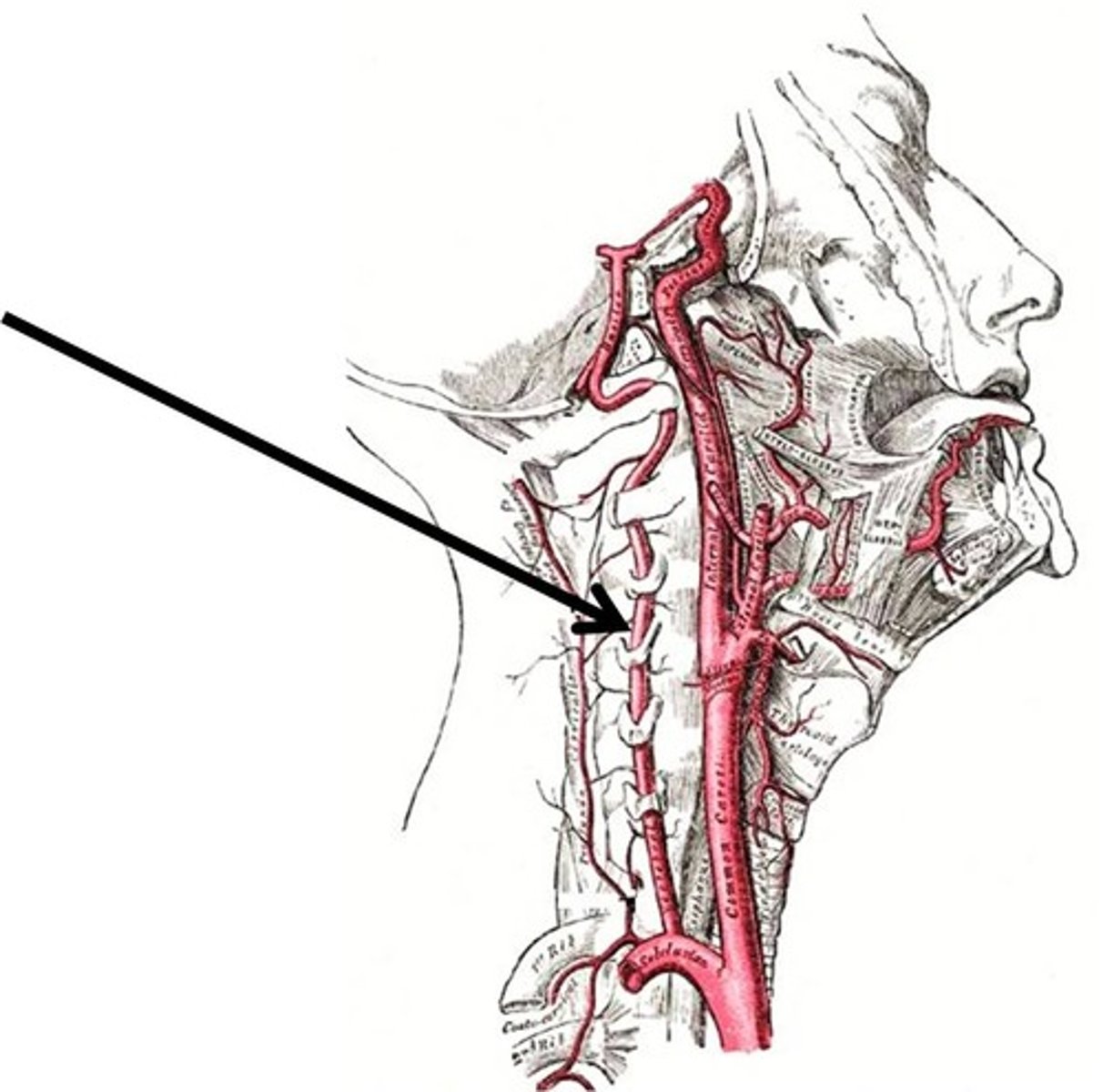
vertebral artery blood supply
the two arteries bifurcate into the basilar artery, then posterior cerebral artery to supply the posterior cerebral hemisphere
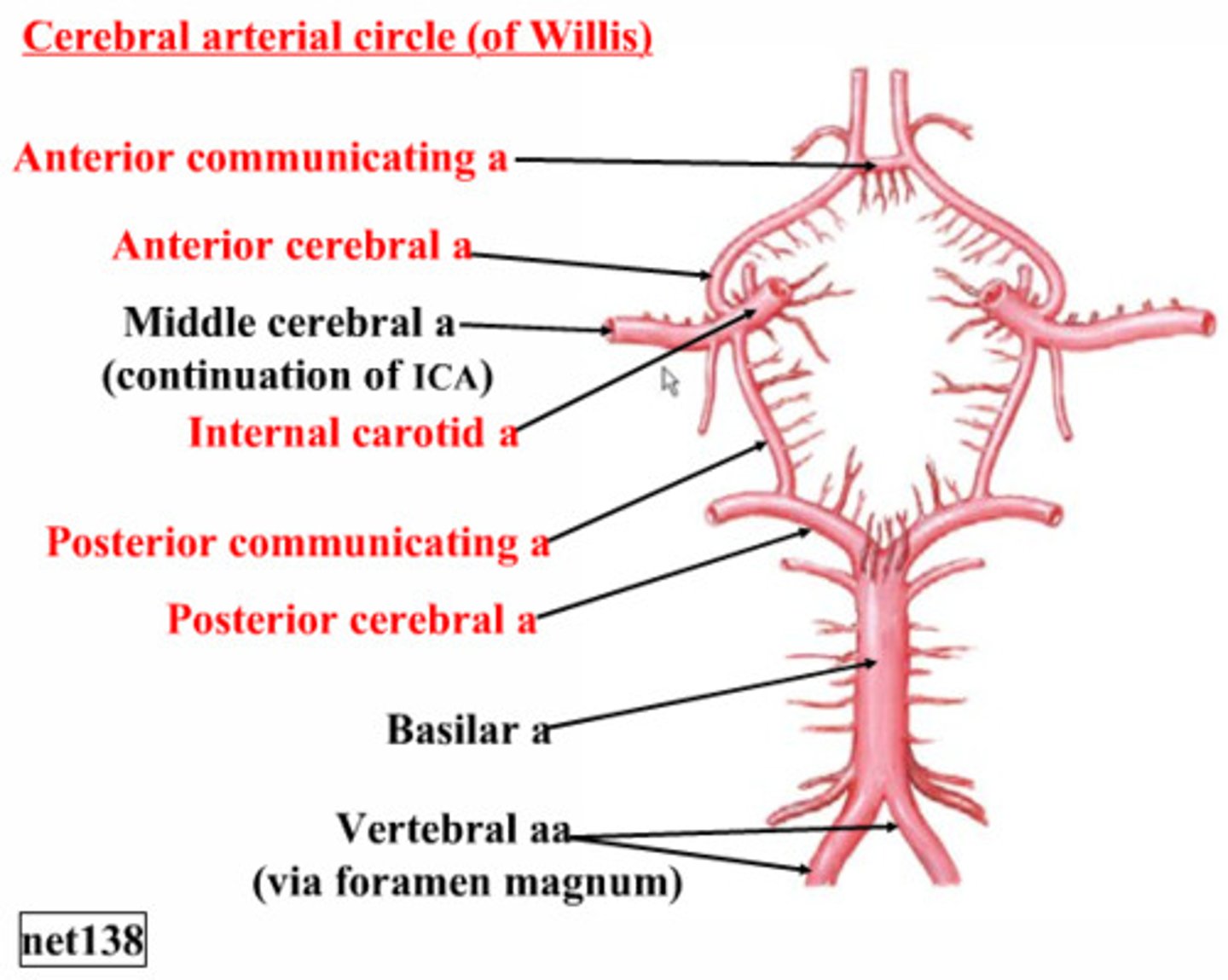
Order of circle of willis
Vertebral arteries --> basilar artery --> posterior cerebral arteries --> posterior communicating branches --> internal jugular veins --> middle cerebral arteries --> anterior cerebral arteries --> connected into a circle by the anterior communicating branch
