Genetic Engineering
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 14: Monday, November 24th: Genetic Engineering; Plasmids; Operon Preview
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
_______ is artificial DNA from recombined genetic information from host cells in different kindgoms/domains via transformation
recombinant DNA (rDNA)
bioinformatics via NCI allows you to find _______ and a _______ for genetic engineering
gene of interest, model organisms
with the gene of interest, you can use _______ to see what it does, remove it using _______, then add it into a vector using _______
knock-down, knock-out, knock-in
a plasmid/virus that carries the inserted gene and markers (contruct) is called a _______
vector
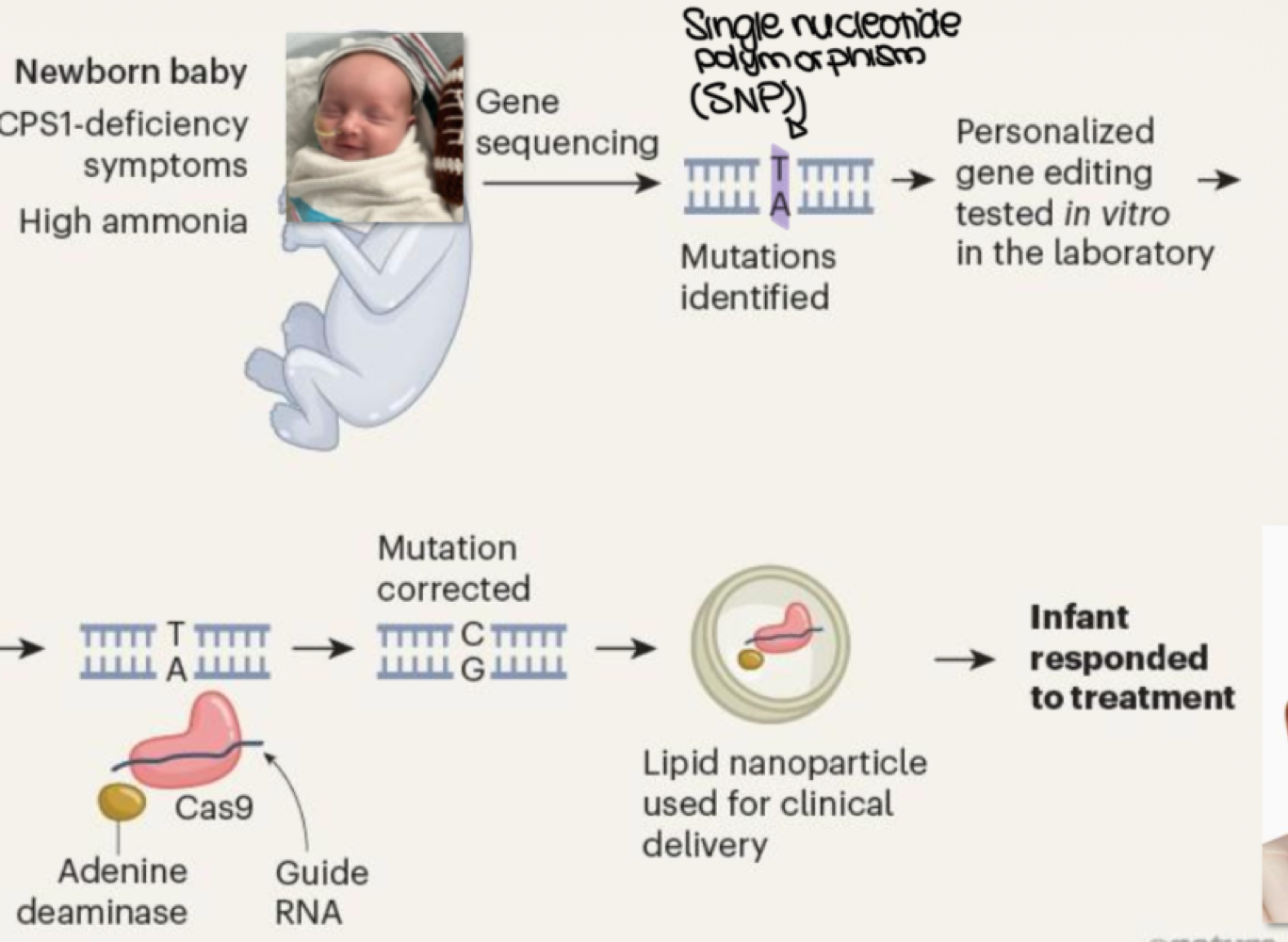
CRISPR does single-base editing to correct _______
single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP)
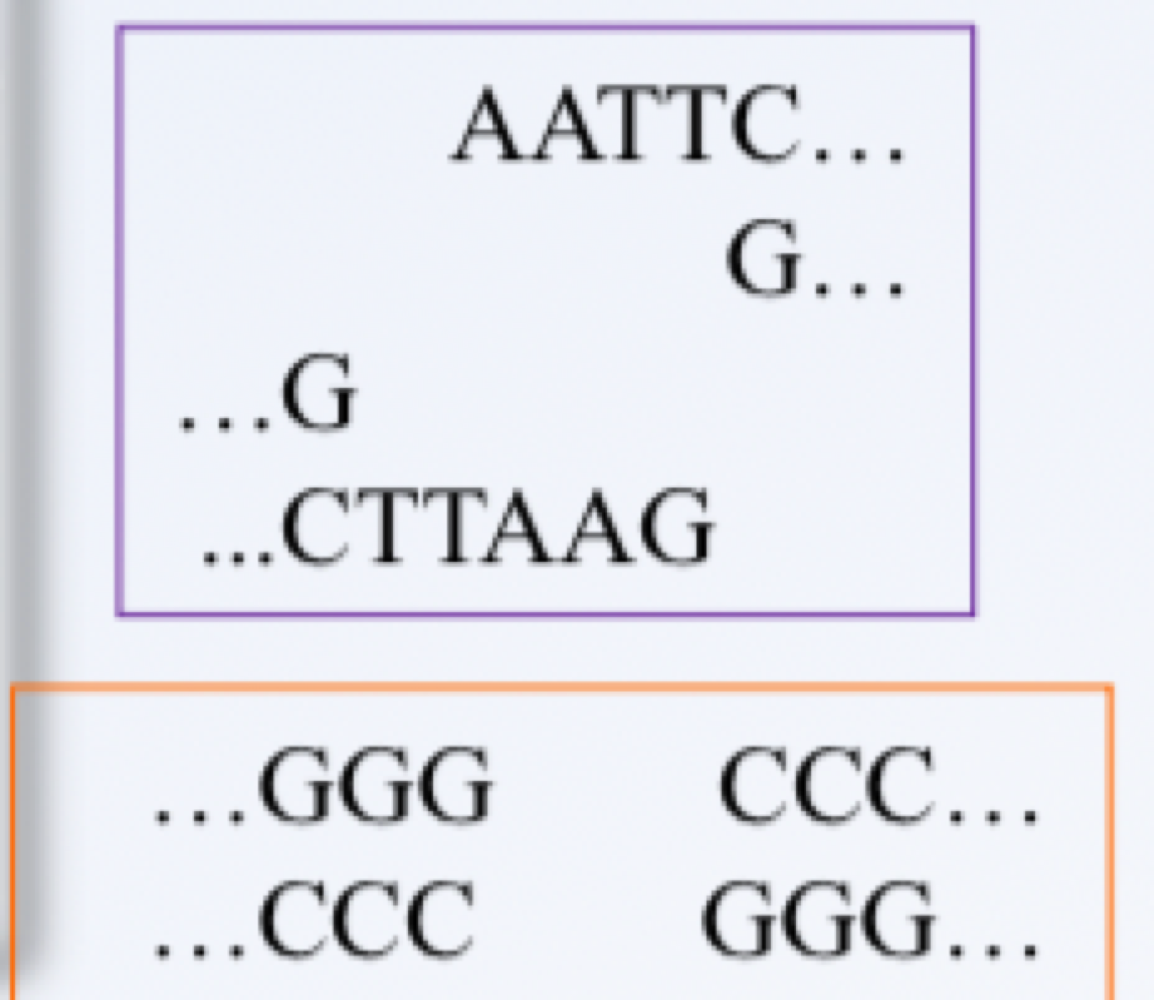
bacteria secrete _______ that recognize the restriction site (specific motifs)
restriction enzymes
why does bacteria methylate its own version of the restriction site?
so that the restriction enzyme will bind to the foreign virus’s sequence, which is unmethylated
_______ is a type 2 endonuclease cut that produces _______, whereas a _______ produces a _______
sticky ends, 3’ overhang, blunt cuts, cleaved ssDNA
the first step of forming a recombinant DNA molecule is _______, during which you grind the donor samples in liquid N2 to free the DNA by lysing the cell
lysis
the second step of forming a recombinant DNA molecule is _______, during which you use sodium and alcohol to precipitate the DNA
precipitation
the third step of forming a recombinant DNA molecule is _______, during which you use ethanol to wash away everything else
purification
_______ is the proces of moving a transgene into a plasmid
cloning
_______ is the process of replicating the transformed plasmid inde the competent bacteria
subcloning
what do you need to do when moving a eukaryotic gene into a plasmid?
