UNIT 1 - BIOCHEMISTRY
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Ratio of C, H and O in a carbohydrate
1:2:1
What do alpha-glucose polymers form?
Starch
What do beta-glucose polymers form?
Cellulose
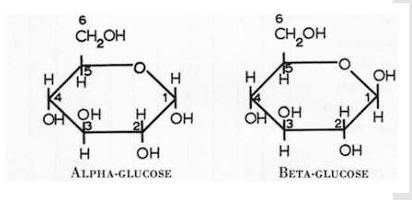
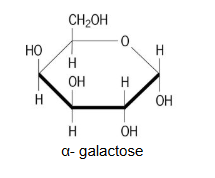
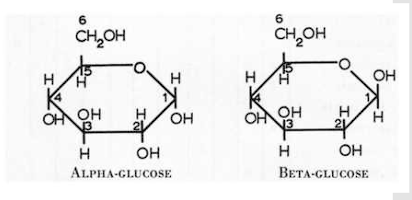
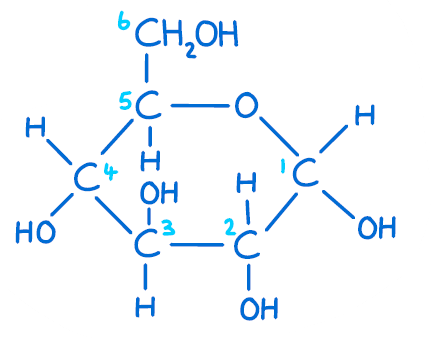
Which carbon determines whether a molecule is glucose or galactose?
#4
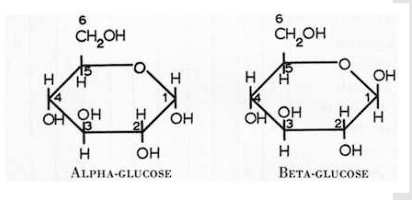
(T/F) In Galactose, the hydroxyl group is at the bottom of the 4th carbon
False. The hydroxyl is located on top.
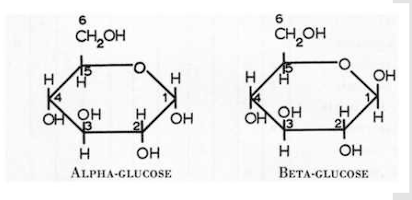
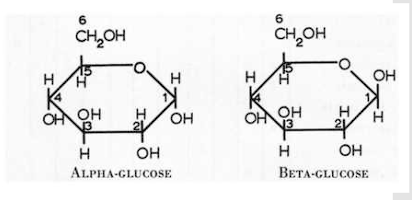
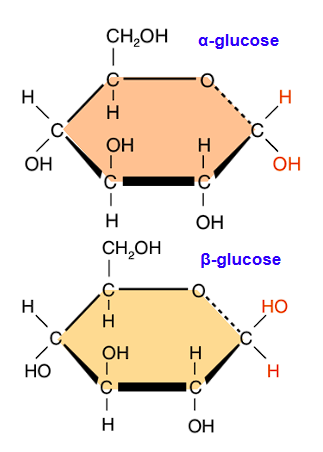
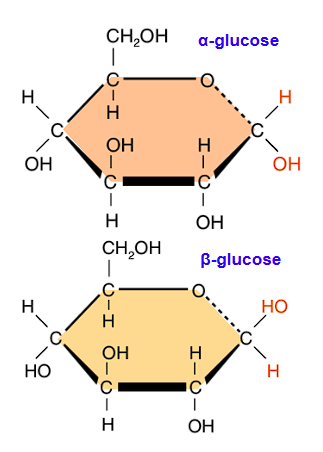
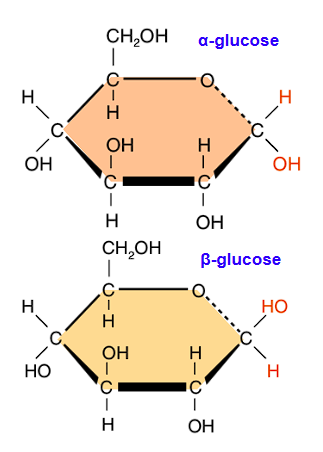
In alpha-polymers, the OH group attached to C #1 will be…
On the bottom
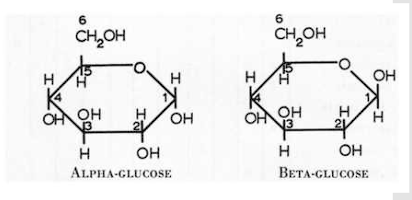
Draw a glycosidic linkage between 2 glucose molecules.
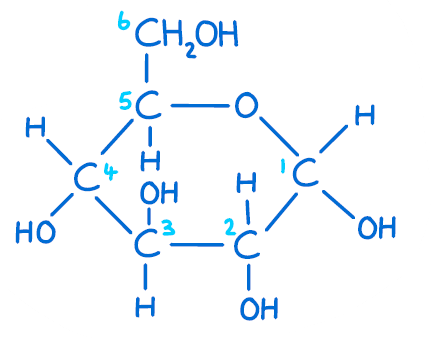
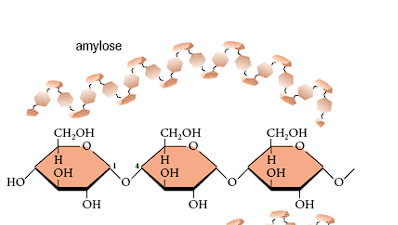
What links are Starch molecules composed of?
alpha 1-4 links for the chain, alpha 1-6 links for branches
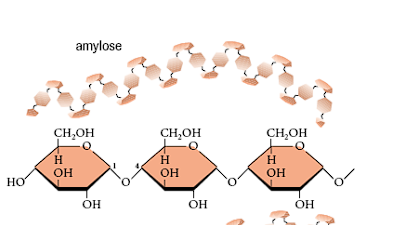
What links is glycogen composed of?
alpha 1-4 links, alpha 1-6 links where it branches.
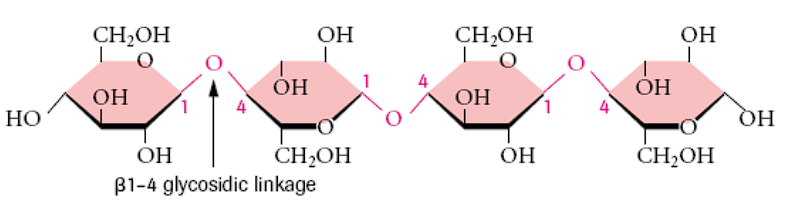
What links are cellulose molecules composed of?
beta-1-4 glycosidic linkages
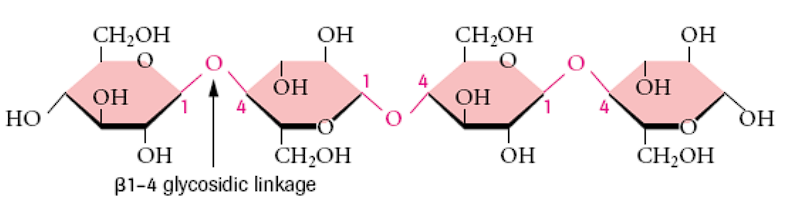
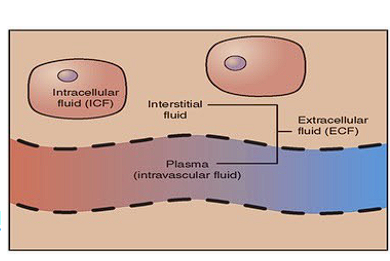
What is homeostasis?
The internal balance that a cell membrane helps maintain.
