Behavioral Neuro - Ch 13
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Feeding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Why do we eat and drink?
Internal and external (sensory) experiences drive feeding behaviors to restore balance
How do you determine if you need food?
homeostasis (balance between the internal and external environments)
glucose levels, proteins, fats, salts, water, etc.
How do you determine if you want food?
incentive motivation
flavors, reward, hedonic tone, etc.
Describe homeostasis
maintaining the “set point”
monitors physiological mechanisms
blood glucose, body fat, salt levels, etc.
What happens homeostasis is in a deficient?
stimulate seeking/feeding
a little hungry after you come home from class
hungry after a swim practice
extremely hungry/starving if you get lost while hiking
What happens homeostasis is in a surplus?
suppress seeking/feeding
negative feedback regulation of feeding
deviation from the set point leads to compensation to return to set point
Define redundancies
multiple mechanisms of maintaining homeostasis that work at the same time
Define endotherms
species that produce their own heat through metabolic processes
metabolism and muscles
greater muscle activity through increased use of oxygen
What does the pre-optic area (POA) do?
Organizes thermoregular responses and sends information to other brain regions.
What do we do if we’re cold?
shiver to produce heat
increase metabolism to generate heat/energy
reduce sweat
decrease blood flow to reduce heat loss
increase respiration
can also change behavior
redundancies makes it more complicated!
What is an example of homeostasis?
fluid regulation
Define osmolality
number of particles (salts) per unit volume of water
isotonic
hypertonic
hypotonic
Describe an isotonic salt solution
0.9% NaCl
0.9 grams of NaCl in 100 milliliters of water
Define hypertonic solution
more salty than an isotonic solution
Define hypotonic solution
less salty than an isotonic solution
What is a 0.5% NaCl solution?
hypotonic
Define aquaporins
specialized channels for H2O
H2O moves based on concentrations within or outside the cell
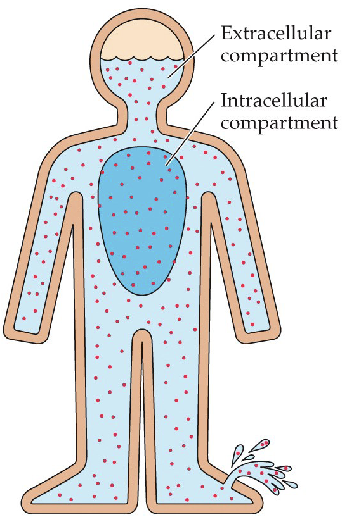
Define the intracellular compartment
Within cells
Define the extracellular compartment
Outside of cell (includes fluid between cells [interstitial fluid] and blood plasma [protein rich])
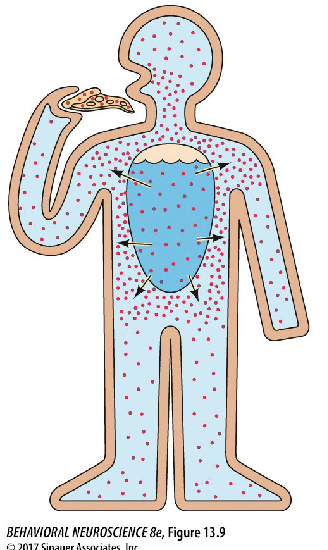
Describe osmotic thirst
high salt concentration in extracellular compartment
regular water loss (respiration, perspiration, urine)
eat something salty
water flows out of cells
H2O flows out of cell into [NaCl] area
Where are osmosensory neurons located?
hypothalamus
Describe osmosensory neurons
located in the hypothalamus
cell changes size based on osmolarity and water pressure
What occurs when there is too much salt outside of a osmosensory neuron?
cell shrinks
ion channel open
action potential triggers the pre-optic area
triggers osmotic thirst response
vasopressin release
Is vasopressin released when an osmosensory neuron shrinks or swells?
when it shrinks
What does vasopressin release do?
reduces urination
What is partnered with an osmotic thirst response?
vasopressin release
Describe hypovolemic thirst
too little volume of extracellular fluid
large water loss (vomiting, hemorrhage, diarrhea)
lose water AND salts so no change in osmolarity/concentration of salt within the cells
What flows out of cells in osmotic thirst?
water only (causing a high salt concentration in the extracellular compartment)
What flows out of cells in hypovolemic thirst?
water and salts (causing NO change of osmolarity in the extracellular compartment)
What is the different cravings between osmotic and hypovolemic thirst?
osmotic = crave water
hypovolemic = crave water AND salt
What do the baroreceptors in the blood vessels/heart do in