OB Unit 6- Fetal Abdomen 24- 38
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are anomalies the liver is also associated with?
Diaphragmatic hernia
Omphalocele
The liver is _______ affected by isolated hepatic lesions in utero (parenchymal cysts, hemangiomas, hamartomas have been reported)
Rarely
What are US findings for liver lesions?
Tumors appear hypoechoic, solid masses within liver, may have cystic components
~ 5% are calcified
If multiple calcifications present? if from infection—- brain & spleen may be affected from infection also
What is Situs Inversus?
•Total reversal of abdominal & thoracic organs
What is Partial reversal?
Mirror image of some organs
What is the mortality rate percentage for partial reversal?
90-95%
What is Situs Inversus associated with?
Asplenia or Polysplenia
Cardiac malformations – common (99% in Asplenia; 90% in Polysplenia)
What is Situs inversus also known as?
Heterotaxy Syndrome or Situs Ambiguous
What are the ultrasound findings of total situs?
Right side – heart, aorta, spleen, stomach
Left side – liver, GB, IVC
What are the US findings of partial situs?
Right side – stomach
Left side – liver
Dextrocardia – heart on right side of chest with normal stomach position
What are some other anomalies of the hepatobiliary system?
•GI
•GU
•NTD-neural tube defects
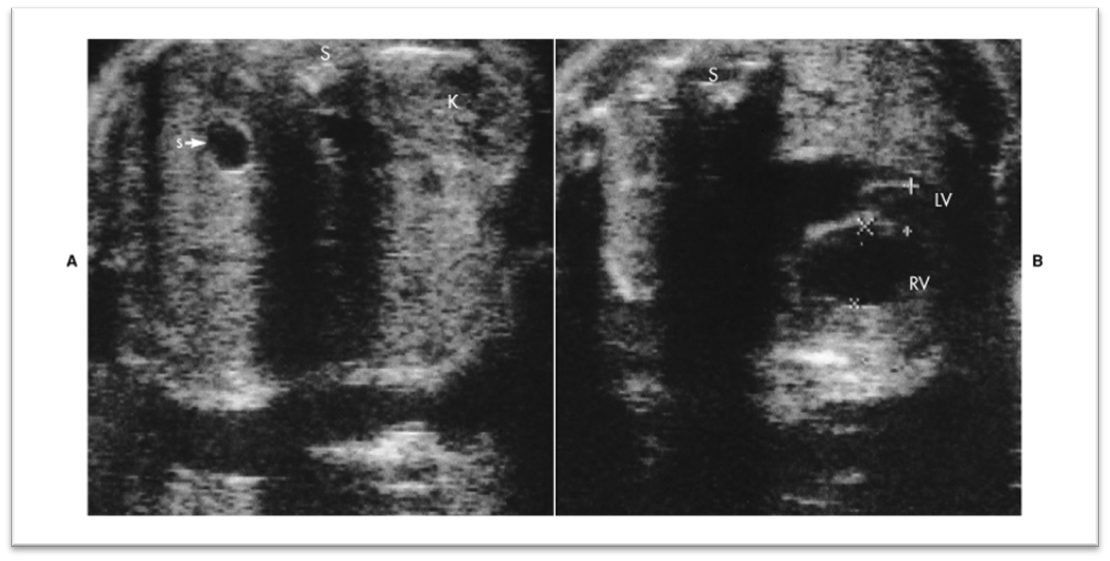
What is this image showing?
Partial situs- stomach on right and hypoplastic left heart
What is pseudoascites?