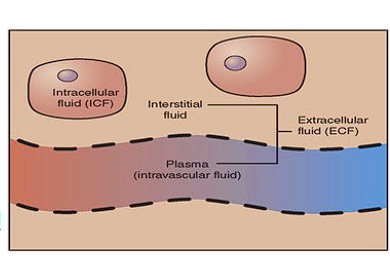
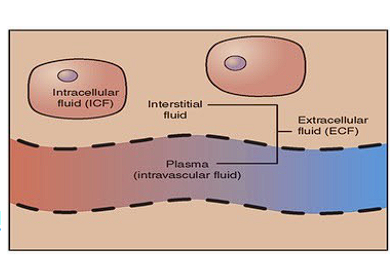
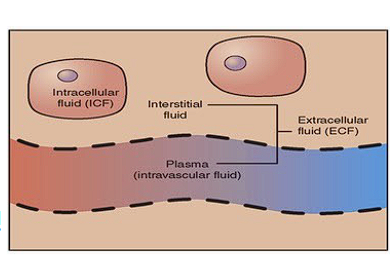
Word for fluid inside a cell?
Intracellular
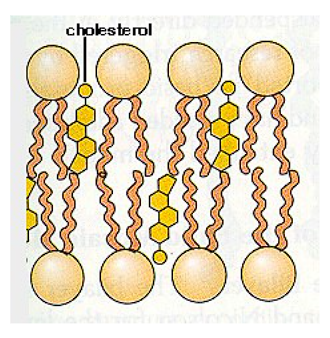
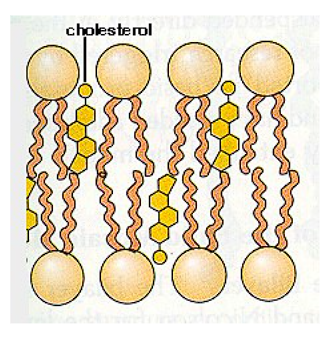
What does the Hydroxyl group in Cholesterol align with?
Polar (Phosphate) side of phospholipids
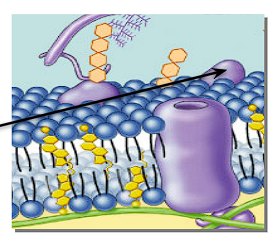
What is a peripheral protein + its position on a cell membrane?
A protein that is loosely bound to the surface of a membrane.
Helps with transportation + communication
“Identity marker”
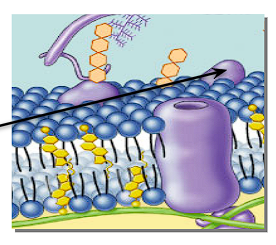
What is an Integral/transmembrane protein + its position in a cell membrane?
A protein embedded in the cell membrane
Channels + pumps proteins through the cell membrane
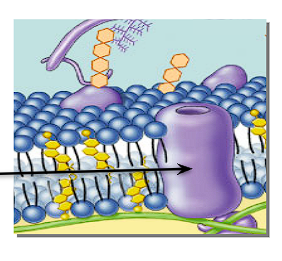
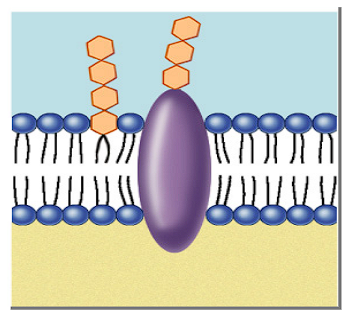
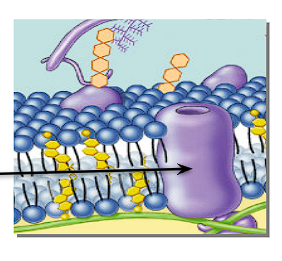
Function of glycoproteins in a cell membrane?
Act as a receptor, “recognizes” hormones to permit access to the cell
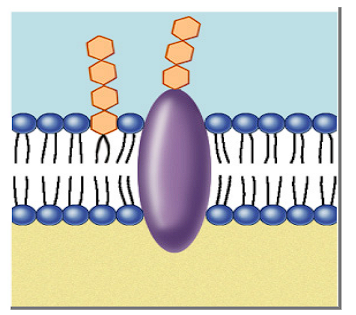
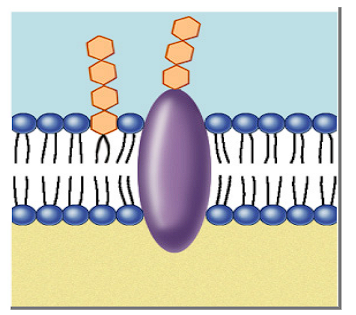
Function of glycolipids in a cell membrane?
Lipids with a carbohydrate attached
Provide energy
Marker for cell recognition
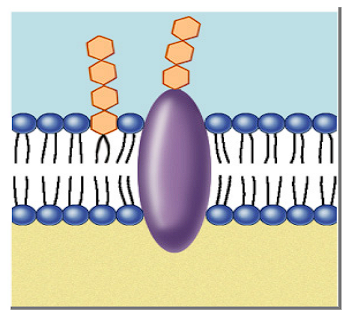
What is a concentration gradient?
Difference between concentration on inside and outside of membrane
What is a passive mechanism?
Substance moves w/concentration gradient and does not require energy
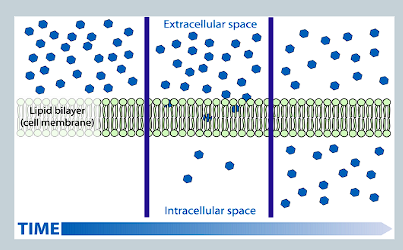
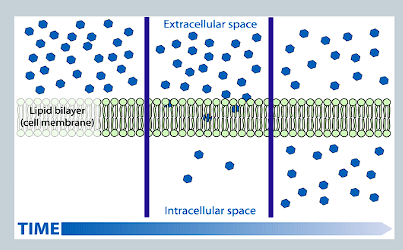
What is diffusion and does it require an energy input?
Natural movement of ions/molecules from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration
Does not require energy
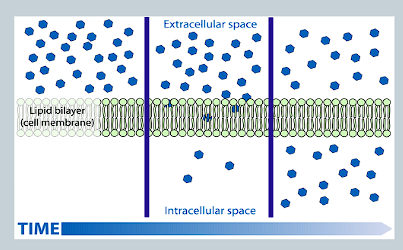
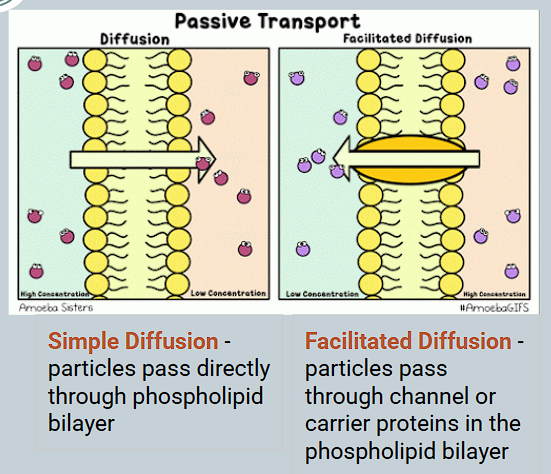
What is simple diffusion?
Molecules move via diffusion directly through the lipid bilayer
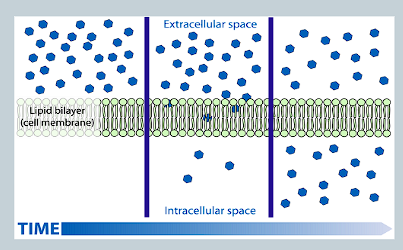
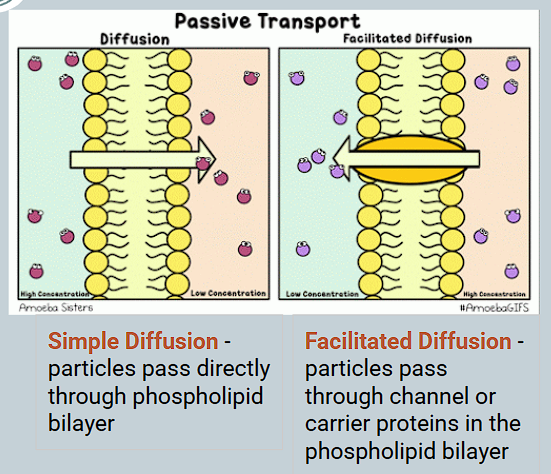
What is facilitated diffusion?
