Chemistry Reactivity 1.2 Energy Cycles
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Enthalpy of formation
What is the product of burning of Hydrocarbon (compound made up of carbon and hydrogen) and oxygen
CO2 and H2O
A→B+C How to calculate the enthalpies change
A - (B+C) is the enthalpies of formation
2A→ B+3C
2A-(B+3C) is the enthalpies change. The cofficient must be taken into account.
What is the standard enthalpies change
enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of that substance is formed from its constituent elements, with all participating species in their standard states.
What is lattice enthalpies
Lattice enthalpy (AH}) is the standard enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of structural units of a solid lattice is separated into gaseous ions: M_X,(s) — aM"(g) + bX“(g)
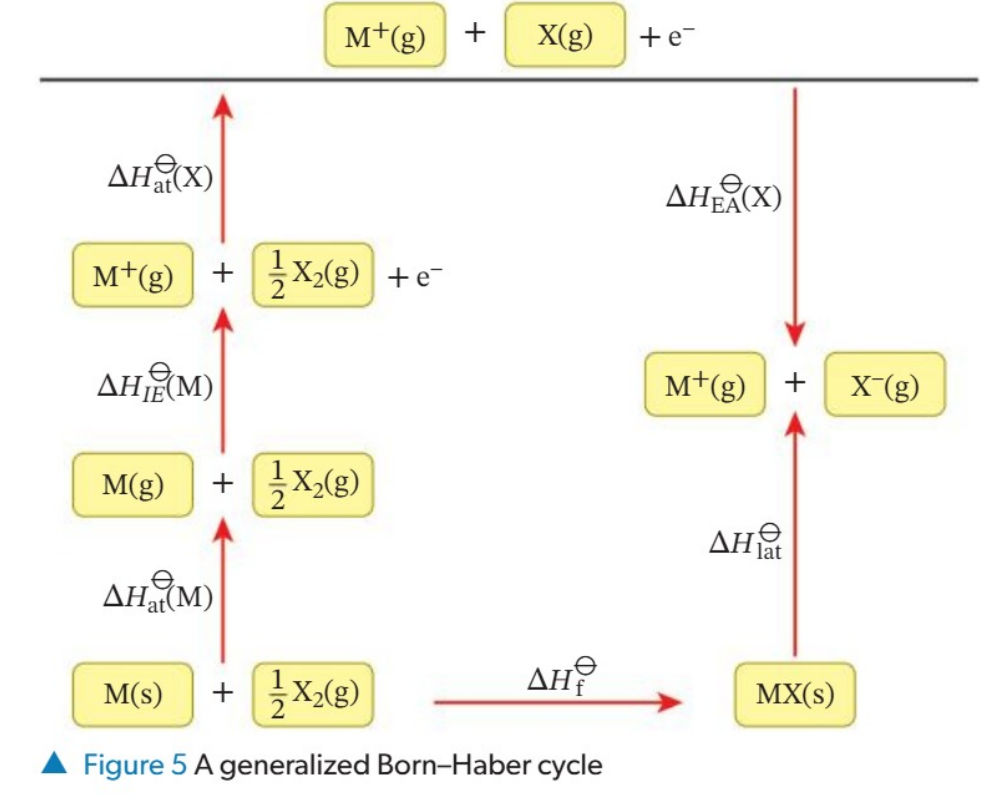
What is MX(s) — M*(g) + X(g)
MX(s) = M(s) + 3 X,(@) = M(g) + 3 X,(8) = M'(@) + 3 X,(@) + & — M(g) + X(g) + & — M(g) + X (g)
Therefore AHP (MX) = -AHf’(MX, 8) + AHO(M) + AH)(M) + AHS:(X) +AH?, (X)