BSCI 170 - Metabolism and Oxidation & Reduction
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is metabolism?
the collection of all biochemical reactions that occur in a cell
What are catabolic reactions often accompanied by?
the transfer of electrons between reactants
Energy Storage
We talk about energy being stored in glycogen, starch, and lipids
Where exactly is the energy stored?
If electrons are rearranged or released, then potential energy can be ______.
the excess energy is _______.
the energy is stored in chemical bonds (covalent > weak), mostly in electrons, as potential energy
reduced
released
Combustion of Organics
What is combustion?
Organics + O2 —> CO2 + H2O + Energy
Example: Combustion of Glucose
C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O + 686,000 cal/mol
We know that the reaction is ________ because energy is released
combustion is rapid chemical combination with oxygen, exergonic
Oxidation
A reaction with _______ is also a form of oxidation
Rust is a result of the oxidation (slow combustion) of iron
oxygen gas
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Energy is stored in _______ bonds
______ bonds result from electron sharing
When covalent bonds are broken or rearranged, electrons can be transferred between _________.
These electron-transfer reactions are called __________-_________ reactions
also called redox reactions
covalent, covalent, reactants, oxidation, reduction
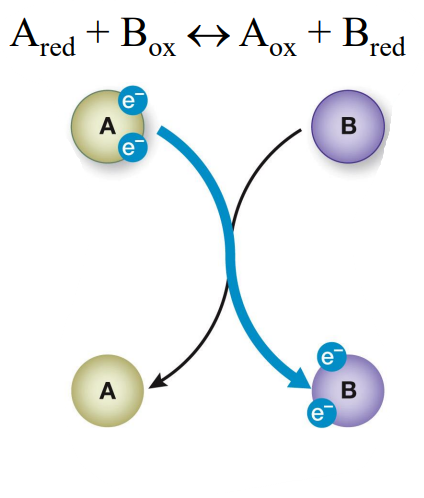
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
What is the top compound A?
What is the bottom compound A?
What is the top compound B?
What is the bottom compound B?
the reducing agent
the oxidized compound
the oxidizing agent
the reduced compound
What is oxidation?
an electron is lost
What is reduction?
an electron is gained, addition of a negatively charged electron reduces overall charge of the molecule
Mneumonic for Remembering
OIL RIG
Oxidation is Loss
Reduction is Gain
LEO the Lion says GER
Loss Equals Oxidation
Gain Equals Reduction
N/A
Practice:
Na + Cl —> Na+ + Cl-
Na loses an electron, so it is _______
Cl gains an electron, so it is ________
oxidized, reduced
What is the generalized equation for redox reactions?
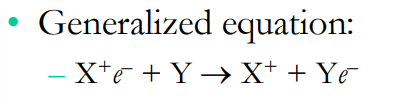
In this equation what are the reducing and oxidizing agents?
the reducing agent is CH4 (methane) and the oxidizing agent is 2O2
True or False: Oxidations and reductions occur in isolation
false, oxidations and reductions NEVER occur in isolation
electrons are not floating freely in solution like H+
If one reactant is oxidized, then another reactant MUST be ________
reduced
Redox Reactions
It is not always easy to determine which molecule is more reduced
In biological reactions, electrons rarely move alone.
Electrons often combine with ______ as they move
The molecule with more _________ is usually the more reduced one.
protons, hydrogens
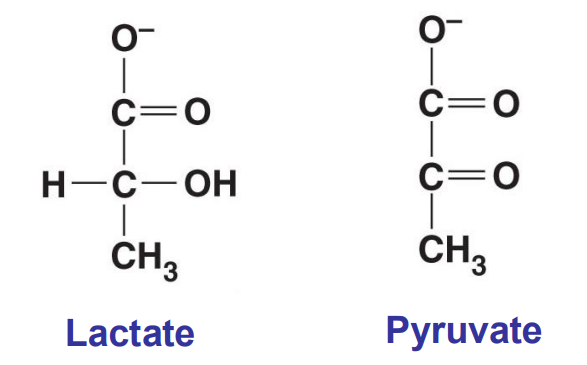
What is reduced and what is oxidized?
lactate is reduced and pyruvate is oxidized
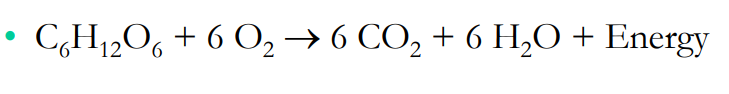
What is reduced and what is oxidized and why?