The transport of ions/molecules across a membrane through a carrier protein
Occurs ALONG THE CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
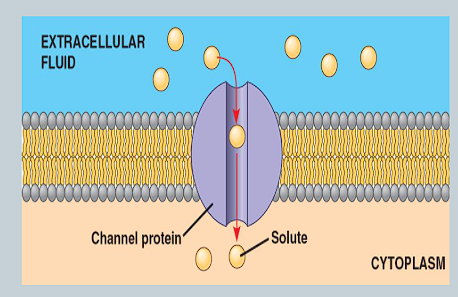
What is a channel protein?
An integral protein that remainss open all the time so substances can ‘flow through’
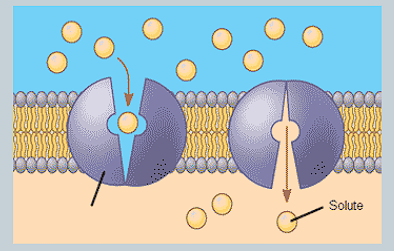
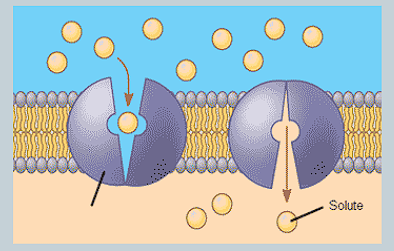
What is a carrier protein? How does it transport specific molecules?
A protein that binds to specific molecules, then changes them before releasing into the other side.
E.g glucose transporters
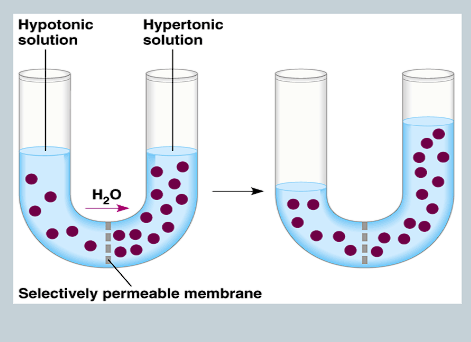
What is Osmosis?
The movement of water from an area of higher to lower concentration.
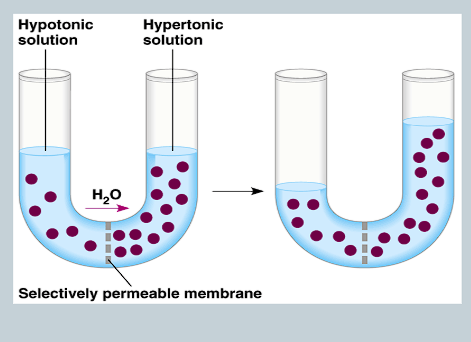
What is Osmotic Concentration?
The concentration of all solutes in a solution
What is a hypertonic concentration?
A solution with a higher solute concentration that another
What does it mean when two solutions are isotonic?
They have the same solute concentration.
What is Osmotic Pressure?
the pressure of a solution against a semipermeable membrane to prevent water from flowing across the membrane
When referring to cell membranes, the use of hypertonic/hypotonic refers to…
The concentration of solutes OUTSIDE the cell.
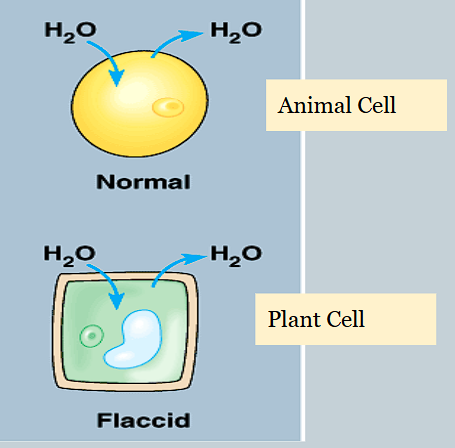
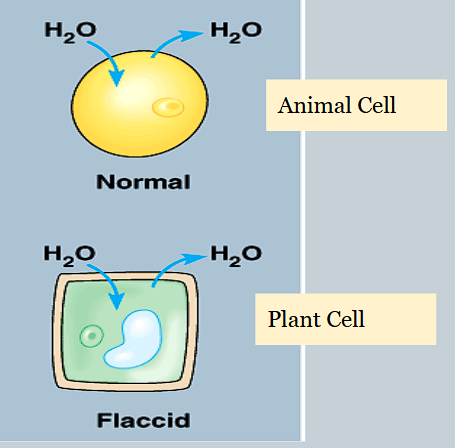
How do isotonic solutions affect osmosis in cells?
There is no net movement of water, it flows in both directions
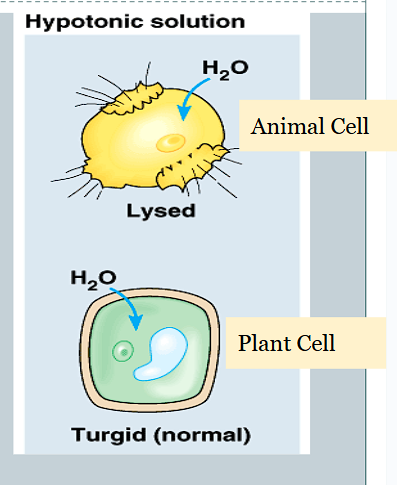
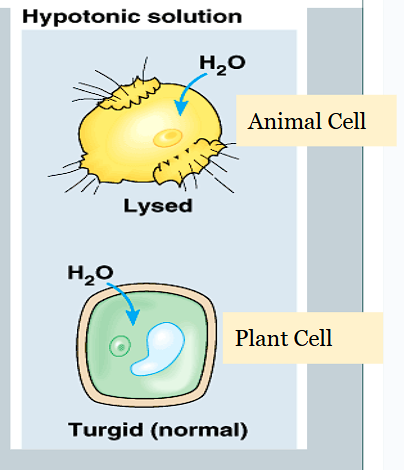
How do hypotonic solutions affect osmosis in cells?
Net movement of water is into the cell.
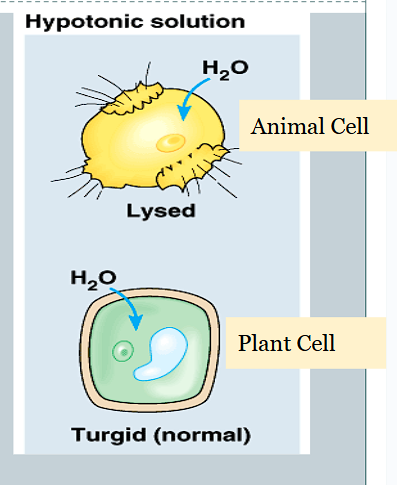
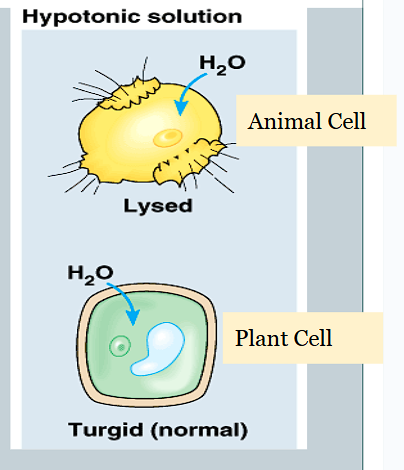
What happens when an animal cell bursts due to too much water?
It Lyses
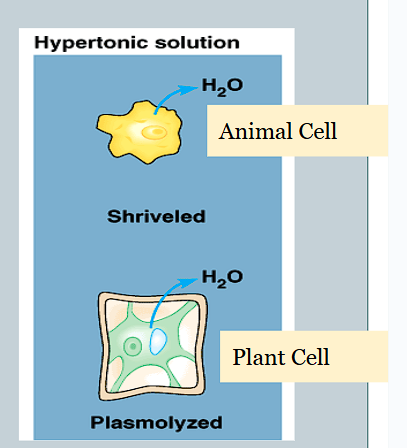
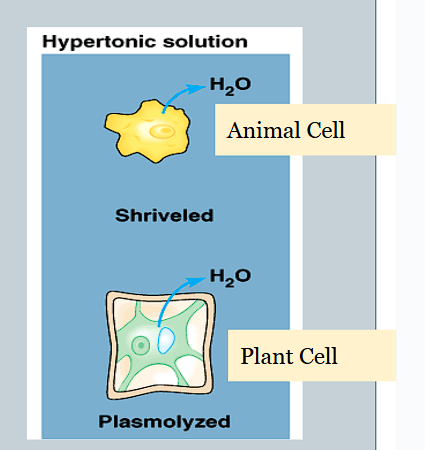
How do hypertonic solutions affect osmosis in cells?
