ecology test one
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
OEcology
Ernst Haekel “struggle for existence
Thomas Malthus
Population would out stripe food supply(bad guy)
Darwin
Natural selection
Succession
Change of species or habitat over time
Henry Cowles
all plants are one super organism
Clement
Hierarchy of different species
Gleason
No hierarchy- every species is a result of in-fluctuating environmental conditions
Elton
“Niche” animal place
Lotta
Looked at everything as one entire energy
Lindeman
10% law
Amphibians
“Biological indicators” for an environment
Interspecific
Competition with different species
Intraspecific
Competition of same species
Population
Groups of same species
Habitat
Environment for specific species
Community
Population of different species
Ecosystem
Community and its surrounding
dominant species
Most abundant
Keystone species
Most important species in a ecosystem (otters)→urchins→kelp→sea lion
Ecological Niche
1.) habitat
2.) function of organism
3.) interrelationship
Specialist
(Panda) lives in Bamboo forest and eats bamboo
Generalist
(Raccoons) lives anywhere eats anything
Resource partitioning
Different species share resources
Morphological resource partitioning
Ex- different beaks on birds
Temporal resource partitioning
Animals come out at different times/seasons
Fundamental niche
Full range a species could live
Realized niche
Actual conditions where species live
Competition
Loss, loss
Predation
Loss, gain
Parasitism
Loss, gain
Commensalism
Gain, no affect
Mutualism
Gain, gain
Extinction increase on small island
More competition and more disease
Immigration
Higher if island is closer
Solar radiation (input)
1.) 50% of energy is absorbed at earths surface
2.) 30% is reflected by atmosphere
3.) 20% absorbed by atmosphere
Solar radiation (output)