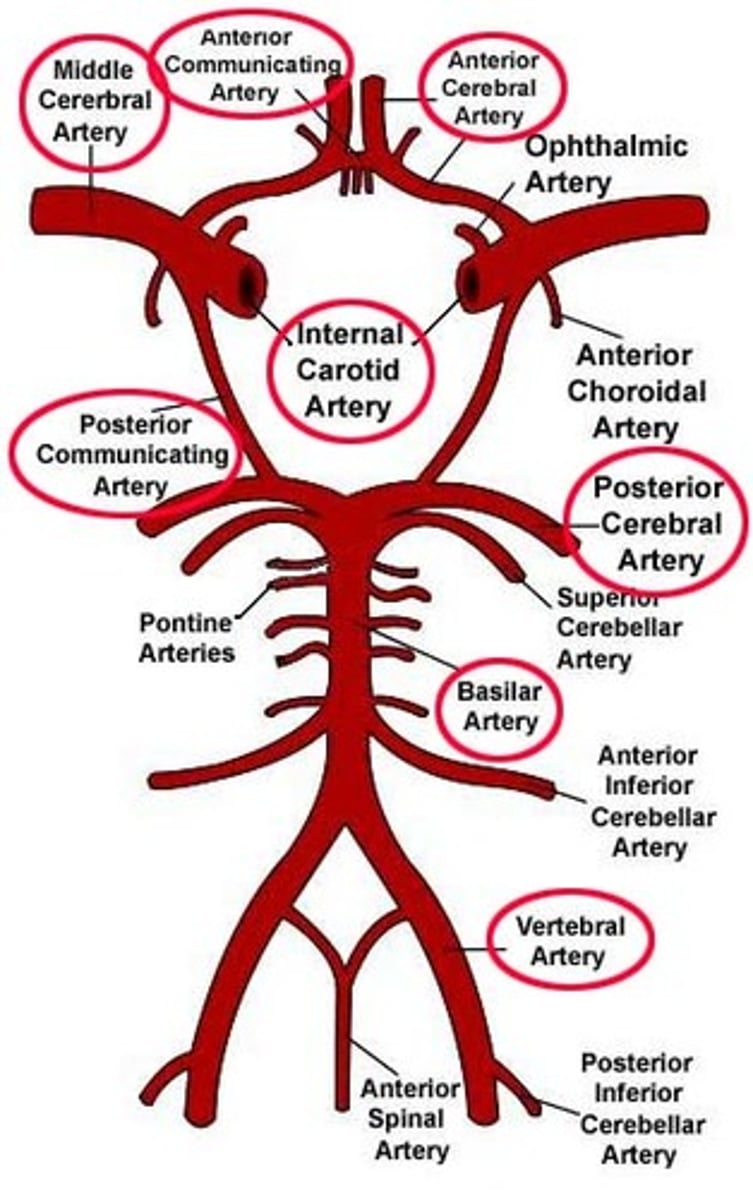
why does it form a cerebral circle?
to form collateral circulation; provides alternate blood flow in the case of an occluded artery
how would blood flow in the event of an internal carotid artery occlusion?
blood will flow through the posterior cerebral and posterior communicating arteries and/or the anterior cerebral and anterior communicating arteries
how would blood flow in the event of a basilar artery occlusion?
