Module 3: Endocrine System (Intro and Pituitary Gland)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
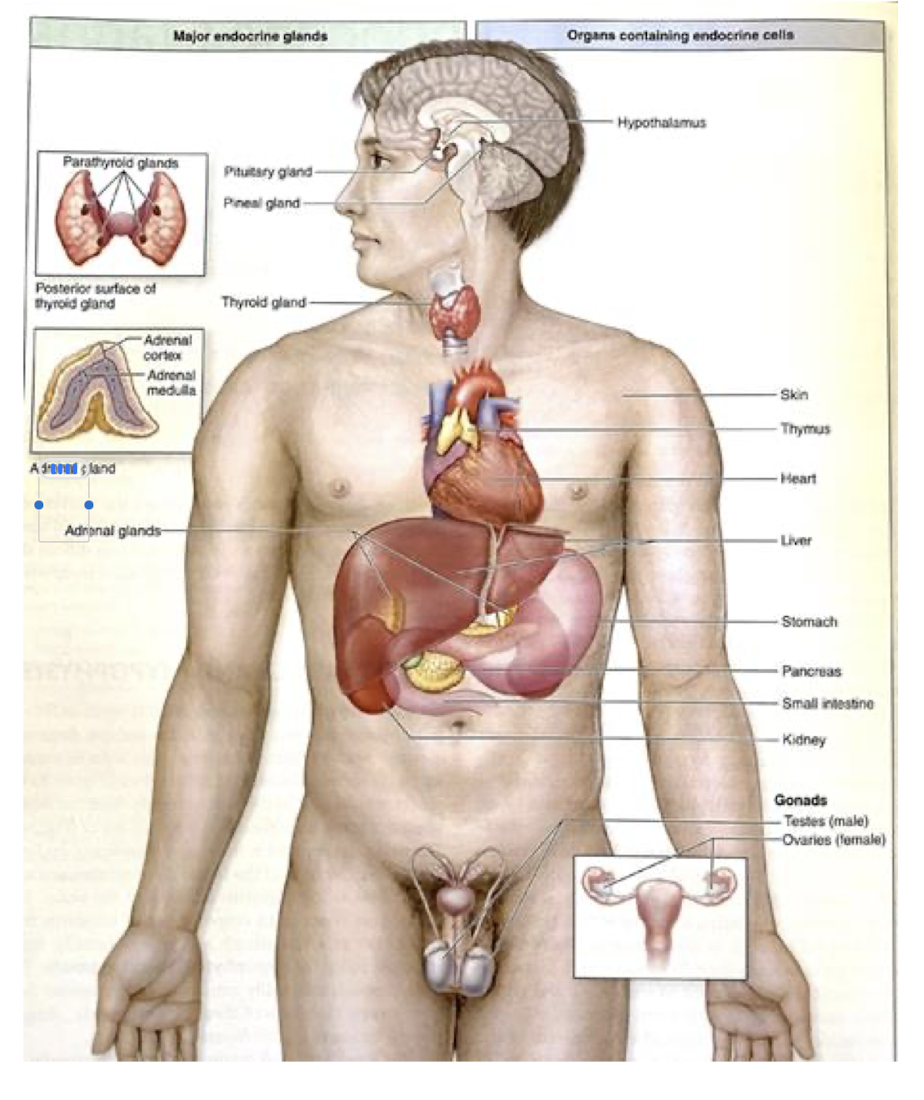
Endocrine System:
Exocrine glands have ___
Endocrine glands present as what?
What does in secrete into the bloodstream?
Exocrine: Ducts
Endocrine: Cell Clusters
Secrete Hormones
Endocrine System:
T/F: Tissue are NOT considered Endocrine Glands even though they may have Endocrine Function
Heart, Thymus, Gut, Kidney, Adipocytes
True
Endocrine Dysfunction: General S/S
What are considered SYSTEMIC S/S? (Pt 1 - 6)
Polydipsia
Excessive Thirst
Growth Dysfunction
Skin Pigmentation
Dark Spots @ Neck, Armpits, Antecubital Fossa, Knees
Skin Tags (@ Neck)
Polyuria
Excessive Urination
Frequent Hypoglycemia/Sugar Cravings
Endocrine Dysfunction: General S/S
What are considered SYSTEMIC S/S? (Pt 2- 5)
Increased Vitals
Gair Loss/Thinning
Brittle Nails
Nervousness/Anxiety
Dysmenorrhea
Endocrine Dysfunction: General S/S
WHat are considered NEUROMUSCULAR S/S? (7)
Muscle Weakness
Periarthritis
Myalgia
Arthralgia (General Stiffness)
OA
Muscle Atrophy
Frozen Shoulder
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland:
Embryology means partially formed by what?