reverse transcribe it into CDS
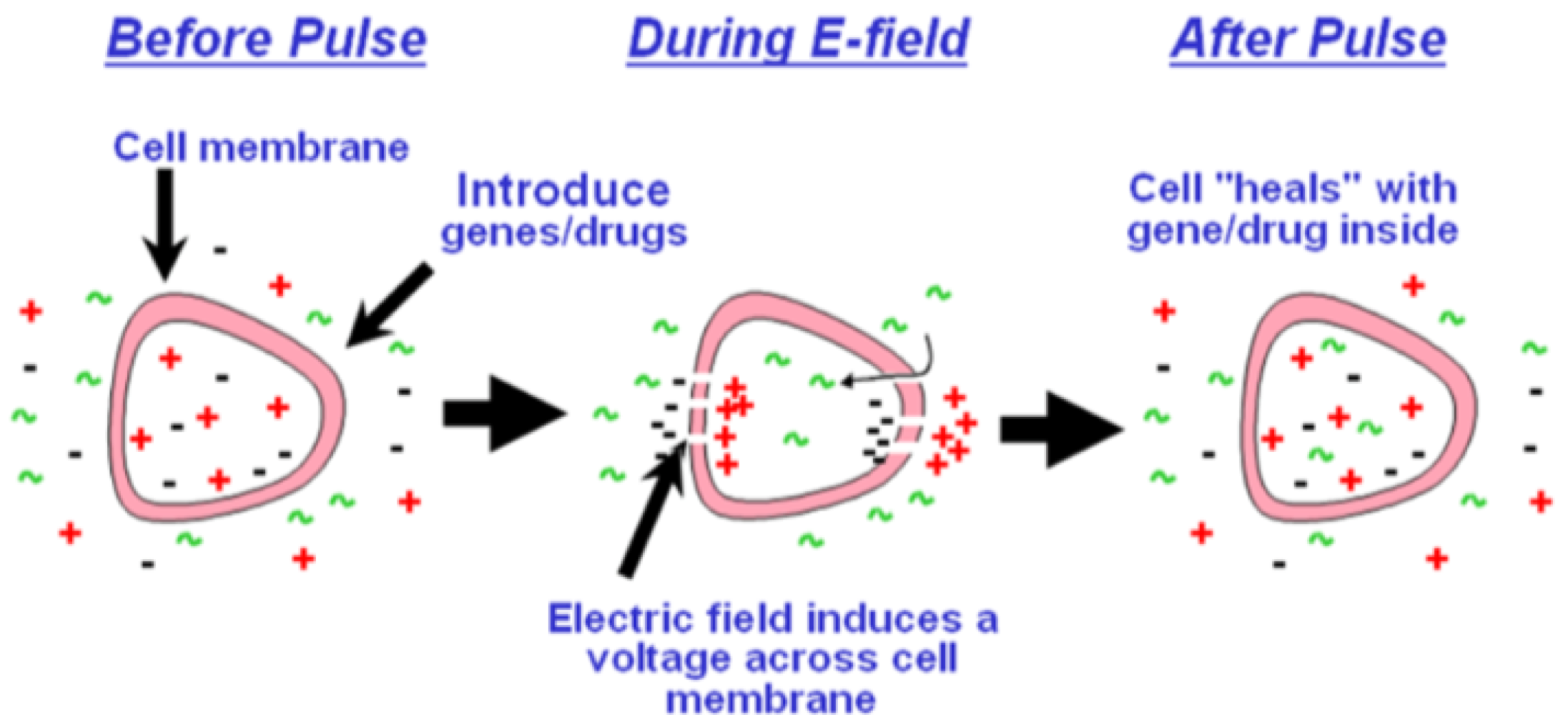
what are three ways to sub clone the transfected plasmid once its in the competent bacteria?
heat, chemicals (calcium chloride), electrophoresis
what does the plasmid need to place the gene?