blood will flow through the middle cerebral and posterior communicating arteries
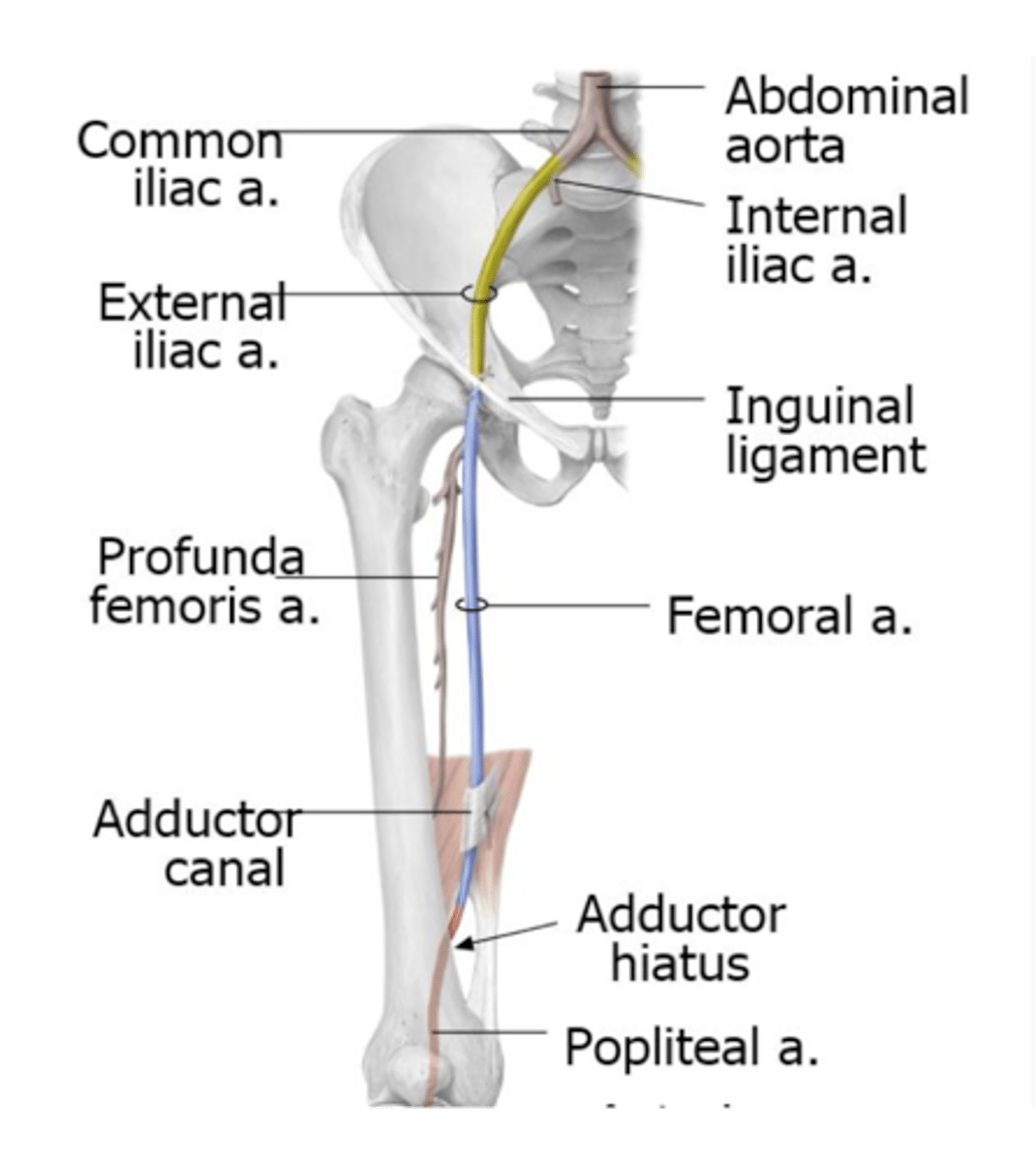
what does the external iliac artery become and when?
Becomes the femoral artery after passing under the inguinal ligament
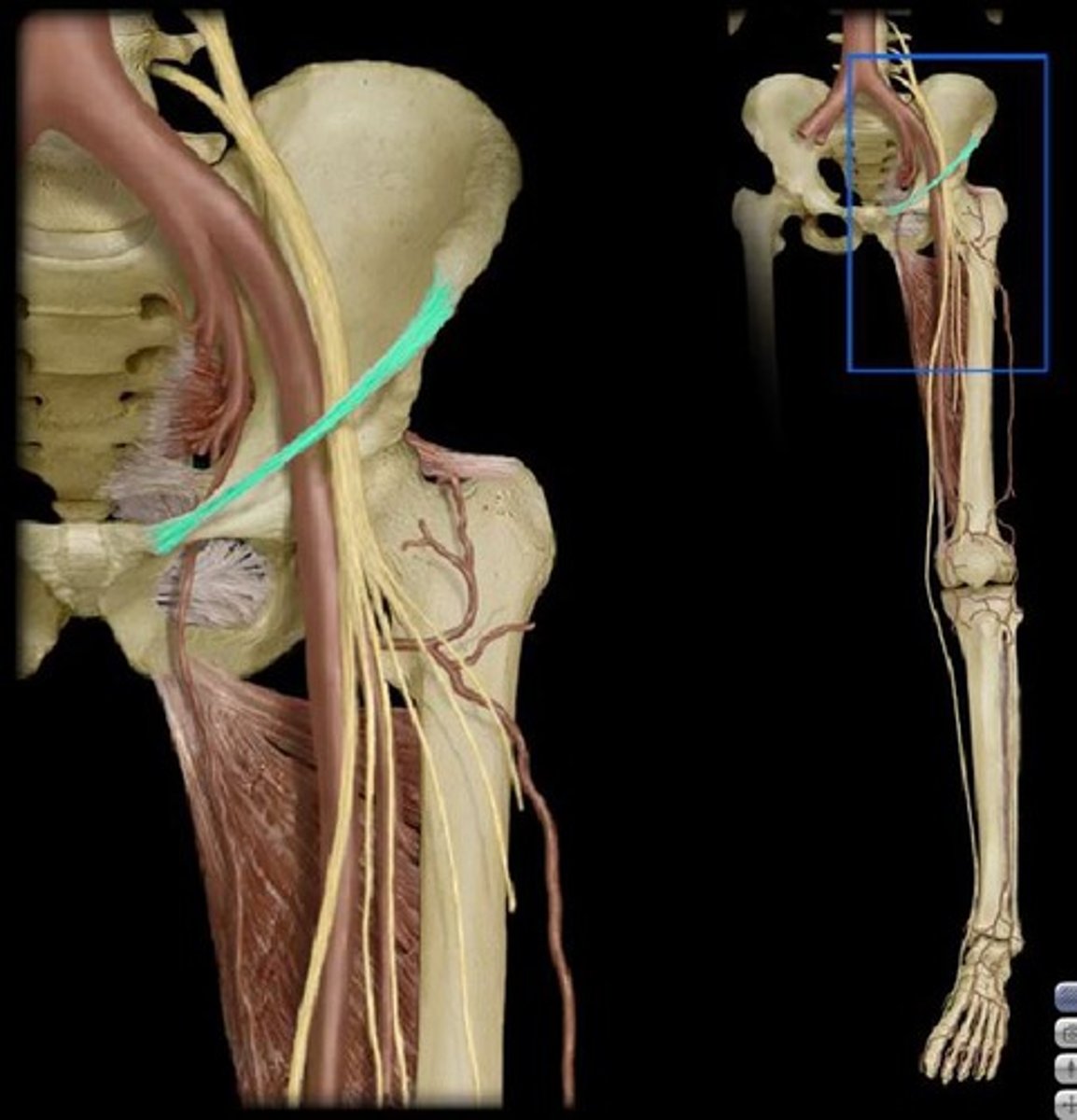
what does the femoral artery give rise to?
courses down the anterior thigh, forming a deep femoral vein to supply the posterior thigh (hammies)
what does the femoral artery become and when?
