D103 Cytokinesis and Meiosis (ALS 25. Vid 38)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
phases of cytokinesis
early cytokinesis
mid-cytokinesis
late cytokinesis
overview of cytokinesis
in interphase cells, actin and myosin II filaments form a cortical network underneath the PM
some cells can also form stress fibers
as cells enter mitosis, actin and myosin arrays disassemble
anter anaphase, a contractile ring of actin and myosin provides the force required to constrict the equator and divide the cytoplasm to form 2 daughter cells
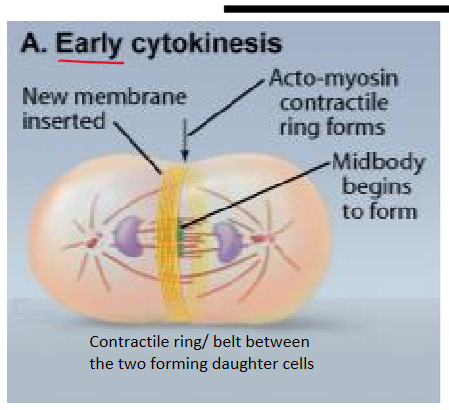
early cytokinesis
new membrane inserted
acto-myosin contractile ring forms
midbody begins to form
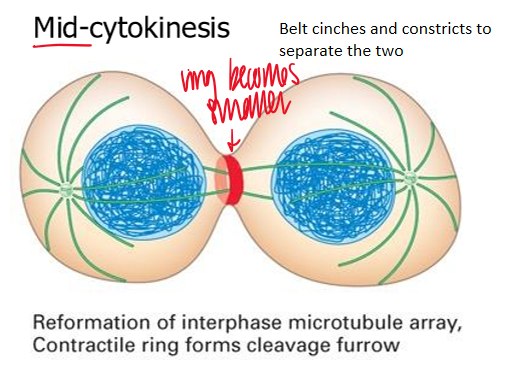
mid-cytokinesis
reformation of interphase microtubule array
contractile ring forms cleavage furrow
belt cinches and constricts to separate the 2
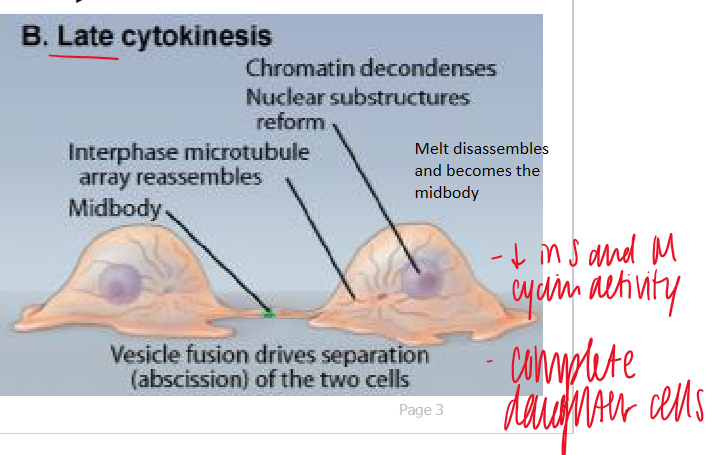
late cytokinesis
vesicle fusion drives separation (absicissin) of the 2 cells
chromatin decondenses
nuclear substructures reform
belt disassembles and becoms the midbody
decrease in S and M cyclin activity
complete daughter cells form
purpose of the contractile ring
actin and myosin II generate force required for cytokinesis
little actin remains in periphery of the daughter cells
myosin II colocalizes with the belt at the cleavage furrow
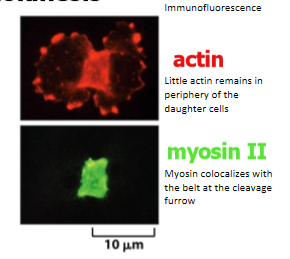
overview of contractile ring fuction
during anaphase - begins to asemble at the plane of the metaphase plate (in part due to activation of formins)
after anaphase - contractile ring begins to constrict via acto-myosin contraction similar to that in muscle
ring constricts → maintains the same thickness suggesting that its total volume and number of actin and myosin filaments gradually decreases
surface area of daughter cells
SA is 40% greater than the pre-division cell
