CPT Section 3
1/246
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
247 Terms
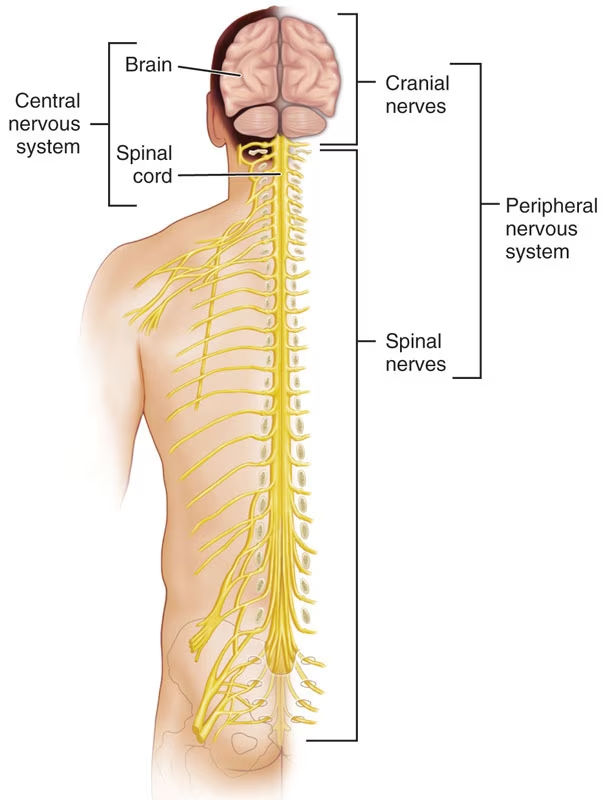
Define ligament.
fibrous tissues that connect bone to bone and provide static and dynamic stability & sensory input to the nervous system that aids proprioception
Define collagen.
protein found in connective tissue, muscles, and skin that provides strength and structure; most abundant protein in human body
Define elastin.
protein that provides elasticity to skin, tendons, ligaments, and other structures
Define growth plate.
specialized cartilage disc located in epiphysis that is responsible for bone length growth
What factors affect peak bone mass?
environmental, dietary, hormonal, lifestyle, physical activity, genetic influences
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
contract and produce movement, support skeletal system, and produce heat
Define fascia.
first layer of connective tissue in bone; surrounds skeletal muscles & connects them to other muscles
Define epimysium.
layer of fascia that directly surrounds an entire muscle; “deep fascia”
Define fascicles.
largest bundles of muscle fibers
Define perimysium.
connective tissue that wraps around each fascicle
Define endomysium.
surrounds individual muscle fibers
Define sarcomere.
the structural unit of a myofibril composed of actin and myosin filaments between two Z-lines
Define myofibril.
contractile components of a muscle cell
Define myofilaments
the filaments of a myofibril; include actin and myosin
Know the order of a muscle anatomy flowchart.
muscle → fascicle → muscle fiber → myofibril → sarcomere → myofilament
Define neural activation.
the nervous system’s signal that tells a muscle to contract
Define neuromuscular junction.
the site where the nervous system communicates directly with muscle fibers
Define synapse.
a junction/small gap between motor neuron and muscle cells
Define motor unit.
a motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
Define action potential.
nerve impulse relayed from CNS to PNS to neuromuscular junction
What are the steps of excitation-contraction coupling?
action potential is caused by Na+ and K+
acetylcholine is released into neuromuscular junction
nerve impulse travels, stimulates sarcoplasmic reticulum to release Ca2+
myosin & actin are stimulated, causing muscle contraction
What are the two major chemicals involved in excitation-contraction?
calcium and acetylcholine
What are characteristics of type-1 muscle fibers?
small, fatigue-resistant, slow contraction, increased oxygen delivery (ex. postural or stabilization muscles)
What are characteristics of type-2 muscle fibers?
large, fatigue prone, quick force generation, decreased oxygen delivery