Brain and Oral Cavity
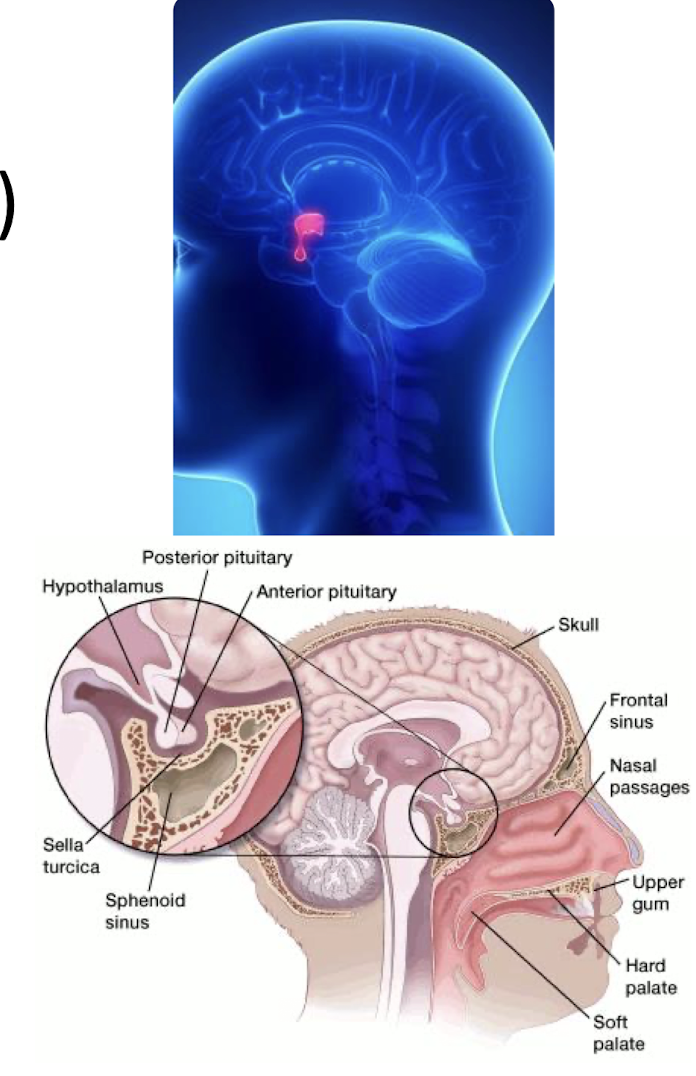
Anterior Pituitary Gland:
____ connections via what Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal _____ system
Synthesizes what?
