Electricity
1/38
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
identify common materials that are electrical conductors
copper, aluminium, silver and gold
identify common materials that are electrical insulators
rubber, plastic, glass, ceramic, and dry wood
how can insulating materials be charged by friction?
Two insulators are rubbed together
friction causes electrons to move from one to the other
Material that loses electrons becomes positively charged
material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged
magnitude of charge on each material is equal- they lose/gain the same number of electrons
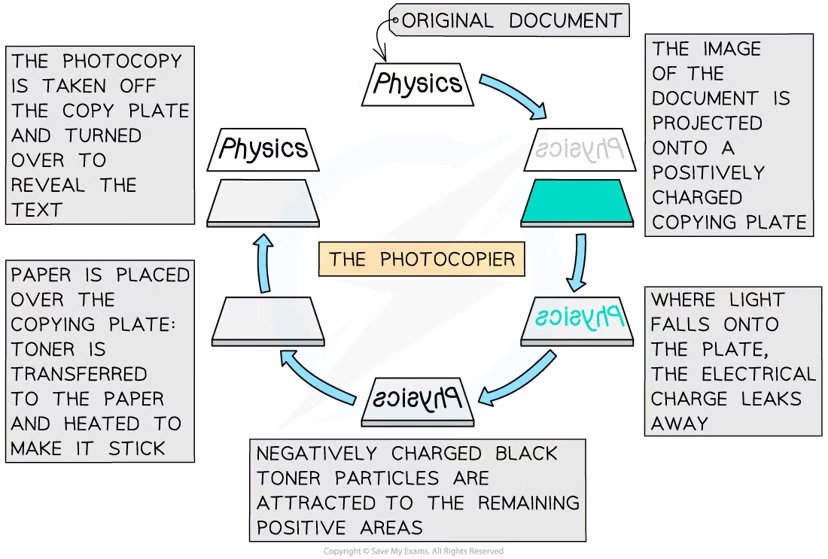
explain the uses of electrostatic charges in a photocopier
image of document is projected onto a positively charged plate
light falls onto the plate, the charge leaks away
negatively charged toner particles are attracted to the remaining positive areas
paper is placed over the plate, toner is transferred to it- making the photocopy
explain the uses of electrostatic charges in inkjet printers
droplets of ink are charged and pass betwen two charged metal plates
one has a positive charge and the other a negative charge
droplets are attracted to the plate with the opposite charge
and replled by the plate with the same charge
deflected towards a specific place on the paper
What are the potential dangers of electricity?
Damaged insulation
Overheating of cables
Electric shock

