Skills Lab Midterm Exam (Weeks 1-6)
1/190
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
CrCl → Cockcroft-Gault Equation (male)
CrCl = (140 - Age) x Weight in kg / 72 x SCr
CrCl → Cockcroft-Gault Equation (female)
CrCl = 0.85 x [(140 - Age) x Weight in kg / 72 x SCr]
In the Cockcroft-Gault equation, what will the SCr value be rounded to for a patient whose 65 years and older?
1.0
How to calculate IBWmale
IBW = 50kg + 2.3kg for each inch over 5 feet
How to calculate IBWfemale
IBW = 45.5kg + 2.3kg for each inch over 5 feet
How to calculate AdjBW
AdjBW = IBW + 0.4 (ABW - IBW)
How to calculate BMI
BMI = lbs / in2 (703)
When do you use ABW as the ‘Wt’ in CrCl equation?
When the patient’s BMI indicates underweight → BMI < 18.5
When do you use IBW as the ‘Wt’ in CrCl equation?
When the patient’s BMI indicates normal weight → BMI < 25
When do you use AdjBW as the ‘Wt’ in CrCl equation?
When the patient’s BMI indicates overweight/obesity → BMI >/ 25
What is a sphygmomanometer used for measuring?
BP
How to get an accurate BP reading
Empty bladder first (full bladder adds 10 mmHg)
Support back/feet (unsupported back/feet adds 6.5 mmHg)
Keep legs uncrossed (crossed legs add 2-8 mmHg)
Don’t have a conversation (talking or active listening adds 10 mmHg)
Put cuff on bare arm (cuff over clothing adds 5-50 mmHg)
Use correct cuff size (cuff too small adds 2-10 mmHg)
Support arm at heart level (unsupported arm adds 10 mmHg)
When should a patient have a follow-up when having their bp taken?
2 weeks (1 week if bp is abnormally high)
What factors will affect a bp reading when occurred within 30 minutes of taking bp?
Physical activity
Smoking (nicotine)
Caffeine
Stress
What does IPPA stand for?
Inspection
Palpation
Percussion
Auscultation
What is the main purpose of the pharmacist performing physical exams?
To evaluate and monitor drug therapy
Which of the following best describes systemic blood pressure?
a. Pressure in the arteries during cardiac relaxation
b. Pressure in the veins when the heart stops
c. Force of blood during cardiac contraction
d. Pressure different between arteries and veins
c. Force of blood during cardiac contraction
The auscultatory gap refers to:
a. The point when no sounds are heard because of equipment malfunction
b. The temporary disappearance of Korotkoff sounds during BP measurement
c. A difference between systolic and diastolic pressures
d. A silent pause caused by rapid cuff deflation
b. The temporary disappearance of Korotkoff sounds during BP measurement
When deflating the cuff during BP measurement, the first Korotkoff sound corresponds to:
a. Diastolic pressure
b. Mean arterial pressure
c. Systolic pressure
d. Pulse pressure
c. Systolic pressure
T/F: Palpation involves tapping on a surface to determine underlying structures.
False
That’s percussion; palpation involves touching/feeling
T/F: The cuff pressure must exceed brachial artery pressure to temporarily stop blood flow during BP measurement.
True
T/F: A true BP reading is recorded at the start of two consecutive beats.
True
The two main components of BP are ______ and _______.
Systolic; diastolic
The purpose of a SOAP note is to accurately document the patient’s Subjective, Objective, Assessment, and _______ data.
Plan
Pharmacists’ Patient Care Process: ‘Collect’
The pharmacist ensures the collection of necessary subjective and objective information about the patient to understand the relevant medication and medical history, overall health status, and other pertinent factors.
Information may be gathered and verified from multiple sources
Patient
Caregiver
Observations
Existing patient records
Health care professionals
Pharmacists’ Patient Care Process: ‘Assess’
The pharmacist assesses the collected information to identify and prioritize patient needs to inform the establishment of a care plan.
Pharmacists’ Patient Care Process: ‘Plan’
The pharmacist develops a person-centered, evidence-based, cost-conscious care plan in partnership with the patient and/or caregiver, and in coordination with other care team members.
Pharmacists’ Patient Care Process: ‘Implement’
In providing person-centered care, the pharmacist implements a prioritized care plan in partnership with the patient and/or caregiver and in coordination with other care team members.
Pharmacists’ Patient Care Process: ‘Follow Up: Monitor and Evaluate’
The pharmacist follows up to monitor and evaluate the implementation of the care plan and the patient’s overall health in collaboration with the patient, caregiver, and other care team members, as needed.
Sleuthing
Evaluate and monitor drug treatment
Identify drug-related problems
Resolve drug-related problems
Select the best drug-treatment option
What is blood pressure?
Force of blood as it pushes against the arterial walls
Dependent on 2 things:
Cardiac output
Resistance
Systolic pressure
Pressure during contraction
Diastolic pressure
Filling pressure
What do you hear when taking bp?
