Anthropology
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Largest bone in the body
Femur
Smallest bone in the body?
Ossicles (ear)
Forensic Anthropology
Identifies skeletal remains where bones are the only evidence
Organizing Collected Bones
Lay out the bones in anatomical position; palms out, thumb to the outside
Always to the patient’s left and right
Teeth
Analyzed by odontologist-specialized trained dentists
Teeth made of dentin, enamel (hardest substance in the human body), & cementum
FORENSICALLY IMPORTANT because they last longer than bones
Best to determine age of children; acts as a benchmark
Jobs of a Forensic Scientist
Assisting in investigations
Recovering individuals from crime scene; esp. little bones
Examining and analyzing human remains
Reconstruct remains to analyze effects of trauma
Assessing Wounds: Sharp Instruments
Slice/cut bone
Type of instrument and the ANGLE of the cut can be determined
RIBS are most likely to show signs of stabbings
Identifying Human Remains (Legally)
Closure is important, but there is a legal aspect; how did you prove they are actually, LEGALLY, dead?
DEATH CERTIFICATE needed to collect insurance benefits, settle Wells, sell property, and allow surviving spouse to marry again
Medical History
One of the things you can determine from bones
Osteomyelitis: Bone infection common in IV drug users; swelling of the bone
Orthopedic PIns/Replaced Joints: Serial numbers can be used to identify
Breaks/fractures: Remnant scar tissue and bone remodeling (the way bones heal has signatures that can be tracked)
Habitual Actions
One of the things you can determine from bones (part of the medical history)
Behavior that you constantly repeat can have an affect on how the bones appear
Causes markings or shape CHANGE on bone
Left/Right Handedness: Arthritic changes in shoulder on dominant side
Dental Work
One of the things you can determine from bones (part of medical history)
Teeth are VERY unique
Fillings, crowns, dentures compared to
DNA
One of the things you can determine from bones
DNA “expires” and degrades at some point; does not stay useful FOREVER
MITOCHONDRIAL DNA (separate from the DNA of the cell) is useful for tracing maternal parents
Less helpful; could only prove match on mom’s side
Five Functions of the Skeletal System
1) Internal structure & support
2) Protection of vital organs (heart, lungs, brain)
3) Attachment for muscles
4) To make blood cells
Fluid (bone marrow) in the bones; makes red blood cells, platelets,
5) Storage of minerals
The 4 Shapes of Bones
1) Long
Longer than they are wide
2) Short
Length and width are about the same
3) Flat
Thin
4) Irregular
Funky shape that ISN’T thin
What is bone made of?
Mostly collagen and dense materials including calcium phosphate
Fossilization: Organic compounds replaced with various minerals overtime
Made of a series of vertical tubes (osteons); each tube
Determining TIME of death (ALGOR MORTIS)
Algor Mortis: Cooling of the body after death
On average, it’s going to cool 1-1.5 degrees F per hour under it matches environmental temperature
Most effective within the first 12 hours of death
Factors to Consider…
Environmental temp
Type of clothing; was the clothing wet?