Vascular Connections VIA Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal Portal System
Synthesizes its own 6 hormones
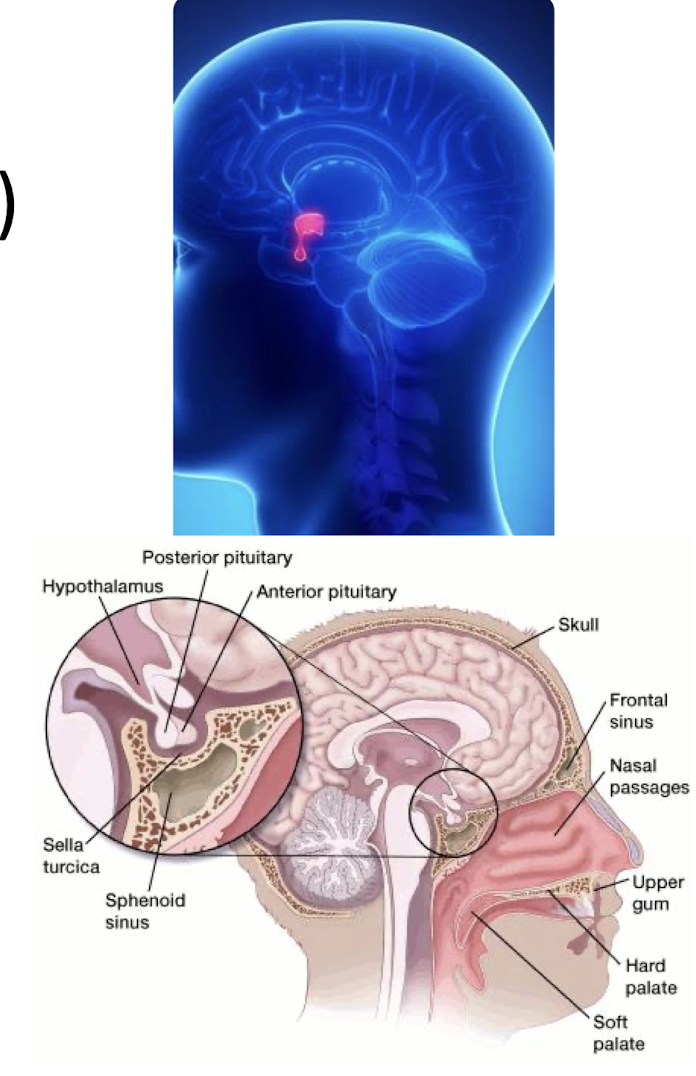
Posterior Pituitary Gland:
____ connections via Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal ____ through Infundibulum to Hypothalamus
Storage/release site of ___ hormones synthesized where?
Neural connections VIA Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal Tract
2; Hypothalamus
Anterior Pituitary Gland:
What are the 6 main hormones secreted by the Anterior Pituitary Gland?
Prolactin
Human Growth Hormone
Adrenocortictropin (ACTH)
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Luteinizing Hormone
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Prolactin:
Stimulates production of what after childbirth
Affects sex hormone levels from what organs:
Men:
Women:
Also affects what?
Breast Milk Production
Affects Sex Hormones
Men: Testes
Women: Ovaries
Affects Fertility
Human Growth Hormone:
Stimulates what in childhood?
Is important for maintaining what 2 things in adulthood?
In adults, GH is important for maintaining what? (2)
Also affects distribution of what in the body?
Growth
Maintaining Healthy Body Composition and Well-Being in adults
Maintaining Muscle and Bone Mass
Fat Distribution
Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH):
Stimulates the production of what by what gland?
Cortisol by Adrenal Gland
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH):
Stimulates what gland to produce what hormones?
Thyroid Gland to produce Thyroid Hormones
Luteinizing Hormone:
Stimulates production of what hormone in MEN?
Stimulates the release of what in WOMEN?
Men: Testosterone Hormone production
Women: Egg Release (Ovulation)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH):
Promotes production of what in MEN?
Stimulates ____ to produce and develop what in WOMEN?
Men: Sperm Production
Women:
Stimulates Ovaries
Produce Estrogen
Develop Eggs
Posterior Pituitary Gland:
Secretory neurons w cell bodies in the ____ produce hormones which are stored in the ____ until a nerve impulse stimulates relase and subsequent capillary ____
Hypothalamus
Axons
Uptake
Posterior Pituitary Gland:
What are the 2 hormones released by the Posterior Pituitary Gland?
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
AKA Vasopressin
Oxytocin
Antidiuretic Hormone (Vasopressin):
Retains water by increasing what?
Reuptake in the Kidneys
Oxytocin:
Stimulates what during labor?
Stimulates secretion of what from Mammillary Glands?
This secretion is induced by what?
Also produces what type of bonding?
