Nurs 307 (exam 2): ears
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
External ear is called
auricle or pinna
Shape serves to funnel sound waves into its opening which is called the ______ ______ _______
external auditory canal
The auditor canal is line with glands that secrete ________
ceruman
t/f cerumen is suppose to be there
true
(external ear): inner _____ ______ consists of ______ covered by thin sensitive skin
two thirds
bone
Lymphatic drainage of ______ ______ flows to parotid, mastoid, and superficial cervical nodes
external ear
Tympanic Membrane is also called eardrum and separates ______ and ______ ear
external
middle
(Tympanic Membrane) is a _______ membrane with a pearly _______ color
translucent
gray
know anatomy of ear
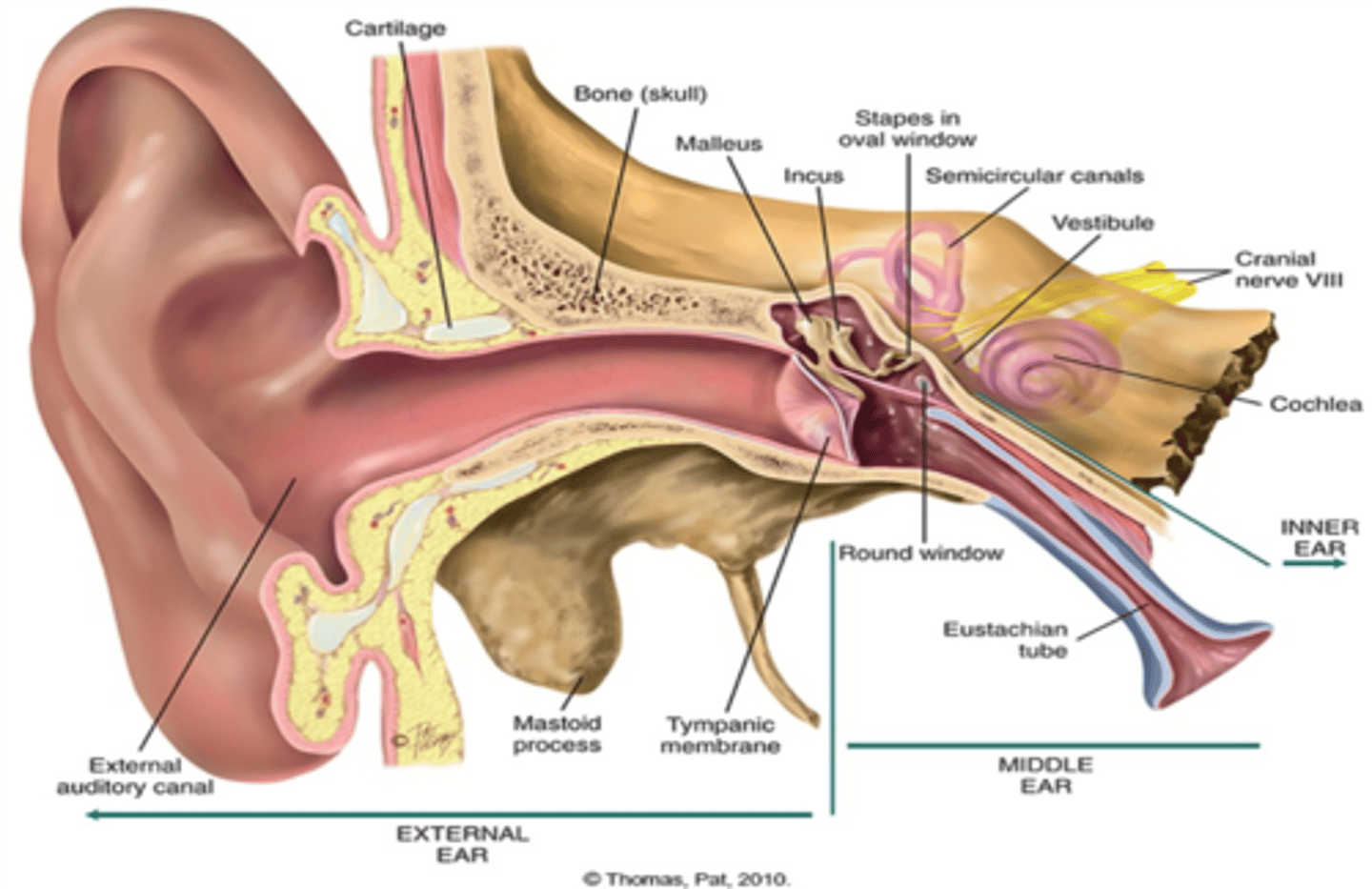
(Middle Ear): to the outer ear and inner ear __________ tube
Eustachian tube
Eustachian tube connects _____ ____ with the ________ and allows passage of AIR
middle ear
nasopharynx
First function of the middle ear:
Conducts ______ vibrations from the OUTER EAR to central _______ apparatus in the inner ear
- sound
- hearing apparatus
Second function of the middle ear:
Protects inner ear by reducing _______ of loud sounds
amplitude
Third function of the middle ear:
Eustachian tube allows _________ of _____ ______ on each side of the TM so the it does not rupture
- equalization
- air pressure
Inner ear contains the ______ ________, which holds ______ organs for ____ and hearing
bony labyrinth
sensory
equilibrium
________ and the semicircular canals within the bony labyrinth compose the ______ ________
vestibule
vestibular appratus
although the inner ear is not accessible to direct examination, its function can be ______
assessed
(hearing)
the auditory system can be divided into three levels:
-
-
-
peripheral
brainstem
cerebral cortex
at PERIPHERAL level, ear transmit ______ and CONVERTS its vibrations into _____ ______, which can be analyzed by the BRAIN
- sound
- electrical impulses
Amplitude: is _______
loudness
Frequency: _______ or NUMBER of cycles per second
pitch
sound waves produce vibrations on _____ _____
TM
Numerous ______ along basilar membrane are receptor ____ CELLS of organ of Cortisones, the sensory organ of HEARING
fibers
hair cells