ORI, promoters, markers, multiple replication sites (MCS)
if youre moving up to 15kb into a plasmid, you should use _______ as vectors
phages
if you’re moving 35-45kb into a plasmid, you should use _______ as vectors
fosmids (lambda phages)
if you’re moving 100-350 kb into a plasmid, you should use _______ as vectors
BACs (bacterial artificial chromsome)
_______ PCR starts at high temperatures to avoid incorrect primer binding
Hot start
_______ PCR makes cDNA with reverse transcriptase of mRNA to make dsDNA/RNA (measures a specific gene)
reverse-transcriptase (RT-PCR)
_______ PCR reverse transcribes all transcripts at specific times to quantify how much is being expressed and when (measures all expressed jeans)
real-time quantitative (RT-qPCR)
_______ are next gen PCR sequencing that produces short reads is cheaper, whereas _______ makes longer reads
2nd gen, 3rd gen
_______ is a 2nd gen PCR technique that is best for difficut sequences
Illumina

_______ is a 3rd gen PCR technique that produces the best reads, allowing telomere-to-telomere sequencing to make circularized DNA
HiFi Pac Bio
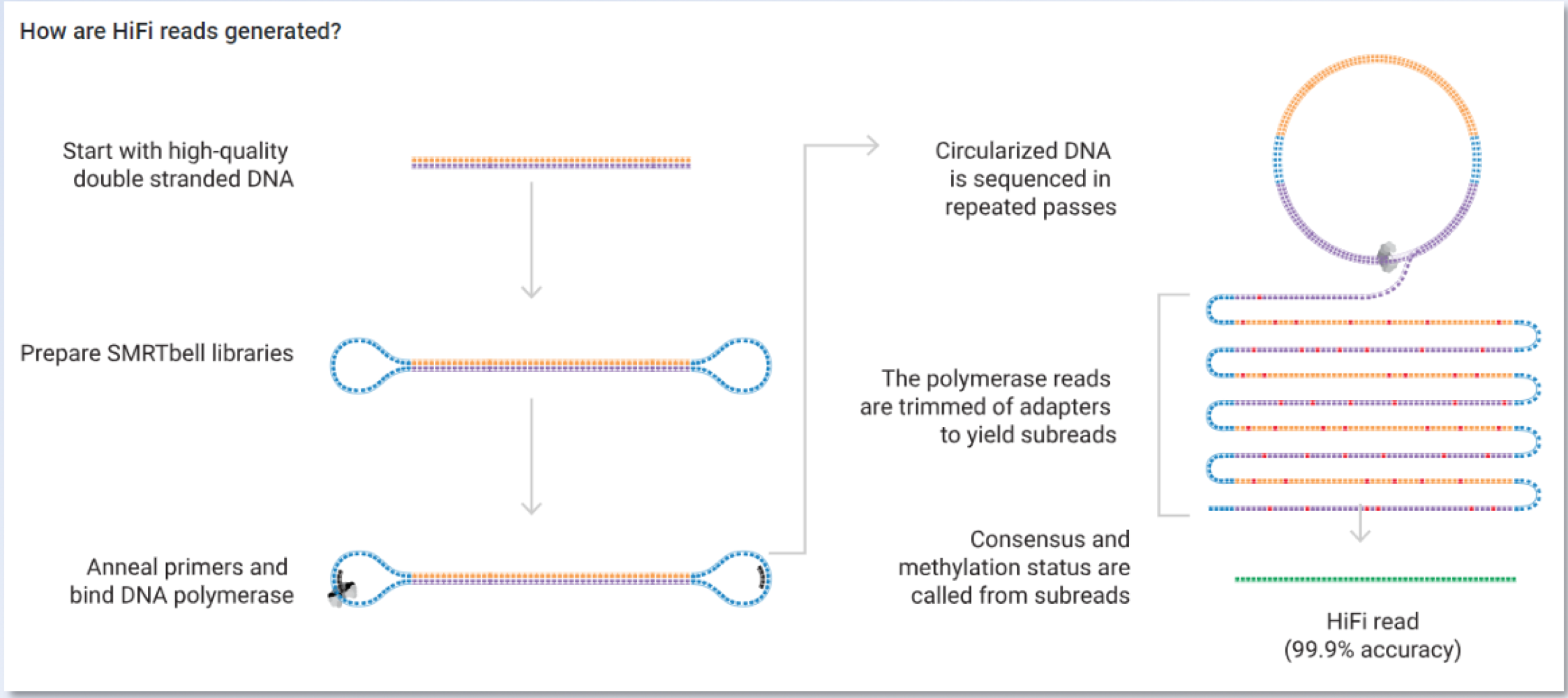
_______ is a 3rd gen PCR technique that requires less prep and reads bases quikcly because amplification and sequencing aren’t needed
Nanopore