The net movement of water is out of the cell
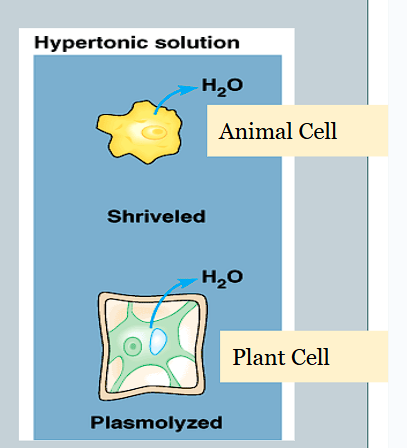
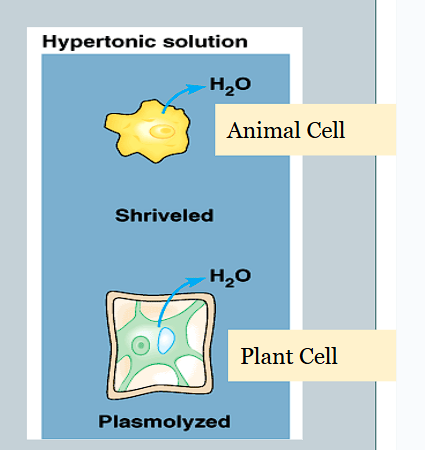
What is it called when the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall (PLANT)
Plasmolysis
What is it called when only one type of substance is actively transported through a membrane?
Uniport
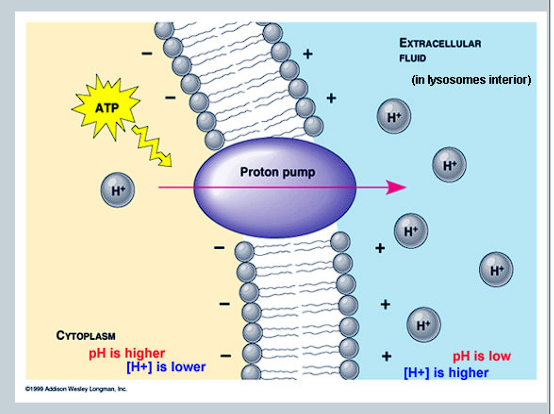
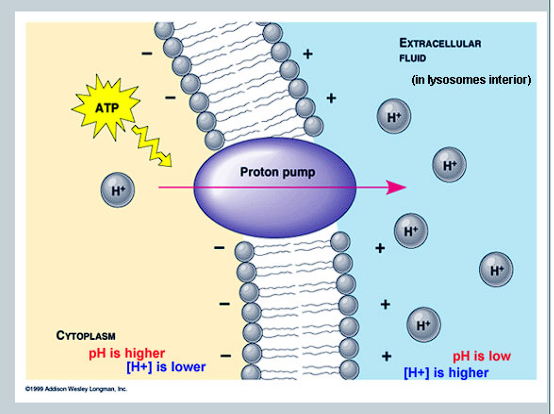
What is a proton pump?
uses energy from ATP to pump hydrogen ions across the membrane
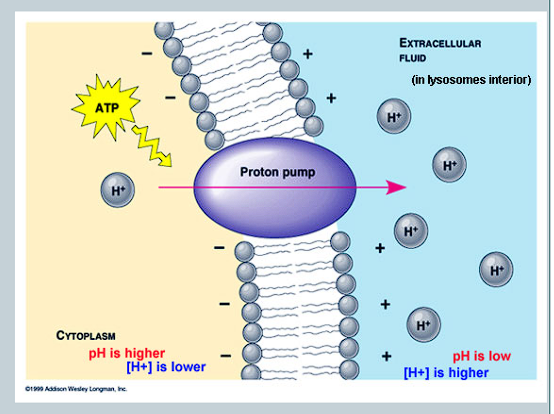
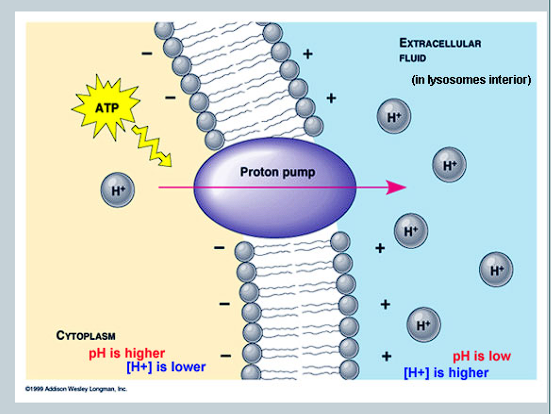
What is created as a result of the transportation of H+ ions, and what effect does it have on the concentration gradient?
A large difference in charge is created due to the charge of H+
Builds up a concentration gradient
Creates an electrochemical gradient that stores potential energy
What is cotransport?
When two substances are simultaneously transported across a membrane by one protein.
What are the two types of Cotransport?
Symport - Both substances going in the same direction
Antiport - Two substances are being transported in opposite directions
What is Membrane-assisted transport?
Transport method used to move material too large to cross the cell memnbrane through a channel/carrier protein (REQUIRES ENERGY)
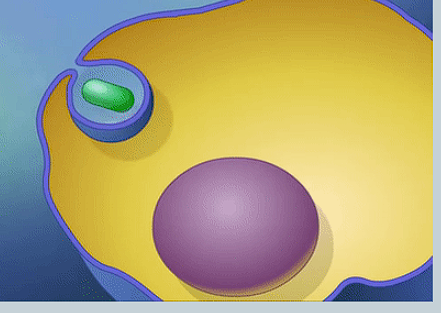
What is Endocytosis?
When a cell absorbs material by folding the cell membrane around it, then pinching off
What is phagocytosis?
Endocytosis involving solid particles
What is pinocytosis?
Endocytosis involving liquid particles
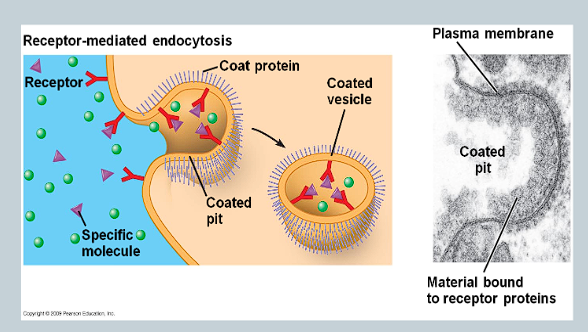
What is receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME)?
Parts of the cell membrane are covered in receptor proteins
These proteins will only bind to specific molecules
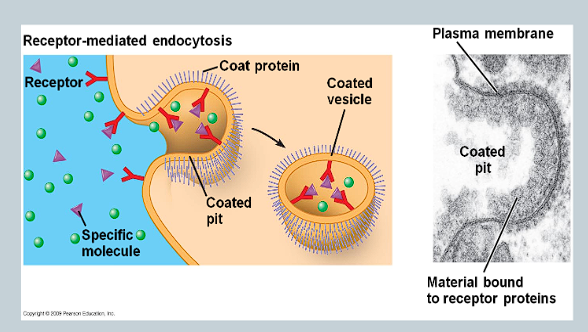
What is Exocytosis?
A vesicle fuses with the cell membrane to release its contents outside of the cell.