courses down the anterior thigh before passing from anterior to posterior via the adductor hiatus (hole), where it courses posteriorly as the popliteal artery
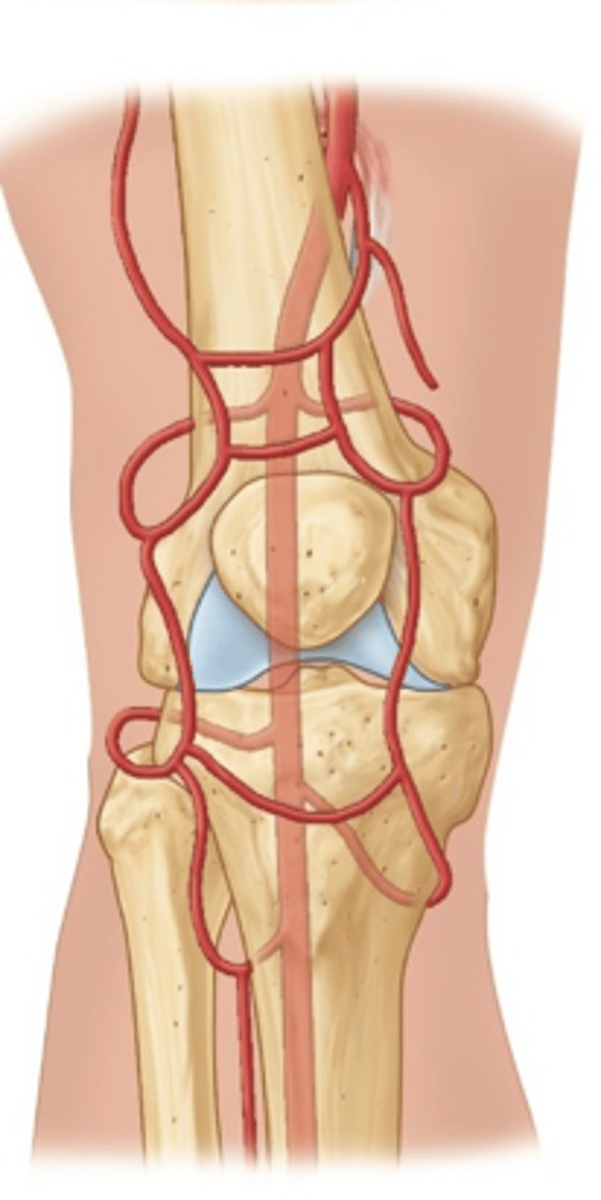
how does blood flow maintain if the popliteal artery was occluded?
Collateral circulation around the knee allows blood flow to continue on and reach the full leg --> called genicular arteries
- located between the femoral artery and anterior/posterior tibial arteries
what does the popliteal artery become?
courses down the leg posteriorly before bifurcating into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries, where the anterior courses anteriorly through the foreleg bones
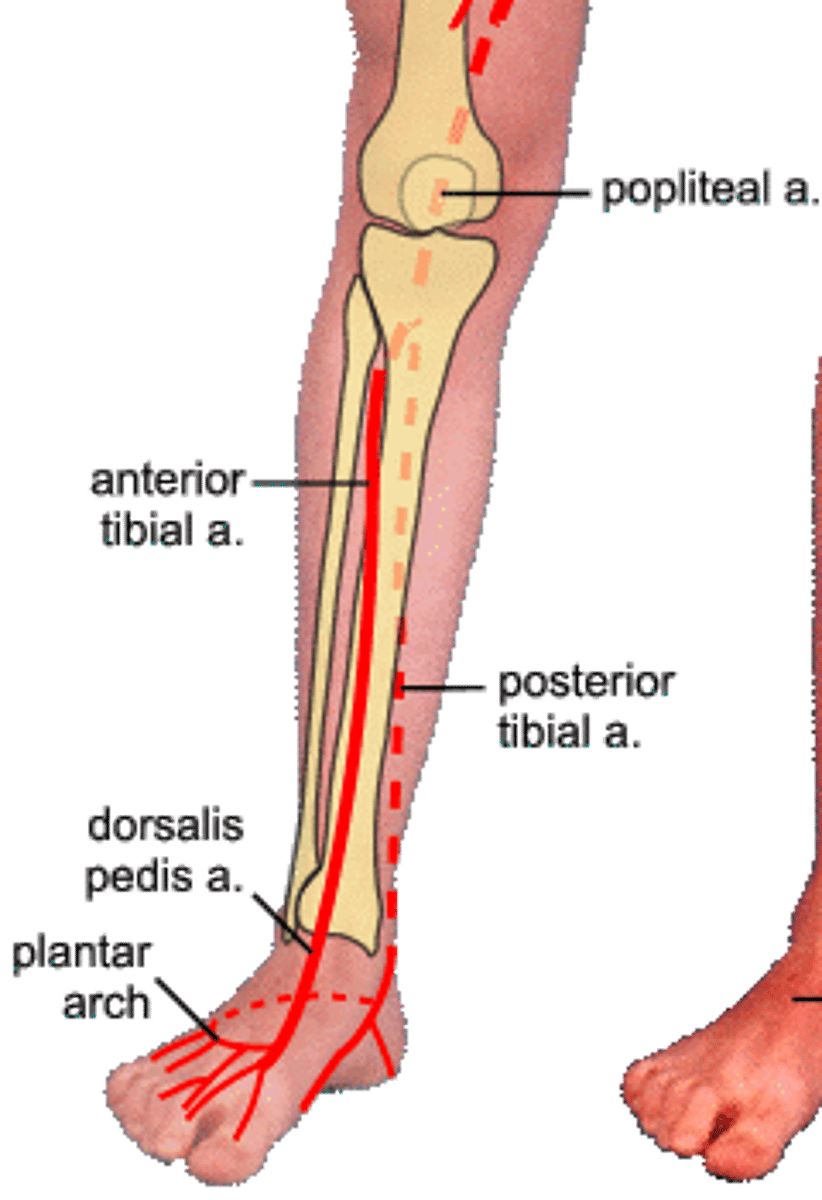
what does the posterior tibial artery form?
