organic functional 4 not finished (copy)
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What does the lower pKa value mean?
Increasing Acidity
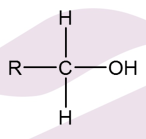
What is a primary alcohol oxidised into?
Aldehyde
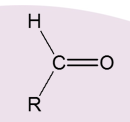
What is the aldehyde oxidised into?
Carboxylic Acid
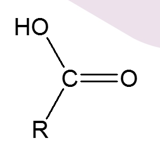
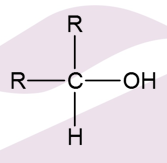
What is a Secondary Alcohol oxidised into?
Ketone
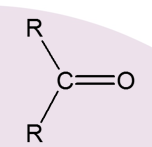
What is the product of a tertiary Alcohol?
None
What forms an ester?
Reaction of an alcohol and acid
What is the general formula for ethers?
R-O-R
Can ethers H-bond with each other?
No
What are low RMM ethers(2)?
gases or liquids at room temp
Soluble in water
What do ethers form in the air?
Peroxides
What are the 2 Carbonyl C=O group
Ketones and aldehydes
Do carbonyl compounds have H-bonds?
No
Are low RMM carbonyl compounds soluble in water?
Yes
What do C=O groups react with?
Nucleophiles
What does an Alkene reduce into with H2?
An alcohol
What is an acyl group?
R-C=O
What happens if we have electron withdrawing groups attached to the R?
Acid strength increases
What happens if we have electron donating groups attached to the R?
Acid strength decreases
What is the product when the nucleophile in an alcohol?
An ester
What is the general boiling point of esters?
Low
What is the general boiling point of amides?
high
What reacts faster, amides or esters?
esters
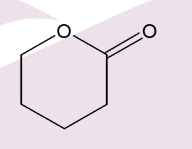
What are cyclic esters called?
Lactones
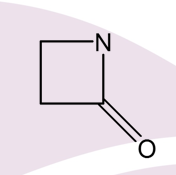
What are cyclic amides called?
Lactams
General structure of amines
R-NH2
What are low RMM amines at room temp?
Gases due to weak intermolecular forces
What are high RMM amines at room temp?
liquids