29. Proprioception
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
the ________ plans motor movements and the _______ takes those plans and modulates them via what type of input?
cortex
cerebellum
proprioceptive and vestibular input
what is the voluntary portion of the nervous system?
somatic NS with sensory and motor
proprioception
body's ability to sense its location in space, movement, and actions
what input is for head position and balance input? what about for body body and its position?
vestibular, somatosensory
Body position information is transmitted in two parts
1. cerebellum which receives ___________ proprioception
2. somatosensory cortex which receives ___________ proprioception
unconscious, conscious
what are the receptor types for proprioception?
mechanoreceptors, proprioreceptors
Muscle spindles are located throughout skeletal muscle. They detect phases of muscle movement through (stretch/tension)
stretch
T/F: muscle spindles require contraction of surrounding extrafusal muscle fibers
false, have own gamma motor neuron to maintain tone
Gogli tendon organs are encapsulated afferent nerve ending at the junction of a muscle and tendon that detect (stretch/tension) induced by muscle contraction
tension
Which funiculi are ascending pathways found in?
dorsal and lateral
Explain signals for conscious proprioception
left side of body -> thalamus -> somatosensory cortex in cerebrum -> right cortex
explain signals for unconscious proprioception
left side of body -> ipsilateral cerebellum
_____________ interprets subconscious proprioception (hint: make smooth and correct movement)
cerebellum
explain signals for subconscious proprioception
stretch mecahnoreceptor -> peripheral nerve -> DRG -> spinocerebellar or spinocuneocerebellar tract -> ipsilateral cerebellim
spinocuneocerebellar tract
a. function
b. funiculus
transmits unconscious proprioceptive info to cerebellum from thoracic limb
dorsal
spinocerebellar tract
a. function
b. tract
transmits unconscious proprioceptive info to cerebellum from pelvic limb
lateral