Gives off a branch called the fibular artery, which supplys and innervates the lateral compartment of the leg, where the posterior tibial artery stays posterior
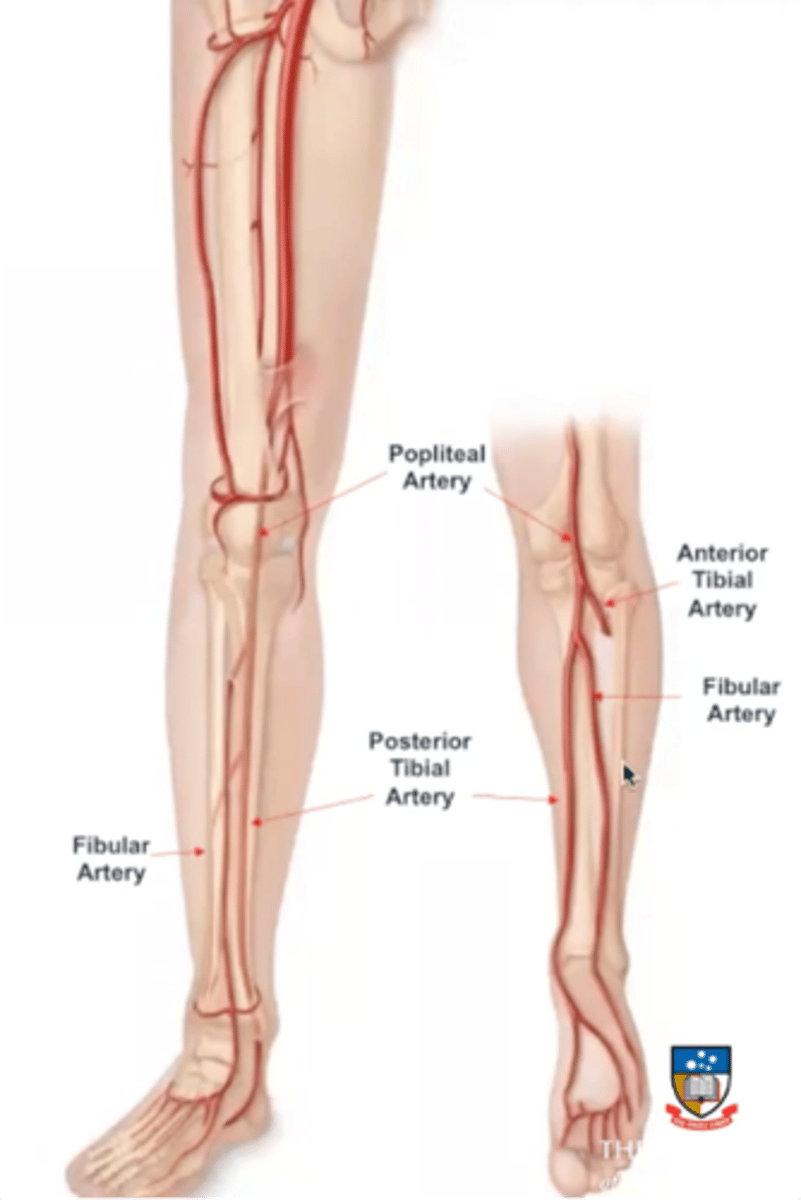
what does the posterior tibial artery become and when?
branches to become plantar arteries to supply the plantar (bottom) muscles of the foot after passing an imaginary line passing from the medial/lateral malleolus
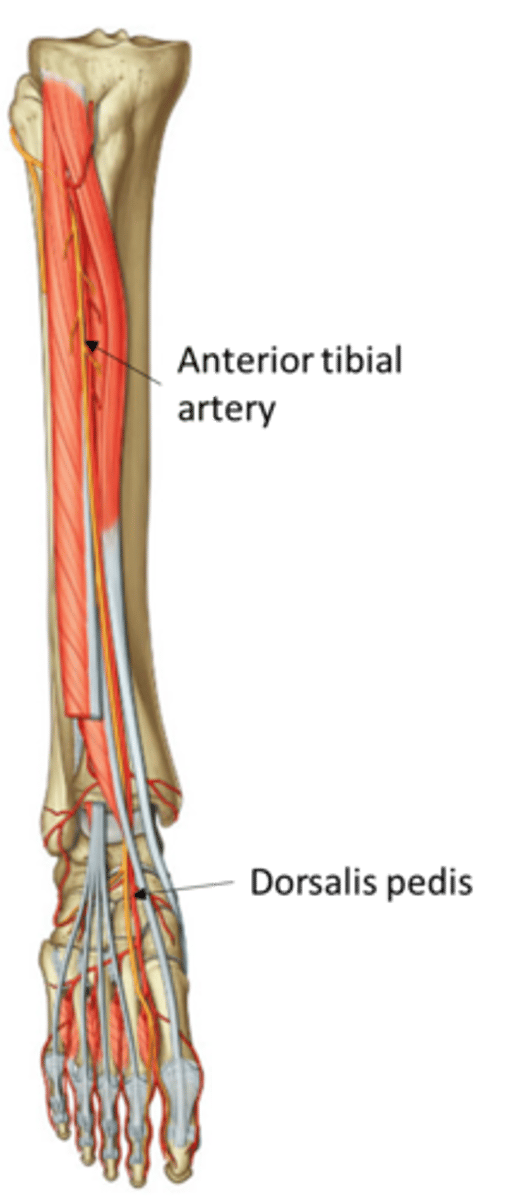
what does the anterior tibial artery become and when?
courses anteriorly, supplying the anterior foreleg before becoming the dorsalis pedis artery to supply the dorsum (top) of foot after passing an imaginary line passing from the medial/lateral malleolus
how is blood flow maintained if the posterior/anterior tibial arteries were occluded?
collateral circulation around the ankle and foot allows to blood flow to be maintained via the anastomosis of the arcuate artery (of the anterior tibial) and the planter arteries
what does the thoracic aorta form in order to innervate the muscles of the thorax?
