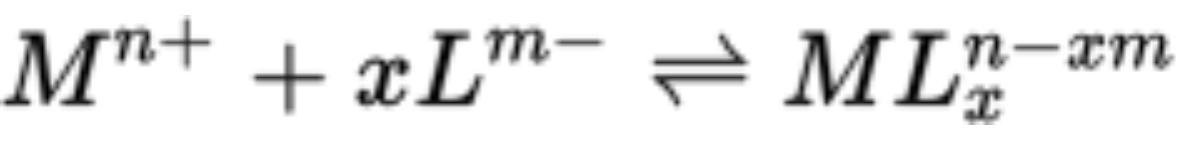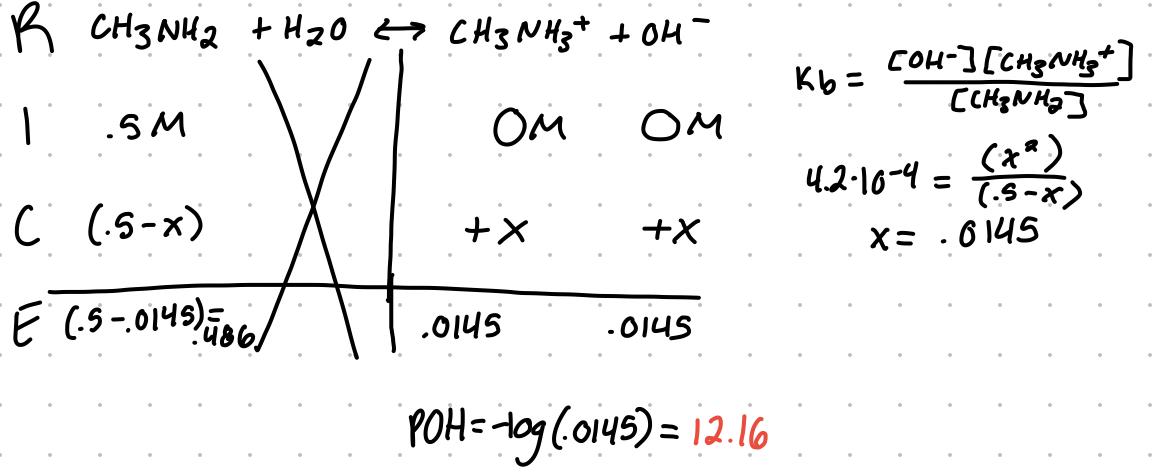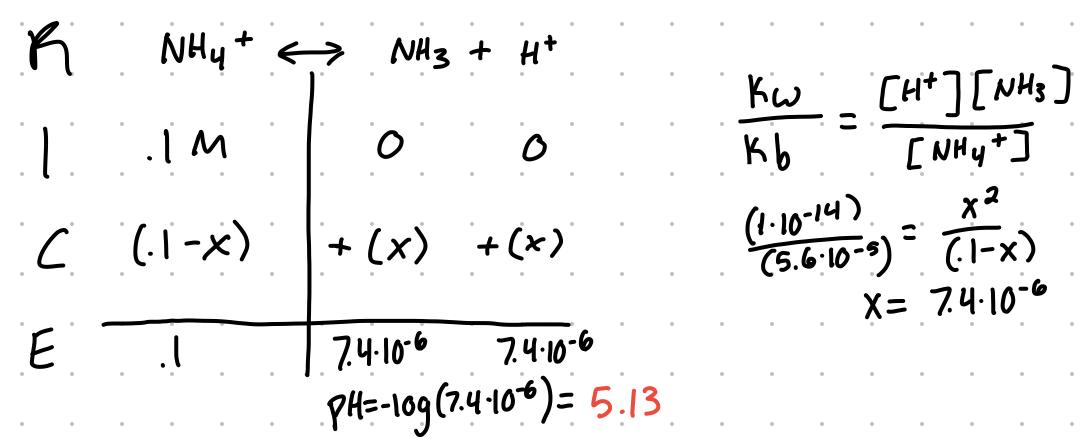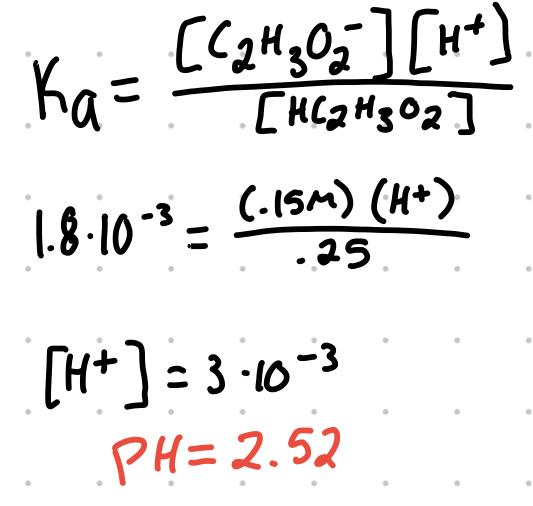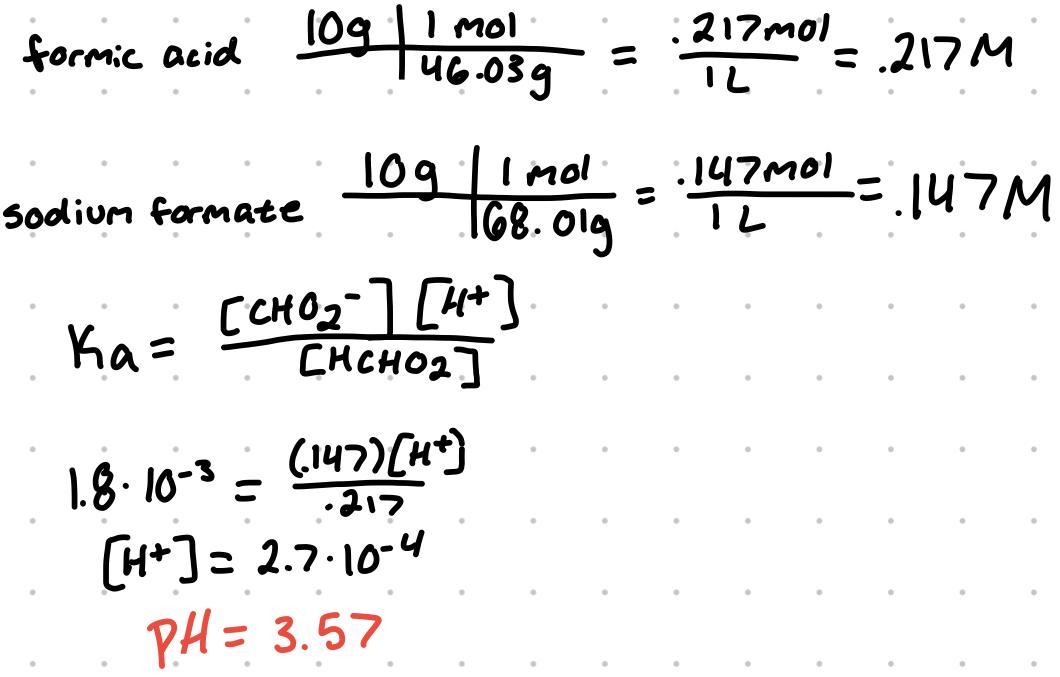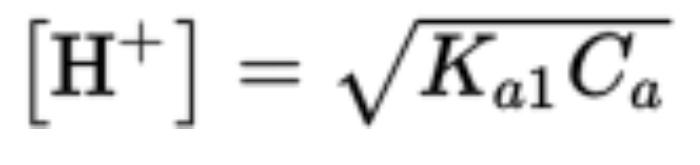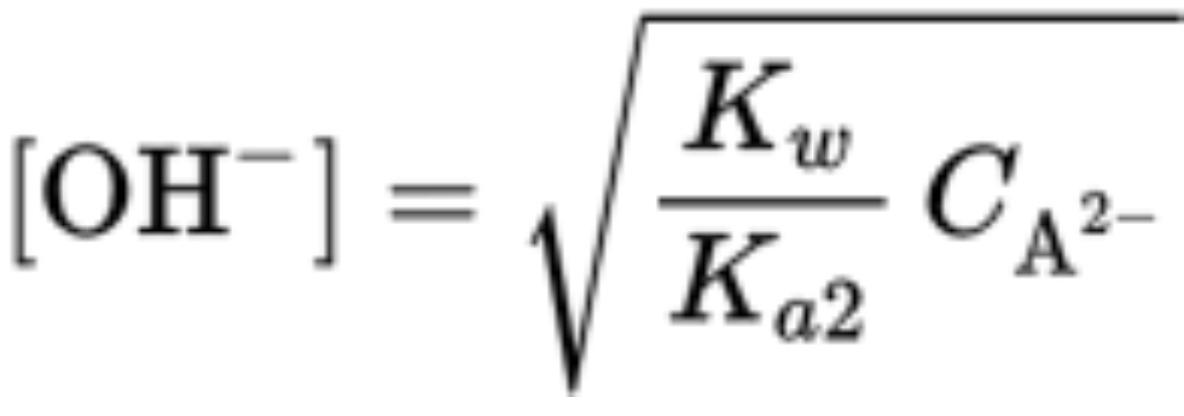Chapter 13: Acids and Bases
Acid-Base Theories
- Arrhenius Theory
- An acid adds hydrogen ions to a solution, and a base add hydroxide ions to a solution
- Bronsted-Lowry
- An acid is a proton donor, and a base is a proton acceptor
Arrhenius Theory
- An acid is any substance that increases hydrogen ion concentration in an aqueous solution.