Uterine Contraction
Breast Milk Secretion
Induced by Infant Sucking and Crying
Pair Bonding (Baby and Mom bonding post labor)
Benign Pituitary Adenoma:
Acromegaly/Giantism =
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency =
Cushing’s Syndrome =
Diabetes Insipidus =
___pituitarism
Acromegaly/Giantism = Excess GH
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency = Insufficient GH
Cushing’s Syndrome = Excess Cortisol
Diabetes Insipidus = ADH
___pituitarism = HYPOpituitarism
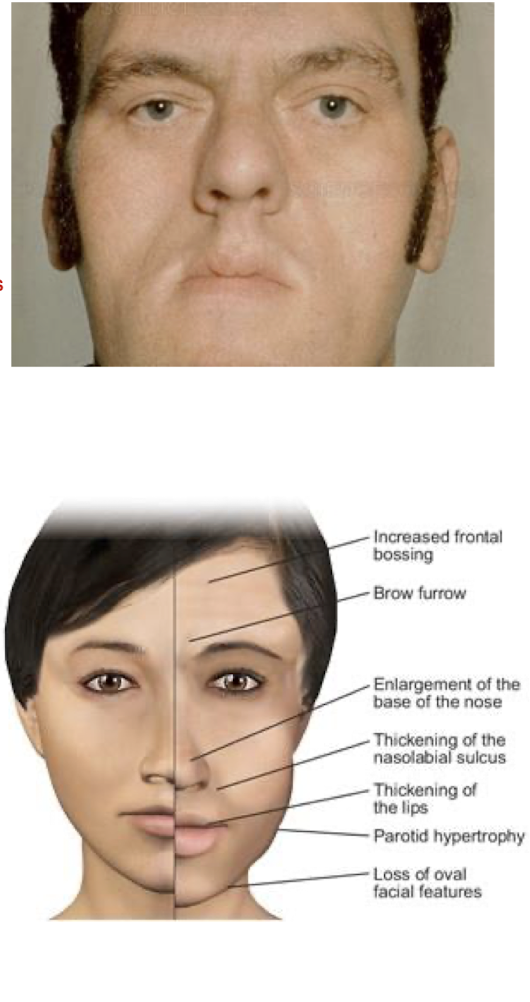
Excess GH:
“Giantism” occurs when?
“Acromegaly” occurs when?
G = Childhood BEFORE closure of growth plates
A = Adulthood AFTER closure of growth plates
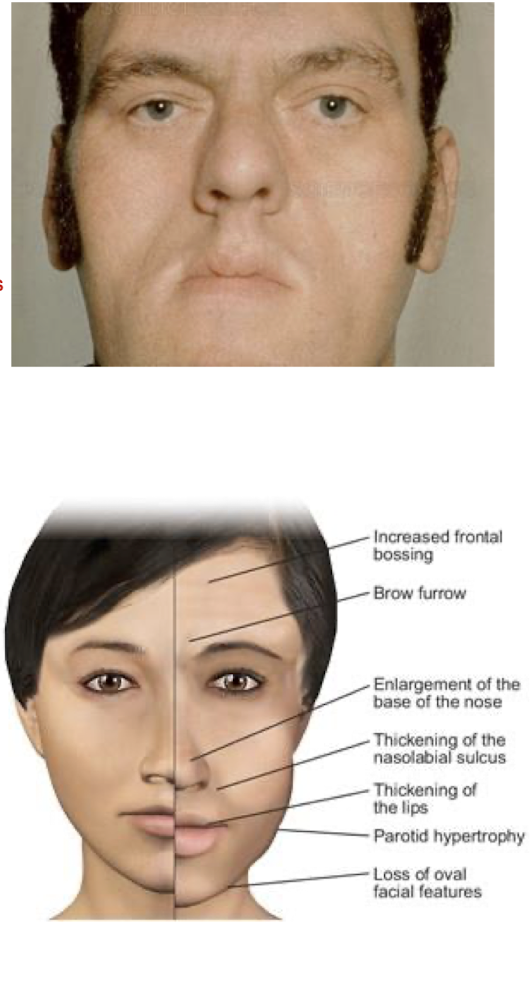
Excess GH:
What physical characteristics occur for people w Excessive GH? (6)
Enlarged lips, nose, tongue, pores
Deepened forehead creases
Deep Voice
due to enlarged vocal cords and sinuses
Thick, coarse, oily skin w Psoriasis, Hyperhydrosis, Skin Odor
Skin Tags
Tiny projections on the skin
HA, Fatigue, Weakness, Achy Joints