gives off posterior intercostals arteries and internal thoracic arteries that give rise to anterior intercostals
- internal thoracic arteries supply the diaphragm '
- posterior and anterior intercostals arteries supply the intercostal muscles
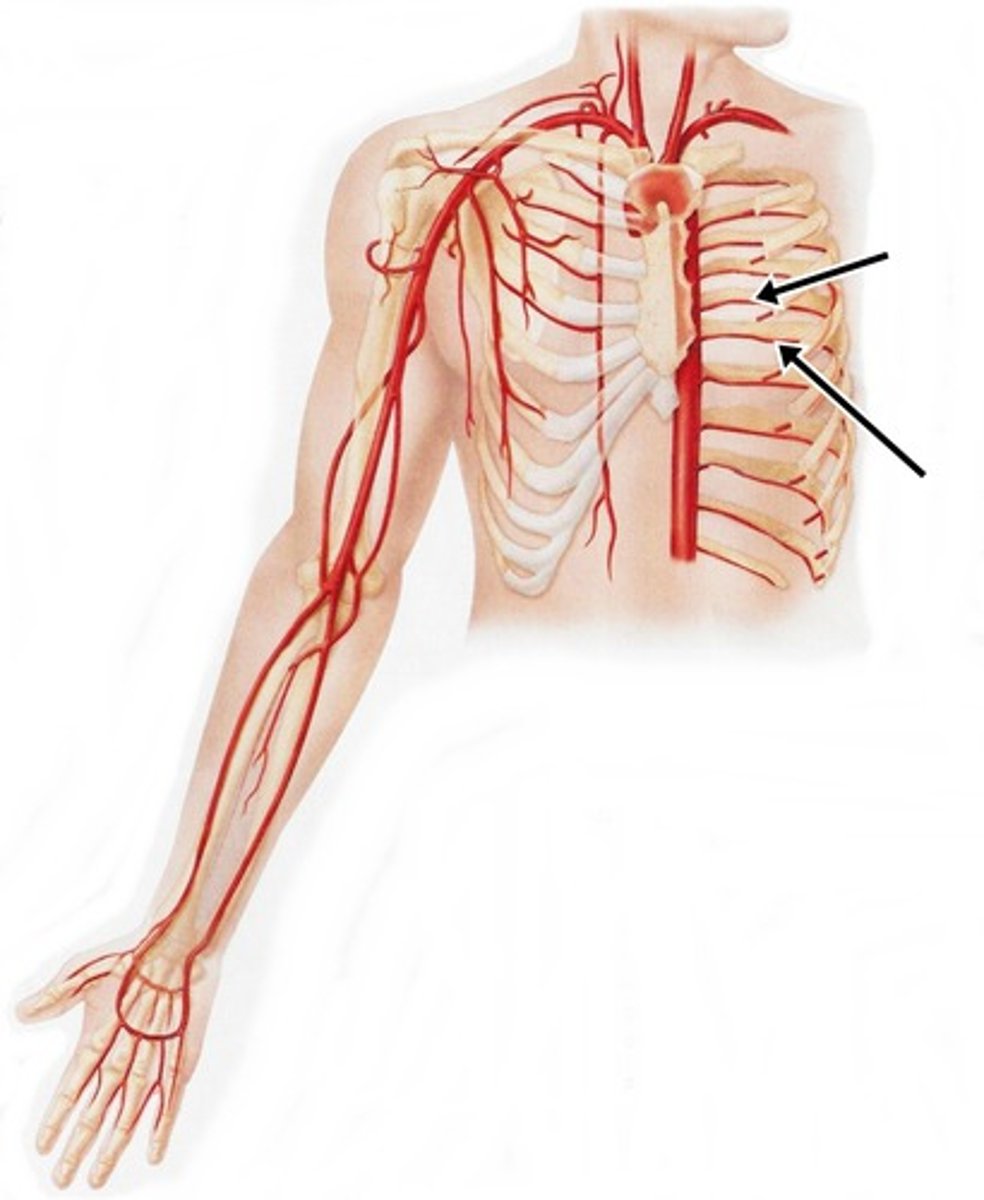
how is blood flow maintained if the posterior/anterior intercostals arteries were occluded?
collateral circulation to the intercostal muscles is achieved by the anastomosis of the two arteries