to provide the additional membrane required, vesicles are inserted adjacent to the leading edge of the cleavage furrow
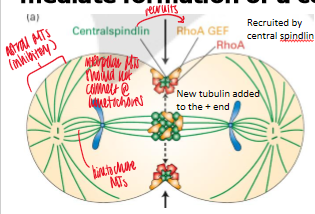
what does the central spindle colocalize
molecules that stimulate Rho A activity to mediate formation of a contractile ring of actin and myosin II
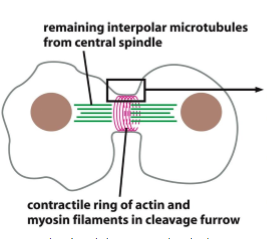
where does the actin-myosin ii contractile ring form
overlapping interpolar MTs provide a signal for motor proteins to deliver components of contractile ring (signals also emanate from other locations)
centralspindlin
protein that recruits an activator (GEF) of Rho A to the cell cortex overlying the overlapping interpolar MTs
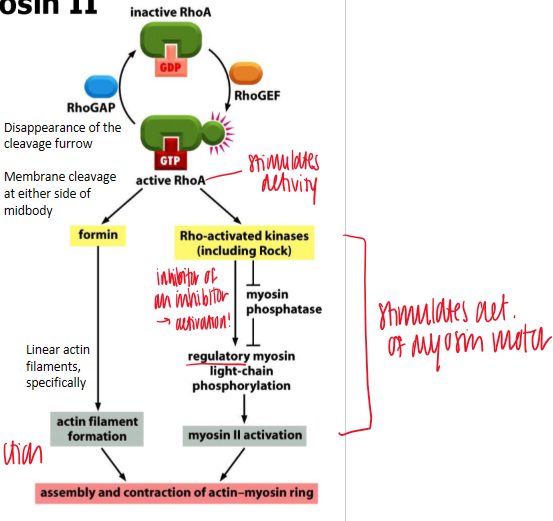
result of membrane localized Rho A
coordinates activation of formins that cause actin filament formation and Rho kinases that activate myosin II
lack this protein = cannot complete cytookinesis
what completes cytokinesis
completed by abscission involving constriction and severing of the membranes on either side of the midbody
how does meiosis facilitate genetic diversity
contributes to diversity among members of a species
valuable trait for survival of a species
genetic diversity primarily arises from the independent assortment of maternal and paternal homologs during meiosis
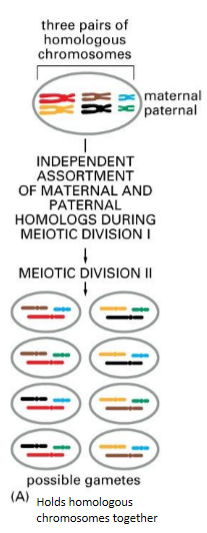
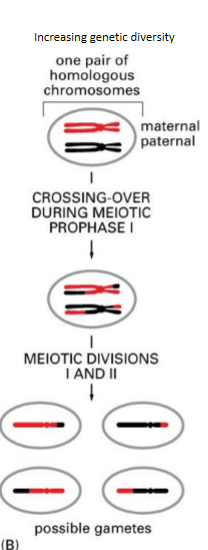
recombo for genetic diversity
permits new versions of chromosomes to be formed that have novel combos of different alleles of the gene s
greatly increases the possible number of genetic combos of alleles
helps hold homologs together, so they are correctly segregated to 2 daughter nuclei produced during meiosis I
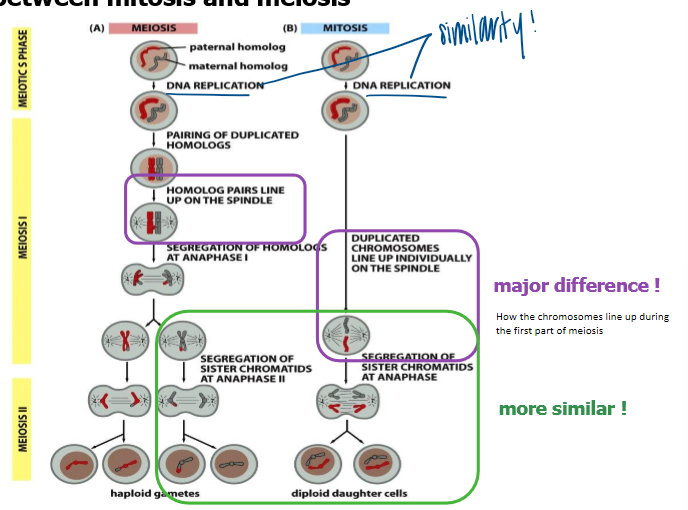
mitosis vs meiosis
meiotic S phase
both undergo dna replication
meiosis I (major difference)
meiosis: homolog pairs line up on the spindle
mitosis: duplicated chromosomes line up indvidiually on the spindle
meiosis II
