2.2 Demand and PED
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is demand
The willingness and ability to purchase a good or service at the given price in a given period of time
What is the law of demand
For most products the quantity demanded varies inversely with its price
I.e. as the price rises, the quantity will fall
How does the law of demand work?
as price of good or service falls, consumers have more money left over and are more able to afford the product, so more likely to buy it
Draw an ordinary demand curve
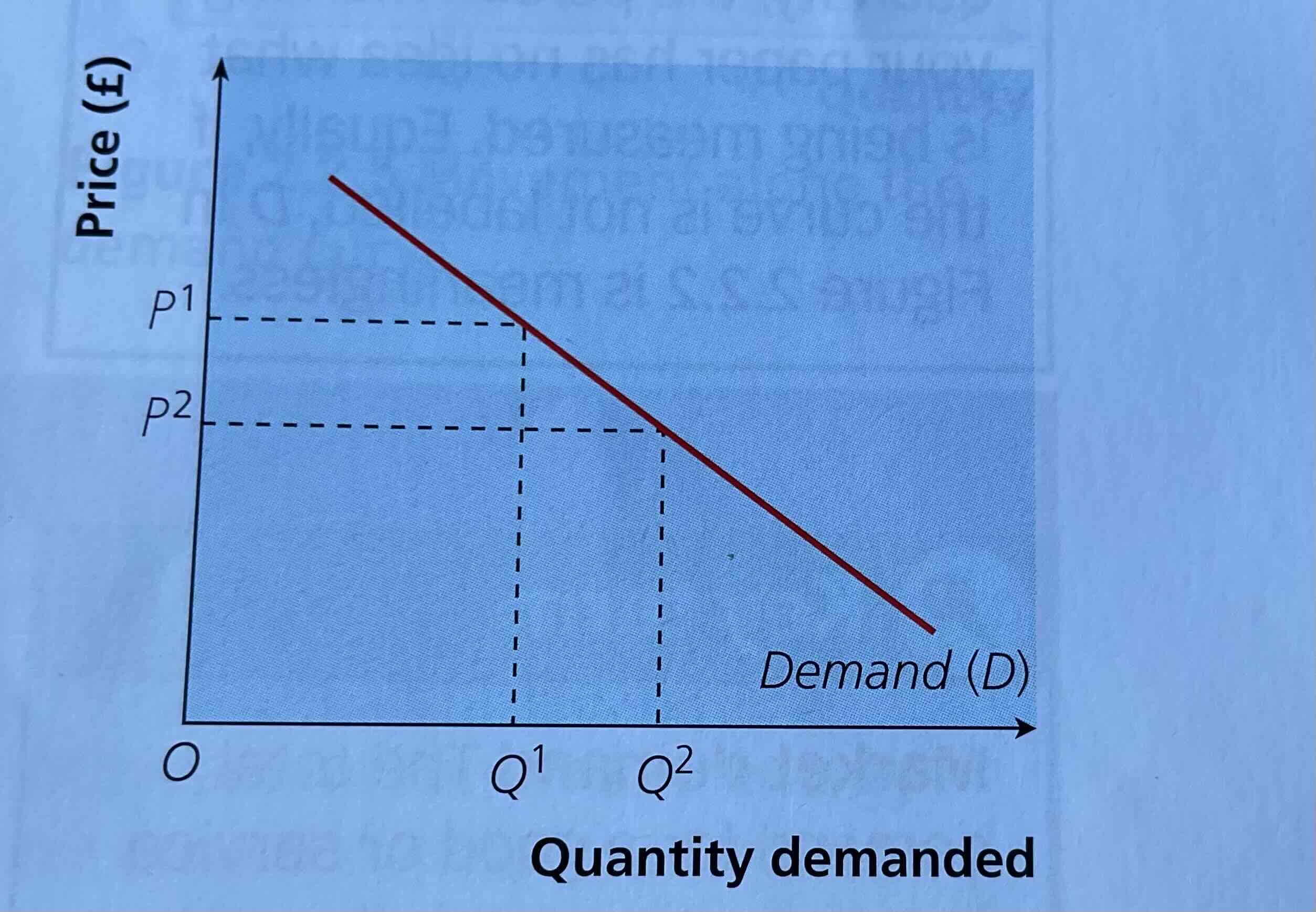
Define individual and market demand
Individual demand: The demand for a good or service by an individual consumer
Market demand: the total demand for a good or service
What are shifts of the demand curve
A complete movement of the existing demand curve either outward (to the right) or inward (to the left).
