9.1 Signaling molecules and cellular receptors
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology 1230
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a ligand?
A molecule that binds another specific molecule and is a signaling molecule
What do ligands interact with?
the proteins inside target cells
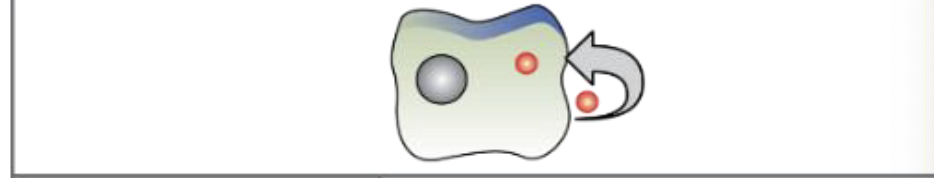
What chemical signaling is this?
Autocrine signaling
What is autocrine signaling?
The signaling cell and the target cell can be the same or similar
Produced by signaling cells that bind to the ligand that’s released
Occurs during the early development of cells
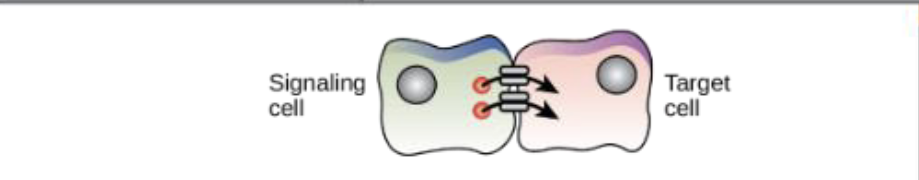
What chemical signaling is this?
Direct signaling across gap junctions
What is direct signaling across gap junctions?
Intracellular mediators that allow small signaling molecules to move between cells
A cell targets a cell connected by gap junctions
Rapid signaling but channels are specific
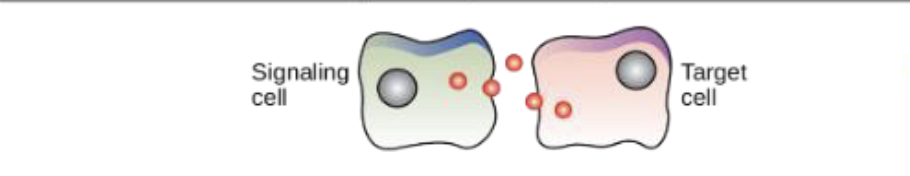
What chemical signaling is this?
Paracrine signaling
What is paracrine signaling?
Signals move by diffusion through the extracellular matrix
quick responses that last a short time
When cells are nearby, the signaling cell will target the nearby cell
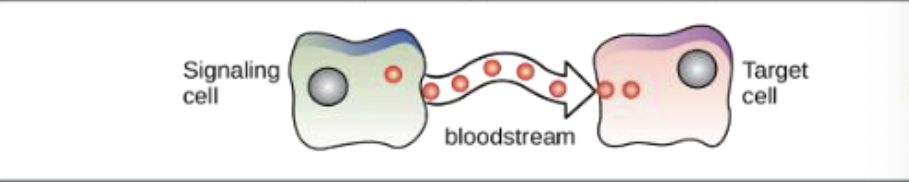
What chemical signaling is this?
Endocrine signaling
What is endocrine signaling?
Has a slower response with a long lasting effect
Hormones travel long distances through the bloodstream to the target cell
What is an example of paracrine signaling?
The transfer of signals across a synapses between nerve cells since the distance between presynaptic cell and postsynaptic cell is small allowing rapid diffusion
What are receptors?
Protein molecules in the target cell or on the surface to bind the ligand
What are internal receptors?
Also called intracellular or cytoplasmic receptors
Found in the cytoplasm of the cell
Respond to hydrophobic ligand molecules
What are ion channel linked receptors?
The receptor is also an ion channel and binds to a ligand and opens a channel in the plasma membrane allowing specific ions to pass through
What is a G-protein linked receptor?
When the ligand binds with the G-protein, it causes the GDP to be swapped out with a GTP. The subunits of the G protein are then split into an alpha, beta/gamma subunit. The GTP is then hydrolyzed to GDP
What is an enzyme linked receptor?
When a ligand binds to the receptor, it causes the two halves of tyrosine kinase protein to come together creating a dimer
What are internal receptors?
Are proteins that diffuse across the plasma membrane and interact with intracellular receptors in the cytoplasm
Cell surface receptors use hydrophilic ligands while internal receptors use hydrophobic ligands