Glucose is oxidized to CO2
Glucose loses electrons and H+
O2 is reduced to H2O
O2 gains electrons and H+
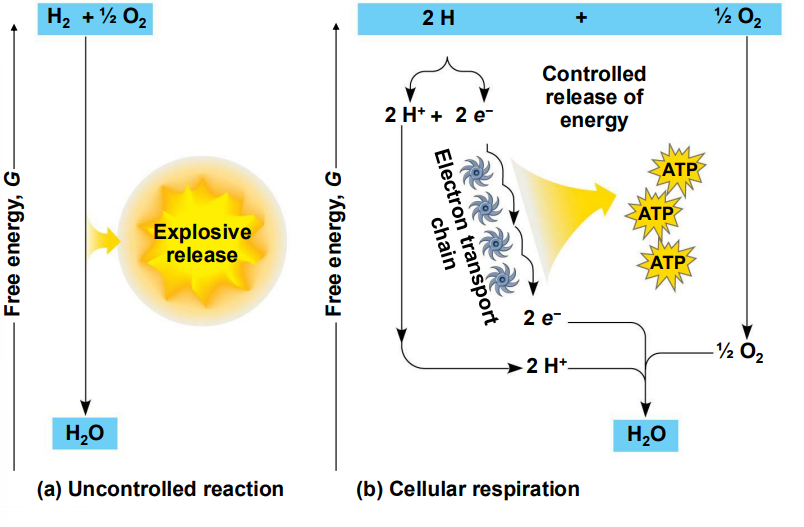
Oxidation of Cellular Fuel
Important Points:
each electron transfer reaction is _________
electrons ____ energy with each transfer
electrons in H2O have ____ (potential) energy than they did in glucose
released free energy drives ___ _________
exergonic, lose, less, ATP synthesis
Stepwise Energy Harvest
Energy from glucose is not released at ____
Glucose is combusted in a series of _____, _______-________
Electrons (and protons) are stripped away and transferred to another molecule (_______ _______)
once, small, enzyme-catalyzed, electron carrier
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Derivative of ______
B vitamin
Oxidized form, NAD+, serves as an important ______ ________ during _______ __________.
niacin, electron acceptor, cellular respiration
What is the reduced form of NAD+?
NADH
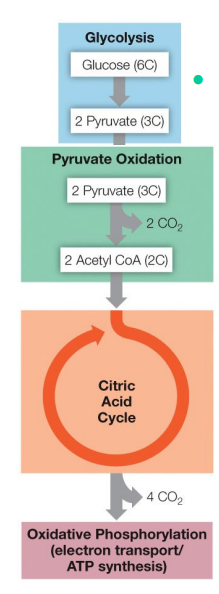
Respiration is the cumulative effect of 4 separate events. What are they?
Glycolysis (lysis of glucose)
Pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle (oxidation of carbon and salvaging of high-energy electrons)
Electron transport (stripping energy from the electrons)
Oxidative phosphorylation (using the energy from the electrons to synthesize ATP)
For your reference
N/A

For your reference
N/A
What is the first step in the complex, multistep process of oxidizing glucose?
glycolysis
Glycolysis means _____ ________
glyco = _________ __ ______
lysis = __ _______
occurs in the _______ of eukaryotes
What is glucose?
sugar splitting, relating to sugar, to unbind, cytosol, one six-carbon sugar
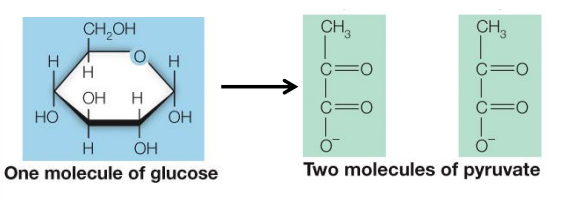
What occurs in glycolysis?