T/F: vestibular lesion is always on the same size as proprioceptive defectis
true
cerebellar lesion may lead to ____lateral proprioceptive defectis
ipsilateral
unilateral spinocerebellar tract damage results in ____lateral proprioceptive deficits
ipsilateral
conscious proprioception pathway
stretch mecahnoreceptor -> peripheral nerve -> DRG -> dorsal funiculus faciculus cuneatus or fasciculus gracilis) -> contralateral somatosensory cortex
Fasciculus gracilis
a. function
b. funiculus
transmits conscious proprioceptive info to cerebrum from trunk and pelvic limbs
dorsal
Fasciculus cuneatus
a. function
b. funiculus
transmits conscious proprioceptive info to cerebrum from thoracic limbs
dorsal
cerebral cortex lesion may lead to ______lateral proprioceptive defecits
contralateral
unilateral spinal cord damage results in _____lateral proprioceptive deficits
ipsilateral
what is the first thing we lose with spinal cord compression? 2nd? 3rd? Explain
proprioception
motor function
conscious pain sensation
proprioceptive fibers are the largest axons with heavy myelination
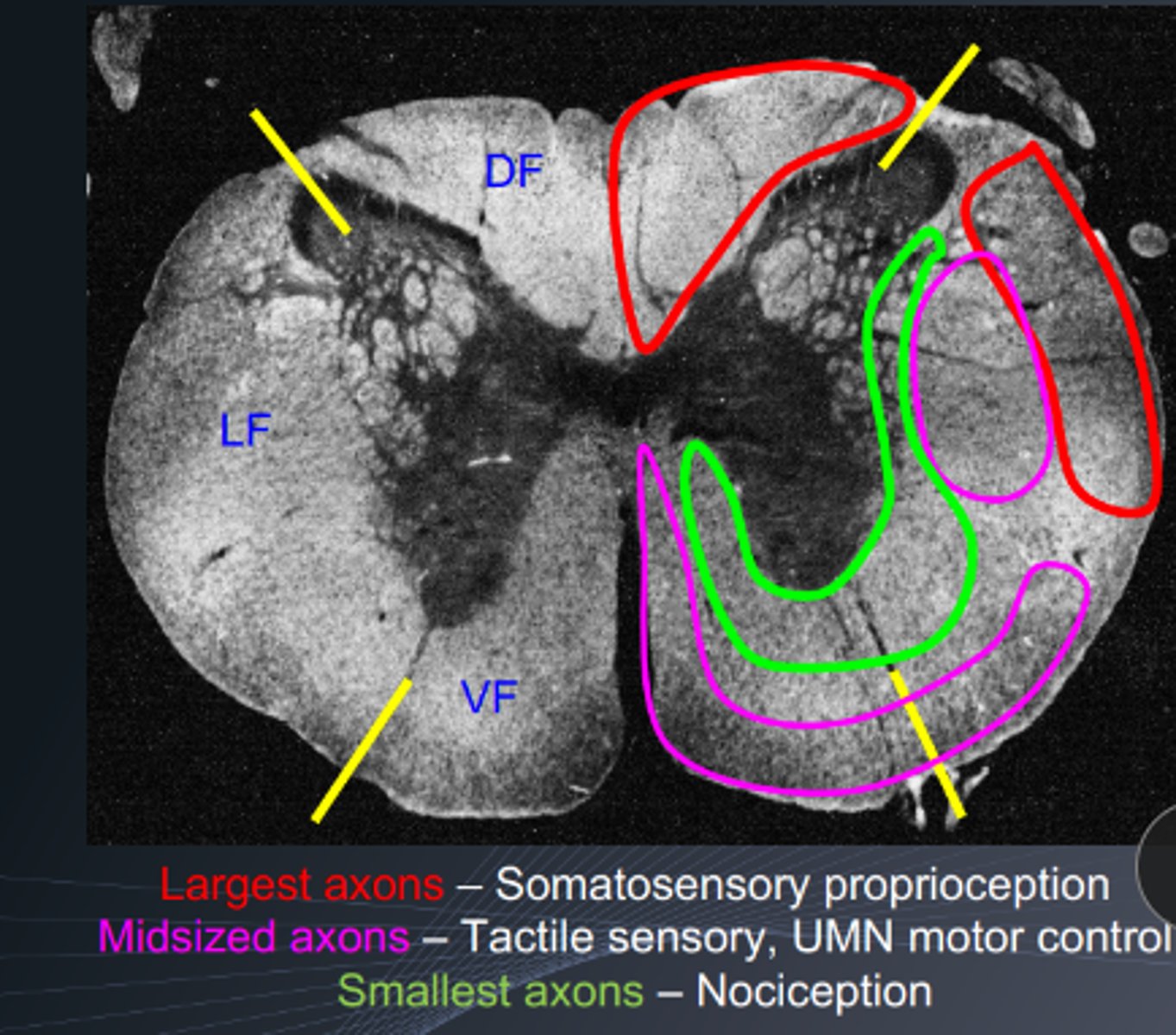
T/F: a deep pain positive dog has a more severe spinal cord compression than a deep pain negative dog
false
T/F: all parts of the neurological system must be intact for postural reaction
true, any damage can lead to deficits
Is there a single test for conscious proprioception?
no
If there is a lesion in left cerebrum where would you see proprioceptive deficits?
right thoracic and pelvic limbs
If there is a lesion in right brainstem where would you see proprioceptive deficits?
right thoracic and pelvic limbs
If there is a lesion in right cerebellum where would you see proprioceptive deficits?
right thoracic and pelvic limbs
If there is a lesion in right C1-5 and C6-T2 where would you see proprioceptive deficits?
right thoracic and pelvic limbs
If there is a lesion in right T3-L3 and L4-S1 where would you see proprioceptive deficits?
right pelvic limb ONLY
If there is a lesion in right S1-S3 where would you see proprioceptive deficits?
normal