- HCl (aq) → H3O+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
- However, hydrogen ions are unlikely to be in aqueous solutions and are often bound to one or more water molecules
- Such as H3O+
- Bases are anything that can donate hydroxide ions
- KOH (s) → K+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
Bronsted-Lowry Theory
- When NH3 is dissolved in water, it increases the hydroxide concentration. This forced NH3 to be called NH4OH to fit the Arrhenius definition of bases, but NH4OH doesn’t actually exist. However, following the Bronsted-Lowry definition, NH3 could be a base.
Modern Concept of Acids
- Any compound having one or more hydrogen atoms that are weakly bonded to the rest of the molecule
Acid-Base Nomenclature
- Binary acids have a hydrogen and one other atom
- starts with hydro- and ends with -ic.
- hydrofluoric acid (HF), hydrochloric acid (HCl), hydrobromic (HBr), hydroiodic (HI), hydrosulfuric (H2S)
- Polyatomic anions can be the anion of acids.
- if the polyatomic anion ends with -ate, it’s changed to -ic.
- if it ends in -ite, it’s changed to -ous
- sulfate (sulfuric acid, H2SO4), sulfite (sulfurous acid, H2SO3), chlorite (chlorous acid, HClO2)
- Organic acids have a common name and a systematic name
- systematic: ends in -oic acid
| systematic name | common name | formula |
|---|---|---|
| methanoic acid | formic acid | HCOOH |
| ethanoic acid | acetic acid | CH3COOH |
| propanoic acid | propanoic acid | CH3CH2COOH |
| butanoic acid | butyric acid | CH3CH2COOH |
- Hydroxide bases are named by the metal type and hydroxide
- NaOH is sodium hydroxide, Fe(OH)3 is iron (iii) hydroxide
- Nitrogen bases related to ammonia are amines
Acids
Strong Acids
- Strong acids ionize completely in water
| acid | ionization reaction |
|---|---|
| hydrochloric acid | HCl → H+ + Cl- |
| hydrobromic acid | HBr → H+ + Br- |
| hydroiodic | HI → H+ + I- |
| perchloric acid | HClO4 → H+ +ClO4- |
| nitric acid | HNO3 → H+ + NO3- |
| sulfuric acid | H2SO4 → H+ + HSO4- |
- Sulfuric acid is only considered strong with the first hydrogen dissociation, the second is only slight
- These strong acids are sometimes called mineral acids
Weak Acids
- Any acid other than the ones listed above are weak acids that only ionize slightly
- Most weak acids are organic
Acid Strength
Electronegativity and bond strength can be used to compare acid strength
A weakly bonded hydrogen = strong acid. Strongly bonded hydrogen = weak acid
Binary acids get stronger when moving left to right on periodic table
- PH3 is weaker than H2S.