one six-carbon sugar (glucose) is oxidized to two, three-carbon molecules (pyruvate)
Glycolysis
A complex, 10-step biochemical pathway
several ______-________ steps
several ___________ steps (to make ___)
Conceptually, a very simple process
We can do it the hard way or the easy way
oxidation reduction, phosphorylation, ATP
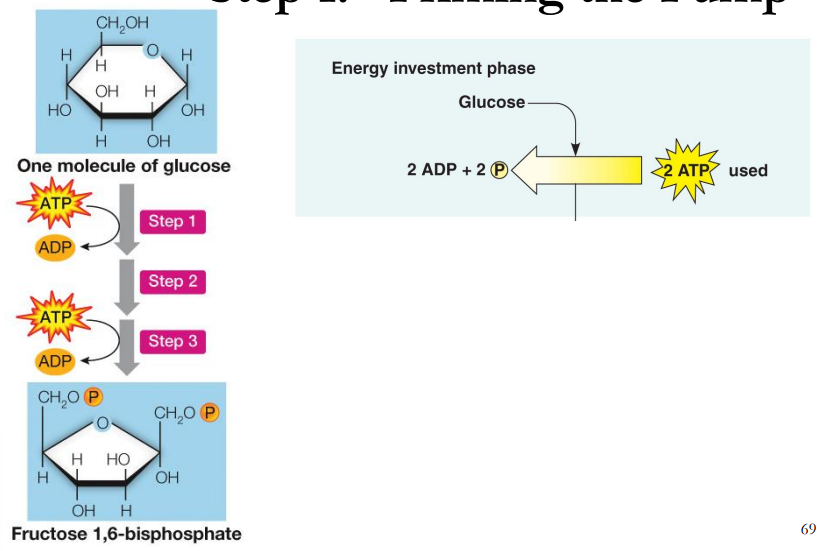
What is step 1 of glycolysis?
“Priming the Pump”
In this phase, the starting molecule of glucose gets rearranged, and two phosphate groups are attached to it. The phosphate groups make the modified sugar—now called fructose-1,6-bisphosphate—unstable, allowing it to split in half and form two phosphate-bearing three-carbon sugars. Because the phosphates used in these steps come from ATP, two ATP molecules get used up.
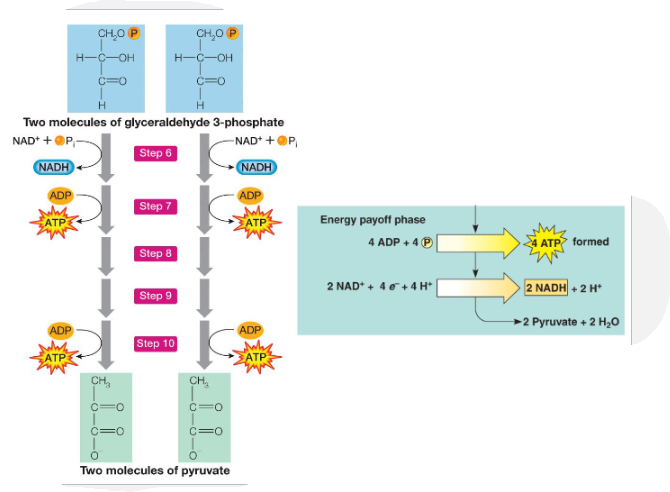
What is step 2 of glycolysis?
Cleavage, Rearrangement & Energy Release
In this phase, each three-carbon sugar is converted into another three-carbon molecule, pyruvate, through a series of reactions. In these reactions, two ATP molecules and one NADH molecule are made. Because this phase takes place twice, once for each of the two three-carbon sugars, it makes four ATP and two NADH overall.
Step 3: Summary
What does one glucose produce?
What is the net ATP produced?
What does 2NAD+ + 4 e- + 4 H+ produce?