Air into cuff raises pressure in the cuff
Cuff pressure exceeds the pressure in the brachial artery; it’s compressed
Compression stops blood flow
As air is being deflated, cuff pressure decreases
Cuff pressure = arterial pressure = blood is flowing again
Checklist for Accurate ‘Office’ BP Measurement
The patient should avoid caffeine, exercise, and smoking for at least 30 min before measurement. Ensure the patient has emptied their bladder.
Use a blood pressure device that has been validated for accuracy.
Use the correct cuff size on a bare arm.
The patient’s arm should be supported at heart level.
Have the patient relax, sitting in a chair (feet on the floor, legs uncrossed, and back supported) for more than 5 min of rest.
Neither the patient nor the clinician should talk during the rest period or during the measurement. The patient should not be using their phone.
Blood pressure measurement should be taken in a temperature-controlled room.
Take 2 or more blood pressure measurements at least 1 min apart. Average the readings, and provide the patient their blood pressure readings both verbally and in writing.
Normal BP
Systolic: < 120 mmHg
AND
Diastolic: < 80 mmHg
Elevated BP
Systolic: 120-129 mmHg
AND
Diastolic: < 80 mmHg
High BP — HTN Stage 1
Systolic: 130-139 mmHg
OR
Diastolic: 80-89 mmHg
High BP — HTN Stage 2
Systolic: 140 mmHg or higher
OR
Diastolic: 90 mmHg or higher
High BP — Hypertensive Crisis (consult dr. immediately)
Systolic: > 180 mmHg
AND/OR
Diastolic: > 120 mmHg
How long after taking a patient’s bp should they have a follow-up?
2 weeks (1 week if bp is abnormally high)
Popliteal pulse
Below knee cap
Pedal pulse
Foot
Radial pulse
Wrist
Brachial pulse
Under bicep
Carotid pulse
Neck
In a SOAP note, how are medication lists written?
Drug (generic name), dose, ROA, frequency
Aspirin 81mg po daily
Albuterol 90mg MDI, inhale 1 puff po q4h prn
What abbreviations are inappropriate when describing medications in a SOAP note?
QD, SQ
When are medical terms use in a SOAP note’s objective section?
HPI → mix of medical terms and patient’s wording (e.g., “patient describes palpitations as heart racing out of chest”)
PMH
FH
Mitral valve
Allows blood to flow from left atrium to left ventricle
Aortic valve
Between left ventricle going out into the aorta
Tricuspid valve
Between right atrium and right ventricle
Pulmonic valve
Between right ventricle and pulmonary artery (where blood perfuses into lungs)
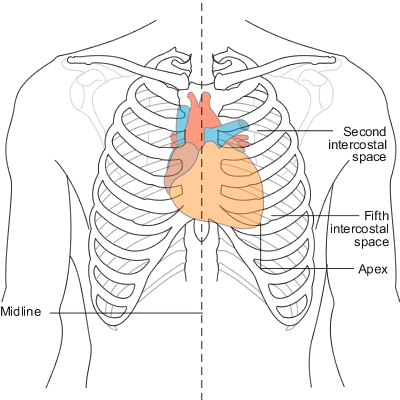
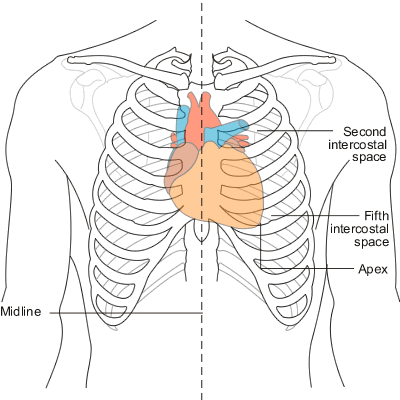
Where is PMI (point of maximal impulse) located in the heart?
Apex in the 5th intercostal space; bottom tip of the heart (where apical pulse is)
Where is the ‘base’ of the heart located?
At the top of the heart
Midsternal line (MSL)
Midclavicular lines (MCL)
Anterior axillary lines
Intercostal spaces (ICS)
Where is the aortic valve heard best?
On the right side, at 2nd ICS
Where is the pulmonic valve heard best?
On the left side, at 2nd ICS
Where is the tricuspid valve heard best?
Midsternal line, at 4th ICS
Where is the mitral valve heard best?
At PMI (apex of the heart), at 5th ICS
Cardiac Exam: Inspection
Coloration — signs of cyanosis (blue/gray)
Pulsations
Neck: carotids and internal/external jugulars
Point of Maximal Impulse (PMI)
Heaves, lifts (where heart is beating/rising)
Cardiac Exam: Palpation
Where:
Carotids
Valves, left sternal border
What:
Heaves, lifts (where heart is beating/rising)
Thrills
PMI
Displaced to the left
Diameter (for larger people)
*Percussion is usually skipped
Cardiac Exam: Auscultation
Carotid bruits — pt holds their breath (use bell of stethoscope)
Listen in order over all valve areas with diaphragm of stethoscope
Concentrate on each part of cardiac cycle in isolation
RRR: Regular Rate Rhythm (heart beating normal)
M/R/G: Murmurs/Rubs/Gallops (DON’T WANT TO HEAR)
S1
Made by: Closure of mitral and tricuspid vales
During: Start of systole
Listen with: Diaphragm
S2
Made by: Closure of aortic and pulmonic valves
During: End of systole
Listen with: Diaphragm
S3 (extra heart sound)
Made by: Ventricular filling
During: Early diastole
Listen with: Bell
S4 (extra heart sound)
Made by: Ventricular filling by atrial kick
During: Late diastole
Listen with: Bell
What sound does S1 make?
