Sociology 1000 - Test 2
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Group Definition - Groups and Organization
Interaction of two or more people based on common interest.
Network - Groups and Organization
Web of social ties that links people that have little common identity or interaction.
Organization - Groups and Organization
A large secondary group of people participating in a division of labor, coordinated leadership for shared goal.
Close-Knit Networks - Groups and Organization
Everyone knows everyone else.
Loose-Knit Networks - Groups and Organization
Only one person knows everyone else.
Other people don’t connect with each other? One person connect others who typically otherwise wouldn’t interact.
Primary Groups - Groups and Organization
Small, Intimate, Long-Term. (eg. Family, Close Friends, etc)
Secondary Groups - Groups and Organization
Larger, less personal, task-orientated (eg. workplace, schools)
In-Groups - Groups and Organization
Groups we feel loyalty towards
Out-Groups - Groups and Organization
Groups we feel opposition towards (Feeling could also be competition)
Reference Groups - Groups and Organization
Groups we compare ourselves to for self-evaluation and improvement?
Strong Ties - Groups and Organization
Close, personal relationships…like primary groups.
“Not who you know but, who knows YOU the most
Weak Ties - Groups and Organization
Distant, less personal connections. Like secondary groups. Groups for career opportunities.
Bonding - Groups and Organization
Strengthen relationships within a group.
Bridging - Groups and Organization
Connecting different groups to spread information and resources.
Informal Groups - Groups and Organization
No defined roles or goals
Formal Groups - Groups and Organization
Explicit goals, roles, rules and responsibilities.
Primary Groups - Groups and Organization
Small groups in which relationships are both personal and enduring
Secondary Groups - Groups and Organization
Larger groups based on specific interest or activity.
Dyads (Group Structure) - Groups and Organization
Groups of two (most intimate but the lest stable)
Triads (Group Structure) - Groups and Organization
Groups of three (more stable but alliance(s) within the group)
Larger Groups (Group Structure) - Groups and Organization
More stable but less personal
Instrumental Leader - Groups and Organization
Focuses on tasks and efficiency
Expressive Leader - Groups and Organization
Focuses on group harmony and emotional well-being…chemistry.
Democratic Leader - Groups and Organization
Encourages group participation
Authoritarian Leader - Groups and Organization
Centralized control, strict rules.
Lassez-Fair Leader - Groups and Organization
Minimal interference, allow self-direction.
Group Cohesion - Groups and Organization
Level of commitment and unity among members.
Group Think - Groups and Organization
When pressure for conformity suppresses dissent and critical thinking.
Formal Organization - Groups and Organization
Larger structured, goal orientated group
Bureaucracy - Groups and Organization
An efficient, structured organization, to perform complex tasks efficiently.
Types of Social Control - Groups and Organization
Coercive power
Utilitarian Power
Normative Power
Alternatives of Control - Groups and Organization
Selection of member
Socialization on members
Characteristics of Bureaucracy - Groups and Organization
Specialization: Each person has a specific role.
Hierarchy of positions: Clear chain of command.
Rules and regulations: Formal guidelines for operations.
Technical competence: People are hired based on skills.
Impersonal relations: Decisions based on rules, not personal connections.
Formal communication: Written records of decisions and actions.
Problems with Bureaucracy- Groups and Organization
Waste and incompetence
Ritualism
Inertia
Alienation
Structured inequality
Definition (Sex) - Human Sexuality
Physical differences between males and females
Gender - Human Sexuality
Social expectations based on sex
Sexual Identity - Human Sexuality
What someone feels like as…male or female
Sexual Orientation - Human Sexuality
Who someone is attracted to
Intersex Persons - Human Sexuality
Born with partial male AND female physical characteristics
Homophobia - Human Sexuality
Irrational FEAR of homosexuality in others
Heterosexism - Human Sexuality
Belifs that deny, deingrate or stigmatize non-heterosexual behaviour.
Sexual Desires - Human Sexuality
A combination of objective physical responses
Sexual Scripts - Human Sexuality
Learned guidelines (through society) for sexual behavior (when, where, how, etc)
Sexual Harassment - Human Sexuality
Unwanted sexual comments, gestures or actions
Sexual Violence (Sexual Assault) - Human Sexuality
Touching someone without consent.