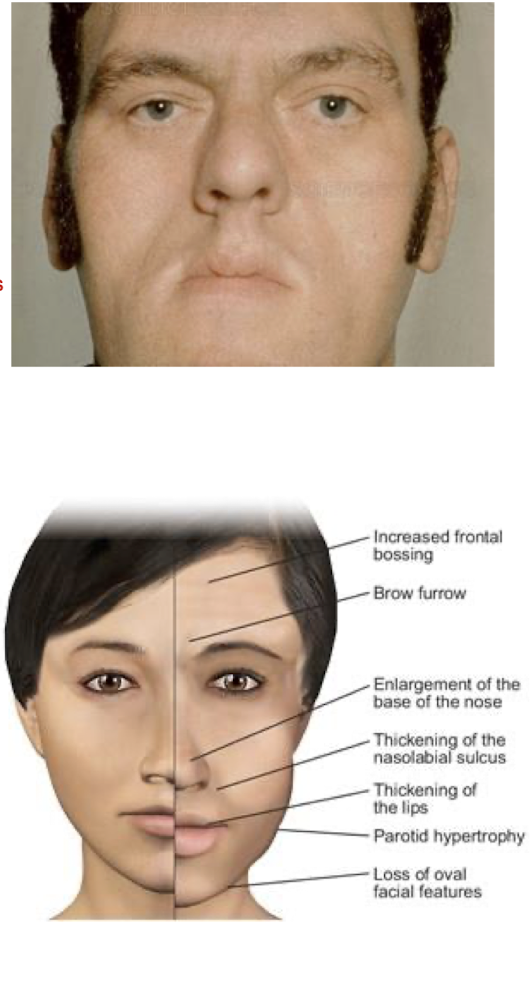
Excess GH:
How does Excess GH affect:
Men:
Women:
Overall:
Men:
Erectile Dysfunction
Women:
Disruption of Menstrual Cycle
Breast Discharge (sometimes)
Overall:
Diminished Libido
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency:
What can cause Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency?
Damage to Pituitary Gland from Tumor or Side Effects of tx of Tumor
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency:
Cause INCREASE: (4)
Increase: (4)
Central Adipose
LDL Levels
Sensitivity to Cold or Heat
Fx rates in Middle + age
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency:
Cause DECREASE (4)
Decrease: (4)
Lean Body Mass
Muscle/Protein Deficiency
Strength, Stamina, Exercise Capacity
Bone Density
HDL Levels
QOL
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency:
Cause EXCESSIVE: (4)
Excessive:
Tiredness
Anxiety
Depression
Social Isolation
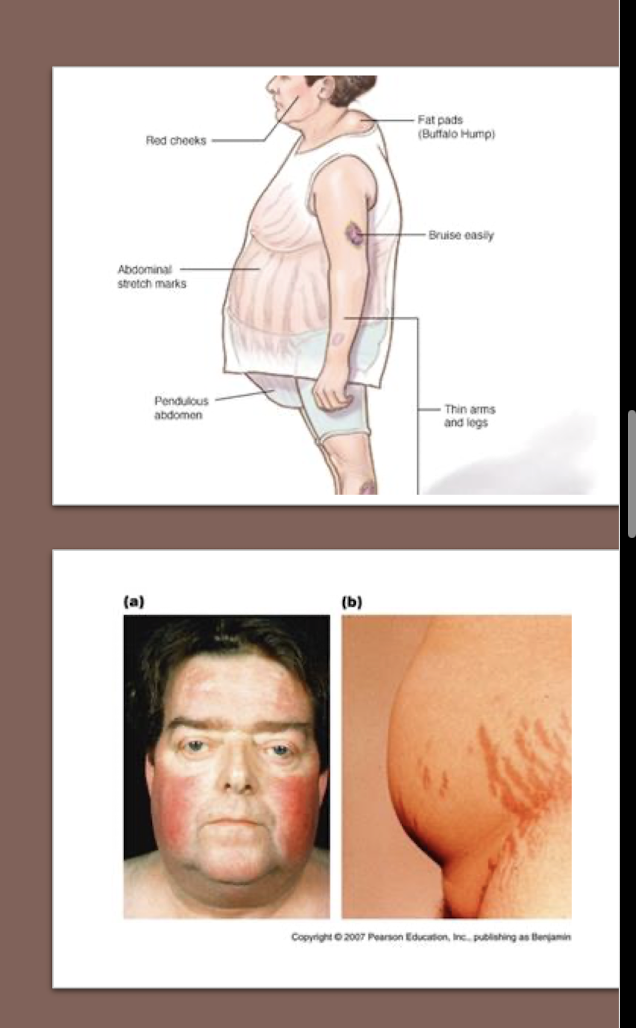
Cushing’ s Disease/Syndrome:
When does Cushing’s SYNDROME occur?