All shifts are caused by non-price factors and occur when the quantity of a good demanded changes even though the price remains the same.
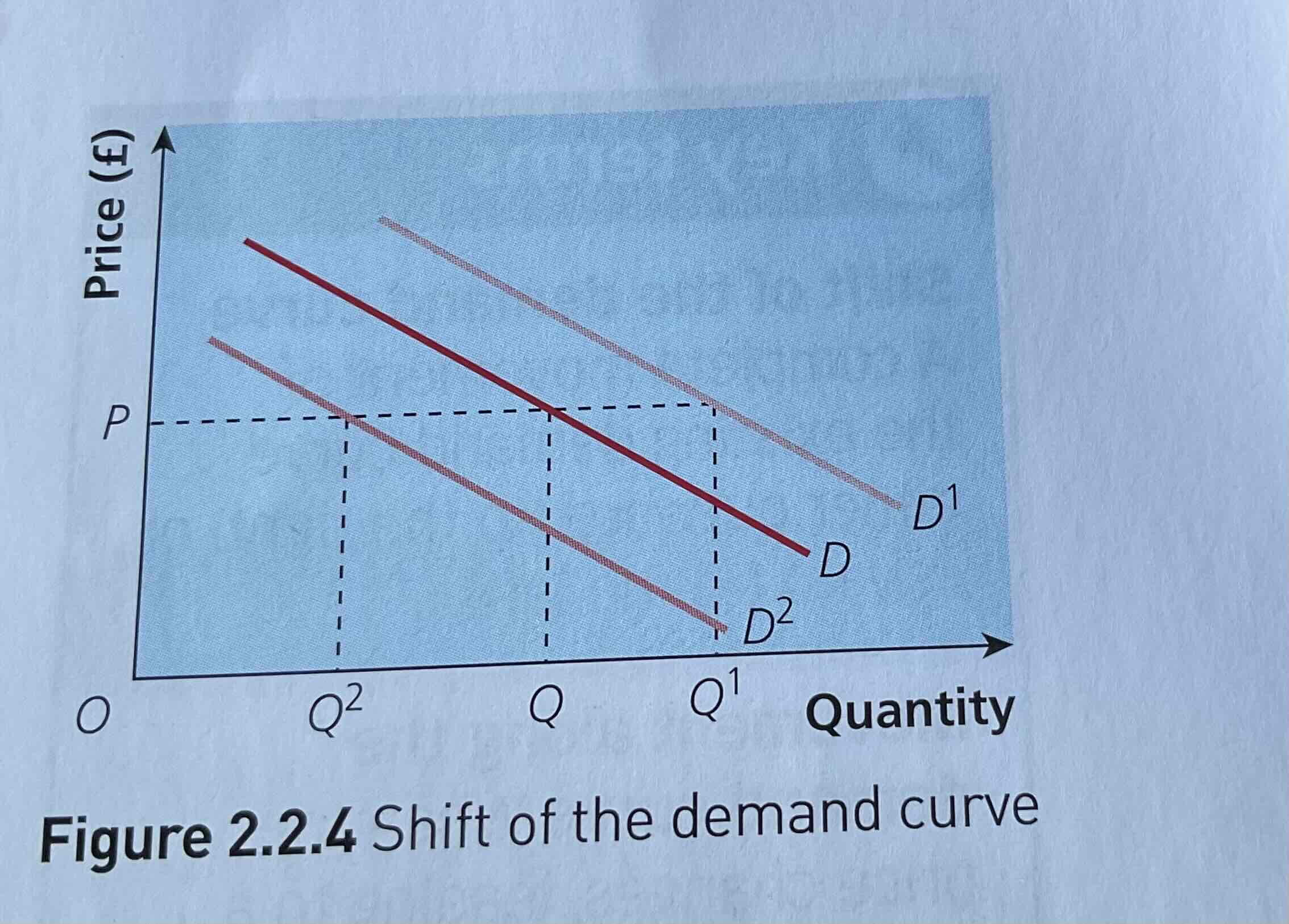
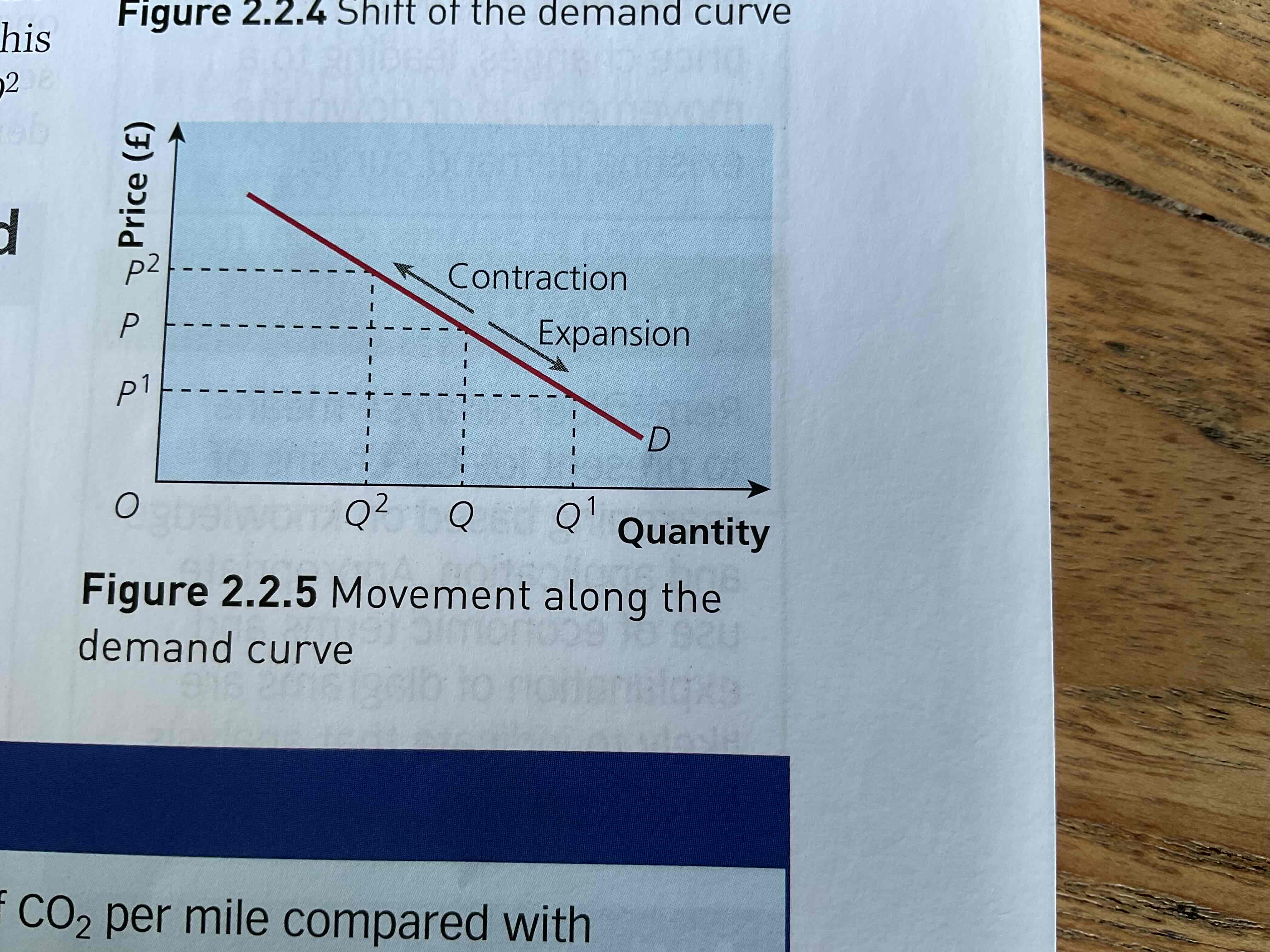
What are movements along the demand curve?