Sex Work - Human Sexuality
Prostitution, escorting, pornography
Adultery - Human Sexuality
A married personal having sexual intercourse with anyone other than their spouse.
Infidelity - Human Sexuality
Any action, sexual or not that is a breach of trust, etc
Polyamory - Human Sexuality
Being in many relationships with consent of the people involved.
Pornography - Human Sexuality
Any written, visual or spoken material that is sexually explicit or graphic and is arousing our intended to be arousing.
Obscenity - Human Sexuality
Material considered offensive by society
Erotica - Human Sexuality
Artistic depictions of sexuality
Deviance - Deviance
Breaking social norms…not necessarily bad.
Crime - Deviance
Breaking the law
Social Control - Deviance
Ways society enforces behavior
Absolutist - Deviance
Deviance is always wrong
Relativist - Deviance
Deviance depends on society’s norms, which can change over time, starts with deviance though
Societal Values and Norms - Deviance
People learn what is acceptable through what they see in others.
Internalization of Norms - Deviance
People voluntarily follow rules
Sanctions - Deviance
Society rewards conformity and punishes deviance.
Positive Sanctions - Deviance
Rewards fro conformity
Negative Sanctions - Deviance
Punishments for deviance
Formal Sanctions - Deviance
Official punishments from institutes. (eg police, courts, suspension from work or something)
Informal Sanctions - Deviance
Unofficial punishments from peers (eg gossip, insults, etc)
Clarifies Moral Boundaries - Deviance
People learn what is acceptable by seeing others punished
Strengthens Social Change - Deviance
Deviants challenge the systems and if there are any holes, they can be fixed.
Strengthens Social Unity - Deviance
Groups unite against deviant behavior
Acts as a Safe Valve - Deviance
Minor deviance prevents bigger social problems
Selective Application of Norms and Laws - Deviance
The powerful define what is deviant and benifit from those definitions.
Medicalization of Deviance - Deviance
Transforming moral/legal deviance into a medical issue. Instead of punishing drug users, we call them sick and send them to rehab.
Labeling Theory - Deviance
Being labeled “Deviant” changes how others see you and consequently how you see yourself
Labeling Theory - Deviance
Primary Deviance = The initial rule-breaking behavior, which doesn’t impact identity.
Example: A student cheats on one test but is still seen as a "good student."
Secondary Deviance = When a person accepts the deviant label and continues deviant behavior.
Example: A student labeled as a "cheater" keeps cheating because everyone expects them to.
Stigma = A powerful negative label that changes a person’s self-concept.
Example: Being labeled as a "criminal" can make it harder to get a job.
Types of Crimes - Deviance
Consensus Crimes = Society agrees they are harmful (e.g., murder, assault).
Contested Crimes = Society debates if they should be crimes (e.g., drug use, prostitution).
White-Collar Crime = Financially motivated crimes by powerful people (e.g., fraud, tax evasion).
Corporate Crime = Crimes committed by businesses (e.g., pollution, false advertising).
Street Crime = Visible crimes like theft and assault.
Organized Crime = Criminal organizations like the Mafia.
Hate Crimes = Crimes motivated by race, religion, or sexual orientation.
Moral Panics and Deviance - Deviance
Moral Panic = Widespread fear that a behavior threatens society.
Example: The "War on Drugs" exaggerated the dangers of marijuana.
Moral Crusaders = People who try to enforce moral laws (e.g., anti-abortion activists).
Social Stratification - Social Class
The ranking of people into a hierarchy based on a system.
Status and Role - Social Class
Basis for stratification. Ascribed or Achieved
Closed Systems - Social Class
No Mobility (Slavery, Caste)
Open Systems - Social Class
Some Mobility (Class System)
Intergenerational Mobility - Social Class
A child moves into a different class than their parents.