When does Cushing’s DISEASE occur?
Conditions associated with (2)
Syndrome:
Excess Cortisol Levels
If it originates ANYWHERE else
Disease:
Source of the problem is the PITUITARY GLAND itself
Benign Pituitary Adenoma
Increases ACTH
Pituitary Hyperplasia
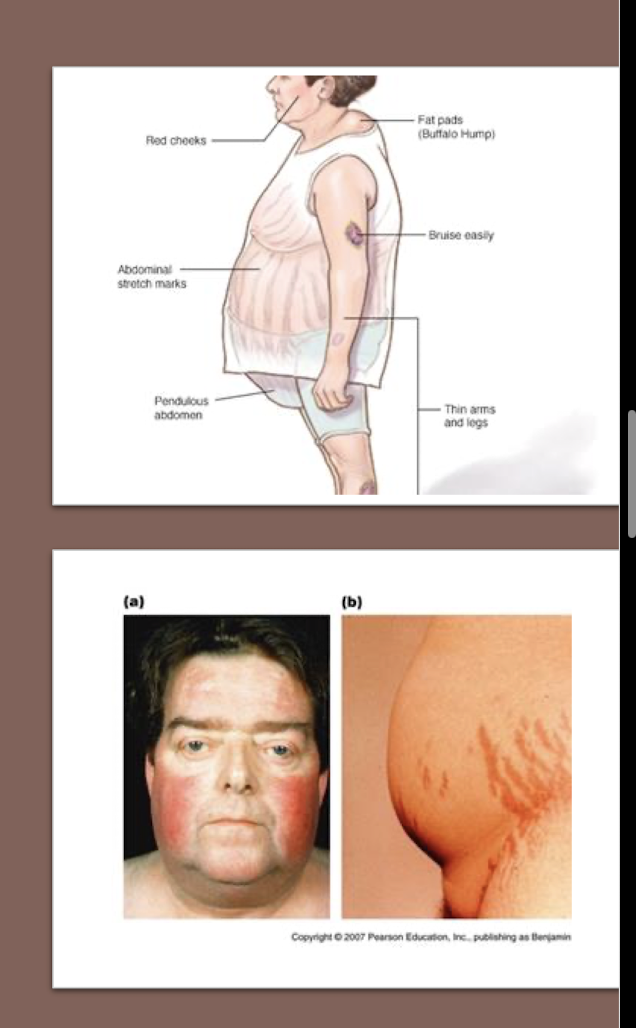
Cushing’s Syndrome:
Long-term use of what?
What medication to use for Anti-Inflammation?
Name of Drug?