- H2S is weaker than HBr
Binary acid strength increases from top to bottom
- HF is weaker than HCl
- HCl is weaker than HBr
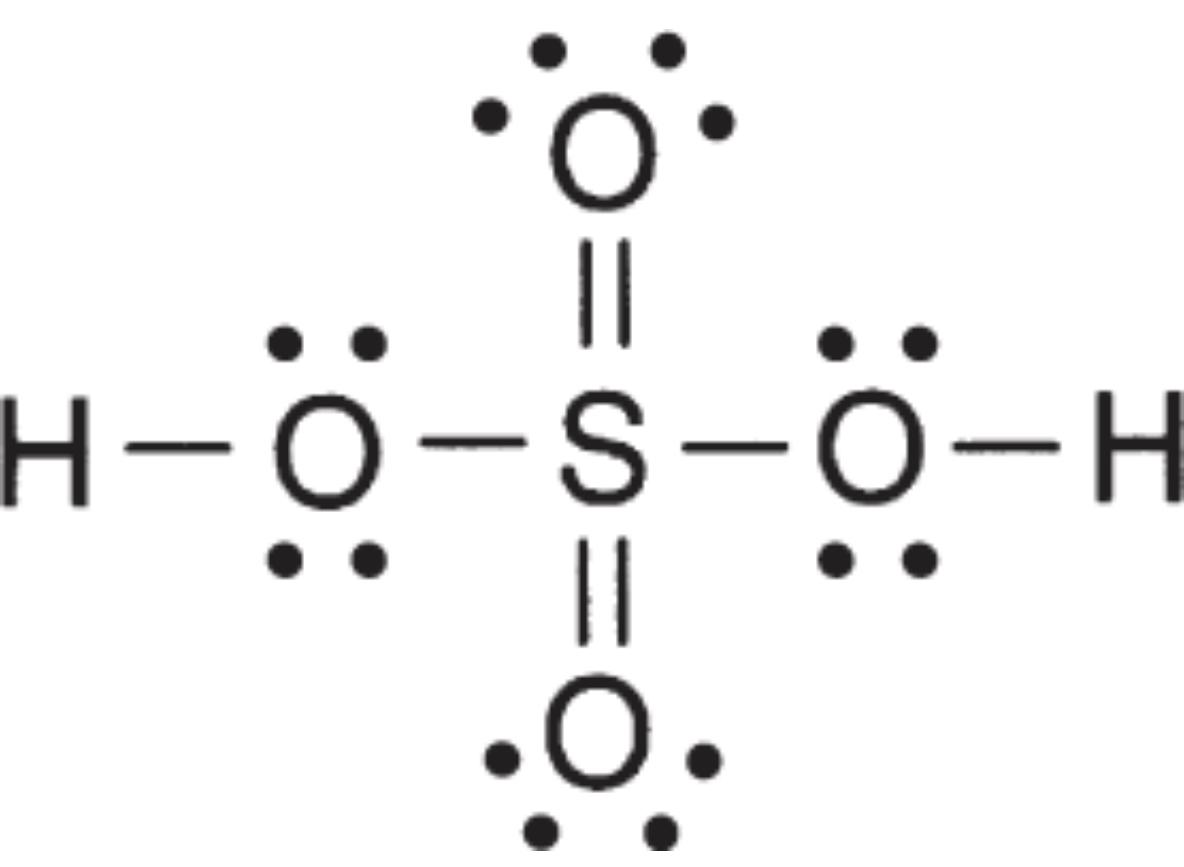
Mineral acids that are not binary are called oxacids: acids that contain hydrogen, oxygen, and another element
Oxygen is bound to central atom and hydrogen is bound to oxygen.
sulfuric acid is an oxacid
Strength of oxacids depends on oxygen-hydrogen bond:
- the number of oxygen atoms per hydrogen in formula
- if the central atom is the same and the number of hydrogens remains unchanged, as the number of oxygens increases, the strength of the acid increases
- electronegativity of central atom
Bases
Strong Bases
- All metal hydroxides are strong bases but most are only slightly soluble
- Group IA metals, strontium, and barium have appreciable solubility
Weak Bases
- All ammonia bases are weak bases.
- Ethylamine and dimethlyamine, for example
Base Strengths
- Stronger bonds means a weak bases
- chloromethylamine is weaker than methylamine
Anhydrides of Acids and Bases
- Anhydride means “without water”
- acidic and basic anhydrides are compounds that become common acids and bases when added to water
- Acid anhydrides are often oxides of nonmetals
- Common acid anhydrides:
- SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
- SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
- CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
- P2O5 + 3 H2O → 2 H3PO4
- Basic anhydrides are the oxides of metals
- Common basic anhydrides
- K2O + H2O → 2KOH
- CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
Neutralization Reaction
- Reaction between acid and bases are called neutralization reactions. Often double-replacement that produces salt and water
- HBr (aq) + KOH (aq) → KBr (aq) + H2O (l)
- HBr is the acid. KOH is the base. KBr is a salt.