1.) 20% energy lost by evaporation
2.) 10% lost by convection/ conduction
Always
High to low
Dessert
30° N&S
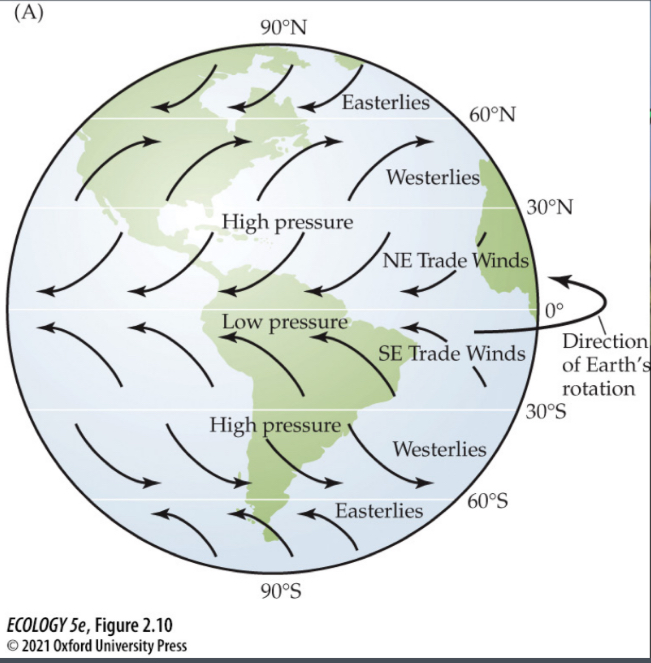
Hadley Cells
Uplift in tropics
High pressure
0° & 60°
Low pressure
30°&90°
Rainforest
60° N&S
Polar Cell
At poles
Hadley cell
Center of earth
Ferrel Cell
Between Hadley and Polar
Coriolis Effect
Straight will be diagonal with earths rotation
Wind name
Origin of winds
Winds (labels)
Maritime Climate
Climate (temp) doesn’t change much
Continental Climate
All four seasons
Rain shadow effect
Mountain- half green half dessert
El Niño
Extra warm
El Nina
colder