Less commonly,
___ ___ is used for Joint Pain
___ for Eczema
Long Term use of Cortisol-Like Rx:
Oral Corticosteroids
Prednisone
Less Commonly
Corticosteroid Injection = Jt Pn
Topical = Eczema
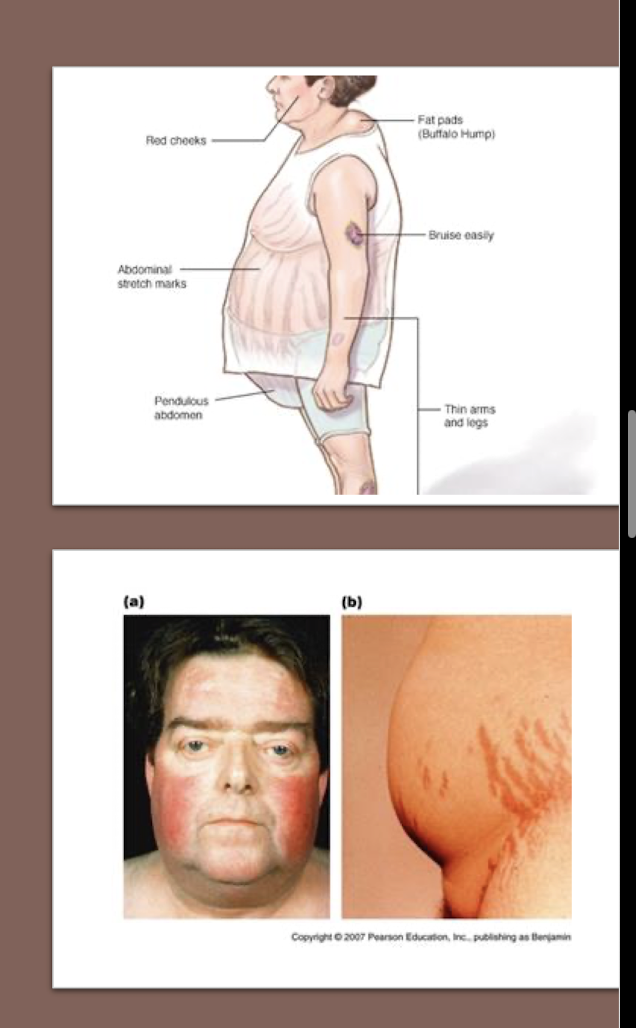
Cushing’s Syndrome:
What are 3 conditions associated with Cushing’s Syndrome?
Benign Adrenal Adenoma
Too much Cortisol from Adrenal Gland
Non-Pituitary Tumors producing ACTH
Family Cushing’s
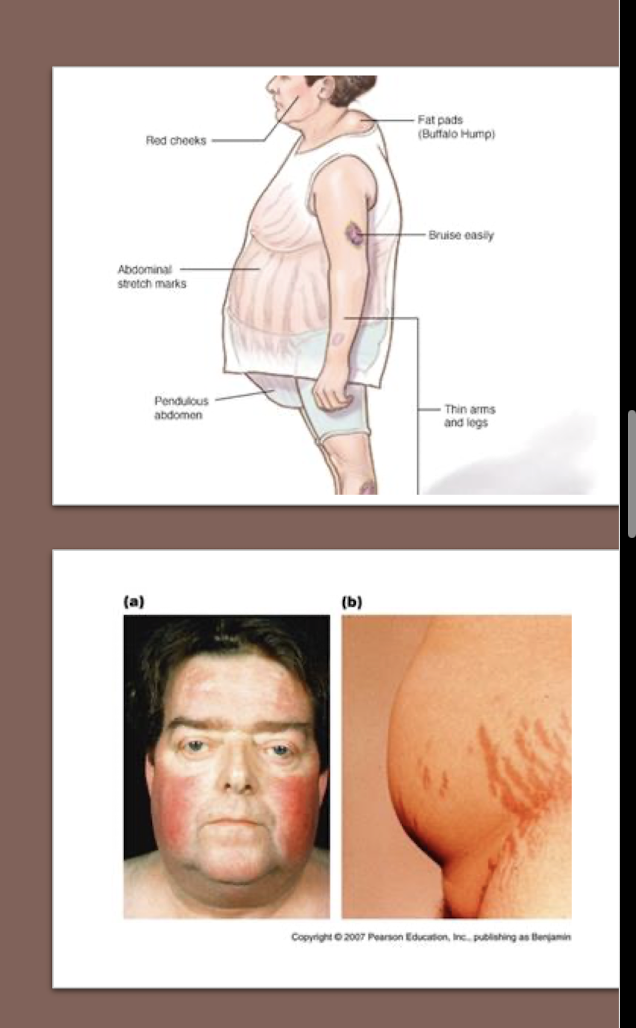
Cushing’s Syndrome:
Gender:
Age:
MC Symptom:
Excessive/Sudden weight gain where?