Surface area/body mass ratio
SMALLER bodies cool more quickly
(98.4 F - internal temperature)/ (1.5 F/hr)
Determining TIME of death (LIVOR MORTIS)
Purple or red discoloration of the skin after death; caused by pooling in the blood due to gravity
Begins ~30 mins after death
Post 12 hrs, the discoloration won’t change regardless of how the body is moved
Area IN CONTACT with ground, chain (any surface) will be whiter —> capillaries are compressed
Determining TIME of death (RIGOR MORTIS)
Stiffness in skeletal muscles
Starts 2-3hrs after death, lasts until ~30 hrs
SMALLER muscles stiffen first
Affected by…
Temperature
Dehydration
Condition of muscles
Use prior to death
Osteology
The study of bones
Animal vs. Human Bone
Human bones are more random— circular osteons can be all different sizes
Animal bones are more uniform; form in a pattern
Osteon Banding: Rows
Plexiform Bone: Rectangular shapes
Sexual Dimorphism
Structure/physical differences between a male and female
Difference in the Male & Female Pelvis
Pelvis differences can be used to determine SEX
Males
Sacrum tilted forward
Ilia closer together
Subpubic angle is a cute
NO prominent ventral arc
Female
Sacrum titled back
Ilia spread wider
Subpubic angle is obtuse
HAS a prominent ventral arc
Ventral Arc
The bony ridge on the front of the public bone, looks like its folding inwards
Estimating Height
Only can be done using LONG bones: humerus, radius, femur, tibia
Accuracy deviates by ± 7.5 cm
Epiphyses
GROWTH plates at the end of long bones that fuse to the bone in early adulthood
The greater the epiphyses; the more the person has to grow
Fusion of Sutures
One method of determining age
SAGITTAL SUTURE
Completely fused closed between 26 and 32 years of age in MEN
Completely fused closed between 29 and 35 of age in WOMEN
Age from the os pubis
One method of determining age
Os Pubis are the bones that connect on both sides to the pubis
Furrows → YOUNGEST
Smooth → MIDDLE
Breakdown of Bone → OLDEST
Determining Ethnicity from Skull
MOST DIFFICULT to assess from the skeleton
Not all are COMPLETELY ONE descent; mixed makes it more ambiguous
Caucasoid Skull
Consists of European, Middle Easter, and East Indian descent)
Long, narrow nasal aperture
Contains a nasal spine
Triangular palate (roof of the mouth)
Oval orbits
Narrow zygomatic arches and mandibles
Negroid Skull
Consists of African, Aborigine, Melanesian descent)