As hair cells ______, they mediate VIBRATIONS into _____ _____, which are conducted by auditory operation of CN ______ to brainstem
- bend
- electric impulses
- VIII
function at brain stem level is _____ interaction
binaural
Brainstem locates direction of a _____ in space, as well as identifying the _____
sound
sound
CN VIIII (acoustic) from each ear sends SIGNALS to both sides of brainstem, which are sensitive to differences in ______ and _____ of messages from two ears, depending on way HEAD is turned
intensity
timing
The function of the CORTEX is to ________ meaning of the ______ and begin appropriate response
interpret
sound
normal pathway of hearing is _______ ________ . it is the most efficient
air conduction
which pathway of sounds is most efficient?
air conduction
what is the alternate pathway of sound?
bone conduction
_____ of the _____ vibrate and are transmitted directly to inner ear and to CN _____
bones
skull
VIII (acoustic)
presbycusis
age related hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss: partial loss because a person is able to hear if ____ amplitude is ______ enough to reach normal elements in inner ear
sound amplitude
increased
sensorineural hearing loss: increase in ______ may not enable a person to understand ______
amplitude
words
________ holds the sensory organ for equilibrium and hearing)
labyrinth
_______ in inner ear constantly feeds information to the brain about body's position in space
labyrinth
How many semicircular canals are there?
three
If the labyrinth ever becomes inflamed, it feeds the wrong information to the brain, creating a staggering gait and a strong, spinning, whirling sensation called _________.
vertigo
in aging persons, _____ lining ear canal become coarse and stiff
cilia
the coarse and stiff cilia may cause cerumen to accumulate and oxidize, which greatly ________ hearing
reduces
cerumen is _____ because of atrophy of apocrine glands
drier `
true or false: impacted cerumen with hearing loss is not reversible
false
______: type of hearing loss that occurs with aging, even if people living in quiet enviroment
presbycusis
presbycusis onset usually occurs in _____s and slowly progresses
50
with Presbycusis, first notice a ____-___ tone loss
high frequency
ringing, roaring, buzzing in ears without external source
tinnitus
tinnitus occurs with which type of hearing loss?