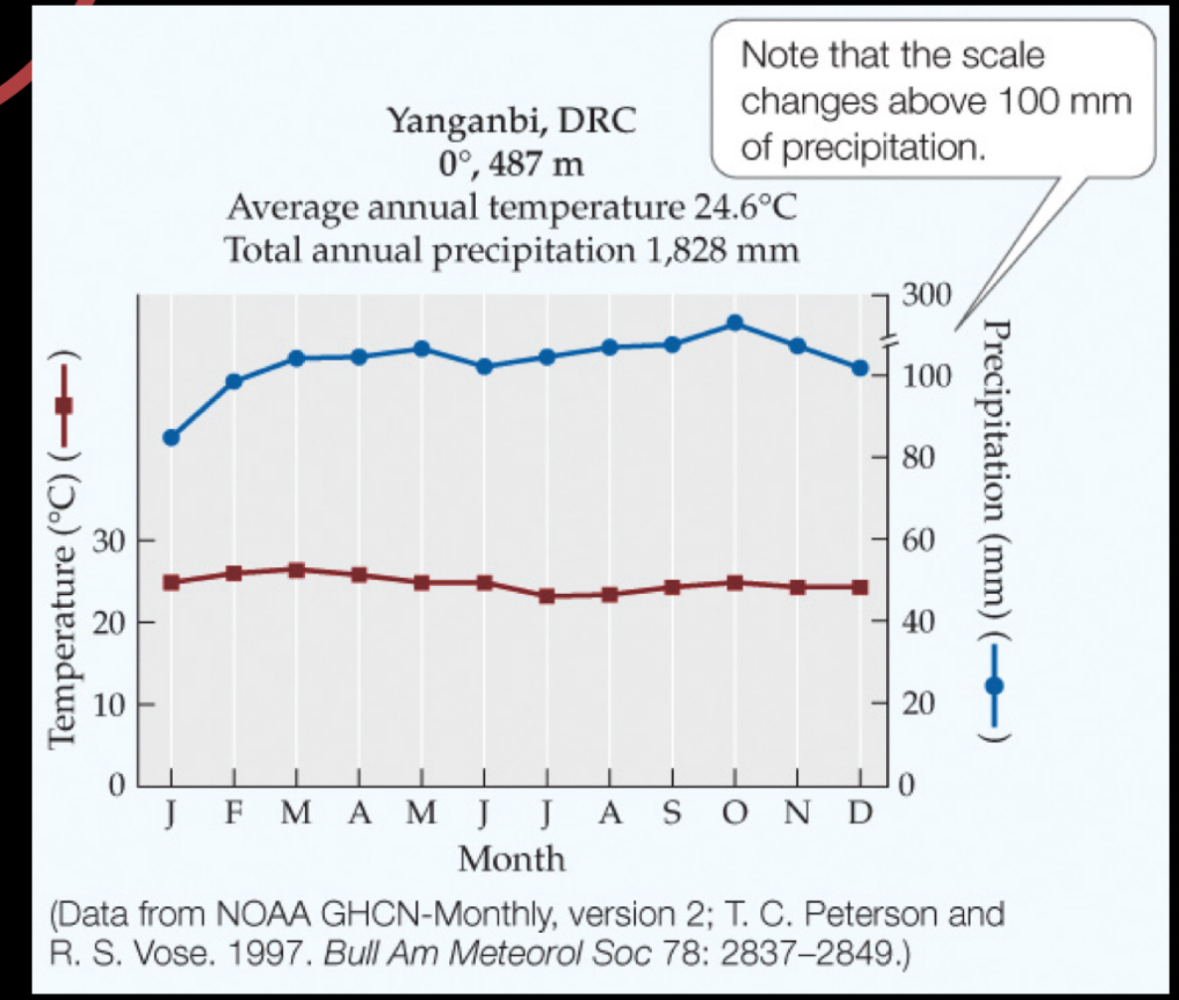
Tropical Rainforest
High rain high temp constant year around 10°
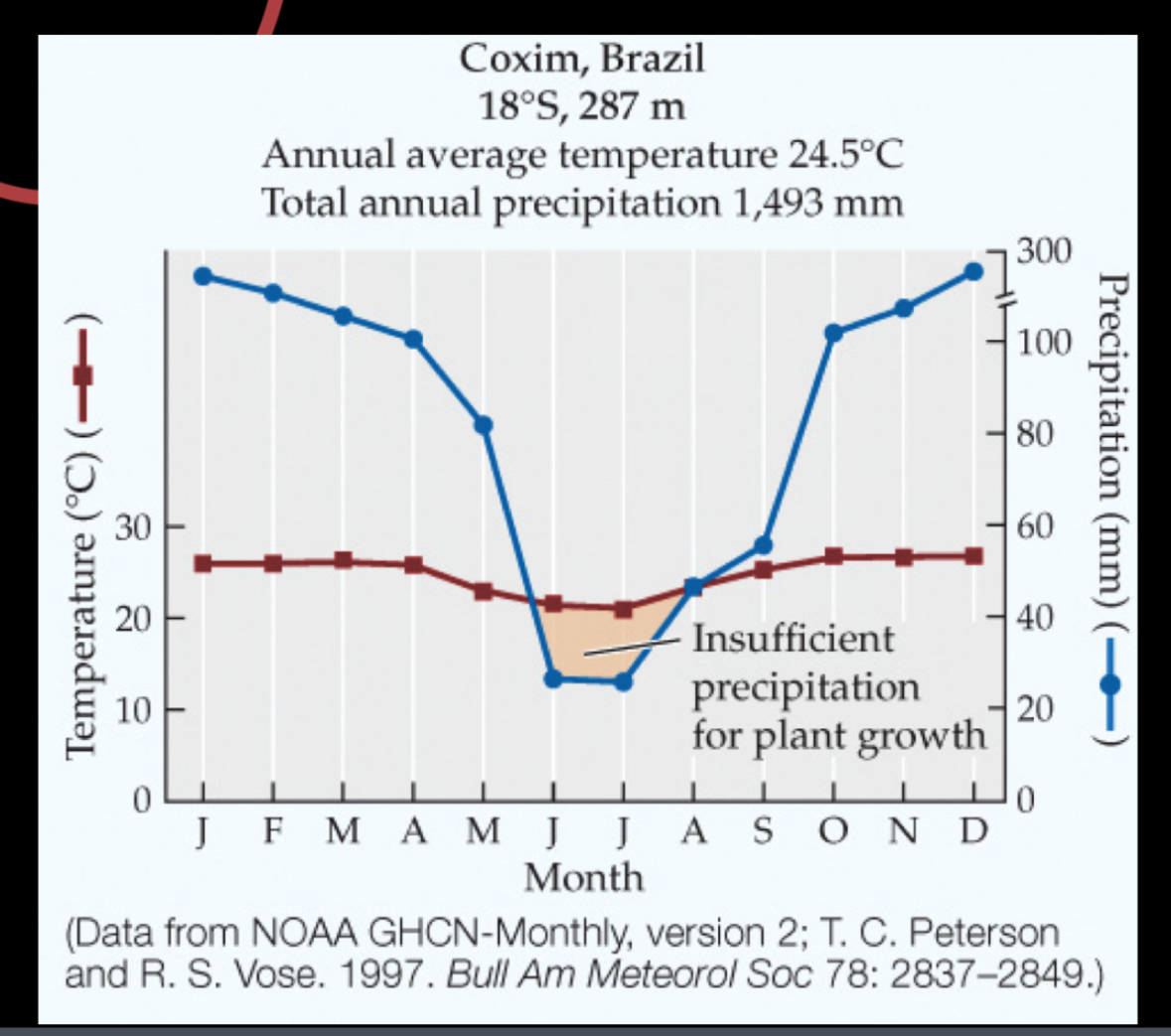
Topical seasonal forest/ savanna
Hot and rainy yearly less rain during summer
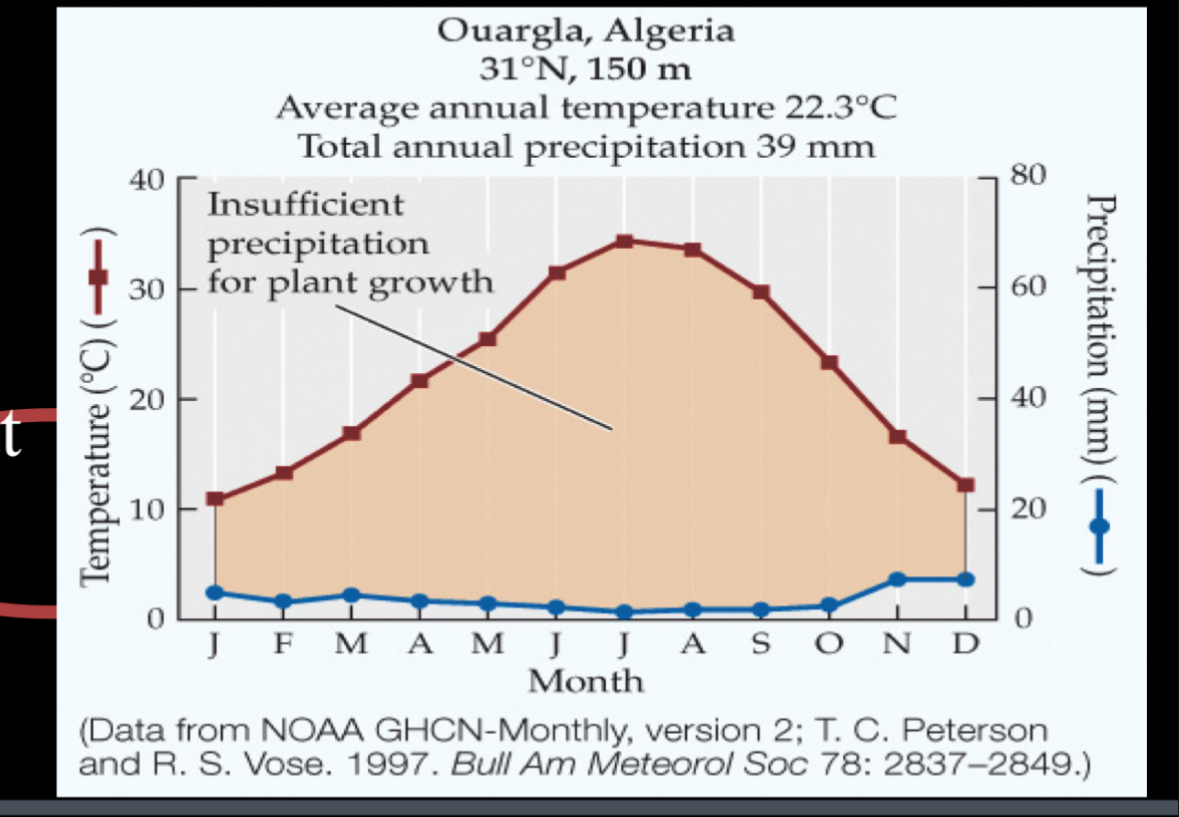
Dessert
Almost not rain and hot yearly higher during summer
Temperate deciduous forest
Negative to high temp and higher rain in summer 30° to 50°N
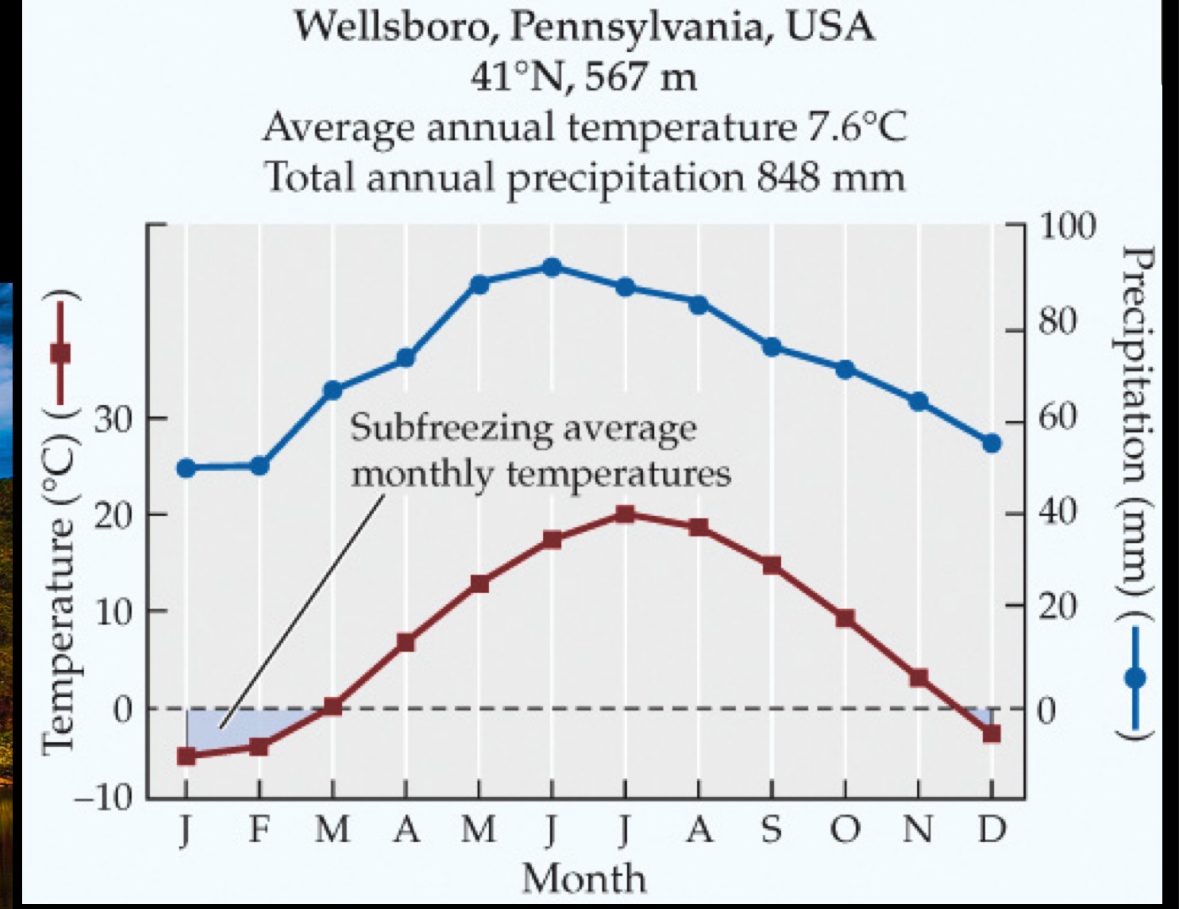
Temperate evergreen forest
High rain and mild winters 30° to 50°S
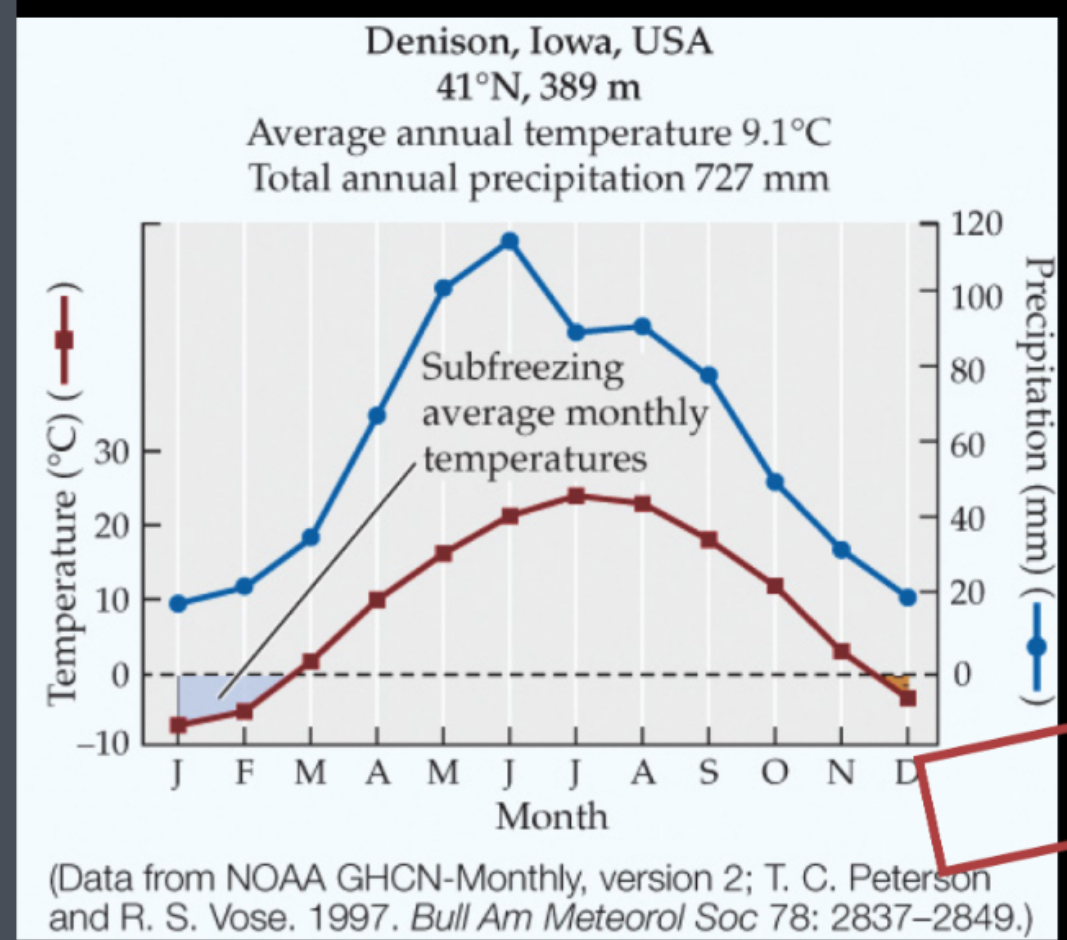
Temperate grasslands
Low to mild temp & lots rain
