Rad Path: Hematopoietic System
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
red bone marrow
primary site of hematopoiesis
precursor cells
stem cells or young cells
RBC
WBC
platelets
erythrocytes
are biconcave disks without a nucleus that contain hemoglobin, an iron-based protein that carries oxygen from the respiratory tract to the body’s tissues.
red bone marrow and lymphoid tissue
where is leukocyte produced?
4.5 - 6 million cubic mm of blood
how many red blood cells are in there?
120 days then broken down by spleen and liver
what is the lifespan of erythrocytes?
5,000 to 10,000 millimeters cubic of blood
how many white blood cells are in the blood?
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophil
lymphocytes
monocyte
Types of leukocytes
neutrophils
most abundant type of WBC that is responsible for phagocytosis.
eosinophils
are red-staining cells whose number greatly increases in allergic and parasitic conditions.
basophils
contains granules that stain blue involved in inflammatory process
lymphocytes
They play a major role in the immune system and aid in the synthesis of antibodies and the production of immunoglobulins.
monocyte
is actively phagocytic and plays an important role in the inflammatory process
platelets
the smallest blood cells, are essential for blood clotting
150,000 to 400,000 every cubic millimeter of blood.
how many platelets in blood?
7 to 10 days
how long does platelets stay in the system?
anemia
refers to a decrease in the amount of oxygen-carrying hemoglobin in the peripheral blood.
decrease
A ______ in the oxygen-carrying hemoglobin impairs the delivery of an adequate oxygen supply to the cells and tissues, leading to fatigue and muscular weakness and often to shortness of breath on exertion (dyspnea).
iron deficiency
most common cause of anemia
hemolytic anemia
The underlying abnormality in hemolytic anemia is a shortened life span of the red blood cells with resulting hemolysis and the release of hemoglobin into the plasma.
Spherocytosis
sickle cell anemia
thalassemia
the major hereditary hemolytic anemias.
Spherocytosis
the erythrocytes have a circular rather than a biconcave shape,
making them fragile and susceptible to rupture
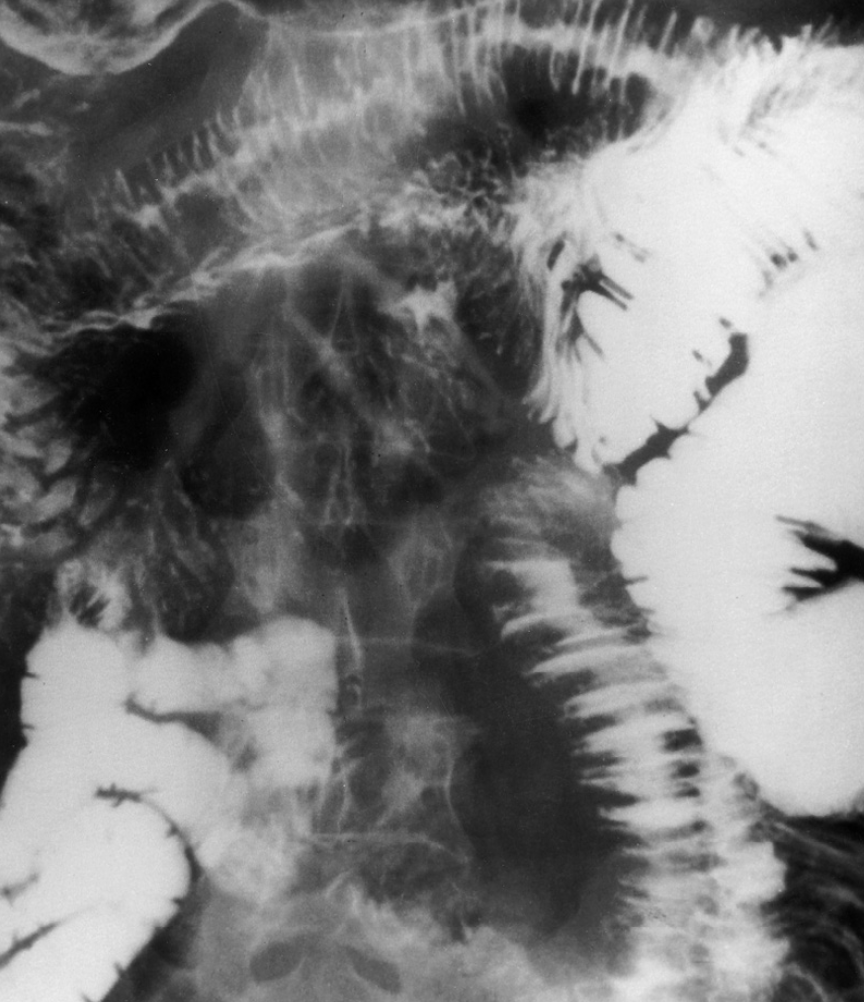
sickle cell anemia
is generally confined to African Americans, the hemoglobin molecule is abnormal and the red blood cells are crescentic or sickle shaped and tend to rupture.