sensorineural hearing loss
_____ - the room is spinning
vertigo
vertigo- room spinning is (_____ vertigo); environment is spinning around you
objective
vertigo - you're spinning (_____ vertigo
subjective
______ not steady, feels like you are losing your balance
dizzy
(indication of possible hearing loss):
_____ _____ or watching your ___ and __ rather than your eyes
lip reading
face
lips
(indication of possible hearing loss):
_____ or straining ______ to hear
frowning
forward
(indication of possible hearing loss):
posturing of head to catch sounds with better ____
ear
(indication of possible hearing loss):
_________ questions; frequently ask you to repeat questions
misunderstands
_____ or shows _____ reflex when you raise your voice
irritable
startle
(indication of possible hearing loss):
the person's speech sounds garbled, _____ sounds distorted
vowel
(indication of possible hearing loss):
inappropriately _____ voice
loud
(indication of possible hearing loss):____ , ____ tone of voice
flat
monotonus
(external noise questions):
Any loud noises at ______ or on the ___?
home
job
(external noise questions):
Are you hearing other noises such as _____ _____, loud persistent _____, or ____ in military or while HUNTING
-heavy machinery
-music
-gunshots
(coping strategies with external noise questions):
do you take any steps to ____ your ears, such as _____ or ______
protect
headphones
earplugs
inspect external ear:
- SIZE and SHAPE of auricle, ___ and ___ on head
position
alignment
inspect external ear:
check ____ and ____ for tenderness
auricle
tragus
inspect external ear:
ears are _____ size bilaterally with no swelling or thickening
equal
inspect external ear:
ears of unusual size and shape may be a ______ familial trait with no clinical significance
normal
Pinna and Tragus should feel ____ and movement should produce no pain
firm
palpating _____ ____ should also produce no pain
mastoid process
normal tympanic membrane should be: ____ and ____ with a ____-____ color
shiny
translucent
pearl-grey
_____ - _____ light reflex prominent in anteroinferior quadrant, a reflection of the otoscope light
cone-shaped
tympanic membrane with some adults may show scarring, which is a dense ____ patch on the TM, a sequence of repeated ear infections
white
screening for hearing acuity begins during ____; how well a person hears during conversational speech
-history
-how well a person hears during conversational speech
if a person answers yes to hearing difficulty, perform _____ testing or refer for _____ testing
audiometric
if a person answers no, screen using _____ ___ ___
whispered voice test
what is a passing score for Whispered Voice Test?
correct repetition of 4 of 6 number/letters
the whispered voice test is use to detect ______-____ /_____ frequency loss
high-tone
high
this test is to asses ability of vestibular apparatus in inner ear to help maintain standing balance
Romberg sign
(infants and young children):
top of the pinna should match an imaginary line extending from corner of ______ to the _______
eye
occiput
(testing hearing acuity for infants and childeren):
Newborn: _____ (_____)reflex, acoustic blink reflex
startle (Moro)
(behavioral manifestation of hearing loss infants and young children):
child is ______ in casual conversation
inattentive
(behavioral manifestation of hearing loss infants and young children):
____ _____ strained or puzzled
facial. expression
(behavioral manifestation of hearing loss infants and young children):
frequently asks to have statements ______
repeated
(behavioral manifestation of hearing loss infants and young children):
confuses words that _____ ______
sound alike
(behavioral manifestation of hearing loss infants and young children):
has accompanying ____ problem
speech
(behavioral manifestation of hearing loss infants and young children):
appears shy and with drawn and lives in his or her _____ world
own
(behavioral manifestation of hearing loss infants and young children):
frequently complains of _____
earaches
(behavioral manifestation of hearing loss infants and young children):
hears better at times when environment is more ____
conducive
(Aging adults):
high-tone frequency loss apparent for those affected with ____
presbycusis
(Aging adults):
difficulty hearing _____ during conversation.
consonants
(Aging adults):
difficulty hearing _____ words in voice tests
whispered
_______ ______ (swimmer's ear). this abnormal finding of external ear
Otitis externa
lumps and lesions on external ear could be a sign of _____
Carcinoma
abnormal finding in ear canal_____ ____
excessive cerumen
abnormal findings of the TM:
-
-
acute otitis media
perforation
(aging adults):
Gradual sensorineural loss caused by ____ _____ in inner ear or auditory nerve
nerve degeneration
(aging adults):
ability to localize _____ is impaired also
sound
(aging adults):
hearing loss is accentuated when unfavorable ______ noise is present
background
(TM):
Inspect TM and entire circumference of _______ for perforations
annulus
(TM)
Normal TM is ______
intact