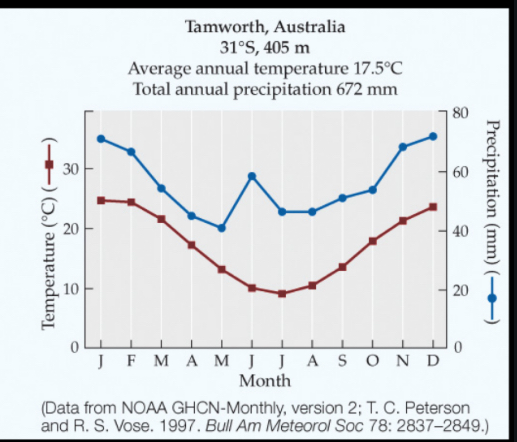
Temperate shrub lands
Mild to high temp high rain but not in summer
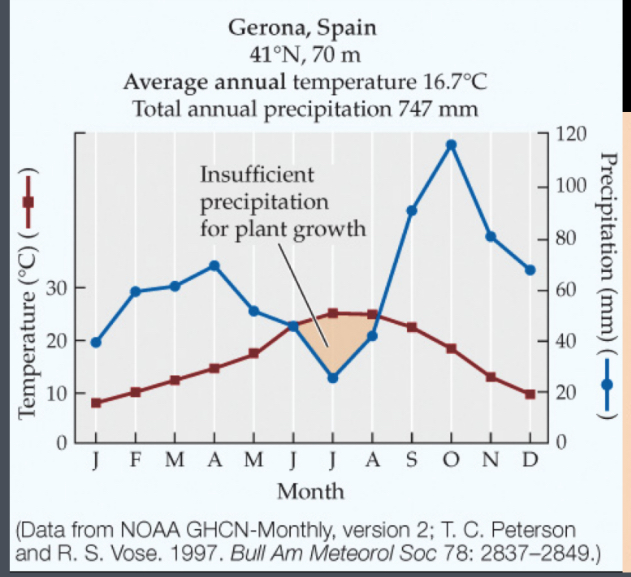
Borea forest
Extremely cold to mild temp with mild rain 50°&56° N
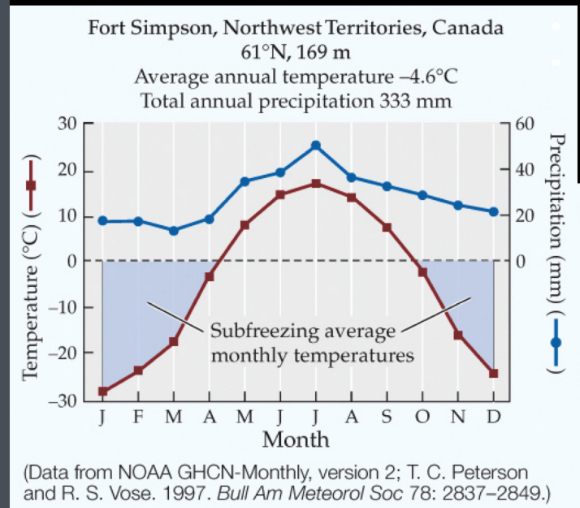
Tundra Biome
-40°c to 5°c and mild rain
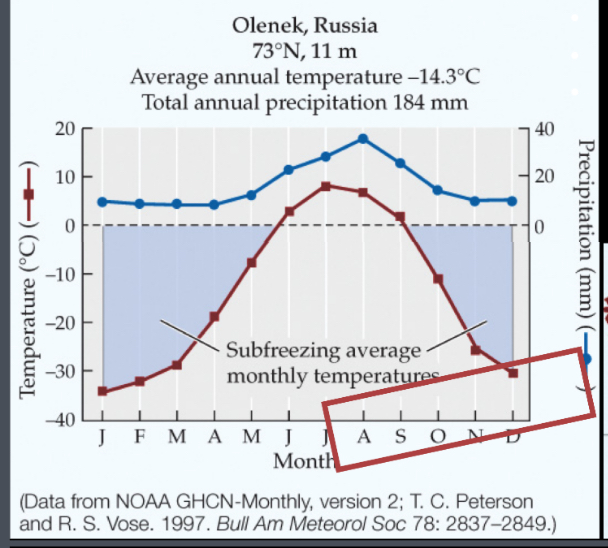
Acclimatization
Changes on an organismal scale, short term, and reversible ( climbing mountain getting less O2)
Hot plant
Smaller leaves, more pubescence, and more stomata
Cold plant
Grows closer to ground, less stomata, and less pubescence
Alpine plants
Can function close to freezing because it has a unsaturated membrane
Soil matric potential
Cohesion between soil and water
Osmotic potential
High to low
Hyperismotic
More saline in environment than organisms cell
Isosmotic
Same saline in environment as an organism
Hypoosmotic
Less saline in environment than organisms cell
Osmoconformers
Same solute in blood as in water
Fresh water fish
lose solute
sea water fish
Lose water

150-60=90
90+45=135 heat in
30+50=80 heat out
Net loss: 135-80=55

30+8=38
55-38=17
Body temp changes with environment
Ectotherms
Body temp doesn’t change with environment
Endotherm