2 Pyruvate + 2 H2O
2 ATP
2 NADH + 2H+
Substrate- Level Phosphorylation
In glycolysis, ATP is generated by the transfer of a _______ _______ from a ___________ ________ to ADP to make ATP
phosphate group, phosphorylated substrate
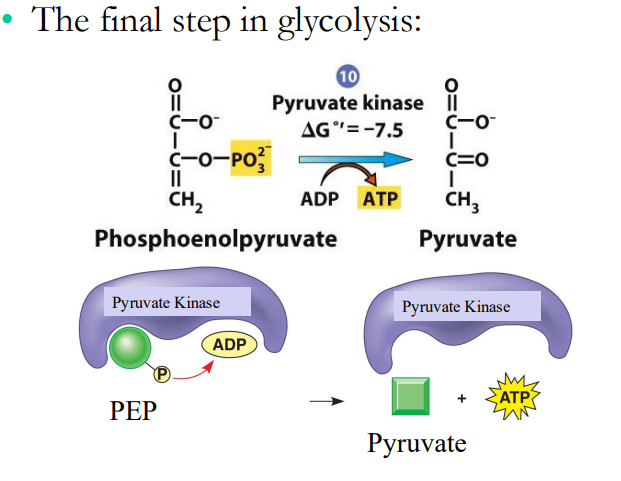
Example of Substrate-Level Phosphorylation:
N/A
Glycolysis: What you need to know
What are the starting reactants?
What are the ending products?
glucose, NAD+, ADP, Pi (inorganic phosphate)
pyruvate, NADH and H+, ATP
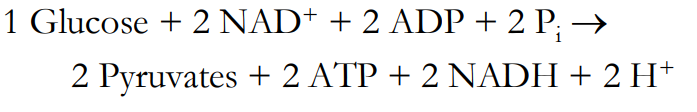
Glycolysis: Final Accounting
All _ carbons originally in _______ are now in the _ pyruvates
No carbons fully oxidized to ___
No __ has been consumed
6, glucose, 2, CO2, O2
Glycolysis Is Fundamental
Glycolysis is a fundamental pathway used by all living organisms
Evolved very early
Before ______ was available in the ___________
Glycolysis is very ________
generates only small numbers of ___ but does it quickly
Sufficient for many ____________
oxygen gas, atmosphere, efficient, ATP, microorganisms
Glycolysis Is Not Enough
Problem: Glycolysis requires a continuous supply of ______ to keep operating, BUT ______ is limiting in cells
Without a mechanism for regenerating ______ from _______ or for obtaining new ____, glycolysis will ____
NAD+, NAD+, NAD+, NADH, NAD+, stop
What is one solution for this problem?
in the absence of oxygen: fermentation
Fermentation
There are many different fermentation pathways
All have two common purposes, what are they?
oxidize NADH to regenerate NAD+
allow glycolysis to continue
pyruvate (or a derivative of pyruvate) is reduced
Reactants: C6H12O6 + 6O2
Products: 6CO2 + 6 H2O
In this reaction, which reactant is being oxidized and which is being reduced?
Which reactant is the oxidizing agent, and which is the reducing agent?
What else is being produced by this reaction?
Does this reaction happen all in one step? Why or why not?
C6H12O6, 6O2
6O2, C6H12O6
Energy
Happens in one step because redox reactions are comprised of a reduced half and an oxidized half
Reactants: 4H2 + CO2
Products: CH4 + 2H2O
In this reaction which reactant is being oxidized and which is being reduced?
Which reactant is the oxidizing agent, and which is the reducing agent?
What else do you think is being produced by this reaction?
CO2, 4H2
4H2, CO2
Energy
Reactants: CH4 + 2O2
Products: CO2 + 2H2O
In this reaction, which reactant is being oxidized and which is being reduced? Why did you choose these?
Which reactant is the oxidizing agent, and which is the reducing agent?
What do you notice about the reactants of this product compared to last reaction?
Why do you think this reaction happens closer to the surface?
2O2, CH4
CH4, 2O2
O2 is present
Closer to the surface because there is more oxygen there
Reactants: COO- + Fe3+
Products: Fe2+ + CO2
In this reaction, which reactant is being oxidized and which is being reduced?
Which reactant is the oxidizing agent, and which is the reducing agent?
What else do you think is being produced by this reaction?
COO-, Fe3+
Fe3+, COO-
Energy
Other electron acceptors (oxidizing agents) do not release as much energy as _______.
oxygen
Cellular respiration is a _______ of reactions that are designed to capture the most ______ from the oxidation of glucose as possible.
series, energy
Oxidation of Glucose
What are the reactants? products?
Oxidation of glucose means elections are protons are removed from _______ and transferred to _______
Complete reaction is highly _________
delta G = -686,000 cal/mol
Reactants C6H12O6, 6O2; Products: 6CO2, 6H2O, Energy
glucose, O2
exergonic