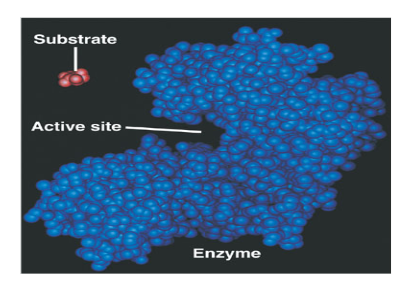
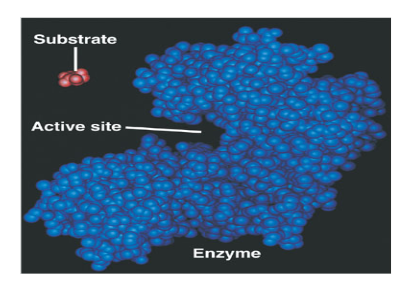
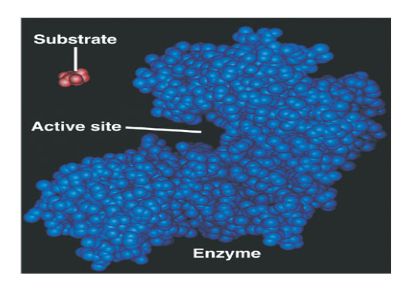
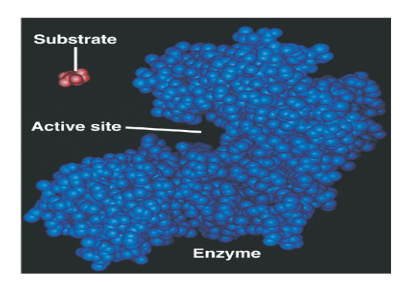
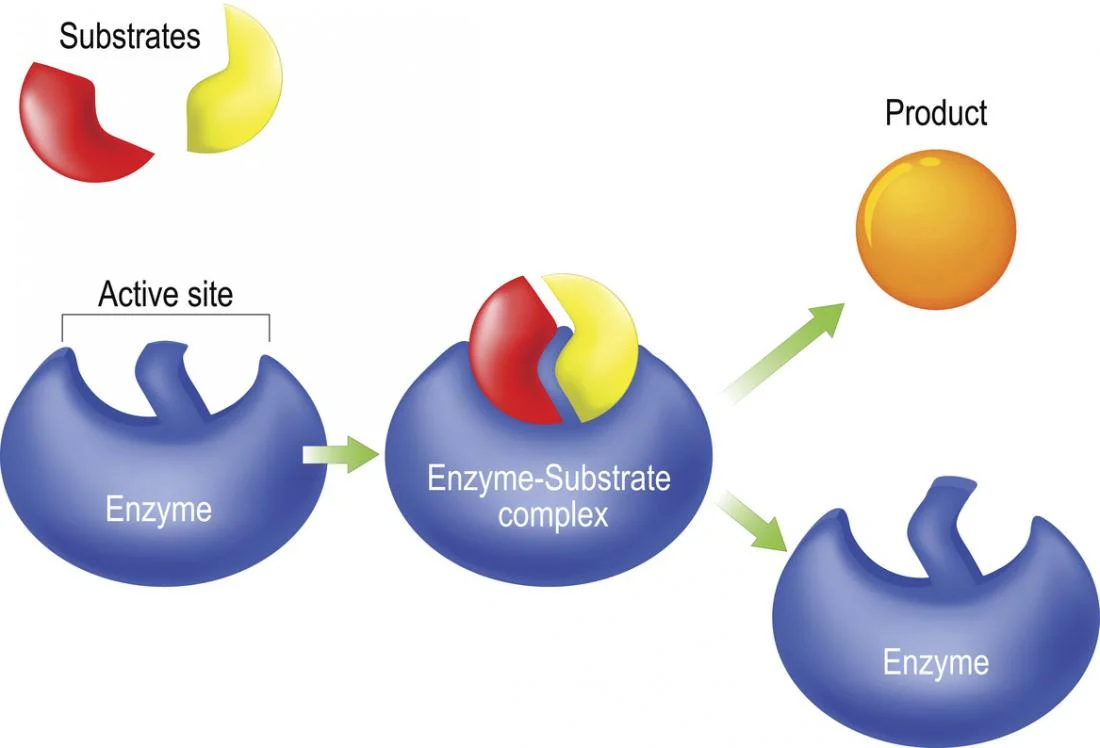
What is an Enzyme?
a protein catalyst
It speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process
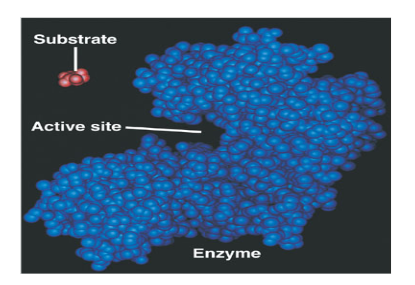
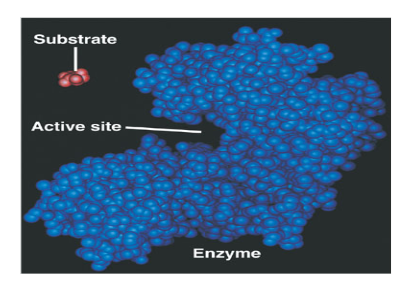
What is a substrate?
A reactant in a reaction involving an enzyme
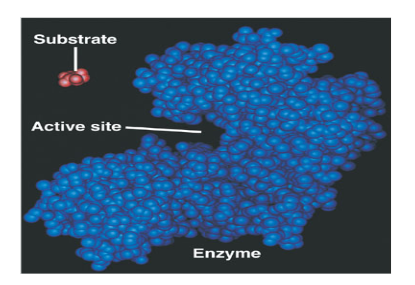
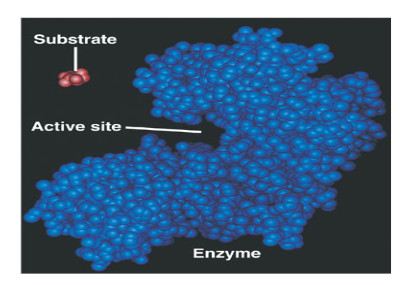
What is an active site?
The region on an enzyme that substrates bind to.
Explain:
Lock and Key Model
Induced Fit Model
Lock and Key Model:
Active site matches substrate exactly
Induced Fit Model:
Active site sort of fits substrate
Once substrate binds, functional groups of various amino acids react and shift, allowing the enzyme to change its shape to better accommodate the substrate
How do enzymes speed up a reaction?
They lower the activation energy required to ‘kick start’ a chemical reaction.
Term for destroying a protein/other macromolecule
Denaturing
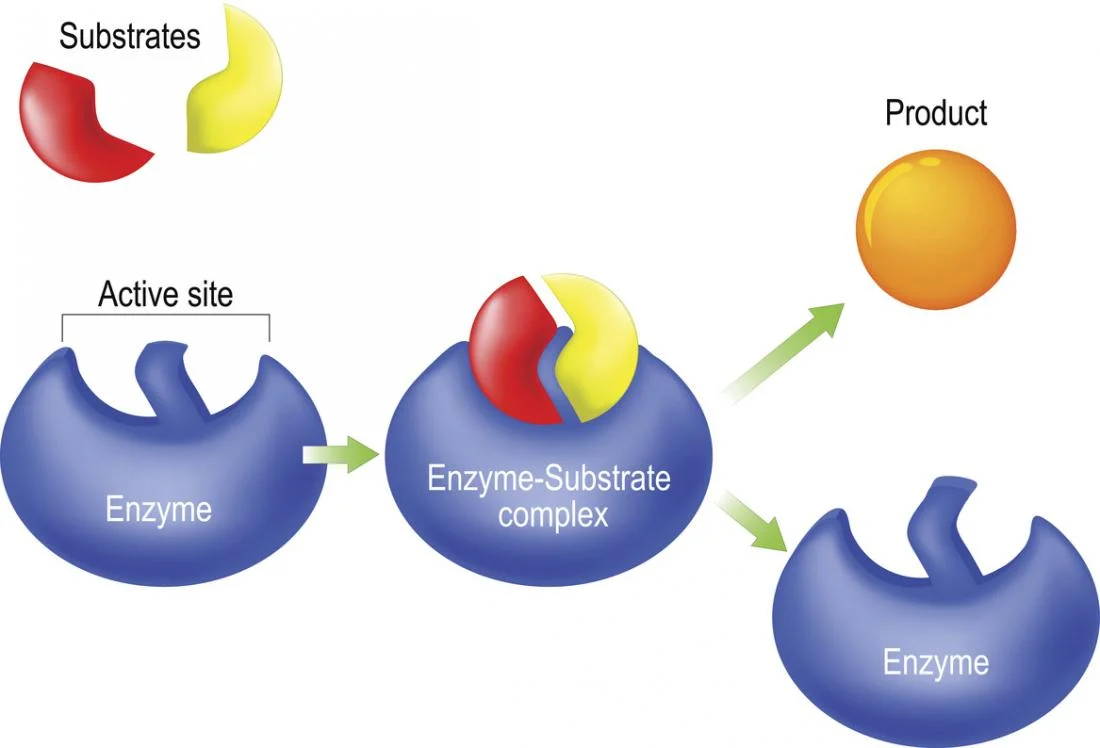
If enzymes do not change the overall reaction, then what do they do?