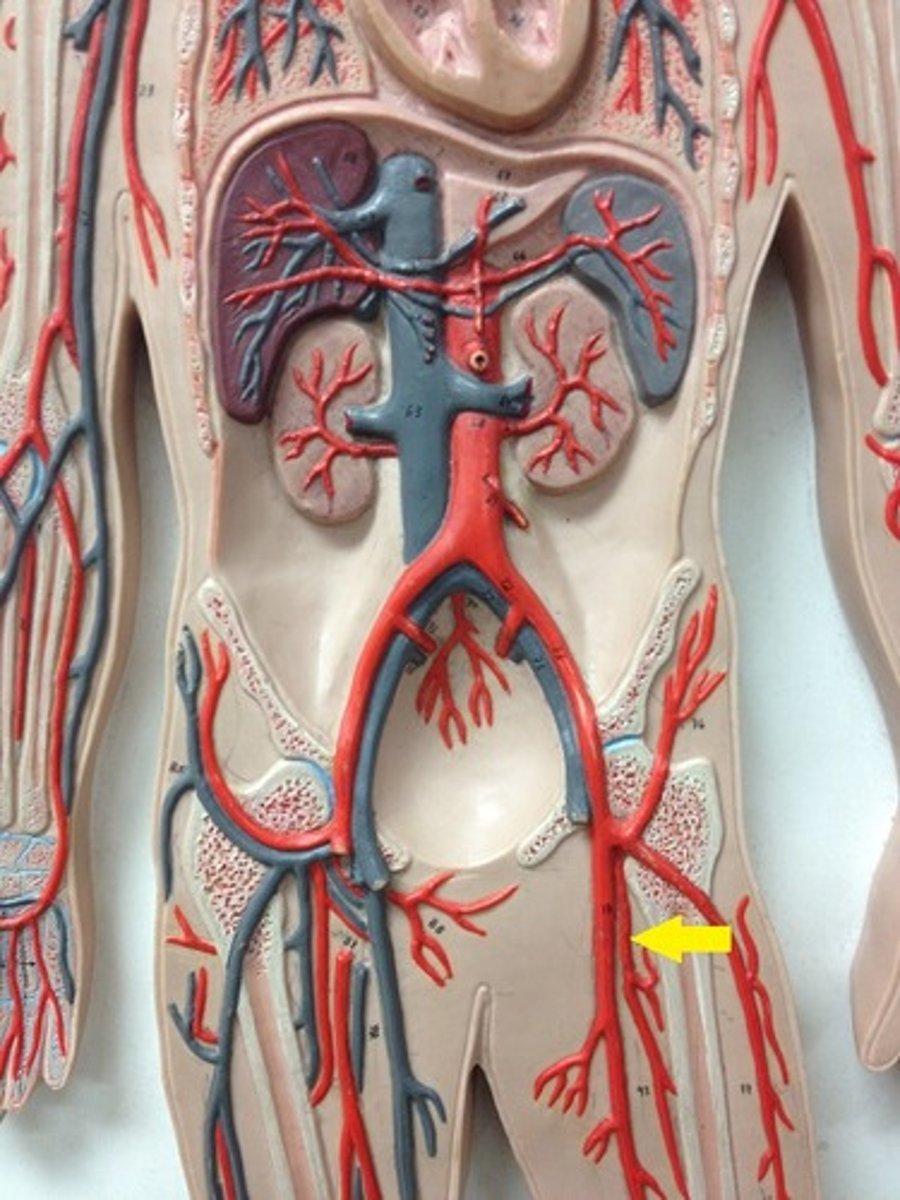
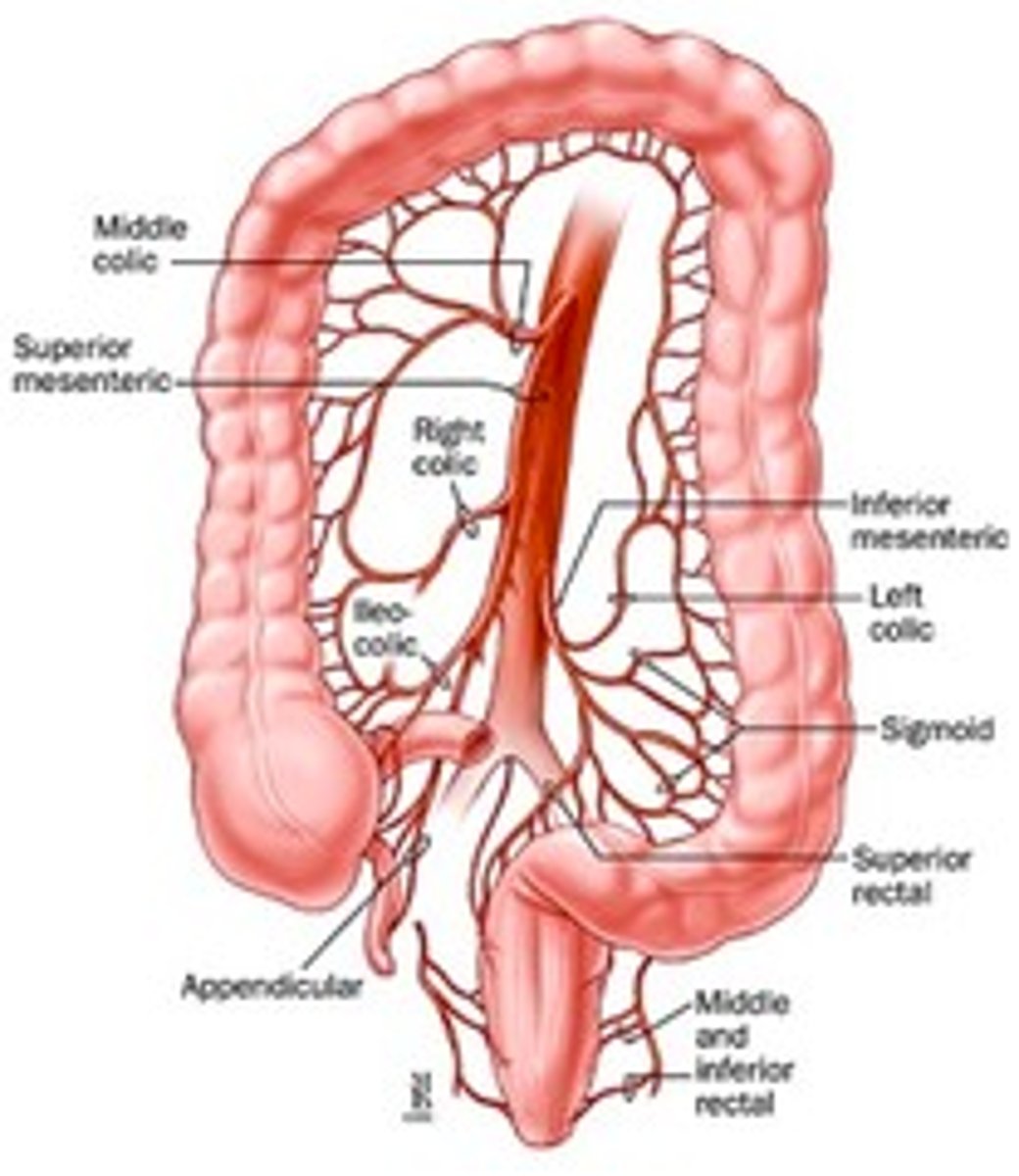
what branches off the abdominal aorta (unpaired) to supply blood to the abdominal region and what do they specifically supply?
Gives rise to three unpaired arteries:
- cephalic trunk: to liver, stomach, and spleen
- superior mesenteric artery: to small and large intestine
- inferior mesenteric artery: to second part of colon and rectum
what branches off the abdominal aorta (paired) to supply blood to the renal and repro. region?