Intragenerational Mobility - Social Class
A child moves into a different class than their parents
Vertical Mobility - Social Class
Moving up or down the class hierarchy
Horizontal Mobility - Social Class
Changing jobs without changing social class
Functionalist Perspective (Davis & Moore) - Social Class
Social inequality is necessary.
Society needs different roles filled, and some jobs are more important than others.
Higher rewards (money, prestige) attract people to important jobs.
Example: Doctors and engineers get paid more because their jobs require skill and education.
Criticism: Ignores how people are born into privilege (e.g., rich kids have advantages).
Conflict Theory (Karl Marx) - Social Class
Social class is based on conflict between two groups:
Bourgeoisie = The rich, who own businesses and exploit workers.
Proletariat = The working class, who must sell their labor.
Capitalism leads to class struggle because:
The bourgeoisie control wages, profits, and production.
The proletariat is exploited and paid low wages.
The rich use ideology (media, education, laws) to stay in power.
Eventually, the workers will revolt and overthrow capitalism (Marx’s prediction).
Criticism: Overlooks middle class and ignores that capitalism allows social mobility.
Max Weber’s Social Class Theory - Social Class
Weber expanded Marx’s idea and said class has three dimensions:
Class (Wealth) = Economic position (income, assets).
Status (Prestige) = Social honor or respect.
Power (Influence) = The ability to control others.
Example: A teacher may not be rich (low class), but they have prestige (status) and influence over students (power).
Weber also introduced "Status Inconsistency" = When someone has high status in one area but low in another.
Example: A college professor has high prestige but low income
Major Social Classes
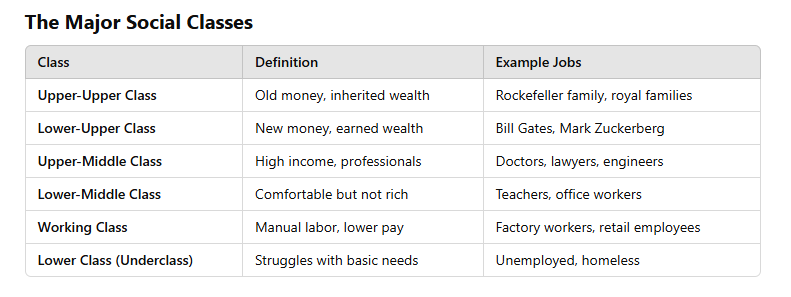
Absolute Poverty - Social Class
Not having basic necessities
Relative Poverty - Social Class
Being poor compared to others in your society
Gender Roles - Gender
Societal expectations for how men and women should behave/life day to day.
Gender Stereotypes - Gender
Overly simple beliefs about what men and women are like.
Men are strong, women are emotional
Gender Stratification - Gender
Unequal access of males and females to poverty, prestige and power.
Glass Ceiling - Gender
Invisible barrier that prevents women from reaching the highest executive level.
Glass Escalator - Gender
Fast-tracking men in women dominated occupations
Glass Cellar- Gender
Men stuck in the most dangerous occupations
Agents of Gender Socialization - Gender
Parents = Treat boys and girls differently (e.g., "Boys don’t cry").
Toys = Dolls vs. action figures reinforce gender roles.
Media = Shows men as dominant and women as passive.
Essentialism (Biological Determinism) - Gender
Gender differences are natural and based on biology.
Example: Men are aggressive because of testosterone.
Criticism: Ignores cultural and historical changes in gender roles.
Social Constructionism (The Argument from Nurture) - Gender
Gender is learned from society.
Example: In some cultures, men wear dresses (e.g., kilts in Scotland).
Criticism: Ignores some biological influences.
Feminist Theory - Gender
Gender inequality is deeply rooted in society.
Types of Feminism:
Liberal Feminism = Seeks equal rights through policy changes.
Radical Feminism = Wants to overthrow patriarchal systems.
Intersectional Feminism = Examines how race, class, and gender interact.
Gender and Media - Gender
Beauty Standards = Women are pressured to meet unrealistic appearance expectations.
Hypermasculinity = Men are taught to suppress emotions and act aggressively.
Sexualization of Women = Women in media are often portrayed as objects of desire.
Race - Ethnicity and Racialized Groups
A social category based on physical traits