Chemistry Chapter 6
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Periodic law
States there is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of elements arranged by increasing atomic number
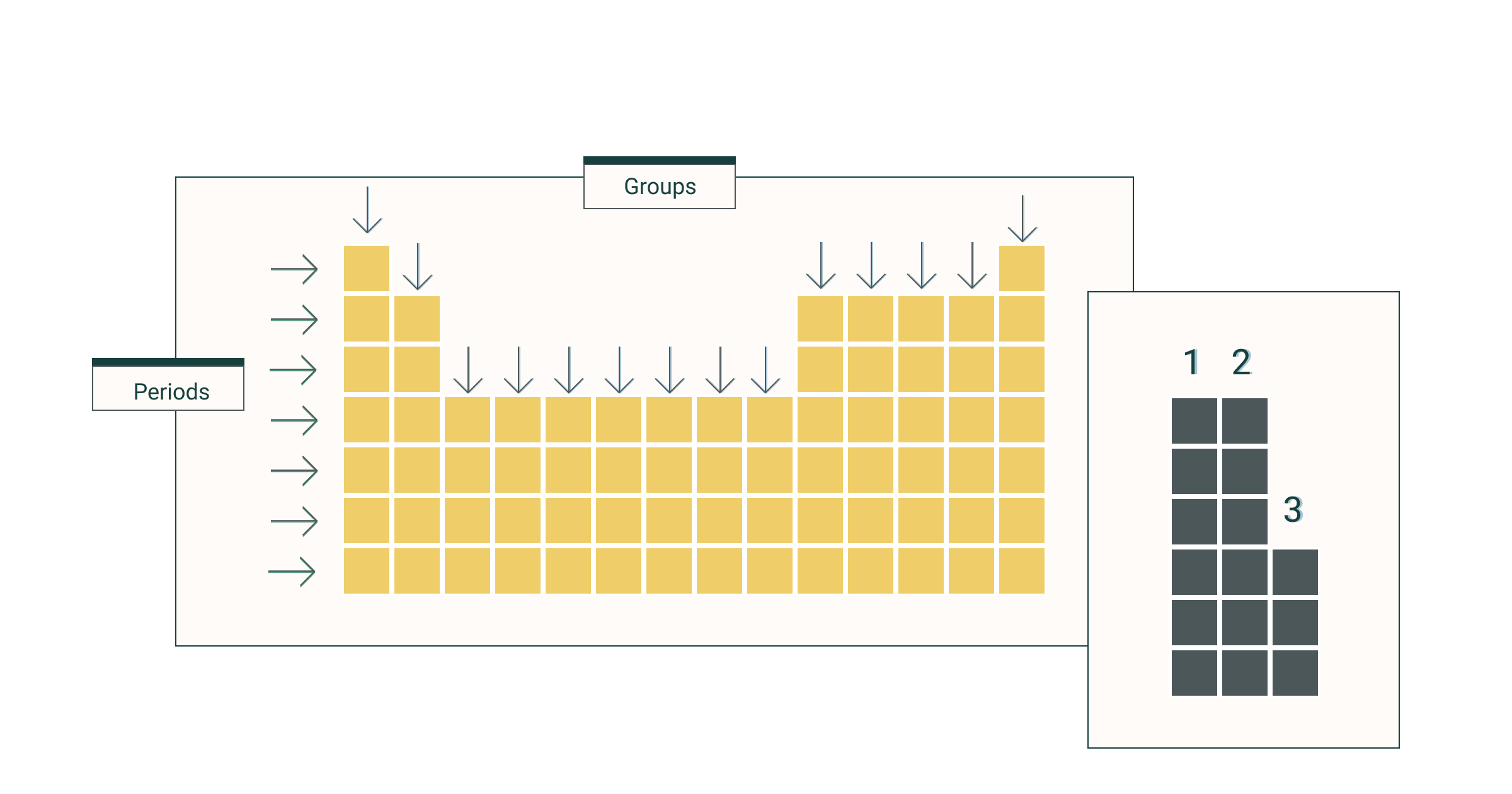
Period
the horizontal rows in the periodic table
Group
the vertical columns on the periodic table
Representative elements
elements with a wide range of chemical and physical properties
Representative element groups
Groups 1, 2, 13 - 18
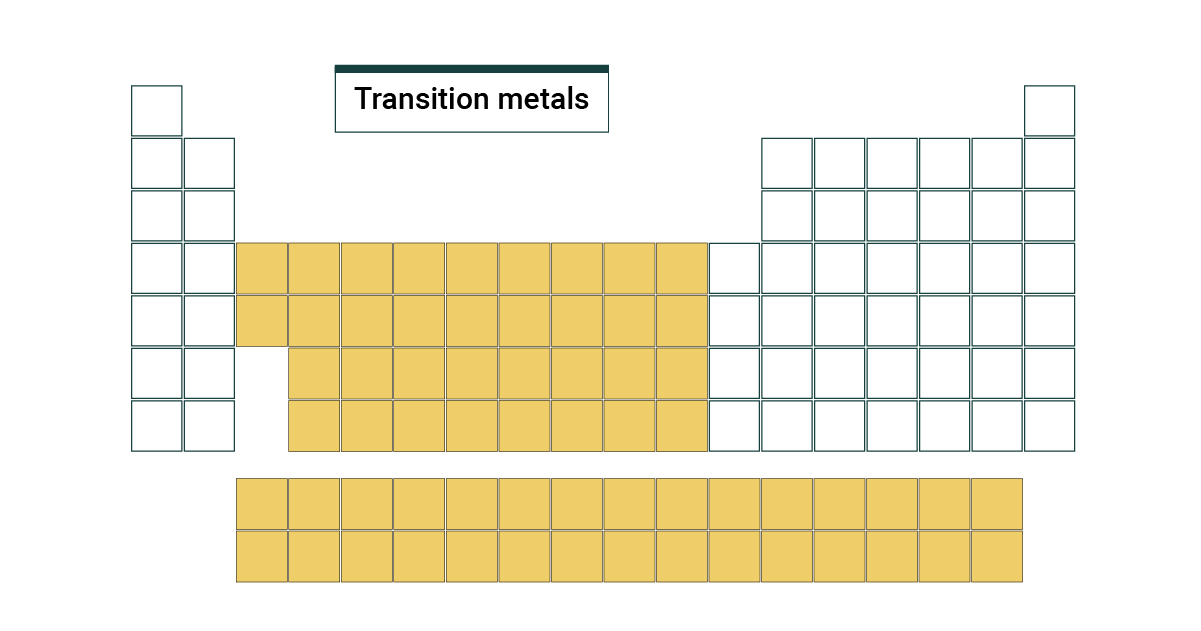
Transition elements groups
Groups 3-12
Metals
conductors of heat and electricity,
Alkali metals
metal group 1 on the periodic table; highly reactive, usually exists as a compound
(Ex. Sodium/Na, Lithium/Li)
Alkaline earth metals
metal group 2 on the periodic table; highly reactive
(Ex. Calcium/Ca, Magnesium/Mg)
Inner transition elements
made of two set groups: lanthanide and actinide
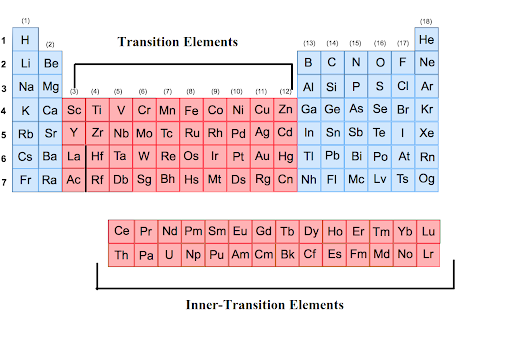
Lanthanide
located at the bottom of the periodic table, these elements emit light when struck by electrons
Actinide
located at the bottom of the periodic table, these elements are strong but light
Nonmetals