WIDEST nasal aperture
NO a nasal spine
Rectangular palate
Square orbits
More pronounced zygomatic arches han Caucasoid
Maxilla bone projected outward → Prognathism
Longer bones with less curvature & more DENSE
Mongoloid
Consists of Asian, Native America, Inut, Polynesian descent)
More rounded nasal aperture
Parabolic palate
Rounded orbits
MOST prominent zygomatic arches (cheek bones)
Pointed Mandibles
Shovel-shaped indentation in the back of upper front teeth
Dr. Thomas Dwight
Considered the “Father of American Forensic Anthropology"
Taught at Harvard, first counted at the end of the 19th century
Looked at clues to ID a person from bones
Dr. George Dorsey (1868 - 1931)
Another leading forensic anthropologist who also worked at Harvard
Most known for the Luetgert murder case in Chicago
Luetgert Case
Adolph Luetgert murders his wife (Louisa Bicknese) and dissolves her body, but they found her ring and a couple bone fragments; able to be convicted of murder
Led by Dr. George Dorsey
Dr. T.D. Stewart
Curator for the Smithsonian Institute
Helped ID casualties from WWII and the Korean War
Central Identification Laboratory in Hawaii (CILHI)
Central spot (close to Pacific theatre, where many wars are fought)
MAIN PURPOSE: Identify and repatriate American soldiers
How are remains analyzed by the CILHI
1) Teams sent out to different locations to try and find remains
2) Remains found are sent back to the base to be further analyzed
3) Statistical methods are used to differentiate remains of those from the native population
4) Biological profiles are created from the remains and compared to a database of all missing soldiers to try and find matches
Assessing Wounds: Dull Instruments
Splinter/crushed bones
Damage depends on the force, angle, # of times struck, type of instrument
SEQUENCE of blows can be determined from the radiating fractures (like glass)
Assessing Wounds: Strangulation
HYOID bone often damaged during manual strangulation
NOT in children because bones are still very flexible
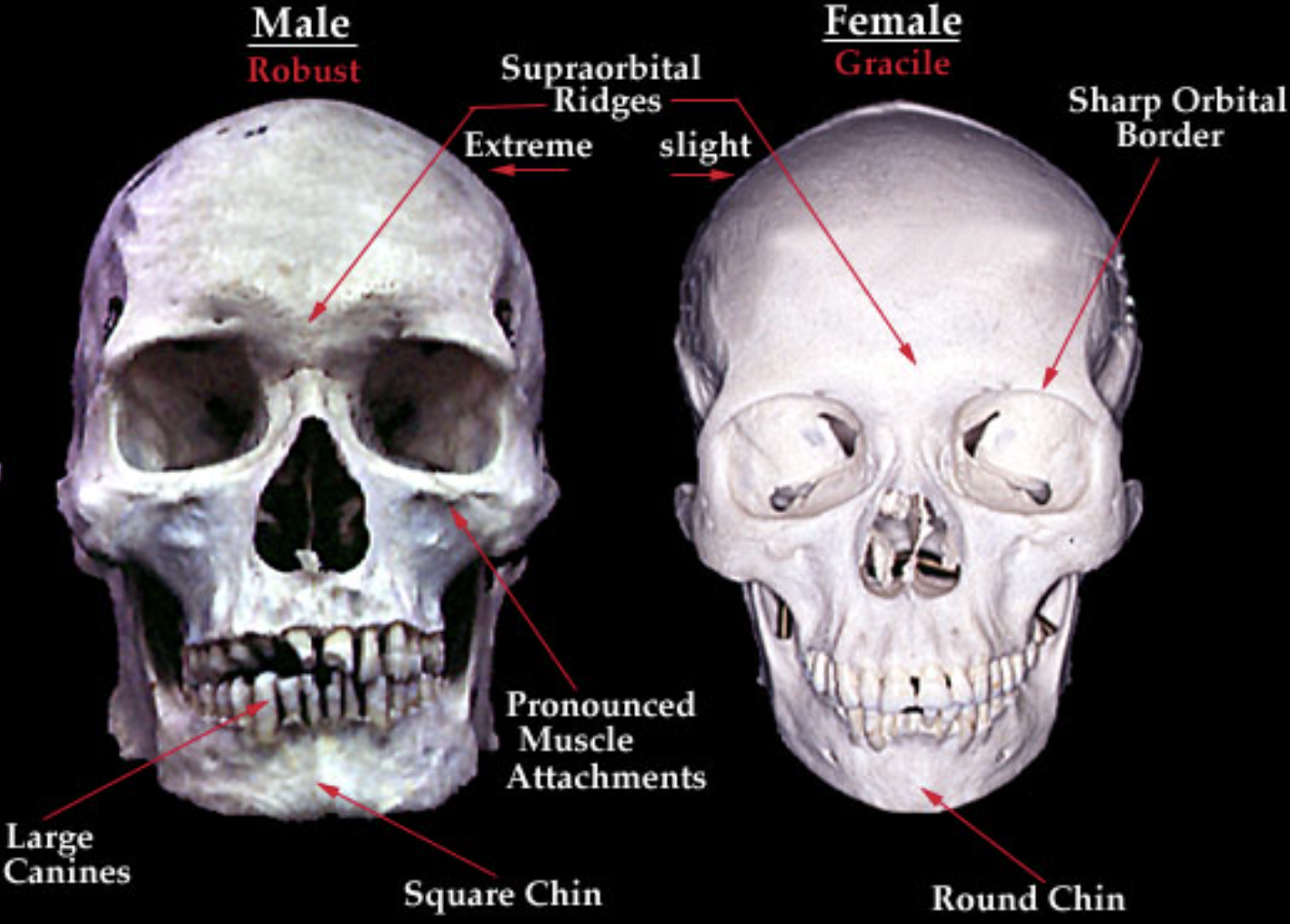
Differences in Male and Female Skulls
FEMALE
1) Overall shape of the head
2) Supraorbital ridges → Slight; not as extreme as male skulls
3) Chin shape → Round chin
4) Orbital border → Sharp
5) Muscle attachments under the eye
6) Forehead → Rounded, vertical forehead
7) Protuberance in the back → Not as prominent as in males