how does the use of insulation/double insulation protect the device/user
Insulation
—> rubber or plastic coating around wires prevents contact with live wires, stopping shocks.
Double Insulation
—> doesn’t need earth wire because outer casing is second layer of insulation, eliminating shock risk even if internal wires wear out.
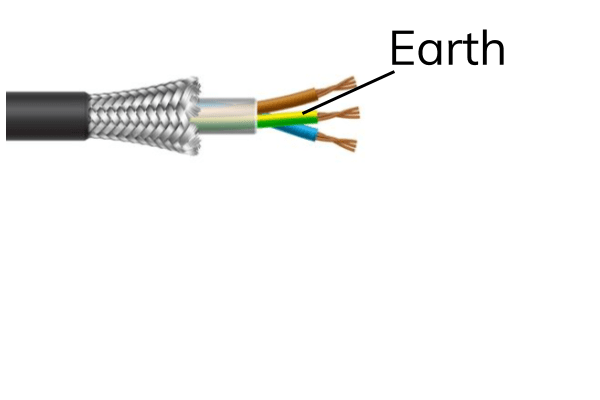
how does the use of earthing protect the device/user
Metal-case is connected to earth wire (green/yellow), if live wire touches case, current flows to earth and blows fuse
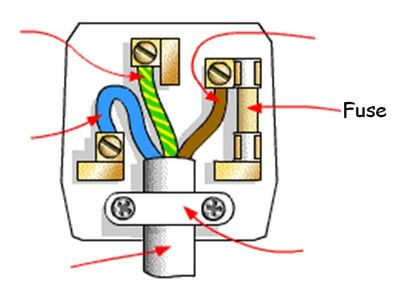
how does the use of fuses and circuit breakers protect the device/user
Contains thin wire that melts if current exceeds its rating, breaking the circuit
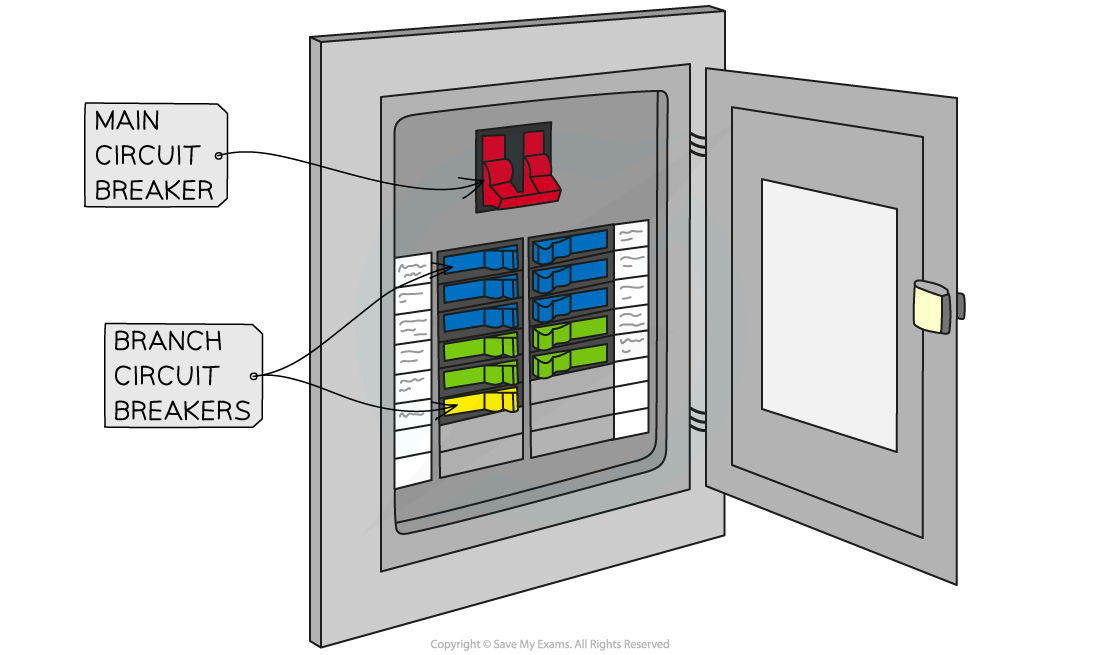
how does the use of circuit breakers protects the device/user
automatic switch that opens circuit when current is too high
why does a current in a resistor result in increase in temperature
Flowing electrons collide with metal ions, transferring kinetic energy into heat, causing resistor to warm
what is the difference between alternating current (a.c.) and direct current (d.c.)
Flow: AC flows back and forth; DC flows one way.
Voltage: AC voltage varies; DC voltage is steady.
why is a series/ parallel circuit more appropriate for particular applications
each device gets full voltage and works independently, meaning one bulb burning out doesn't affect others, unlike series circuits where a single break stops everything
how does the current in a series circuit depend on the applied voltage
the current is directly proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to total resistance, which increases with number and type of components
What is current?
Measured in amps (A)- the rate of flow of charge
What is potential difference?
Measured in volts (V)- work done per unit charge in moving between two points in a circuit
What is resistance?
Measured in ohms- the potential difference divided by the current
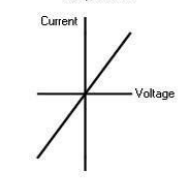
Resistor at a constant temperature
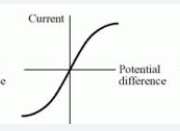
Current and voltage with a filament lamp
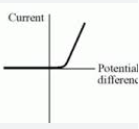
Current and voltage in a diode
Explain the resistor at a constant temperature graph
In an ohmic conductor (resistor at constant temperature) the current is directly proportional to the voltage
Explain the current and voltage with a filament lamp graph
temperature in the filament increases as the current does, which means electrons and ions vibrate and collide more, increasing resistance.
Explain the current and voltage in a diode graph
A diode only allows current to flow in one direction (forward bias)
in reverse direction, diode has very high resistance, and therefore no current flows (reverse bias)
what is electric current in solid metallic conductors?
a flow of negatively charged electrons
why is current conserved at a junction in a circuit
electrons can't be created or destroyed, so total current entering a junction must equal total flow leaving it
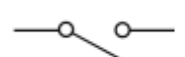
switch
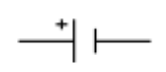
cell
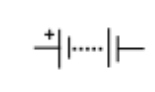
battery
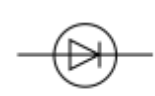
diode

resistor
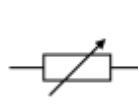
variable resistor

lamp
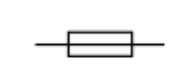
fuse
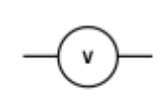
voltmeter
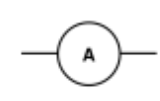
ammeter
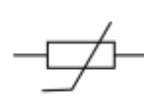
thermistor
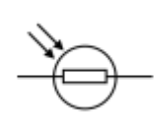
LDR- Light dependent resistor
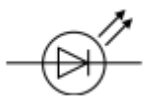
LED- Light emitting diode
function of live wire
carries the high alternating potential difference (240V) from the mains supply to the appliance, delivering the electrical power