They speed up the reaction by lining up the reactant(s). This lines up their bonds to be broken (and new ones formed), and allows for more collisions and overall a greater number of products
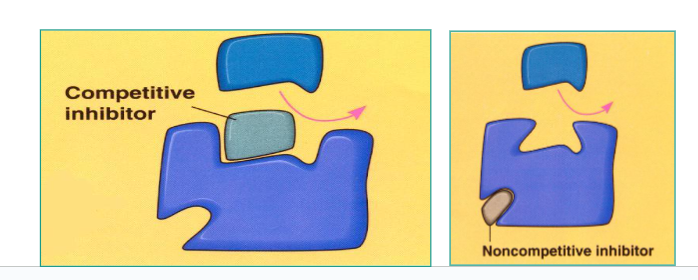
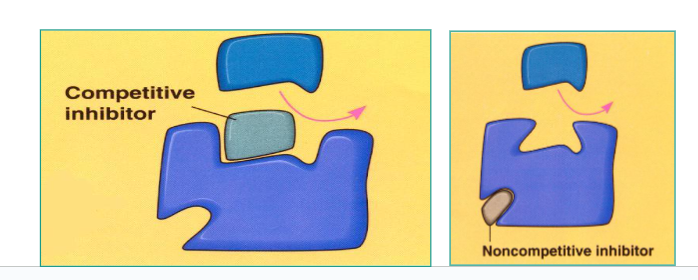
Explain:
Competitive Inhibitor
Non-competitive Inhibitors
Competitive Inhibitor:
Similar to the substrate, binds to active site and blocks normal substrate from binding.
Non-competitive Inhibitors:
Bind to the enzyme at an allosteric (NOT ACTIVE) site, causing a change in the shape of the active site and preventing substrate from binding.
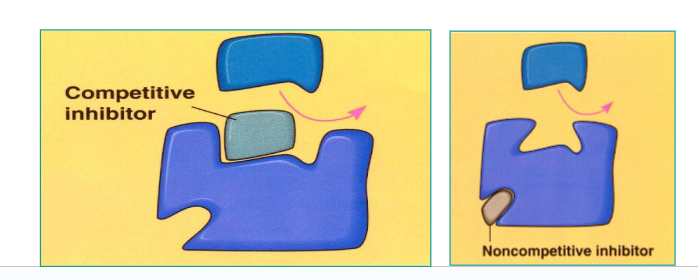
What is an ALLOSTERIC site?
A site that is not the active site.
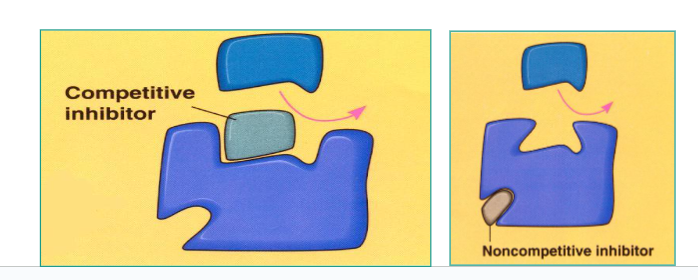
What is an allosteric inhibitor?
An inhibitor that binds to an allosterically controlled enzyme, stabilizing it and making it so that the enzyme CANNOT function
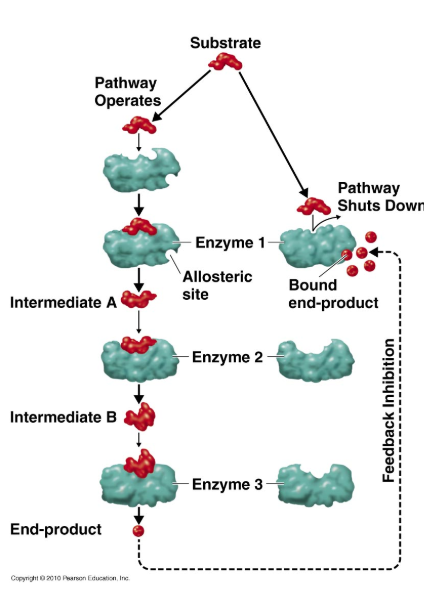
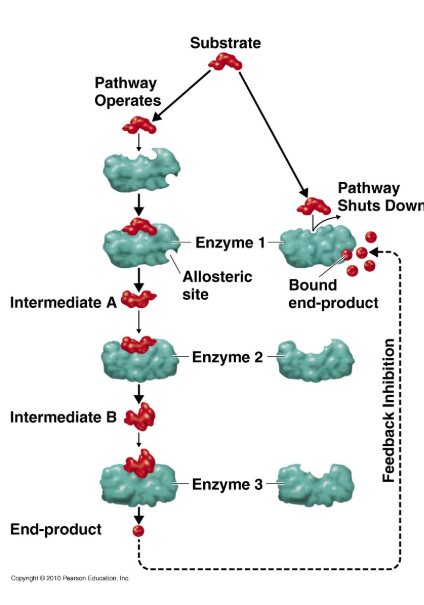
What is feedback inhibition?
Product of an enzyme-substrate complex travels back to inhibit an earlier enzyme in the reaction, interrupting the ‘steps’
What is it called when an enzyme and a substrate react?
An enzyme-substrate complex
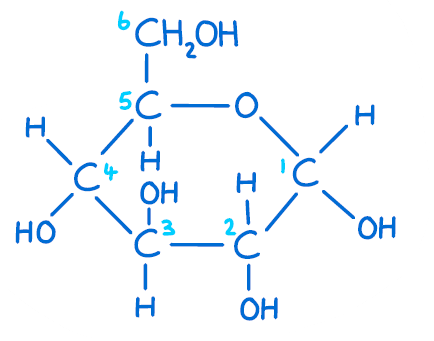
Glucose molecule (C6H12O6)
What is an intermolecular force?
A force that occurs between molecules
Types of Intramolecular Bonds (2)
Ionic
Covalent
What is Adhesion?
Tendency of water molecules to stick to other molecules
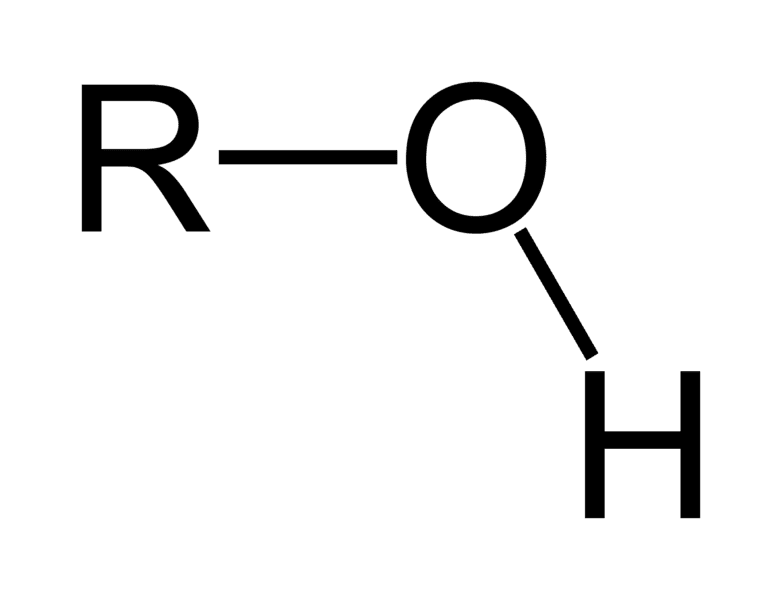
What functional group is this?