both segregate sister chromatids at anaphase
mitosis vs meiosis: cell divisions
mitosis
one cell division, resulting in 2 daughter cells
meiosis
2 cell divisions, resulting in four products of meiosis
mitosis vs meiosis: chromosome number
mitosis
chromosome number per nucleus maintained (diploid, 2n)
meiosis
chromosome number halved in the products (2n → n)
mitosis vs meiosis: s phase
mitosis: one premitotic S phase per cell division
meiosis: one premeiotic S phase for both cell divisions
mitosis vs meiosis: pairing of chromosomes
mitosis: normalliy, no pairing of homologous chromosomes in prophase (no tetrads)
meiosis: full synapsis of homologous chromosomes in prophase (tetrads)
mitosis vs meiosis: recombo
mitosis: norecombo in prophase
meiosis: at least 1 recombo between nonsister chromatids
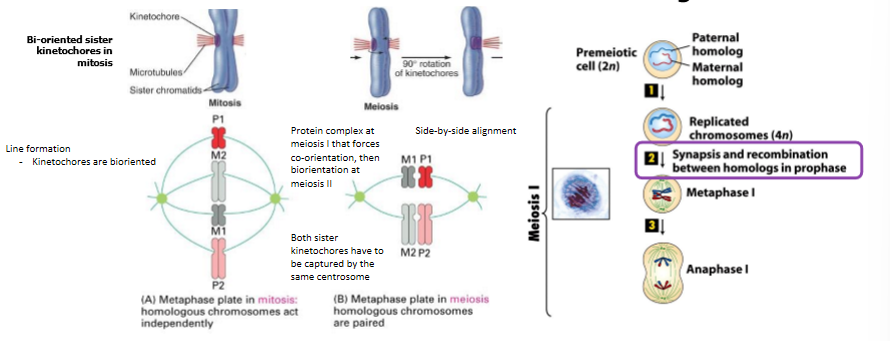
mitosis vs meiosis: orientation
mitosis: bi-oriented sister kinetochores; loss of cohesion between sister chromatid arms during metaphase
meiosis: co-orientation of sister kinetochores; maintainence of cohesion between sister chromatid arms during metaphase of meioses I
mitosis vs meiosis: centromeres
mitosis: centromeres divide at anaphase
conservative process: daughter cells’ genotypes identical with parental genotype
cell undergoing mitosis can be diploid or haploid
meiosis: centromeres do not divide at anaphase I, but do at anaphase II
promotes variation among the products of meiosis
cell udnergoing meiosis is diploid
mitosis vs meiosis: prophase
prophase is much longer in meiosis than it is during mitosis
meiosis prophase I
requires the longest time
increases local conc
between homologous chromosomes
haploid gamete formation
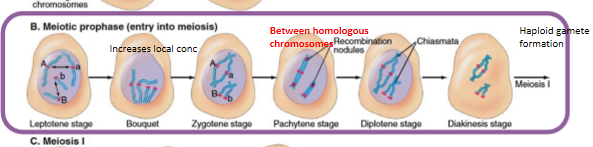
organization of synaptonemal complex during meiotic prophase I
pairing of homologous chromosomes
initiation of recombo
formation of synaptonemal complex
completion of recombo