When the price changes, leading to a movement up(contraction-quantity decreases) or down(extension-quantity increases) the existing curve
Give examples of why the demand curve may shift
income
Marketing
Tastes and fashion
Substitutes
Population
Economic situation
Government policies
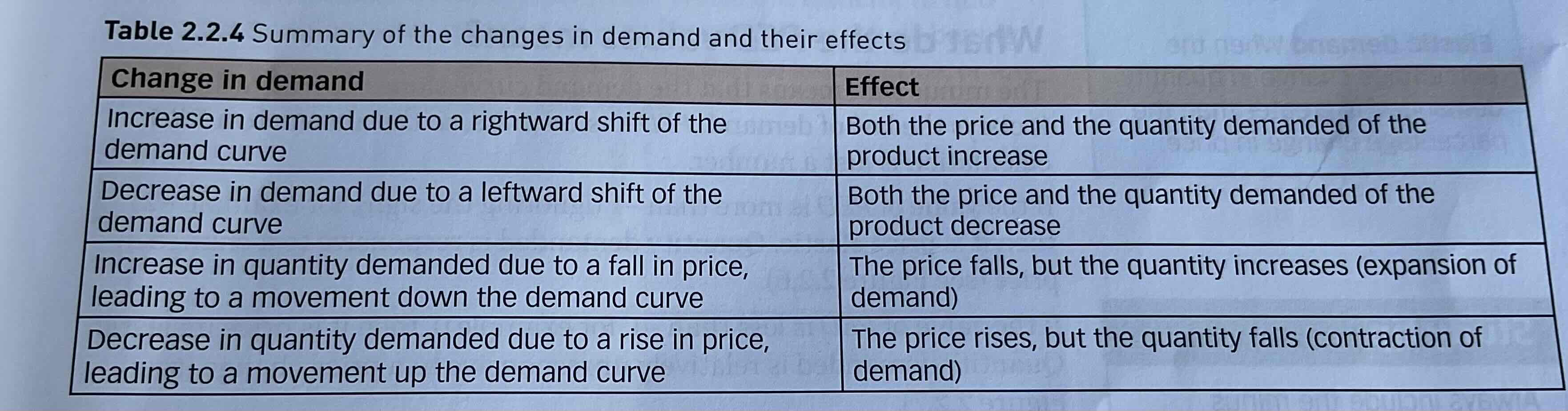
What are the changes in demand and their effect
What is PED
Price elasticity of demand - the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in the price of the product
What is inelastic demand