“Lub”
What sounds does S2 make?
“Dub”
What sound does S3 make?
SLOSH-ing-in (‘lub-dub-ta’)
Murmur
What sounds does S4 make?
a-STIFF-wall (‘ta-lub-dub’)
Inadequate contraction
When are murmurs considered ‘normal'?
In kids, teens, pregnancy
Arterial Insufficiency
Pale, punched-out ulcers, painful distally, elevation hurts
Venous Insufficiency
Black/blue, painless, elevation helps
Vascular Exam: Inspection
Inspect extremities for signs of arterial or venous insufficiency
Skin discoloration or mottling (signs of cyanosis)
Dry, scaly skin
Hair loss (from lack of blood flow)
Poor nail growth (from lack of blood flow)
Ulceration (if not healing, from lack of blood flow)
Varicose veins (venous)
Edema (venous)
Vascular Exam: Palpation: Pulses
Palpate pulses in major arteries
Note symmetry & warmth of extremities
Carotids (if not done in cardiac exam)
Radials ± brachials
± abdominal aorta and femorals
Bilateral dorsalis pedis ± posterior tibial ± popliteal
Pulse Intensity Grading
0 → Absent
1+ → Diminished
2+ → Normal
3+ → Increased
4+ → Bounding
Vascular Exam: Auscultate Bruits
R, L carotid arteries
R, L temporal arteries
R, L subclavian arteries
Abdominal aorta
Renal arteries
Iliac arteries
Femoral arteries
*Bruits represent stenosis or aneurysm
Vascular Exam: Palpation
Capillary refill time
Press nail bed for several seconds
Release
Color should return within 2 seconds
Vascular Exam: Palpation: Edema
Measuring edema — how deep, how high
0+ → No pitting
1+ → Mild pitting, 2mm depression that disappears rapidly
2+ → Moderate pitting, 4mm depression that disappears in 10-15 seconds
3+ → Moderately severe pitting, 6mm depression that may last more than 1 minute
4+ → Severe pitting, 8mm depression that can last more than 2 minutes
JVP
Jugular venous pressure
HJR
Hepatojugular reflux
Vascular Exam: ABI
Ankle:Brachial Index (ABI)
Patient supine
Palpate dorsalis pedis or posterior tibial systolic brachial pulse (ankle cuff) and brachial systolic brachial pulse
Use ultrasound probe
Ankle:arm ratio normally >/ 1
Low ABI = decreased blood flow
1 in ___ people have asthma.
12
Asthmatic lung
Chronic inflammation — feels like you can’t breathe
COPD lung
Airflow limitation not completely reversible; damaged alveoli, can’t function properly
Bronchitis — ‘Blue Bloaters’
Emphysema — ‘Pink Puffers’
Characteristics of Chronic Bronchitis
Clinical diagnosis: daily productive cough for 3 months or more, in at least 2 consecutive years
Overweight and cyanotic (lack of O2)
Elevated hemoglobin
Peripheral edema
Rhonchi and wheezing
Characteristics of Emphysema
Pathologic diagnosis: permanent enlargement and destruction of airspaces distal to the terminal bronchiole
Older and thin
Severe dyspnea (SOB)
Quiet chest
X-ray — hyperinflation with flattened diaphragms (normally curved)
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea
Waking up in the middle of the night with shortness of breath
Orthopnea
Shortness of breath while lying down, that is relieved by sitting or standing up
Symptom Differentiation in COPD & HF
COPD
Coughing up mucusy fluid
Orthopnea (usually w/ 3 pillows); more likely than Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea
HF
Coughing up fluid from lungs that appear frothy
Orthopnea; Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea
Physical Exam: Inspection & Palpation
Inspection — shape and symmetry
Respiratory rate (rate, rhythm, depth and ease of breathing)
Using neck or accessory muscles to help with inspiration
Signs of cyanosis (look at fingertips, ears, nose, lips)
Palpation
Thoracic Expansion: ensure chest expands symmetrically
Tactile Fremitus: feeling lungs inflate at the same time
How many lobes are in the left lung?
2
How many lobes are in the right lung?
3
Tactile Fremitus
Ask patient to say “99” and feel for vibrations — should feel equal on both sides
Physical Exam: Percussion
Evaluate the density of the lung tissue
Lungs are hollow UNLESS there’s a problem
Order of lobes to tap:
Upper
Upper
Middle
Middle
Lower
Lower
Physical Exam: Ausculation
Posterior chest at 9 different points
One full respiration at each location
Compare side to side (left → right)
Wheeze vs Crackle
Bronchophony, egophony, whispered pectoriloquy