Sonolucent band near anterior wall in fetus over 18 weeks gestation
Normal musculature at abd. wall
Always confined to anterior or anterolateral aspect of fetal abdomen
NEVER outlines the falciform ligament
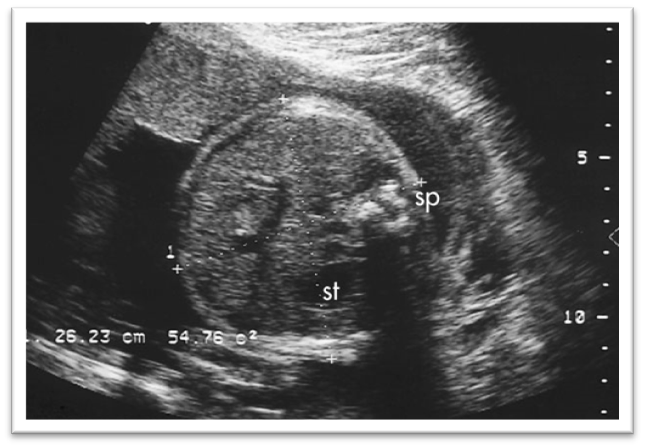
What is this image showing?
Pseudoascites
What is True Ascites?
Is within peritoneal recesses/around organs,
Moves to more dependent portion of abdomen,
Outlines falciform ligament
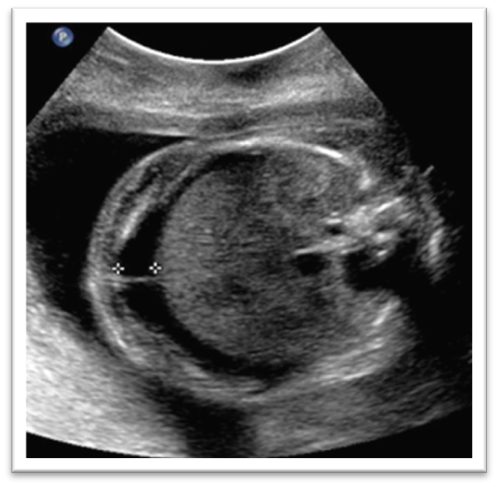
What is this image showing?
True ascites
What pathology can be associated with the gallbladder?
Cholelithiasis
Choledochal cyst
Dilation of common bile duct
What are the US findings for the GB?
Cystic mass adjacent to fetal stomach