When the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price
What is elastic demand
When the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price
Using PED how do you know if its elastic or inelastic demand
If value of PED is less than 1 then its price elastic (0-1)
If value of PED is more than 1 then its price elastic (1-infinity)
*PED IS NEGATIVE, economists just ignore the sign, so it should be -1
What are all five PED’s
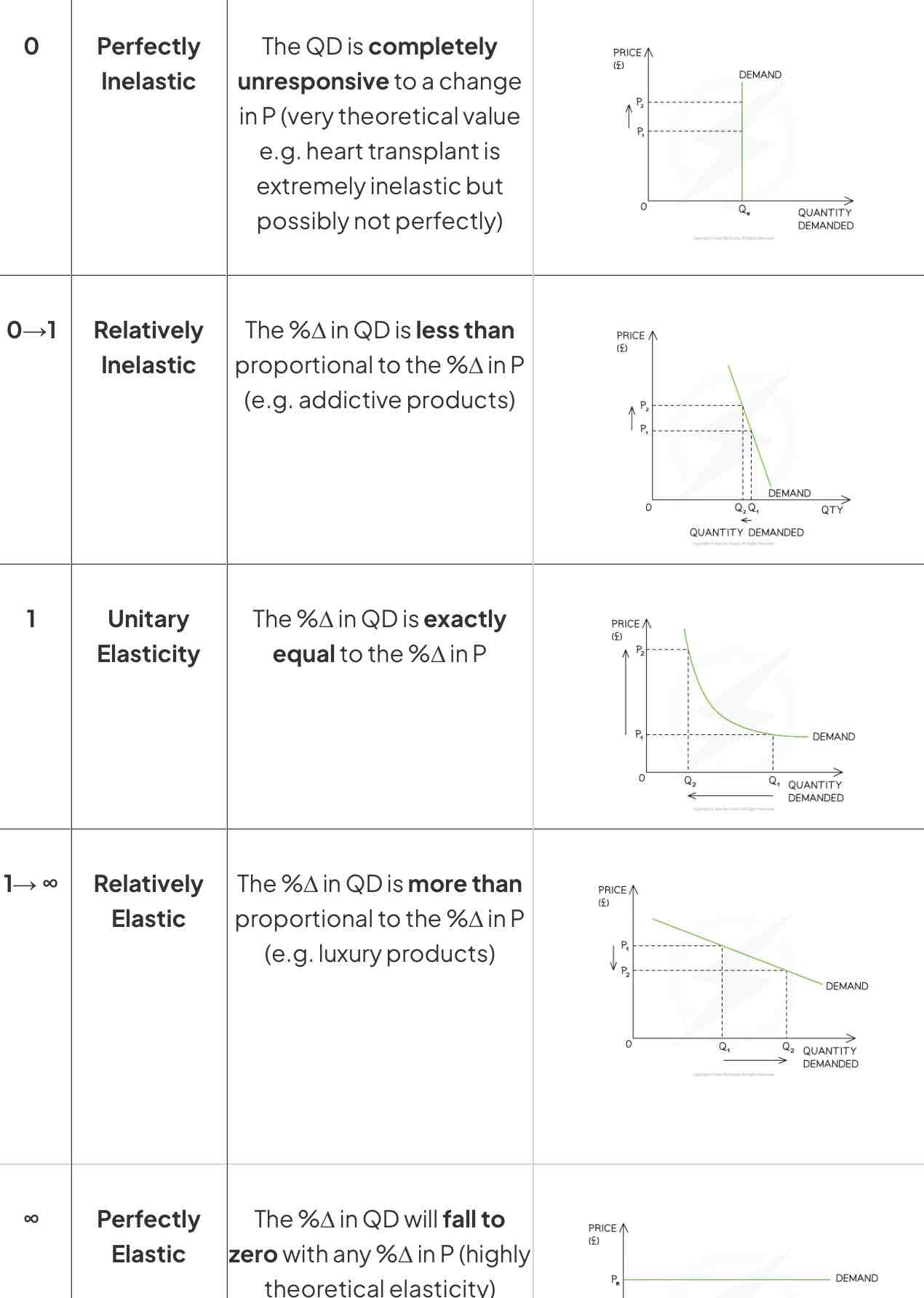
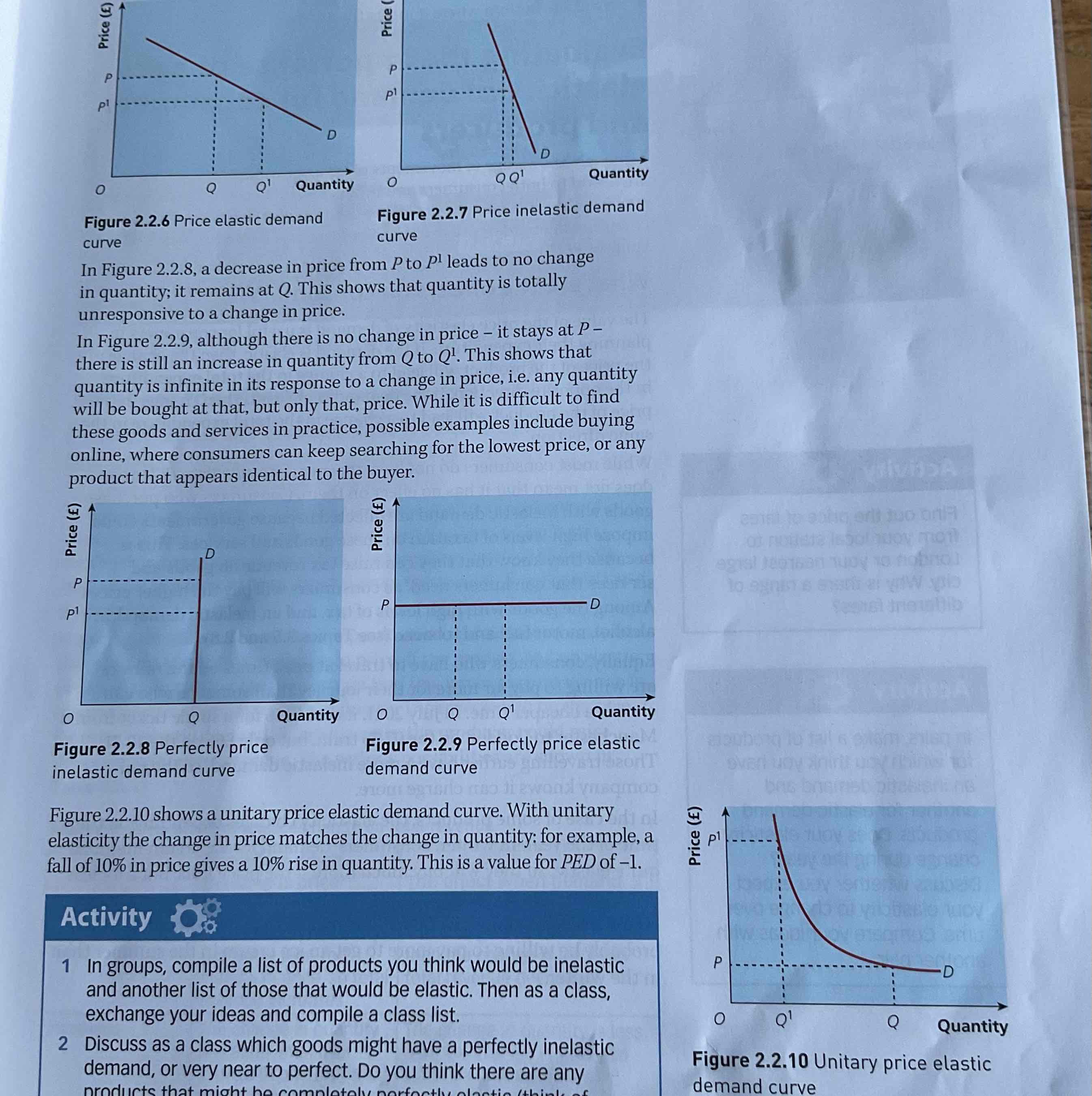
What are the graphs for all the PED’s
What is the PED formula
PED = %change in quantity demanded
%change in price
What are the effects of PED on both consumers and producers?
Consumers: allows consumers to plan their expenditure depending on the PES, if inelastic for example, producers know they can charge more to the consumers.
Producers: they can use PED to increase their total revenue, if elastic PES, producers know to decrease their prices.
What is unitary demand
When the percentage change in quantity is the same as the percentage change in price