Fundamentals of Data Structures
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the 7 different Data Structures?
Queue
Stack
Graph
Tree
Hash Table
Dictionary
Vector
QuickSilverGoTHDV
What are the 3 types of Queue?
Linear
Circular
Priority
What are Data Structures?
Data Structures act as containers for data acting almost as a next level sort of Data Type.
What are the 3 rules of Arrays?
Must be finite
Must be indexed
Must contain the same data type
What is the difference between 1 and 2 dimensional arrays?
One is simply linear with only data being labelled by its index, while 2 dimensional arrays look like tables containing a column and row.
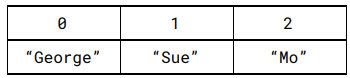
What is an abstract data type?
There truly is no such thing as an abstract data type as all it does is take from other real data types and customize themself in their own way making them different to the original only then being labelled as abstract.
How do you interact with queues?
FIFO (First In First Out)
How does a linear queue function?
With use of 2 pointers:
Front Pointer
Rear Pointer
With these two it will add to the rear (being furthest right) and subtract from the front (being furthest left)
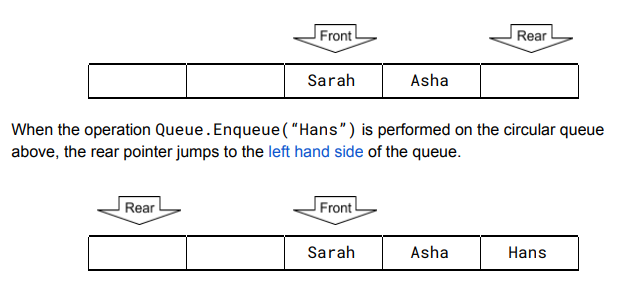
What happens if you reach the end of a linear queue?
CIRCULAR QUEUE!!! in a linear queue it’ll probably just say its full as the pointers always go to the first available space.
Considering a Circular Queue it has the power to go over the edge and loop back round like a circle so if there is space back at the beginning. it can be used.
How does a priority queue work?
Quite similar to that of a weighted graph. Everything is labelled with a value defining its importance in turn saying when it should be dealt with and if there are two of the same variant then simply they are treated as if its a regular queue. (FIFO)
How do you interact with stacks?
FILO (First In Last Out)
How do Stacks work?
Stacks work with a singular pointer known as the top pointer. (Like a stack of books)
What operations can be done on a stack?
Push — Adds an item to the stack
Pop — Removes an item from the stack
Peek — returns the value on top (No Removal)
IsFull , IsEmpty both work.
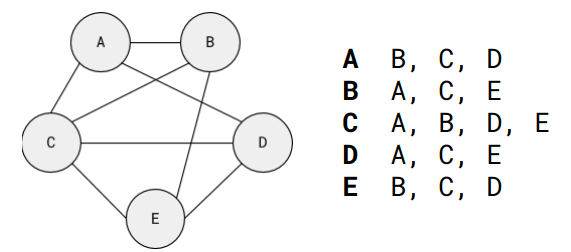
What are the parts of a graph called?
Nodes or Vertices
Get joined together by
Edges or Arcs
A Weighted graph has values assigned to these edges.
Instead of using a graph to present what else could be used?
An Adjacency list which displays all the relationships in a different way.
What is the difference between Adjacency Matrix and List?
Adjacency Matrixes store every possible edge there is even if they dont exist with the downside being it takes up more storage while the lists only look at the edges which exist and in turn take up less storage.
Adjacency Matrix is better for Dense Graphs
Adjacency List is better for Sparse Graphs
What are the 3 rules for trees?
Must be Connected
Must be an undirected graph
must have no cycles.
What makes a root node?
The Root Node is the first node at the top of a tree diagram. These trees contain parents and children.
To be a Root Node you must have no parents.
What is the difference between Trees and Binary Trees?
A Binary tree has no more that 2 children under a single parent.
What do Hash Tables do?
Hash Tables are a way of storing data that allows for it to be retrieved within a constant time complexity.
How do Hash Tables work?
Hash tables take a value and then hash the value masking it with something else and then never again reveal the original input and continue to use the hashed value instead.
How does Dictionary work?
Exactly like it works for compression when a specialized dictionary gets made in order to use duplicates and save entire phrases.
What is the difference between Static and Dynamic?
Static in regard to Data Structures mentions that they are set and final when it comes to questioning the amount of space or rather data they can hold while for dynamic they are able to change their size willingly.
What does sequential mean?
Sequential looks at order stating that one comes after the other.
What is it called if there happens to be too much data in a single structure?
A stack overflow. (An Overflow error)
What does Push do?
Push adds an item to a stack.
What does Pop do?
Pop removes an item from a stack.
What does Peek do?
Without removing anything it will check the top value.
How many pointers does a stack have?
1 — The Top Pointer
How many pointers do queues have?
2 — The Front and Rear Pointers