**Remember ** GB is more anterior than stomach & on right side of abdomen
Dif. Dx.: duodenal atresia
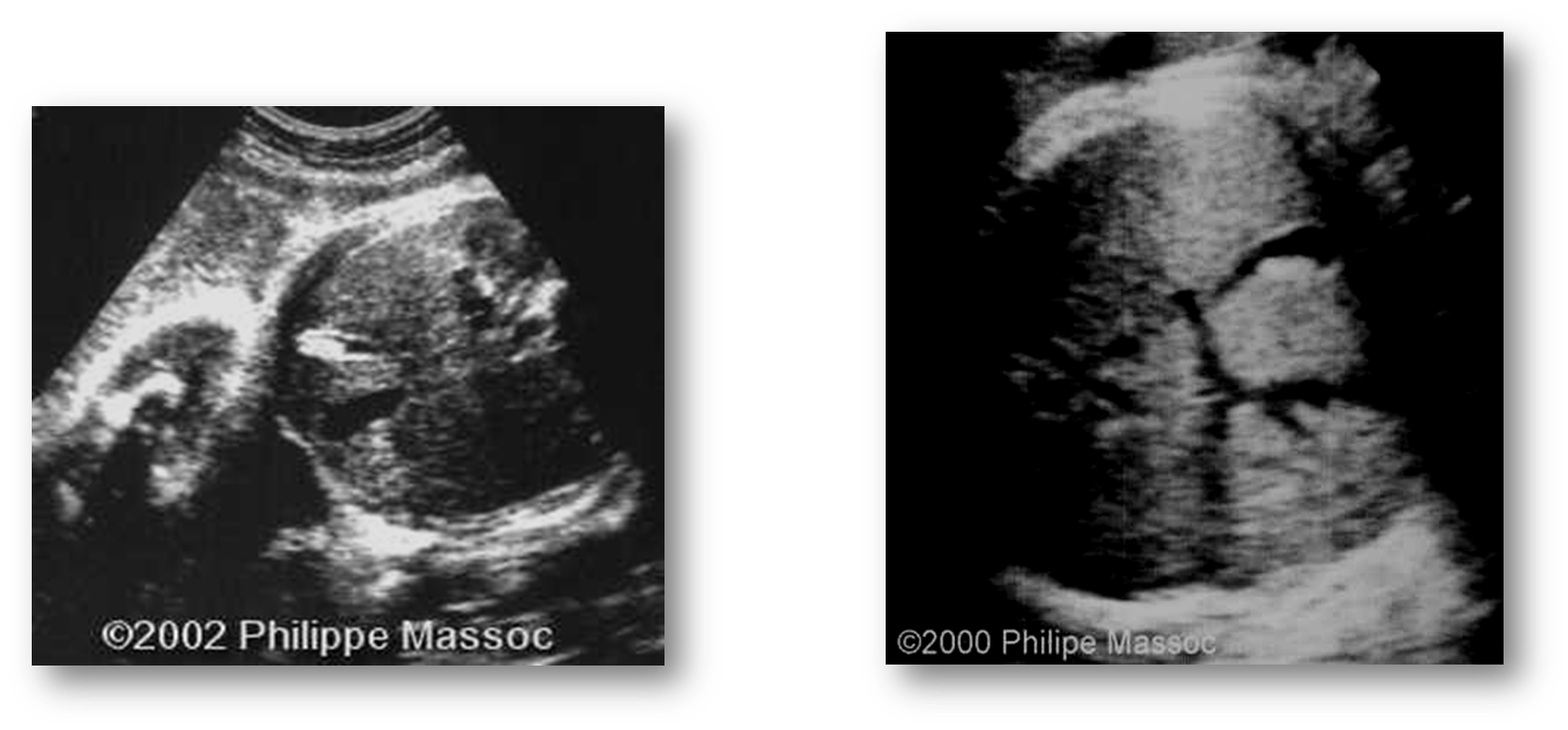
What are these images showing?
Cholelithiasis- stones in the GB
What is the criteria for a choledochal cyst?
Cyst in close proximity to neck of GB
Oval RUQ cyst with an entering duct
Cyst & GB may enlarge as pregnancy progresses
Absence of peristalsis
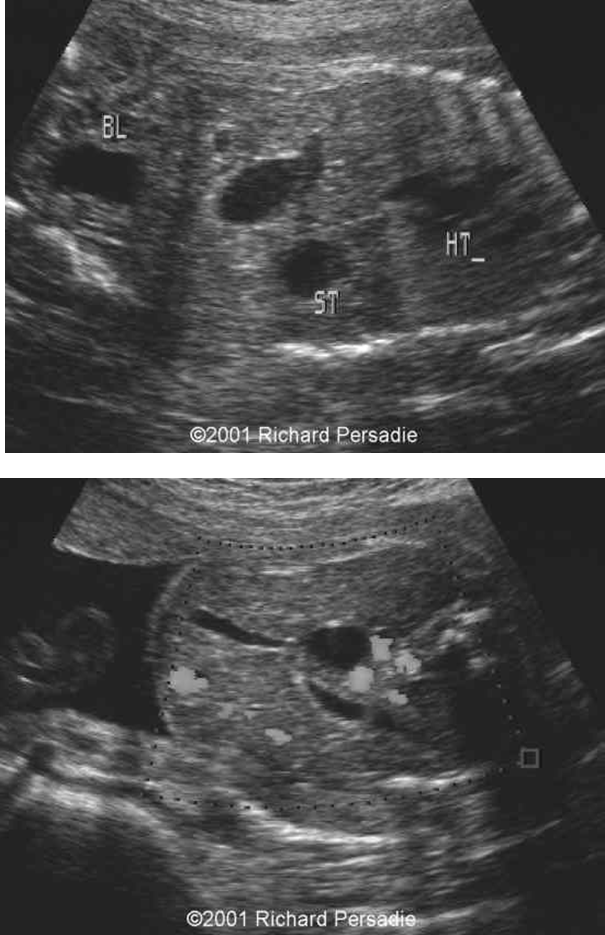
What are these images showing?
Choledochal cyst
What is Extrahepatic Biliary Atresia
Blockage of bile ducts due to failure of recanalization after solid stage of development
With the spleen, what can be identified in utero?
Asplenia
What may be associated with CHD?
