Introduction to Assistive Technology
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Assistive Technology- What is it?
There are two parts to the definition
Device
any item, piece of equipment or product system, whether acquired commercially off the shelf, modified, or customized, that is used to increase, maintain, or improve functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities
a device could be defined as AT for one person, but not another (e.g., an elevator isn’t an AT for me, but it would be an AT for someone who uses a wheelchair)
Service
any service that directly assists an individual with a disability in the selection, acquisition, or the use of an assistive technology device
Definitions Non-federal
“For most people, technology makes things easier; for people with disabilities, however, technology makes things possible.”
Classifications of AT
Assistive vs. Rehabilitative or Educational Technologies
assistive= helping someone to do something; compensatory
e.g., communication device helps someone to communicate
rehabilitative= helps to improve a function that’s been lost; improving
educational= used primarily for education
e.g., to write a paper, to complete a chemistry experiment
all funded by different organizations, so it’s important to use these different terms
High Tech vs. Low Tech
high-tech is usually
electronic, expensive, requires batteries/charging/etc., requires maintenance, requires background of how to use
people ~like~ these tech better
low-tech is usually
not electronic, cheaper, doesn’t require batteries/charging/etc., easier to use
usually better for helping people in ~most~ situations
Hard vs. soft technologies
hard
the pieces required to create the technology
e.g., the software
soft
the people creating the technology
e.g., OTs
Minimal (orthoses) vs. Maximal (prostheses)
minimal= technology provides some assistance or augments the ability to perform a task (than what you might have been able to)
e.g., Grammarly just to check spelling and grammar
maximal= technology takes over the entire task or a majority of it
e.g., wheelchair usage by someone who can’t walk
General vs. specific technologies
general= can be used across a wide range of tasks
e.g., cushion for posture can be used on a bed, chair, floor, etc.
specific= can only be used for 1 purpose
e.g., communication device is soley for improving communication
Custom vs. Commercial
custom= customizing something for a client
e.g., our adaptive devices
commercial
e.g., at Walgreens, CVS
***Appliances vs. Tools
appliances= needs no experience
e.g., put your glasses on —> you see
e.g., plug-in appliance —> it works
tools= require specific expertise/training in order to use
e.g., wheelchair, communication device, certain types of driving equipment
What is an Appliance?
Technology that involves no expertise
eg., you just plug it in!
What is a Tool?
Technology that involves expertise
Service Providers (the organization) of Assistive Technology: Who are They? + requirements to get certified
Rehabilitation therapists
Assistive technology certified professionals (Certified ATP through RESNA: Rehabilitation Engineering and Assistive Technology Society of North America)
Education: Bachelor’s or Associate’s in Rehabilitation Science OR non-rehabilitation field)
Work Experience (# of years and FTE (full-time equivalent))
Examination (4-hour multiple choice)
Renewed annually
Vendors
The AT consumer, family, and friends
AT within OT Practice
different settings is AT practiced in
Delivered in a variety of settings
hospitals,
rehab centers,
SNF,
outpatient,
HHA,
schools,
work sites and
communities
Delivered in a variety of roles (primary therapist, team member, consultant)
Broad range of services (evaluation, recommendation, justification, advocacy, funding, fabrication, customization, training, integration, and follow-up)
“When a person is unable to participate in meaningful activities or occupations, assistive technology may be used as a support”
“The intent is to use technology as a tool to optimize the individual’s participation in areas of occupation”
Service Delivery Settings of AT
Rehabilitation Settings
University Based
State Agency Programs
Private Practice
Durable Medical Equipment Suppliers
Veterans Administration
Local Affiliate of a National Nonprofit Disability
Volunteer Programs
Service Delivery Models
Medical
patient-focused (i.e., clients are actually referred ot as “patients”);
medical necessity;
insurance reimbursement;
DME (Durable Medical Equipment)
Educational
student-focused (e.g., writing aids);
FAPE/IEP;
school budget;
must be left in the school/cannot take it home (e.g., school iPad), as the state/school system pays for it
Vocational rehabilitation
worker focused
vocational need
federal/state funds
e.g., driving controls
can be modified up to $100
Consumer-direct
consumer-focused;
personal choice;
personal funds (pay for whatever they need out of pocket; insurance doesn’t cover);
ECUs (Environmental Control Unit- device that allows people with disabilities to control electronic devices and appliances in their environment through alternative input methods like switches or voice commands)
AT Service-Delivery Process (steps)
Referral and Intake
Initial Evaluation
Recommendation and Report
Implementation
Follow-up
Follow-along

Legislations affecting AT
Rehabilitation Act of 1973
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act of 1997
Assistive Technology Act of 1998
Developmental Disabilities Assistance and Bill of Rights Act
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
only targets clients with developmental disabilities
e.g., making sure they can go to school, get a job, and live independently
prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities
lots of problems, but a great 1st step in the right direction
Medicaid
income-based; can qualify if you are in poverty
largest funding for AT
Medicare
age-based
last resort- should not be the first place you go to; only if nowhere else meets your needs
Low or No Tech: Do Not Dismiss the Importance!
dollar-store/home-made stuff <3
Laptrays, adapted desks
Typing aids, splints
Book holders, 3-ring binders, slant boards
Built-up handles, grips, Crayon TwistUps, etc.
Reachers, mouth sticks, and head/chin pointers
Handheld magnifiers
Raised line paper, writing guides
Homemade devices! Client or therapist!

Look for Non-AT Choices-
Choosing items for ease of use with limited hand function
e.g., flip top squeeze toothpaste, hand mixer, soap pump
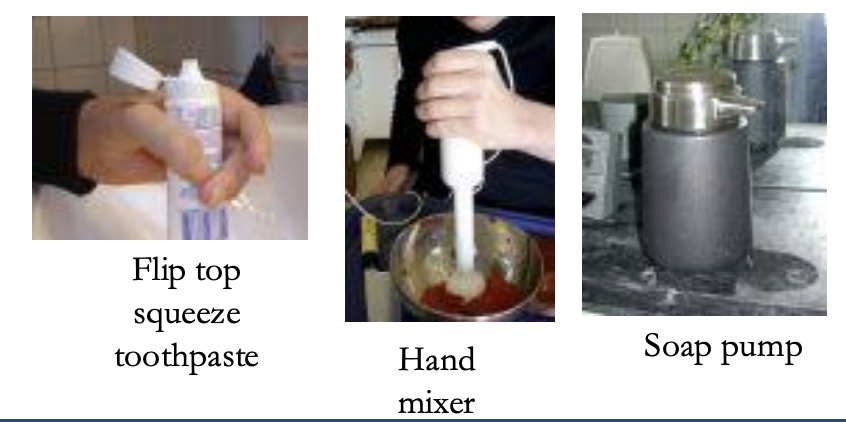

Specific AT that OTs might primarily work with
Assist in seating and positioning and ECU integration
Switch access
Mounting
Writing assistance tools and software
But as an OT gains more expertise in AT, the roles between service providers blend
Goal Setting
Must focus on activity; what the client wants to be able to do!
it is not all about the device- but the activity!