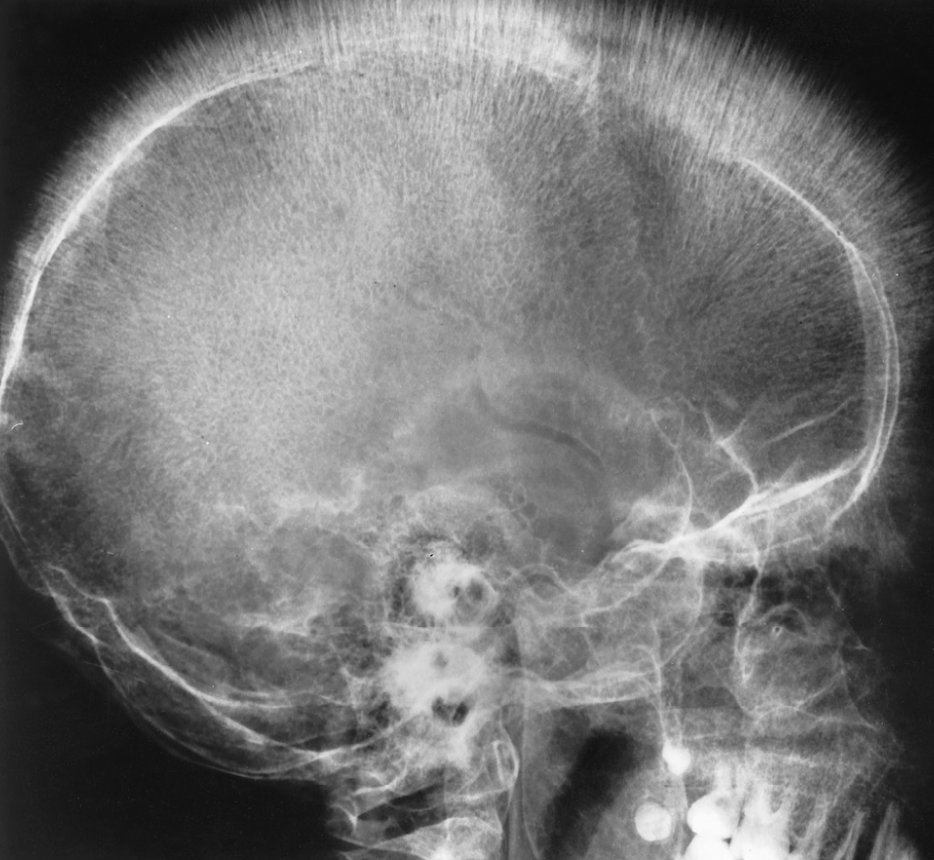
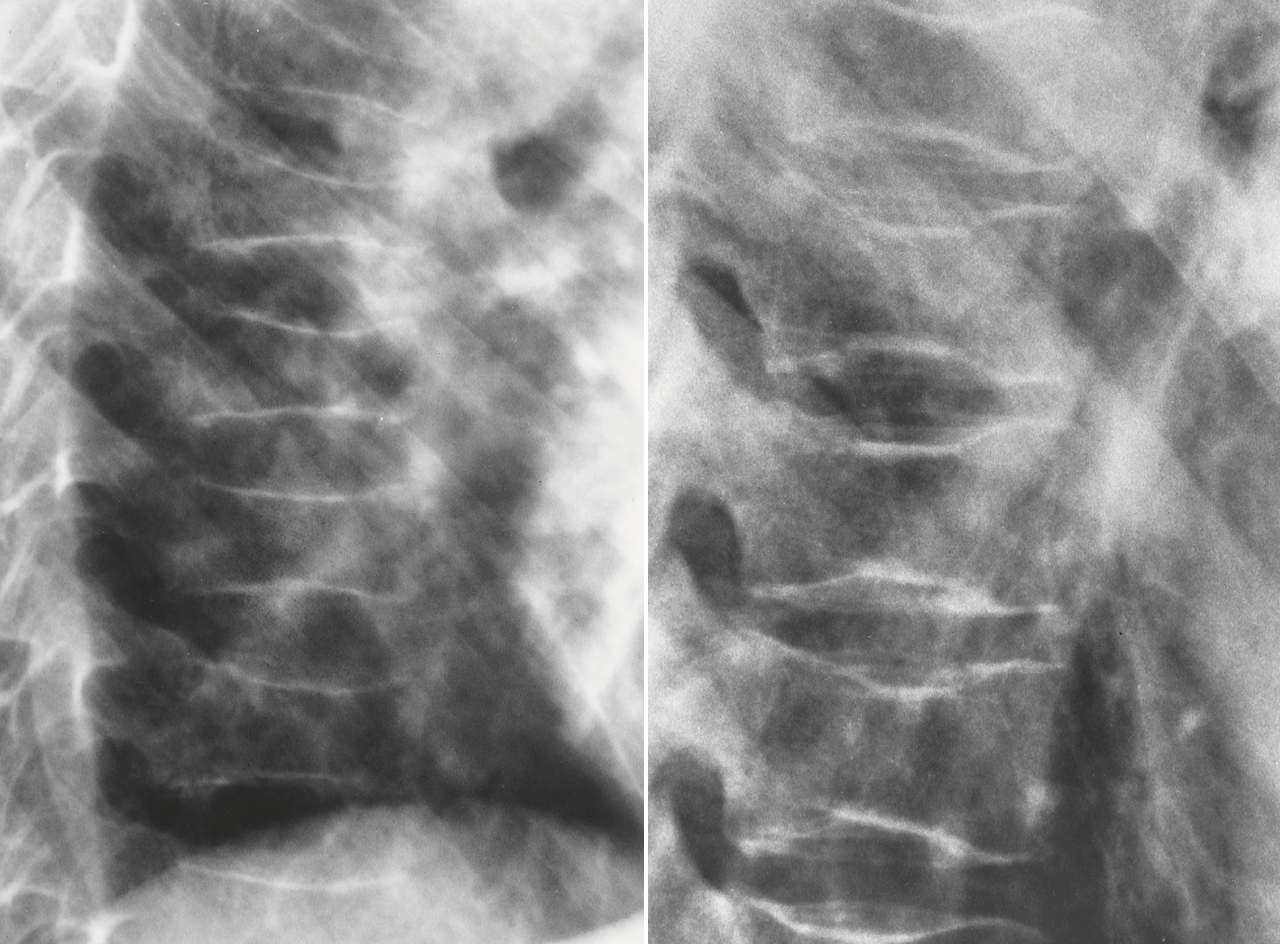
thalassemia
A defect in hemoglobin formation which occurs predominantly in persons living near the Mediterranean Sea, especially those of Italian, Greek, or Sicilian descent
bone thinning
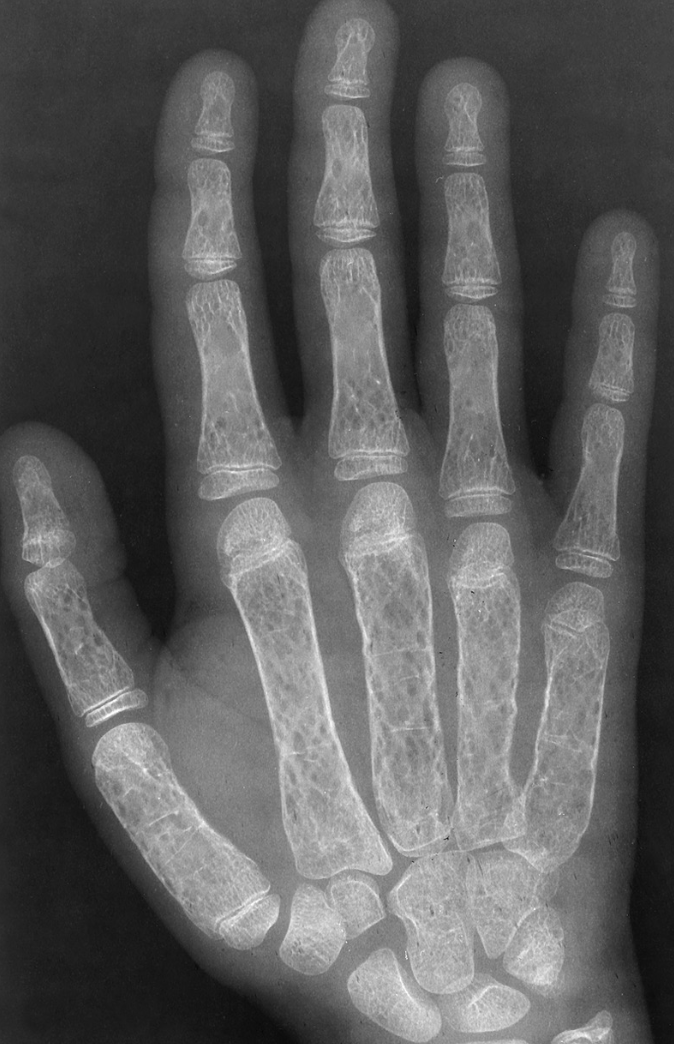