Polysplenia
What is splenomegaly and hepatomegaly associated with?
Rh immunization disease
Beckwith-Weidemann Syndrome
What are the causes of not finding anormal stomach?
Esophageal atresia or Tracheoesophageal fistula
Diaphragmatic hernia
Facial cleft
CNS disorders
Other swallowing disorders
May cause Polyhydramnios
Oligohydramnios from other causes
What is a tracheoesophageal septum?
Separates the esophagus from the trachea
What is esophageal Atresia?
Abnormal deviation of septum posteriorly
Commonly with fistula between trachea & esophagus allowing passage of fluid into stomach
BLOCKAGE
What is esophageal Stenosis?
Narrowing of esophagus distally
Usually distal 1/3
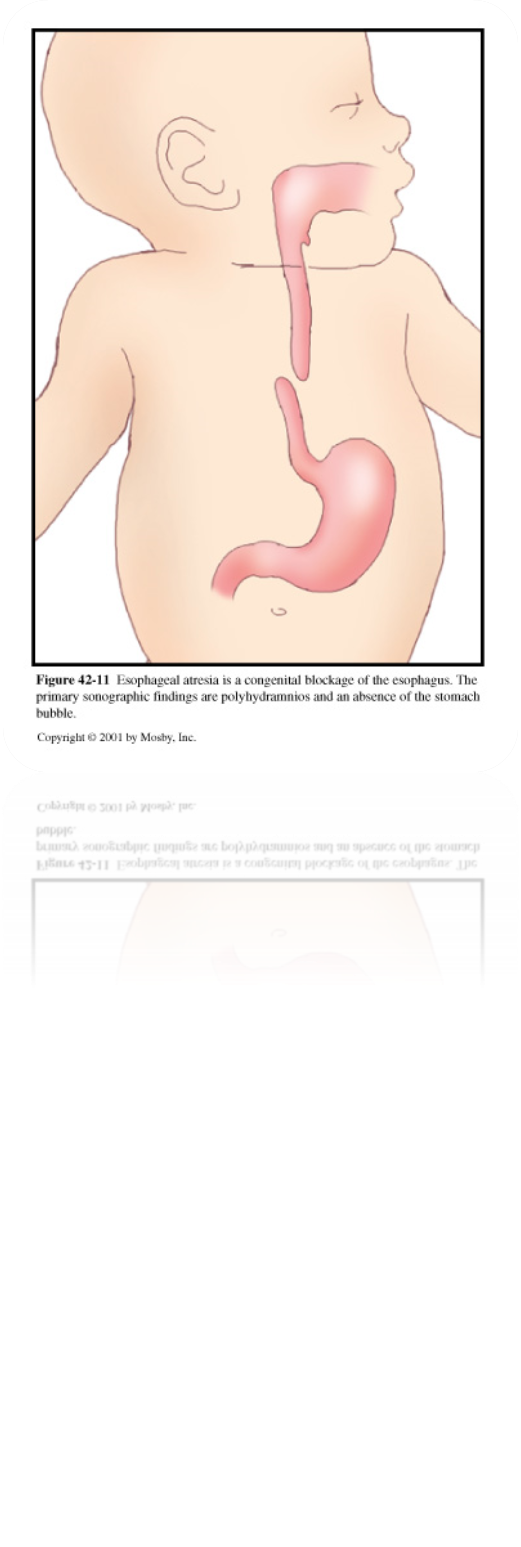
What is this image showing?
Esophageal Atresia
What are the US finding for any esophageal anomalies?
Polyhydramnios – may not develop until 3rd trimester
Absent stomach
BUT…50% stomach is visualized due to fistula
Coexisting anomalies (50-70%)
Anorectal atresia
VACTERL
Growth restriction (40% of cases)
Chromosomal trisomies 18 & 20
What is the term Vacteral?
Trachea and esophagus anomalies
The stomach is a fluid-filled structure in the LUQ and should be seen between what weeks?
14-16 weeks
What should the fluid look like in the stomach?
Fluid should be anechoic
Echogenic debris may sometimes be seen along dependent wall
Vernix, protein, intraamniotic hemorrhage