- Can be written as a molecular, ionic, or net ionic equation
- HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O (molecular equation)
- H+ + Cl- + Na+ + OH- → Na+ + Cl- + H2O (ionic equation)
- H+ + OH- → H2O (net ionic equation)
Polyprotic Acids
- Polyprotic acids can ionize more than once
- Such as H2SO4 and H3PO4
- Ethanoic, HC2H3O2, is not polyprotic despite having 4 hydrogens. Only one can ionize
- All polyprotic acids are weak except for sulfuric.
- Polyprotic acids ionize in a stepwise manner: the first hydrogen reacts before the second
- H3PO4 ⇆ H2PO4- + H+
- H2PO4- ⇆ HPO4(2-) + H+
- HPO4(2-) ⇆ PO4(3-) + H+
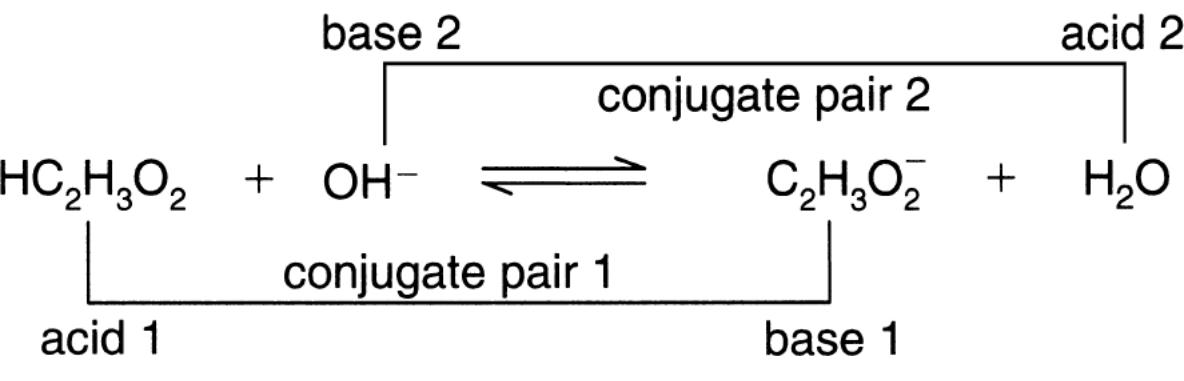
Bronsted-Lowry Theory; Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Bronsted-Lowry Theory came up with the concept of conjugate acid-base pairs
Conjugate acid-base pairs always have formulas that differ by only one H+
Relative Strengths of Conjugate Acids and Bases
- If an acid is weak, it’s conjugate base will be strong
- If an acid is strong, it’s conjugate base will be weak
- HC2H3O3 ⇆ C2H3O2- + H+
- Ethanoic acid is weak, so it’s conjugate base is strong
- NH4+ ⇆ NH3 + H+
- NH4 is a strong acid, so NH3, the conjugate base, will be weak
Amphiprotic and Amphoteric Substances
- Amphiprotic substance can both gain and lose protons
- Amphoteric substance can act as an acid and a base
- Water is an extremely weak acid and extremely weak base
Complexation Reactions
- Complexation reactions occur because of the formation of a coordinate covalent bond
- AgCl is an insoluble salt but can dissolve in ammonia solutions
- AgCl (s) + 2 NH3 → Ag(NH3)2+ + Cl-
Ligands
Ligands, complexing agents, chelates, and sequestering agents are all names that donate pairs of electrons
Most ligands have one pair of electrons to donate but can have two, or even up to six pairs
Complex reactions are written as:
Where M^n+ is a metal ion with a charge of +n and L^m- is a ligand with a charge of -m
number of electron pairs that a metal ion will typically accept is called the coordination number
| ion | C.N. |
|---|---|
| Ag+ | 2 |
| Au3+ | 4 |
| Cu2+ | 4 |
| Zn2+ | 4 |
| Pt2+ | 4 |
| Fe2+, Fe3+ | 6 |
| Co3+ | 6 |
| Ti4+ | 6 |
| Mn2+ | 6 |
| Cr3+ | 6 |
- The total charge of any complex ion is the sum of the charges
- For FeCl6(3-) there is 1 3+ charge and 6 -1 charges, adding up to -3
Coordinate Covalent Bonds
- Instead of each atom donating one electron, each atom donates both electrons.