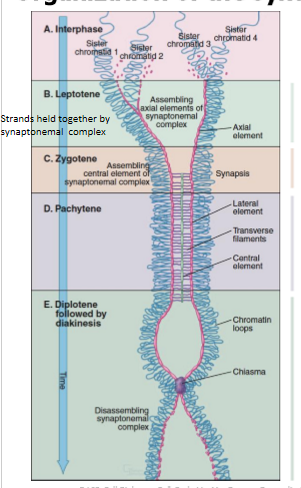
steps fo synaptonemal complex during meiotic prophase I
homologs pair and recombo begns
synaptonemal complex begins to form at sites where recombination has been initiated (involves double strand breaks in chromatids)
assembly of synaptonamal complex complete; longest stage of meiosis
disassembly of synaptonemal complex; condensation and shortening of chromosomes; chiasmata become visible
impact of recombo events
generate diversity and tether homologous chromosomes together at chiasma where a crossover has occurred
normally, every bivalent is linked by at least 1 chiasma (usually 2-3)
linkage analyses of particular aneuploidies indicate reduced levels of recombo in the chromosomes involved in nondisjunction event
in some studies, up to 2.5% of non-recombined bivalents for chromosome 16 have been identified
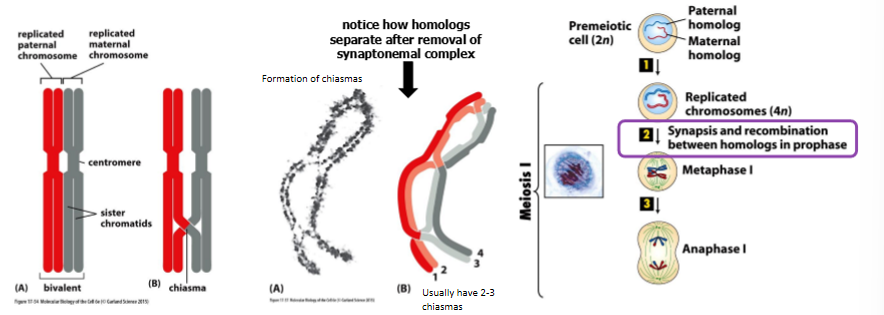
when are kinetochores of sister-chromatids are co-oriented
during meiosis I, homologous chromosomes rather than sister chromatids separate then segregate
mammals: meikin (meiosis-kinetochore) is required for sister kinetochores to become associated with the same spindle pole (ex - co-oriented)
meikin no longer functions during meiosis II when sister chromatids can be bioriented on the spindle as occurs during mitosis
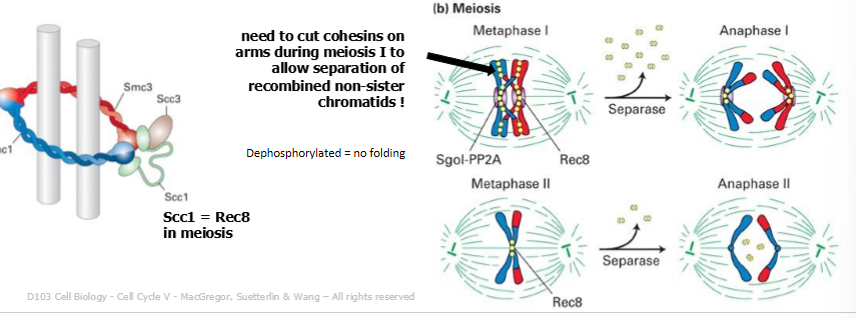
rec8
meiosis specific conhesin subunits that facilitates stepwise removal of cohesins during meiosis
result of Rec8 replsces Scc1 in cohesion complex
the compelx does not dissociate in prophase when it becomes phosphorylated
rec8 in anaphase I
phosphorylated Rec8 on the chromosome arms is cleaved by separase to permit separation of sister chromatids distal to each crossover
however, rec8 located at the centrosome is dephosphorylated and is protected from cleavage due to a phosphatase PP2A localized to the centromere by shugoskin (SgoI)
rec8 in anaphase II