“Hair-on-end appearance” of thalassemia
fish vertebrae
sickle cell anemia appearance
Leukemia
is a neoplastic proliferation of white blood cells.
Myelocytic leukemia
is a cancer of the bone marrow
Lymphatic leukemia
is a malignancy of the lymph nodes
Acute lymphocytic leukemia
has an abrupt onset and progresses rapidly, is the most common form in children
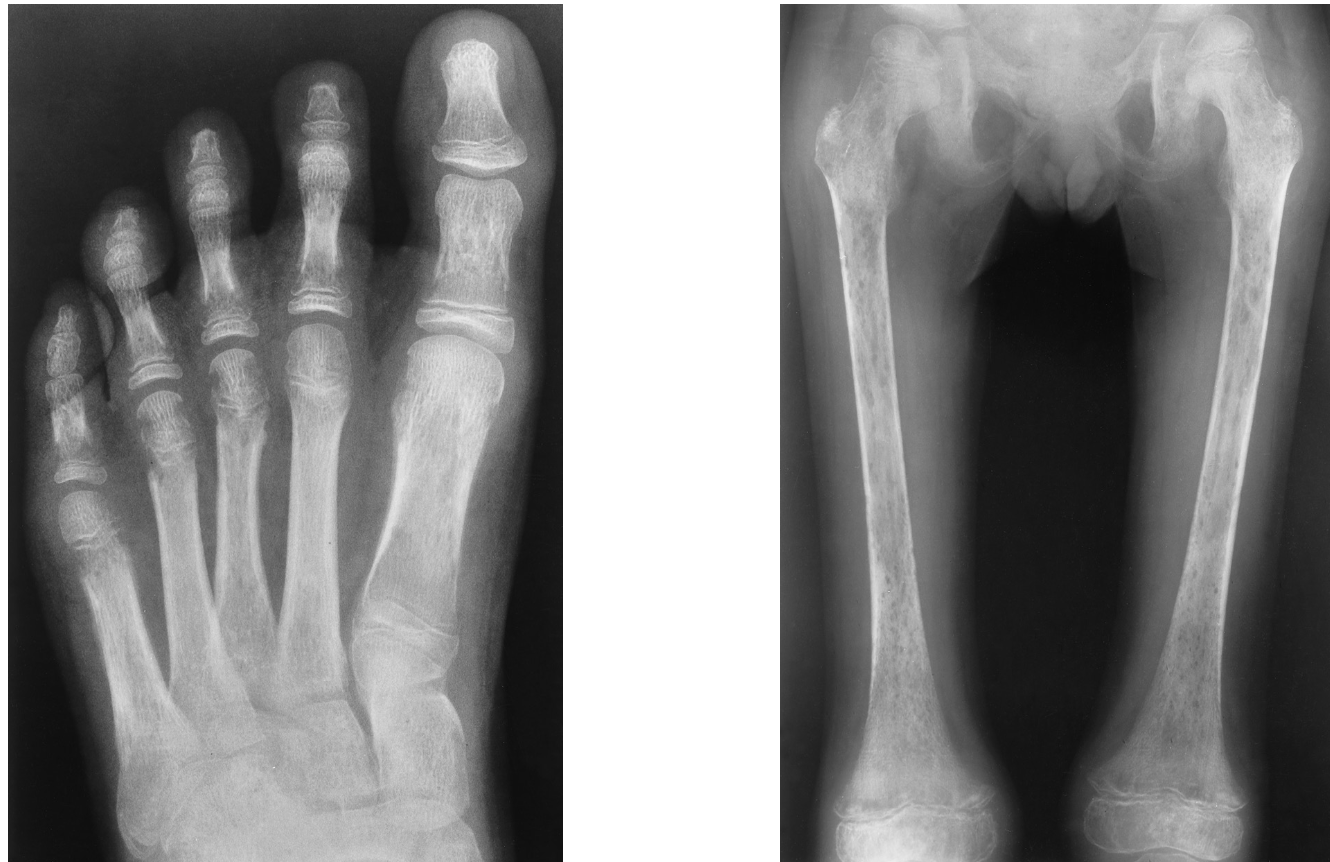
transverse radiolucent bands at the metaphyseal ends of long bones “moth-eaten”
leukemia radiographically
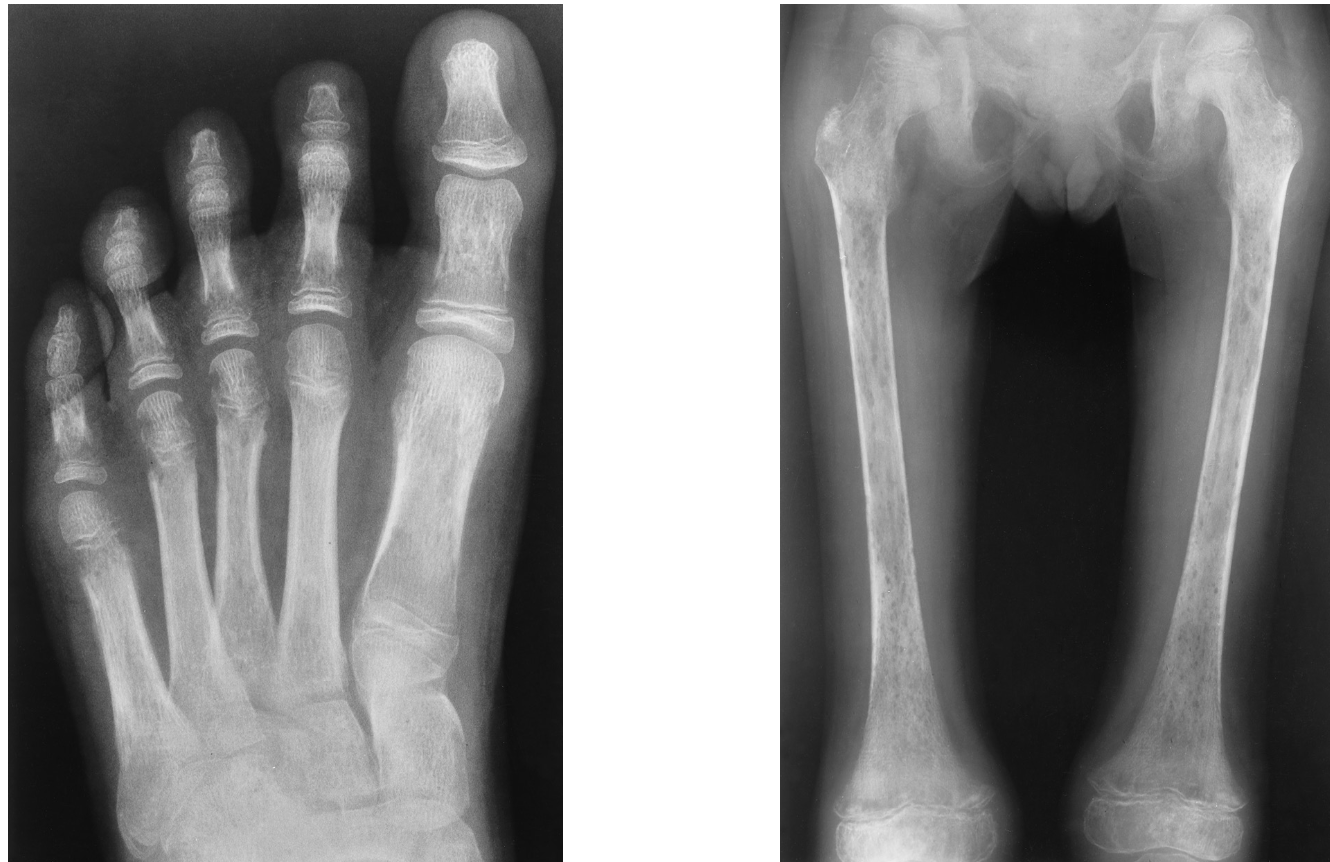
splenomegally
KUB with leukemia can also represent as:
Most common non-skeletal radiographic appearance
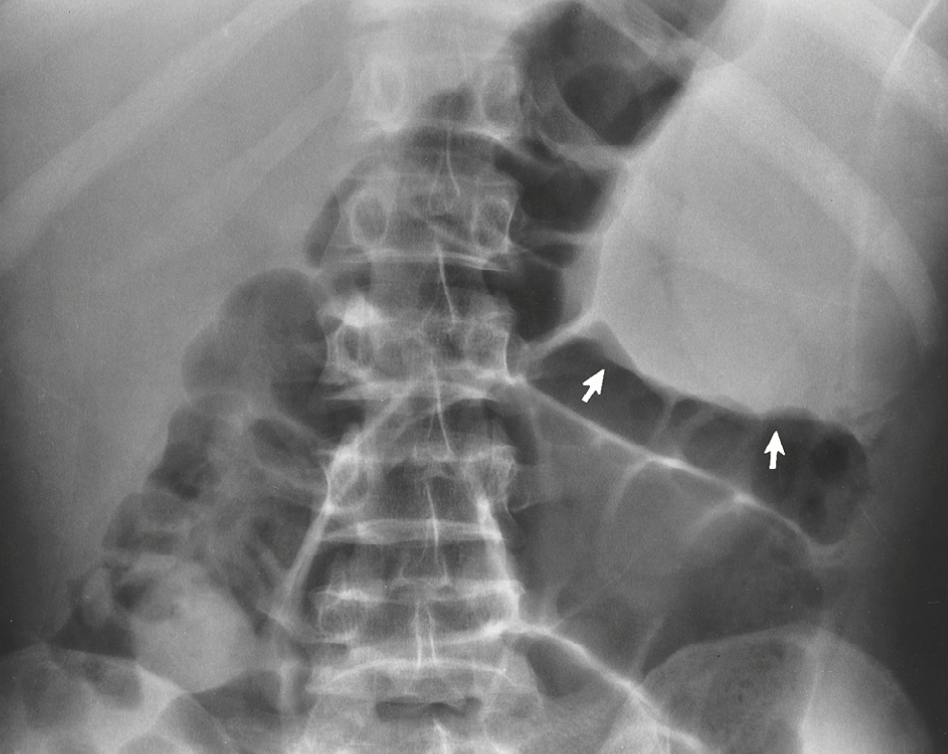
lymphoma
cancer of lymphatic system when affected cells are produced at high rate
hodgkin
non-hodgkin
2 classifications of lymphoma
Mediastinal lymph node enlargement
is the most common radiographic finding in lymphoma
non-hodgkin