elements that are not metals (duh), they are typically gasses or dull-looking solids; they are poor conductors of heat and energy
Halogens
group 17 on the periodic table; highly reactive and are often part of compounds
Noble gases
group 18 on the periodic table; extremely nonreactive
Metalloids (semimetals)
elements with physical and chemical properties of both metals and nonmetals (Zig-Zag)
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge
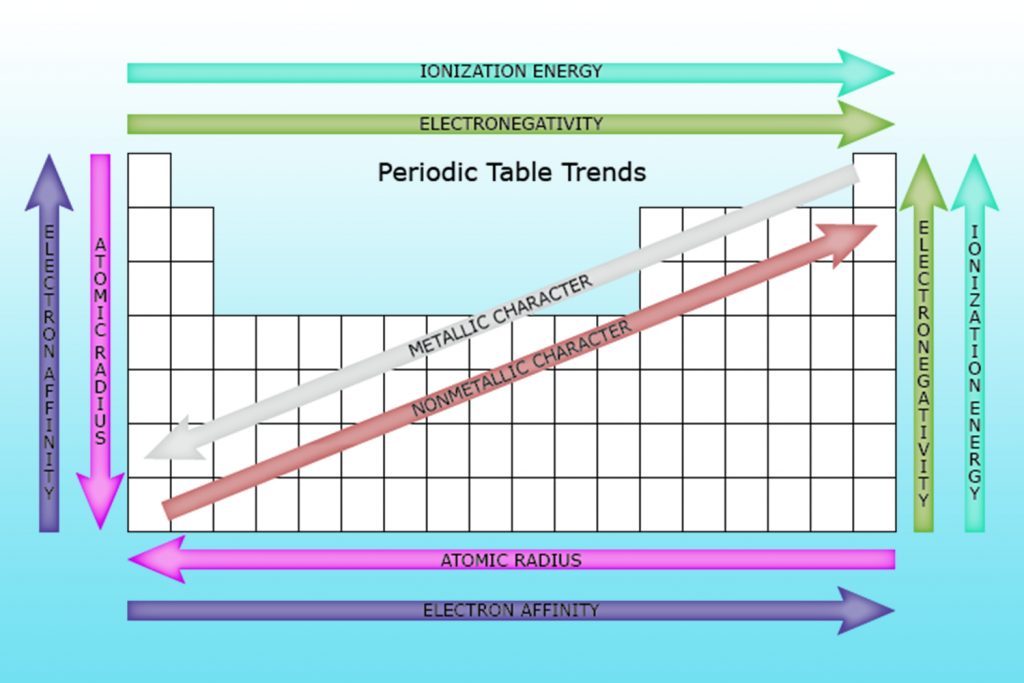
Ionization energy
the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state
Octet rule
states atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a set of 8 valence electrons
Electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a chemical bond
Ionization energy… (trend)
ionization energy increases right, decreases down
electronegativity… (trend)
electronegativity increases until right before group 18, decreases down
atomic radii… (trend)
atomic radii decreases right, increases down
positive ionic radii…
positive ionic radii decreases right, resets at group 13, and continues to decrease; increases down
atomic and ionic radii…
atomic and ionic radii increase going down