Hydroxyl
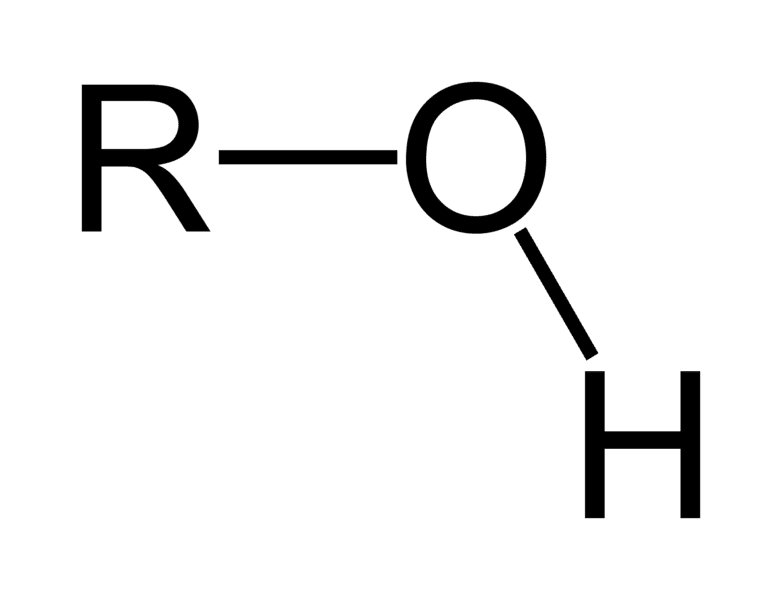
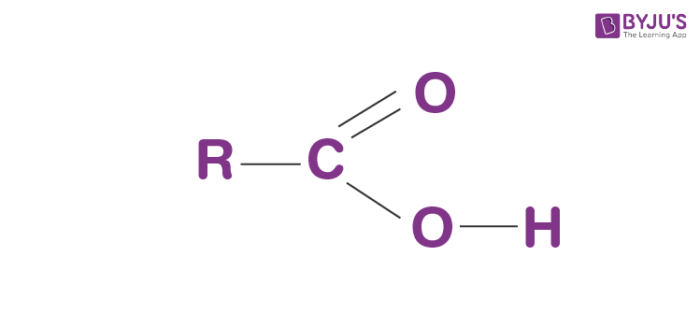
Draw a Carboxyl functional group.
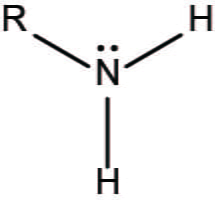
What functional group is this?
Amino
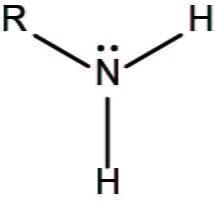
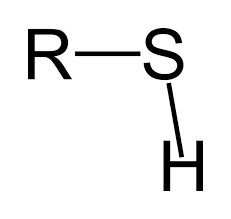
What functional group is this?
Sulfhydryl
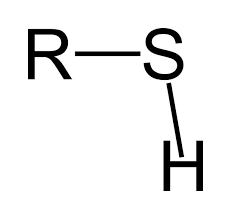
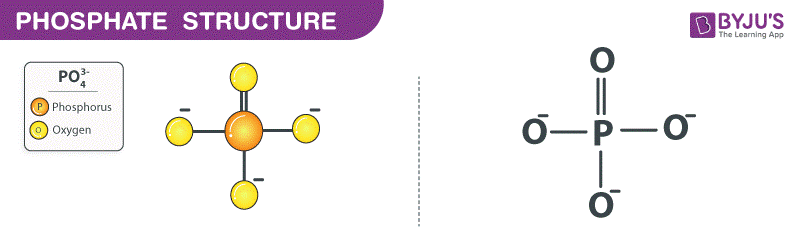
What functional group is this?
Phosphate
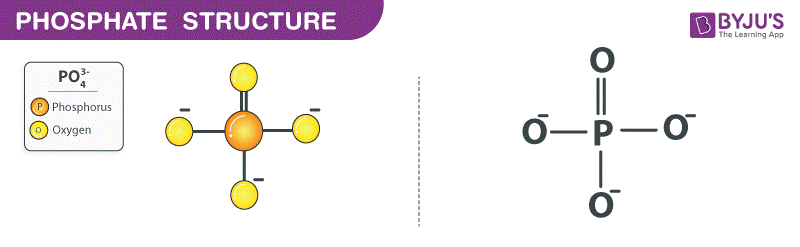
What is a monomer?
The subunit of a polymer.
What is a polymer?
A macromolecule.
Name Monomers For:
Carbohydrates
Lipids (Fats)
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Monosaccharides
Fatty acid/Glycerol
Amino Acids
Nucleotides
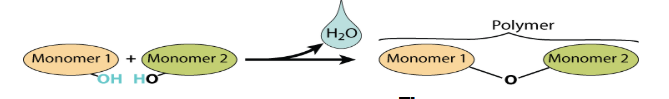
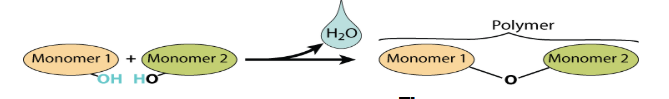
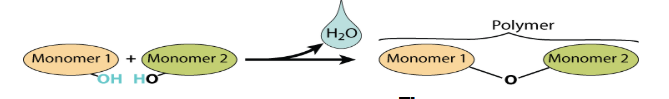
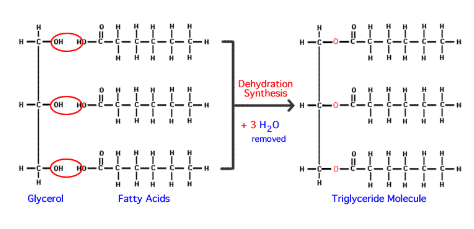
What is dehydration synthesis? What products does it form?
Reaction that forms macromolecules out of their monomer units.
H2O and a polymer (liked via. an O atom) are formed as a product.
What is an Anabolic reaction?
A reaction that produces large molecules from smaller subunits
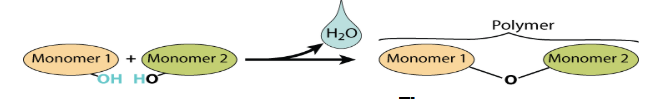
What is Hydrolysis? What are its reactants?
Reaction that breaks macromolecules into its subunits
Reactants are a macromolecule and H2O
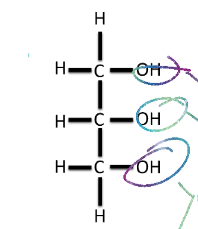
Draw Glycerol
Hint: C3H8O3, 3 Hydroxyl groups
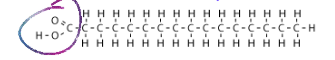
What is a fatty acid?
Hydrocarbon chain with a Carboxyl group on one end
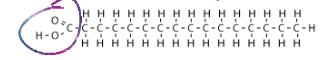
Draw a triglyceride.
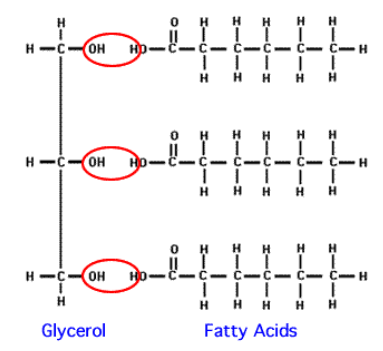
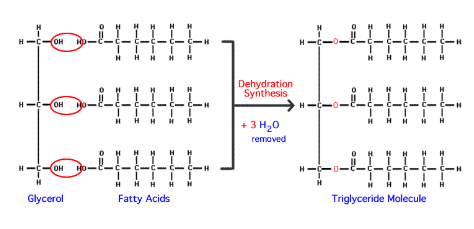
What is an ester linkage?
Dehydration synthesis between a glycerol and three fatty acids.
What is a saturated fatty acid?
Fatty acid has the maximum amount of hydrogen atoms (There are no double bonds between Carbon atoms)
What fats are solid at room temperature?
Saturated fats.