40% happens in parenchymal organs (lymphoma) outside of lymph that is more severe at any age
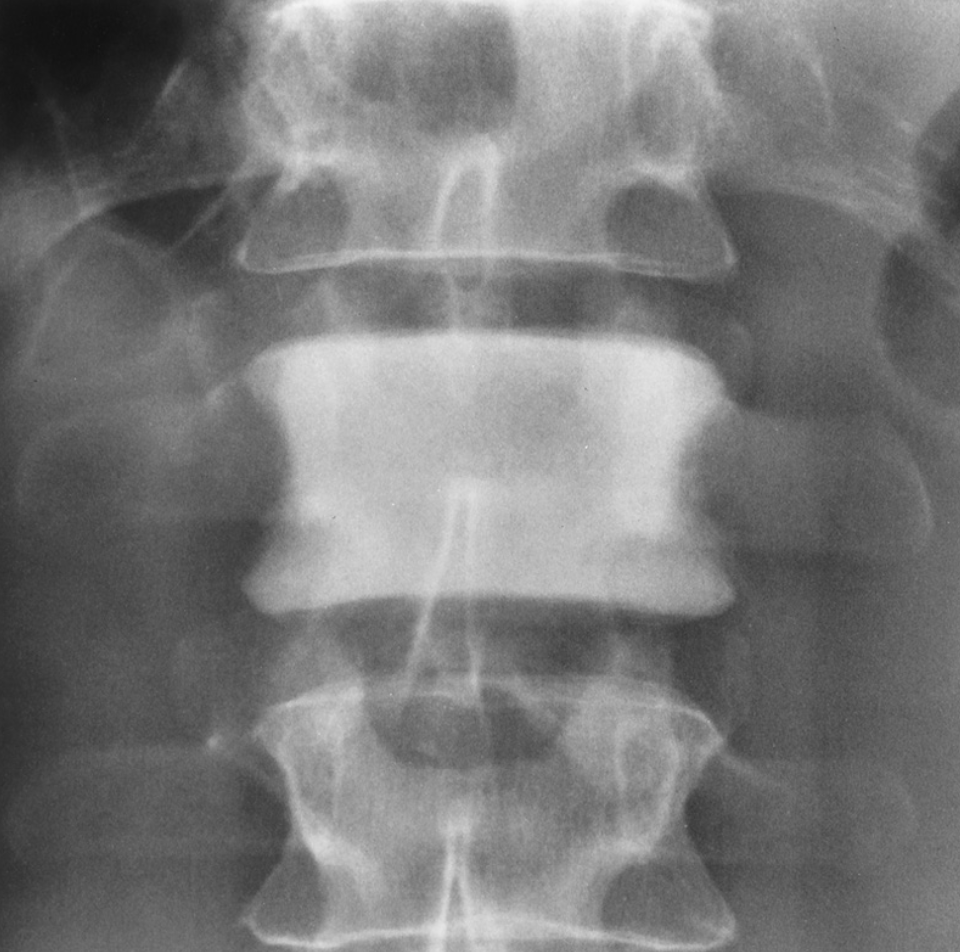
hodgkin
90% originate in lymph nodes
ivory vertebrae (densed vertebrae)
skeletal appearance of lymphoma
Infectious Mononucleosis
is a self-limited viral disease of the lymphoreticular system characterized by vague symptoms of mild fever, fatigue, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes caused by an intense increase of lymphoid cells.
Epstein–Barr virus
cause of infectious Mononucleosis
spread through saliva
why is Infectious Mononucleosis called “kissing disease”?