branch off in pairs
- Gonadal arteries supply to the gonads
- renal arteries supply the kidneys
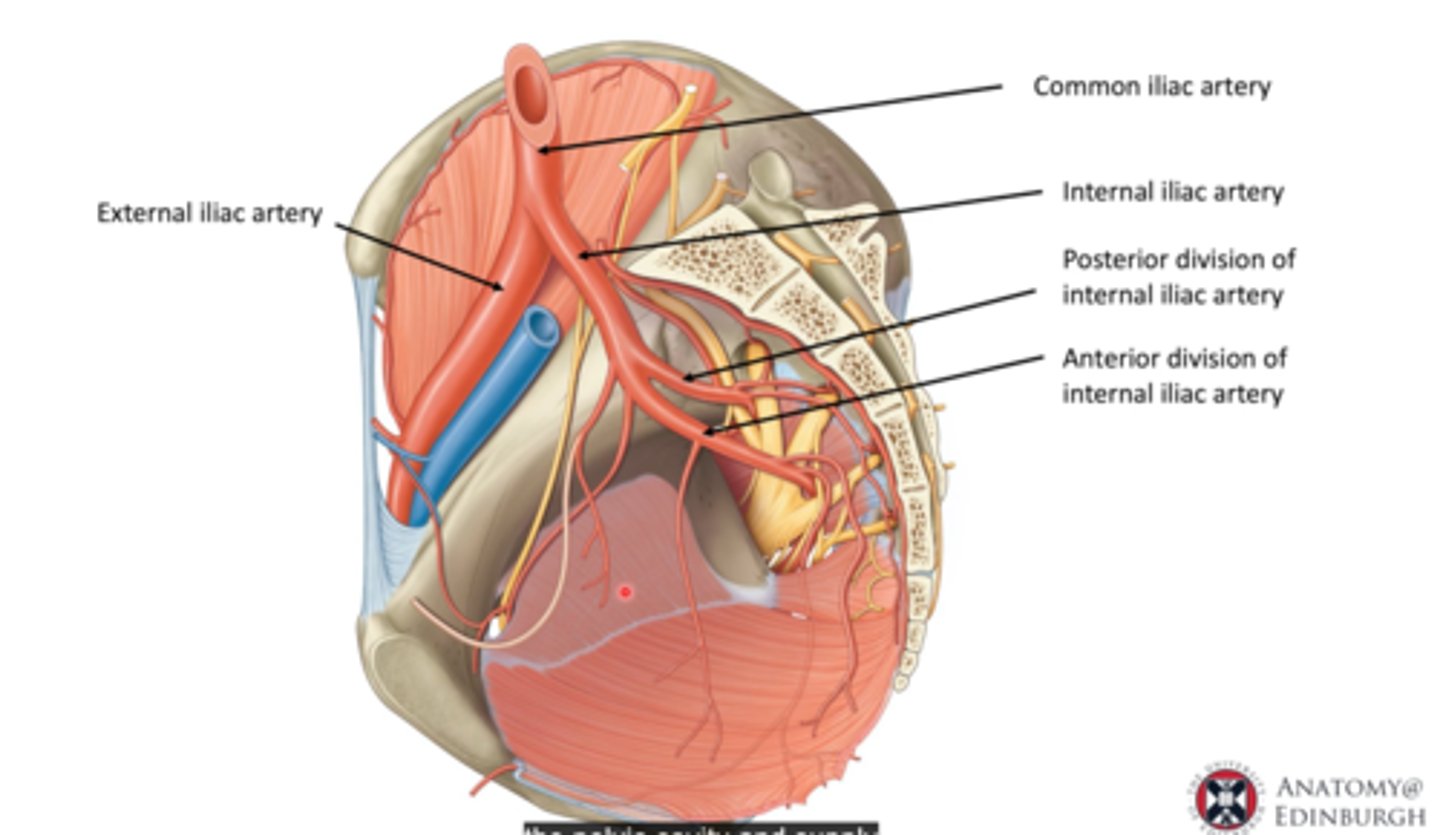
What does the internal iliac artery supply blood to?
supplies blood to:
- bladder
- uterus
- vagina
- rectum
- gluteal muscles via separate arteries that branch off
what arteries supply the gluteal region?
the internal iliac will give branches off called the superior and inferior gluteal arteries, running with the sup/inf. gluteal nerves
- named with respect to their placement around the piriformis muscle
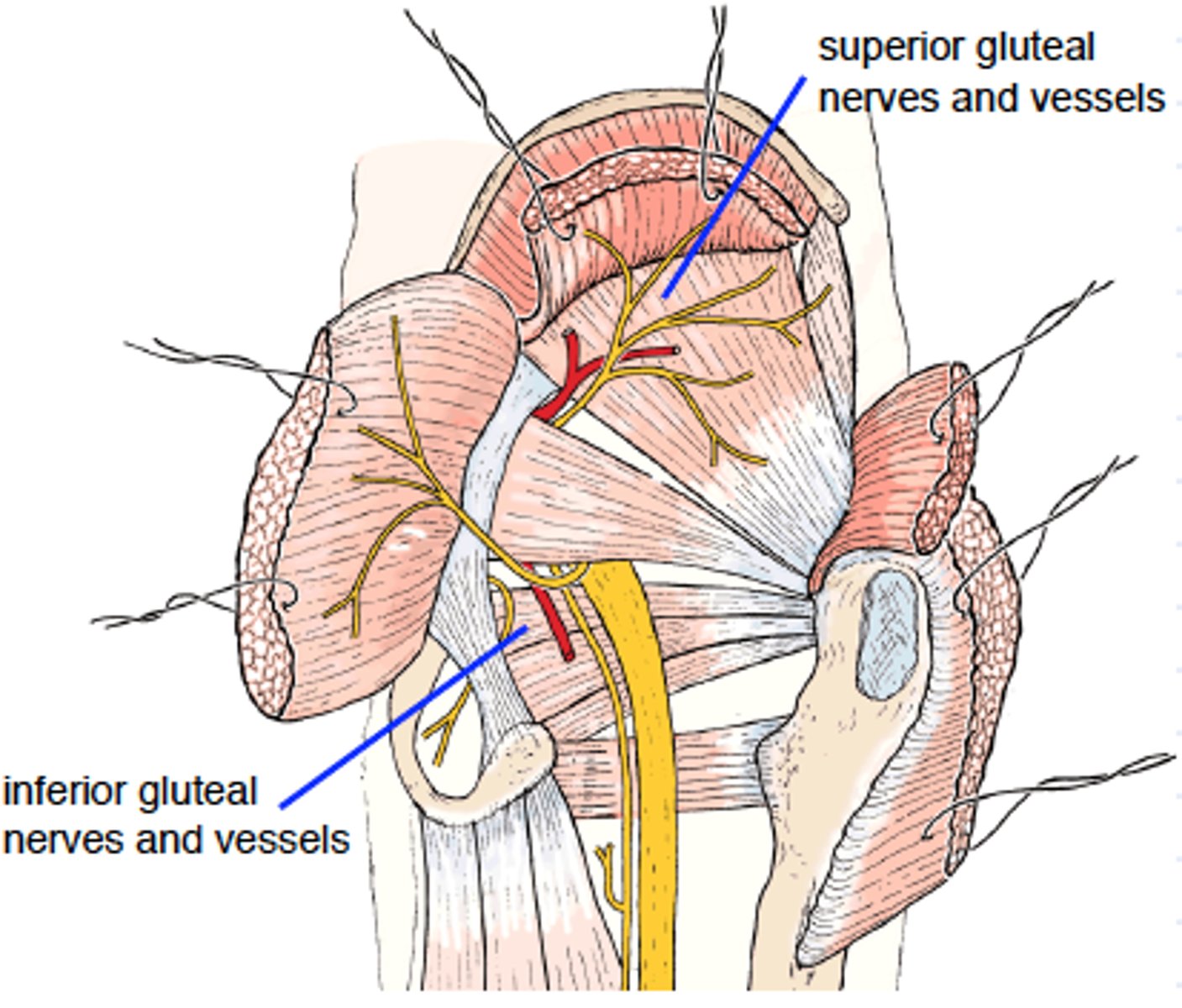
What muscles specifically do the superior and inferior gluteal arteries supply
- superior gluteal: glut. medius and tensor fascia latae
- inferior gluteal: glut. maximus
-- same as nerves