Two other types of lipids:
W___________
S___________
Waxes
Sterols
Why are unsaturated fats liquid at room temperature?
The double-bonds in the carbon chains cause the HC chains to bend away, forming less bonds
What is an immunoglobulin?
A protein that protects against foreign microorganisms + cancerous cells
Possible functions of a protein (4)
Enzyme
Immunoglobulin
Protein carrier
Structural
What is a protein conformation?
The final shape of a protein
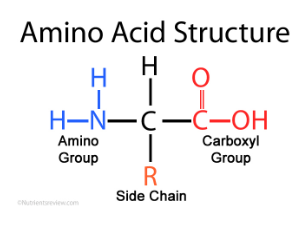
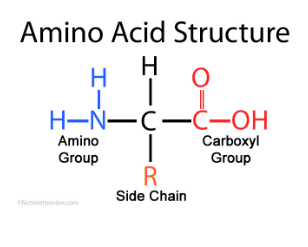
Parts of an Amino acid (3)
Amino group
Side chain
Carboxyl (COOH) group
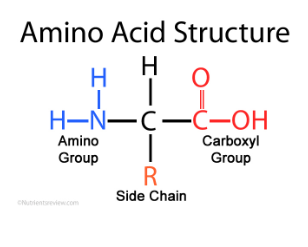
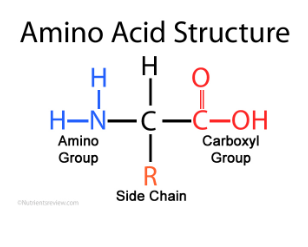
What is an R group?
Determines properties of an amino acid
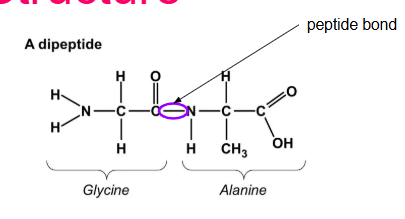
What is a peptide bond? How do they form?
Holds amino acids together
Formed by a D.S reaction between the Amino group of an acid and the carboxyl group of an adjacent amino acid (O—N)
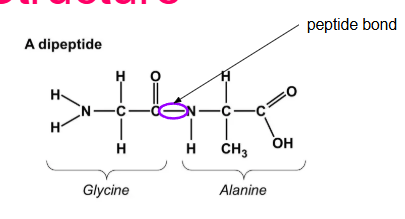
What is a globular protein?
Composed of 1 or more polypeptide chain that takes a round/spherical shape
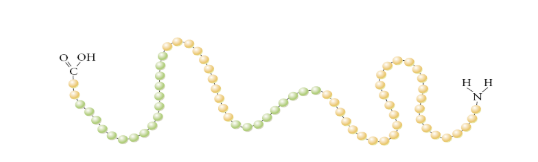
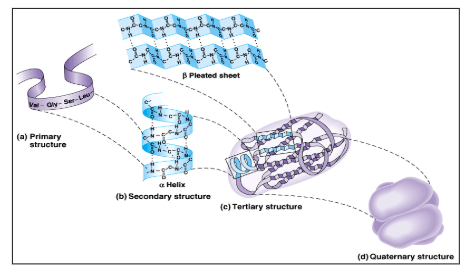
What is a primary protein structure?
Chain of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
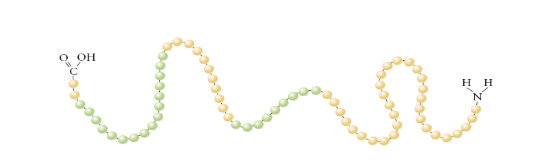
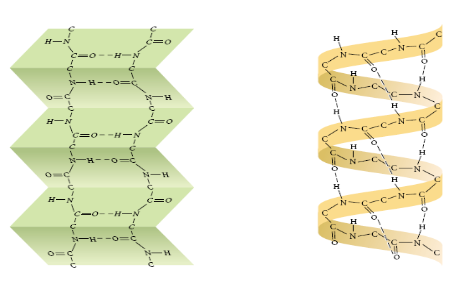
What is a secondary protein structure?
Explain:
Alpha (Helix)
Beta (Pleated sheets)
Formed by hydrogen bonds between O of a carboxyl group and H atoms of an amino group
Alpha (Helix) - Tight coil produces by H-bonds all at the same distance
Beta (Pleated sheets) - H bonds gormed between parallel stretches of a polypeptide
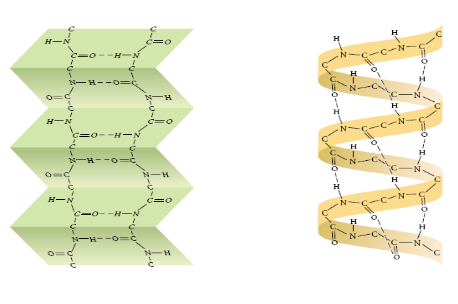
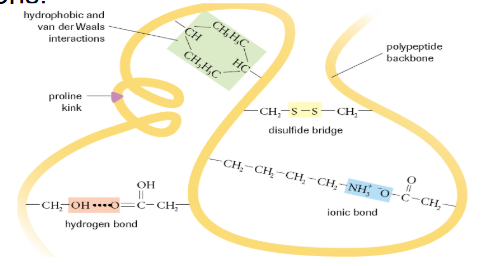
What is tertiary protein structure?
Polypeptide chain is folded additionally due to interactions between R-groups
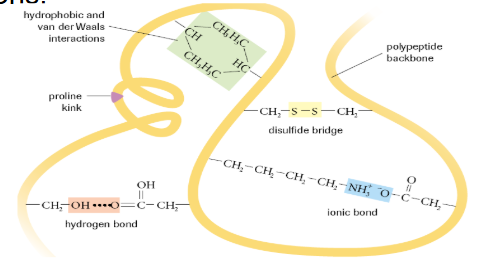
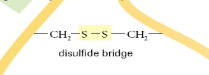
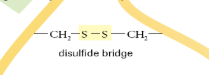
What is a Disulphide Bridge?
The bond formed between 2 sulphurs of nearby cysteines
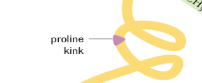
What is a Proline Kink?
A special kink in a polypeptide chain that occurs due to the presence of proline
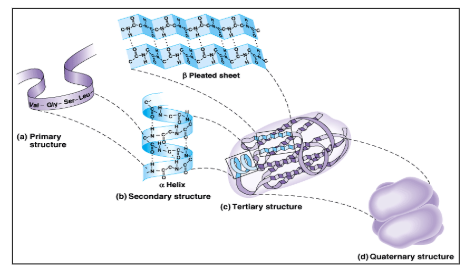
What is quaternary protein structure?
When 2 or more polypeptide chains come together and form a functional protein.
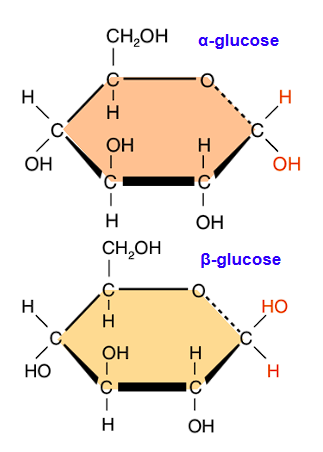
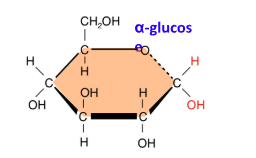
Draw alpha-glucose
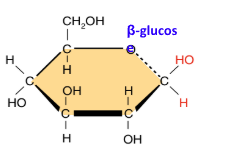
Draw beta-glucose
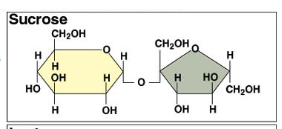
Draw sucrose
a-Glucose + Fructose
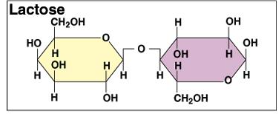
Draw lactose
b Glucose + b Galactose
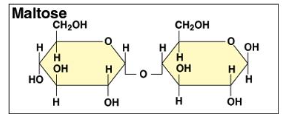
Draw maltose
a-glucose + a-glucose
Draw alpha-galactose