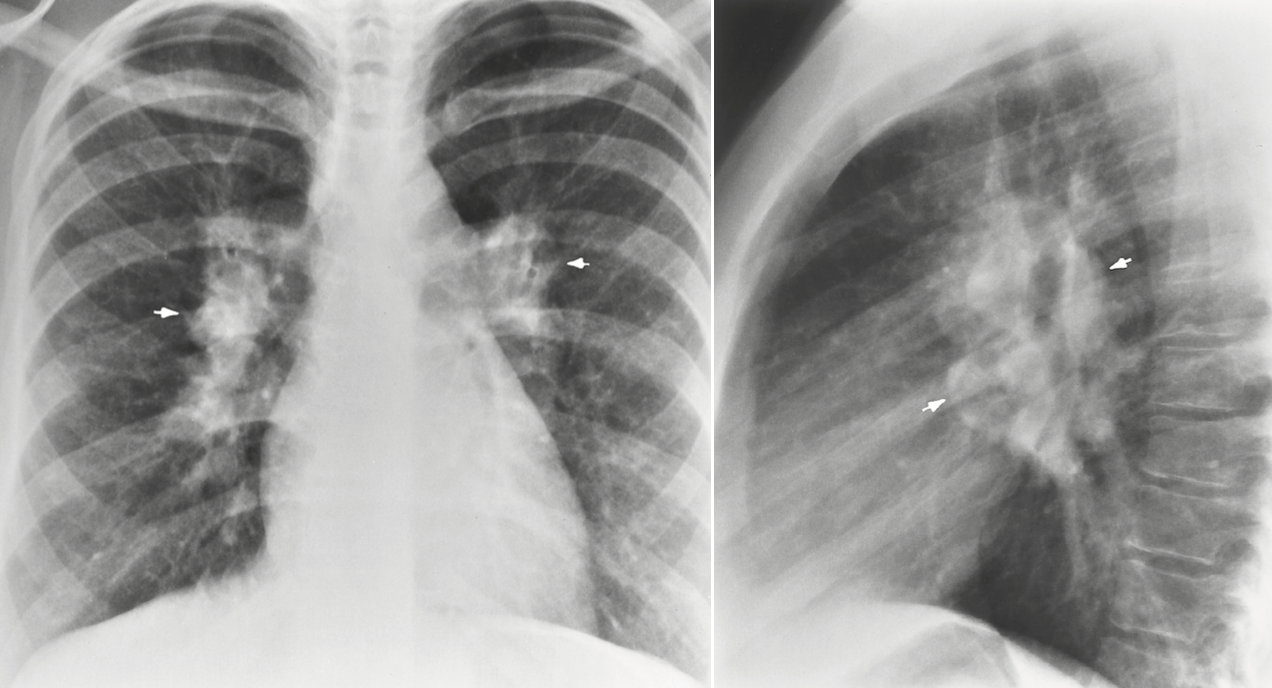
hemophilia
is an inherited (by a sex-linked recessive gene) anomaly of blood coagulation that appears clinically only in males.
easily bruising externally and internally
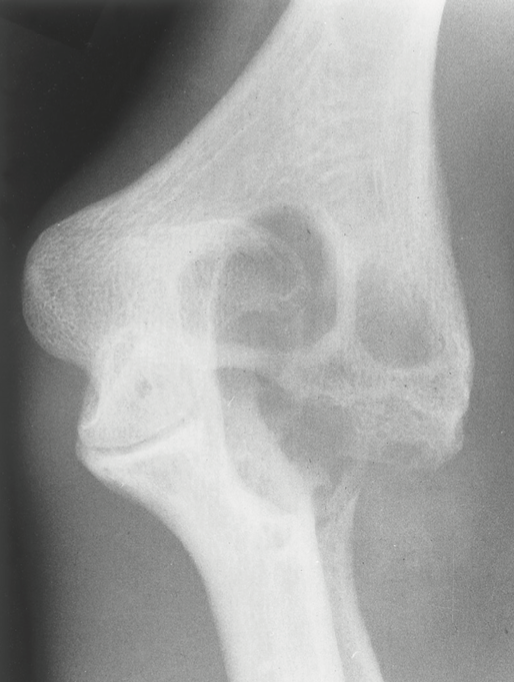
purpura (thrombocytopenia)
a deficiency in the number of platelets, and it results in spontaneous hemorrhages in the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth, and internal organs.