phosphatase activity at the centromere is inhibited
centromeric rec8 is no longer protected, and sister chromatids can separate following cleavage of phosphorylated Rec8
is meiosis error-prone
yes
20-40% of all human conceptuses are aneuploid
majority of trisomies and monosomies result from non disjunction of homologs at maternal MI
trisomy 16 is most common trisomy in human pregnancies
patau’s syndrome
trisomy 13
variable phenotype (some individuals survive)
mental and motor retardation
polydactylyl (extra digits)
microcephaly
holoprosencephaly/ cyclopia
heart defects
downs’s syndrome
partial or complete trisomy for chromosome 21
incidence increases dramatically with maternal age
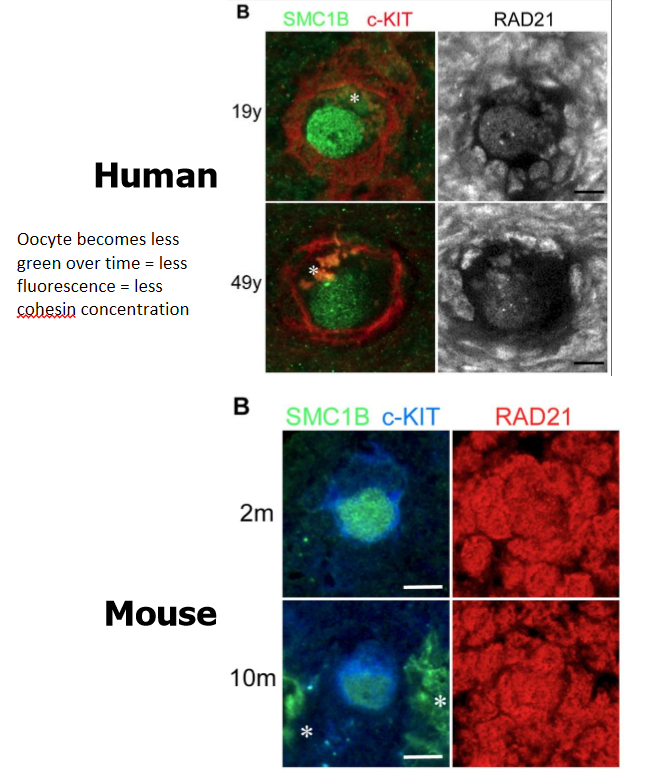
evidence for age-related decrease of meiosis-specific cohesins in human and mouse oocytes
use fo immunostaining demonstrates decline in cohesins (Rec8 and SMC1B) as oocytes age in human and mice
oocyte becomes less green over time = less fluorescence = less cohesin concentration
Which of the following processes in the cell cycle would be most likely to be affected by loss of the molecular motor myosin II ?
A. Capture of condensed chromosomes.
B. Cell division.
C. Separation of chromosomes at anaphase A
D. Separation of the spindle pole body at anaphase B
E. None of these processes would be affected by loss of myosin II
B. Cell division.
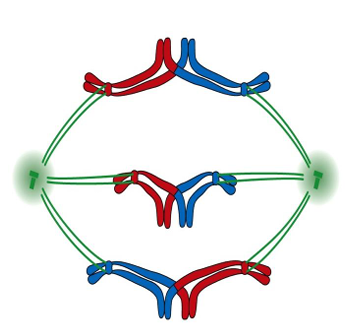
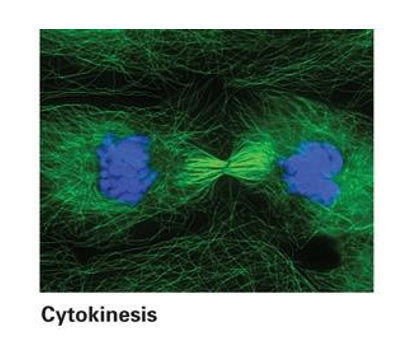
Identify the stage of cell division in the picture
A. Pro-metaphase of meiosis I
B. Pro-metaphase of meiosis II
C. Anaphase of meiosis I
D. Anaphase of meiosis II
C. Anaphase of meiosis I
A mammalian zygote is formed from fusion of a normal sperm with an egg that formed following non-disjunction of a chromosome during meiosis II. Which of the following terms best describes this zygote ?
A. Tetraploid.
B. Polyploid.
C. Haploid.
D. Diploid.
E. Aneuploid.
E. Aneuploid.