- Covalent bond formed this way are coordinate covalent bonds
Quantitative Acid-Base Chemistry
- Acid strength and base strength can be described using their dissociation constants: Ka and Kb
pH and pOH: Measurements of Acidity and Basicity
- Acidity is determined by [H+] or pH
- pH = -log[H+]
- Basicity is determined by [OH-] or pOH
- pOH = -log[OH-]
- Water dissociated into OH- and H+, so the [OH-] and [H+] multiplied equals the water dissociation constant, or the autoionization constant of water (Kw)
- [H+][OH-] = Kw
- [H+[OH-] = 1.0x10^-14
- the -log equals the same
- pKw = pH + pOH =14
pH of Neutral Solutions
- As temperature changes, so does pH values
- only at 25 celsius does Kw = 1x10^-14
[H+] and pH of Strong Acids
- The hydrogen ion concentration of a strong acid is equal to the molar concentration of the acid itself
[OH-], pOH, and pH of Strong Bases
- [OH-] = M x number of OH- ions per mole
- M of strong base
pH of Weak Acids and Weak Bases
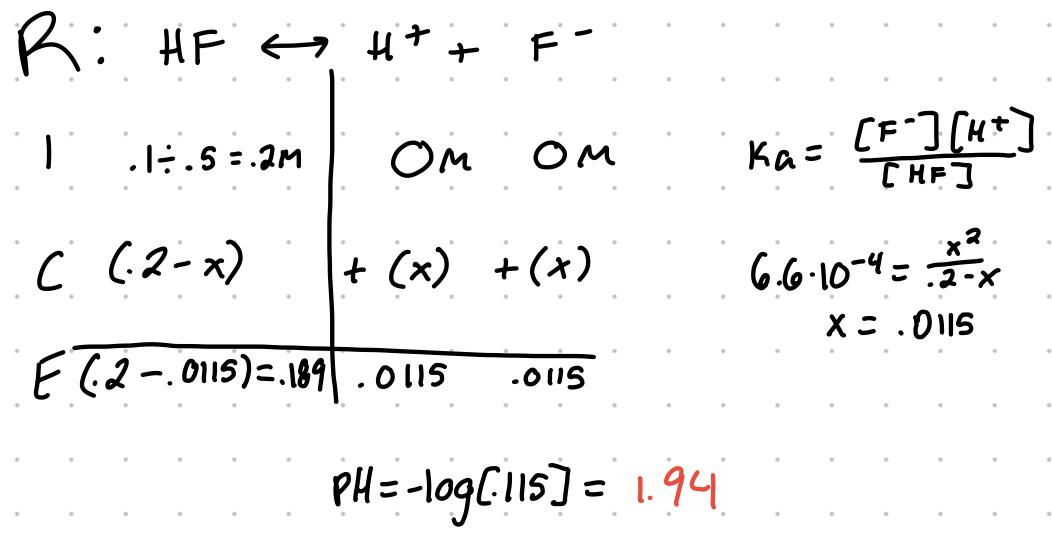
for the equation HF ⇆ H+ + F- the Ka can be written as Ka = [H+][F-]/[HF]
Ka is the acid dissociation constant
Example
If .1mol HF is diluted in 500mL of water, what’s the pH where the Ka = 6.6x10^-4?
For the equation CH3NH3 + H2O ⇆ CH3NH3+ +OH- the Kb = [CH3NH3+][OH-]/[CH3NH2]
Kb is the base dissociation constant
Example
What’s the pOH of a .5M solution of methylamine, Kb = 4.2x10^-4?
pH of Salt Solution; Hydrolysis Reactions
- When an acid is neutralized with a base, a salt is formed. If the anion of that salt is the conjugate base of a weak acid, it will react with water in a hydrolysis reaction
- F- + H2O ⇆ HF + OH-
- If the cation of the salt is the conjugate acid of a weak base, the hydrolysis reaction witll resulte in an acid solution
- NH4+ + H2O ⇆ NH3 + H3O+
Acidity of Salt Solutions and Classification of Salts
- Cation of salt will be the conjugate acid of a strong or weak base
- Anion of a salt will be conjugate base of a strong or weak acid
- Finding pH of salt solution is first done by determining type of salt by adding H+ to anion and OH- to cation in the salt
- For ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), the cation NH4 will bond with OH- to get NH4OH, and the anion Cl will bond with the H+ to get HCl.
