Comp Net Question 1
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
Where/why is it required ?(5 marks)
Used in half-duplex Ethernet LANs to manage how devices share the same transmission medium.
Before sending data, each device listens to check if the channel is free.
If two devices transmit at the same time, a collision occurs and both transmissions are corrupted.
The devices detect the collision, stop transmitting, wait a random time, and try again.
What layer of OSI does CSMA/CD operate (1 mark)
Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model.
Hardware and software are required to configure. a new managed switch/router for the network
How can the initial connection be made?
What is this type of access called? (4 marks)
A console cable and a computer with terminal software (e.g. PuTTY or Tera Term)
Computer connects directly to the console port on the device using the cable.
Allows access to the device’s CLI (Command Line Interface) for initial setup before network connectivity exists.
Called out-of-band management (uses separate path from the network traffic).
Explain Fault Tolerance (2.5 marks)
Limits the impact of failures by ensuring only a small number of devices are affected.
Multiple network paths are required so traffic can reroute if one path fails.
Packet switching allows packets to take different paths across the network, unlike circuit-switched networks.
Explain Scalability (2.5 marks)
Can grow quickly without reducing performance for current users.
Designers follow industry standards to make upgrades and expansions smooth and compatible.
Explain Quality of Service (2.5 marks)
Ensures reliable delivery of different types of data, like video, voice, and regular traffic.
Routers manage data flow using this setting to prioritise time-sensitive traffic (e.g., VoIP).
Explain Security (2.5 marks)
Two main areas: infrastructure security (physical + software access control) and information security (protecting data).
Goals: confidentiality (prevent access), integrity (no tampering), and availability (always accessible to users).
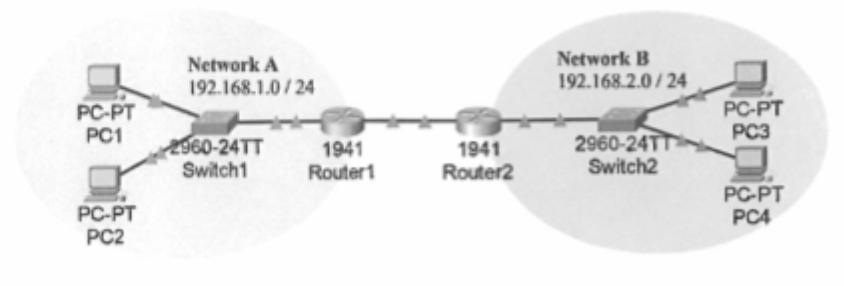
Explain the issue with “far-away” or remote networks that must be considered with multiple routers (4 marks)
Routers only know directly connected networks – they can't automatically reach distant ones ie. 192.168.2.0 to Network A.
Need manual routing – if no route to the destination, packets won’t be delivered.
Multiple routers = multiple paths- must consider where to forward traffic next.
No routing = communication fails- PC1/PC2 can't reach PC3/PC4 without correct routing info.
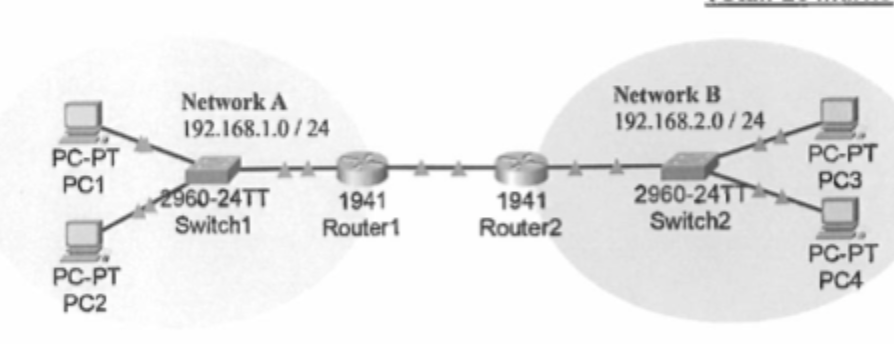
Explain what extra configuration R1 and R2 needs, other than IP address on each interface for successful communication between PC1/ PC2 and PC3/PC4 (4 marks)
Set up routing – Use static routes or a protocol like RIP/OSPF so R1 knows 192.168.2.0 and R2 knows 192.168.1.0.
Enable IP routing – Run IP routing on both routers to allow packet forwarding.
Set correct gateways – PC1/PC2 use R1 as gateway; PC3/PC4 use R2.
Check router link – Make sure the connection between R1 and R2 is up and working.
What is segmentation?
Why is it required (7 marks)
Divides large data into smaller chunks – makes transmission manageable across the network.
Adds headers to each segment – used for tracking, ordering, and reassembly at the receiver.
Supports reliable delivery – lost/ out-of-order segments can be detected + corrected.
Enables multiplexing – multiple applications can use the network at the same time.
Improves efficiency – smaller segments are easier to route/ less likely to be dropped.
Facilitates compatibility with lower layers – adapts data for transport by the network and data link layers. Essential for end-to-end communication – ensures complet/e, accurate delivery from sender to receiver.
What is the purpose of Time-to-Live.
How is it used by commands such as traceroute or ping to identify paths across a network (5 marks)
Limits how long a packet can travel through a network.
Each router reduces TTL by 1 before forwarding the packet.
If it reaches 0, the router discards the packet to prevent infinite loops.
That router sends back an ICMP "Time Exceeded" message to the sender.
Use: To discover the path of routers (hops) by sending packets with gradually increasing TTL values.
What is a Virtual LAN?
Give examples where it could be used in an organisation (5 marks)
Way to split a physical network into separate, logical networks.
Devices in the same one can communicate as if they’re on the same network, even if they’re on different switches.
Improves security and traffic management by isolating departments or groups.
E.g 1: HR dep on VLAN 10 and Finance on VLAN 20, to keep data separate.
Example 2: A school might create VLANs for staff, students, and guests, so each group has different access rights.
Difference between “in-band” and out-of-band”
Uses
Hardware/Software required (8 marks)
