8. Intro and Neurolocalizing in the Brain
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1/15/2026; Dr. Sullivan
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
a neuron completely in the CNS that influences the actions of other neurons
upper motor neuron
a neuron with its NCB in the CNS and axon in the periphery
Lower motor neuron
describe LMN signs
decreased tone, decreased reflexes
describe UMN signs
increased tone, normal to increased reflexes
what are the most reliable spinal reflexes? (4)
-explain what should happen when testing each reflex
Patellar: tap patellar tendon, look for extension of stifle
Withdrawal: pinch toe, look for flexion of carpus, elbow, shoulder or hock, stifle
Perineal: observe anal tone, stimulate perineal region, look for contraction of anus and downward movement of tail
Cutaneous trunci: pinch skin over epaxial mm, look for bilateral twitch of skin over trunk
where are seizures localized to?
forebrain (ALWAYS)
problem: dull mentation
possible neurolocalization: _______
forebrain or brainstem
problem: circling to the right
possible neurolocalization: ___________
right forebrain or right vestibular
problem: left sided postural reaction deficits
possible neurolocalization: ___________
right forebrain, left brain stem, left spinal cord
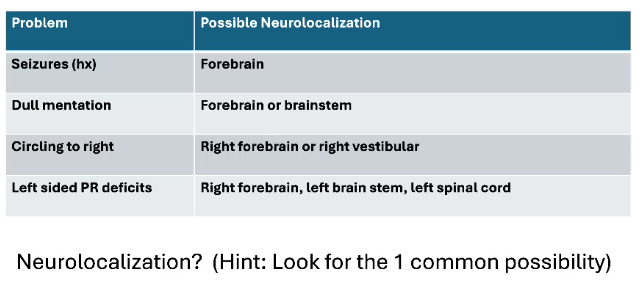
What could be the 1 common possibility for neurolocalization of this lesion
Right Forebrain
describe the functions of the forebrain
alertness
contralateral processing/interpreting sensory information, decision making
forming motor plans
behavior / personality
what makes up the forebrain (2)
cerebrum and diencephalon
what cranial nerves are in the forebrain?
1 (olfactory)
2 (optic)
describe decerebrate posture
laterally recumbent, extension of head/neck & limbs, stupor to coma, grave prognosis
a patient with a forebrain lesion will circle _____ (toward/away) from the lesion
toward the lesion
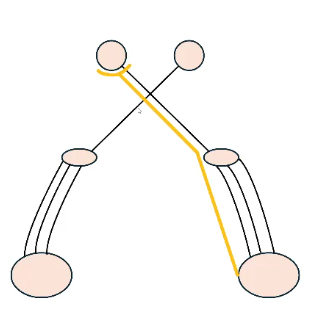
name this neurolocalization test
Menace response
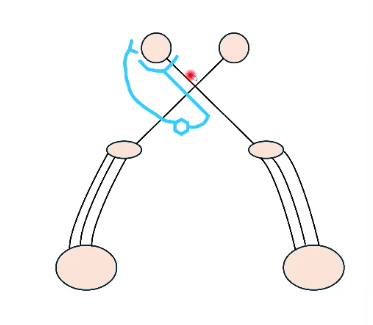
name this neurolocalization test
pupillary light reflex
what is the brainstem comprised of? (3)
midbrain, pons, medulla
what are the functions of the brainstem? (list 4 things)
alertness
ipsilateral motor pathways
ipsilateral sensory pathways
respiration
what cranial nerves are in the brainstem?
-what do these nerves do?
•III, IV, VI Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducens- ocular and pupil movements
•V Trigeminal- motor to mm. of mastication, sensory to face
•VII Facial- motor to mm. of facial expression, exocrine glands (tears), taste
•VIII Vestibulocochlear- hearing, balance
•IX, X, XII Glossopharyngeal, Vagus, Hypoglossal- tongue movements, gag reflex, taste, PS control of heart and gut, laryngeal function
•XI Spinal accessory “the nerve that got lost”- neck muscles
what are the functions of the cerebellum? (2)
smooths and fine tunes movement
coordination and balance
what cranial nerves are in the cerebellum?
none
however, central portions of vestibular system are in cerebellum (and brainstem)
coordination of the blink happens in cerebellum
where does (what portion of the brain) coordination of the blink happen?
cerebellum
describe decerebellate posture.
laterally recumbent, extended head/neck & thoracic limbs, neutral pelvic limbs, normal mentation; prognosis ok
the vestibular system is located within _______
inner ear, brainstem and cerebellum
persistent vertical nystagmus is only seen in _____ (central/peripheral) vestibular lesions
central
Horner’s syndrome is a sign of ______ (centr al/peripheral) vestibular dysfunction
peripheral
is this central or peripheral?
mentally dull
listing to the right
head tilt to the right
horizontal nystagmus, fp to L
decreased R facial sensation
*Determine the overall localization
mentally dull = forebrain or brainstem
listing to the right = R vestibular, central or peripheral
head tilt to the right = R vestibular, central or peripheral
horizontal nystagmus, fast phase to L = R vestibular, central or peripheral
decreased R facial sensation = Right trigeminal nerve or brainstem
SO overall localization = Right central vestibular
paradoxical vestibular is a subcategory of ______ (central/peripheral) vestibular
central
case: determine the neurolocalization
dull mentation
R postural reaction deficits
L head tilt
horizontal nystagmus, fast phase R
dull mentation = Forebrain or brainstem
R postural reaction deficits = L forebrain, R brainstem or cord
L head tilt = L vestibular, central or peripheral
horizontal nystagmus, fast phase R = L vestibular, central or peripheral
So, overall = Right Paradoxical (central) vestibular