- Since NH4OH is a weak base and the HCl is a strong acid, the resulting solution will be more acidic than basic
pH of Salt Solution
Kw = (Ka)(Kb)
Example
What’s the pH of a .1M solution of ammonium chloride?
Buffer Solutions
Buffer solutions are made using a weak acid or weak base and the salt of that weak acid or base
Buffer solutions withstand pH changes when a small amount of strong acid or base is added
Example: find pH of the buffer solutions:
.25M ethanoic acid and .15M sodium ethanoate
a solution with 10g formic acid and sodium formate in 1L H2O
Preparations of Buffers
- Decide what pH is required
- decide final volume required
- choose appropriate conjugated acid-base system based on the required pH
- determine moles per liter the reaction will generate
- the sum of concentration of conjugate acid and conjugate base should be twenty times the values estimated in step 4
- based on steps 1, 3, and 5 calculate the separate concentrations of conjugate acid and base needed
- use steps 2 and 6 to determine masses of conjugate acid and base to use
- measure out amounts determine in step 7, dissolve in distilled water, and dilute to volume determined in step 2
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- pH = pKa + log ([A-] /[HA])
- the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation also works for weak bases
pH Values of Polyprotic Acids and Their Salts
Each dissociation constant of polyprotic acids is smaller than the one before it
Ka1 is the first dissociation constant
Ca is initial constant of polyprotic acid
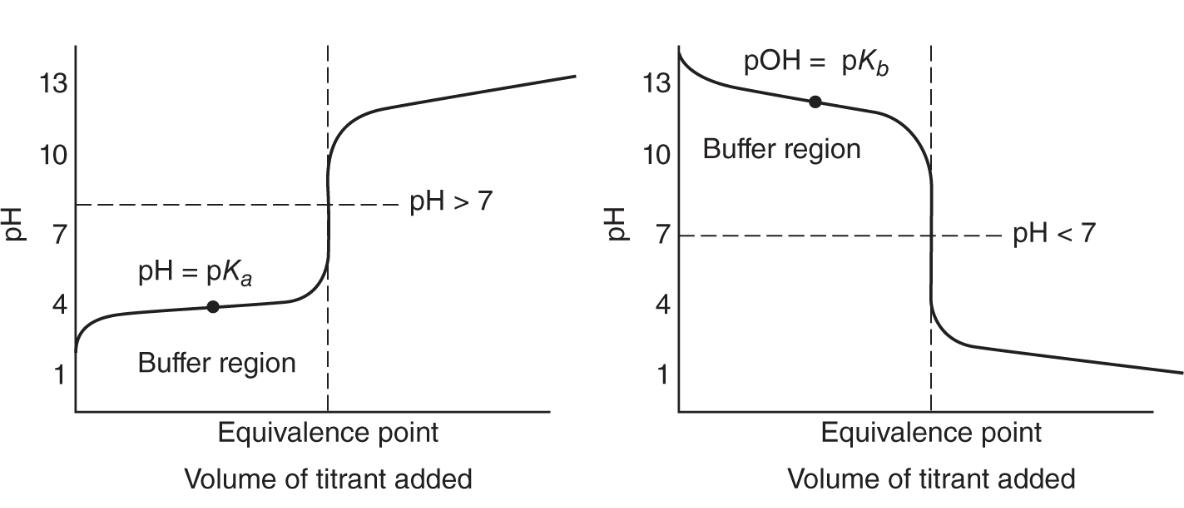
Titration Curves
Four major points of titrations:
- Start of titration where there's only one acid or base
- region where titrant is added up to the equivalence point and the solution now contains a mixture of unreacted sample and products
- equivalence point, where all reactant is products
- region after equivalence point where solution constants product and excess titrant
End point is the experimentally determines end of a titration
Equivalence point is the theoretical or calculated end of a titration
A plot of pH versus volume of titrant is called titration curve
Polyprotic acids have more than one equivalence points because of the dissociation steps
Buffer solution titration curve: (left is weak acid and strong base) (right is weak base with strong acid)
pH Indicators
- Indicators are weak acids and weak bases with the conjugate being a different color