Gender: W > M
Age: 30-40 years
Moon Face
Face rounded and red
Around Trunk (GI distress)
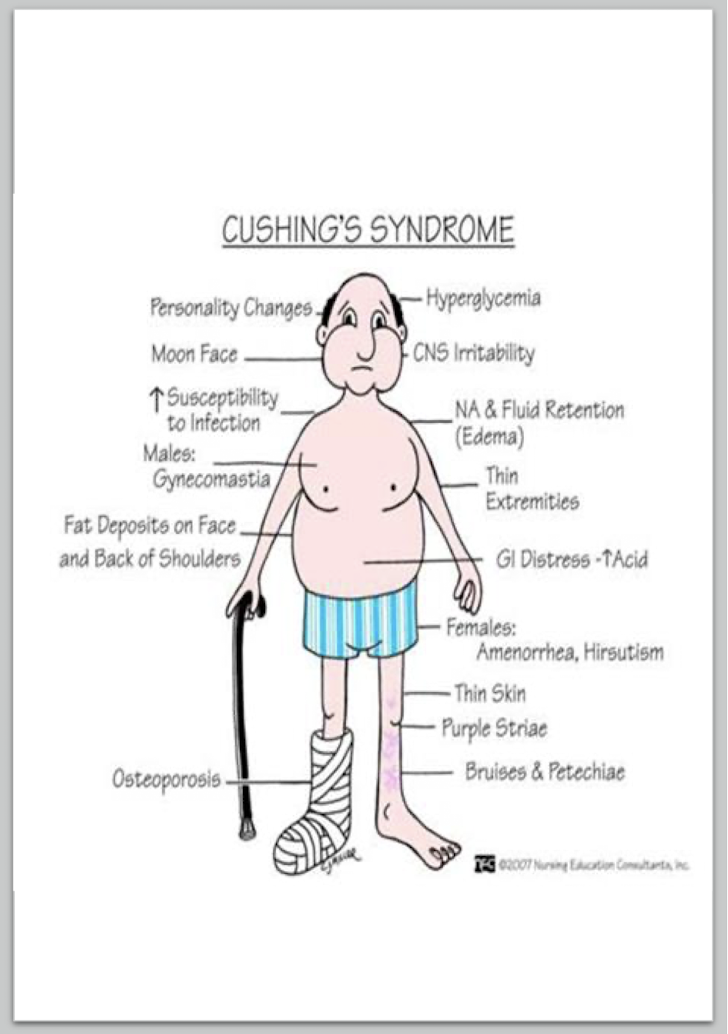
Cushing’s Syndrome:
6 Other Symptoms:
Edema
Weak Muscles (ESPECIALLY LE)
Weak Bones
Susceptible to Fx
Bruise easily, thin skin, red/purple stretch marks (Striae)
Irregular Menstrual Periods, Hirsutism
Mood swings, brain fog, poor concentration/memory loss
Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
DI is a problem with production or action of what hormone?
Lack of __ __ leading to excessive thirst and urination
How is DI an EMERGENCY?
ADH/Vasopressin
Lack of Fluid Retention
EMERGENCY
Will succumb to SEVER DEHYDRATION if left untreated = ER
DI:
Central DI is related to damage of what structures from Sx, Tumor, Virus, or Head Injury
Nephrogenic DI:
Related to what disease?
Can cause side effects from what 2 drugs?
Central DI:
Pituitary Gland
OR
Hypothalamus
Nephrogenic DI:
Genetic Chronic Kidney Disease
Drugs
Lithium (Bipolar)
Foscarnet (Antiviral)
DI:
Gestation DI is related to what?
Idiopathic DI probably has ____ implications
Gastro:
RARE
Placental Enzyme destroys ADH
Idio:
Autoimmune
Hypopituitarism:
Main Symptoms (Pt 1 - 6)
Excessive tiredness, decreased energy
Muscle weakness
Reduced body hair
Decreased libido
Weight gain
Increase sensitivity to temp
Hypopituitarism:
Main Symptoms (Pt 2 - 6)
Constipation
Dry Skin
Pale Appearance
Low BP, HA, Dizziness
Vision Disturbance
DI
Hypopituitarism:
Symptoms specific to:
Males:
Females:
M: Erectile Dysfunction
F: Irregular Periods