Glycolysis, PPP, Cori Cycle
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What are the products of glycolysis?
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
The anaerobic pathway of glycolysis produces _______ in animals
lactate
The anaerobic pathway of glycolysis produces _______ in yeast
ethanol
Aerobic pathway of cellular respiration
Glycolysis -> TCA -> ETC
Why does glucose get phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate?
So it cannot leave the cell
Glucose -> Glucose-6-phosphate catalyzed by
Hexokinase
Glucose-6-phosphate -> Fructose-6-phosphate catalyzed by
Phosphohexose isomerase
Fructose-6-phosphate -> Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate catalyzed by
Phosphofructokinase-1
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate -> Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate & dihydroxyacetone phosphate catalyzed by
Aldolase
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate -> Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate catalyzed by
Triosephosphate isomerase
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate -> 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate catalyzed by
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate -> 3-phosphoglycerate catalyzed by
Phosphoglycerate kinase
3-phosphoglycerate -> 2-phosphoglycerate catalyzed by
Phosphoglycerate mutase
2-phosphoglycerate -> phosphoenolpyruvate catalyzed by
Enolase
Phosphoenolpyruvate -> pyruvate catalyzed by
Pyruvate kinase
Order of Glycolysis
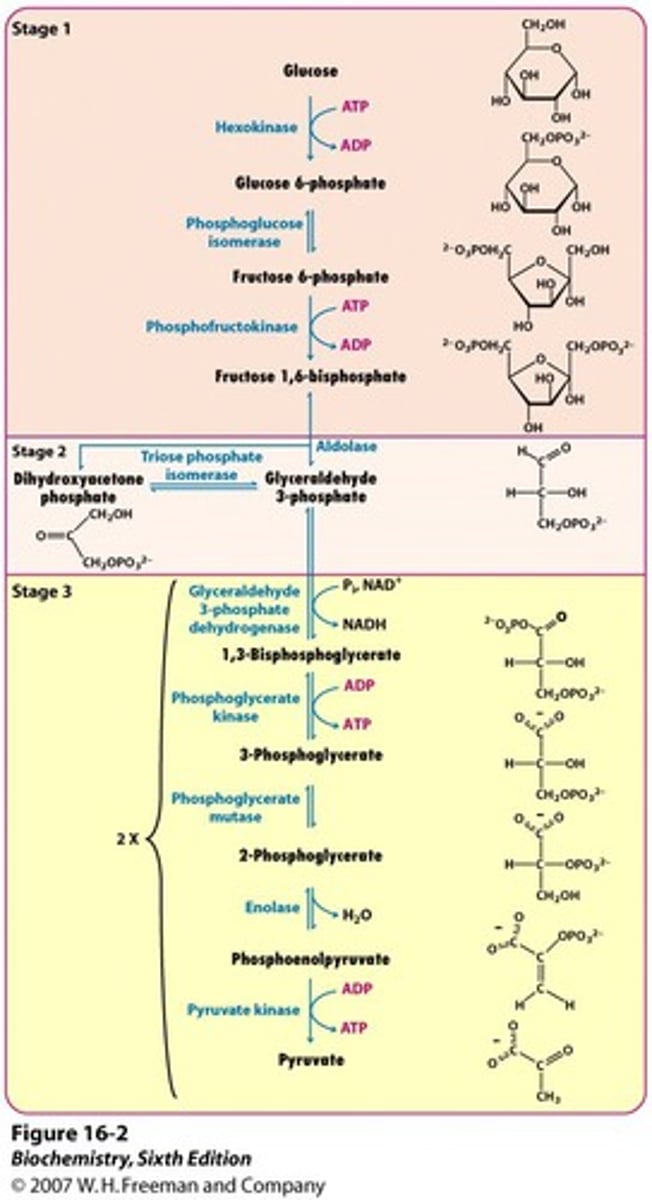
What are the control points of glycolysis?
Step 1: Glucose -> Glucose-6-phosphate
Step 3: Fructose-6-phosphate -> Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Step 10: Phosphoenolpyruvate -> Pyruvate
What is the step that commits glucose to glycolysis and what enzyme catalyzes it?
Fructose-6-phosphate -> Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Phosphofructokinase-1
What does ketoacidosis do?
Decrease blood pH
What are the biproducts of fatty acid oxidation?
Acetoacetate & β-hydroxybutyrate
Insulin is released by what kind of cells?
pancreatic β cells
What does lactate dehydrogenase do?
converts pyruvate to lactate
it allows glycolysis to continue producing ATP in the absence of oxygen but does not affect the glycolytic pathway
What enzyme catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to ethanol during alcohol fermentation?
alcohol dehydrogenase
What is fetal alcohol syndrome?
ethanol is broken down to acetaldehyde; high levels of acetaldehyde can cross the placenta and accumulate in fetal liver
What is beriberi?
Thiamine deficiency that causes neurological issues and other symptoms
Found in people that are alcoholics but don't eat
What is gluconeogenesis?
Making glucose from a non-carbohydrate source
It is not the reverse of glycolysis
What is the pentose phosphate pathway?
It makes NADPH and pentose sugars with phosphate group
What do the oxidative reactions of the pentose phosphate pathway produce?
NADPH
What do the non-oxidative reactions of the pentose phosphate pathway produce?
5 carbon sugars (specifically ribose-5-phosphate)
What inhibits phosphofructokinase?
High concentrations of ATP
What activates phosphofructokinase?
High concentrations of AMP
Gluconeogenesis steps that replace glycolysis control points
1. Glucose-6-phosphate -> Glucose is catalyzed by Glucose-6-phosphatase
3. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate -> Fructose-6-phosphate is catalyzed by Fructose-bis-phosphate phosphatase
10. Pyruvate -> Phosphoenolpyruvate happens in 2 steps
Step 1: Pyruvate -> Oxaloacetate is catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase
Step 2: Oxaloacetate -> Phosphoenolpyruvate is catalyzed by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
Oxaloacetate is an intermediate that is not present in glycolysis but is in gluconeogenesis
What is TPP (Vitamin B1)?
A key factor in decarboxylation reactions
ex: pyruvate carboxylase catalyzes pyruvate -> oxaloacetate
What is the Cori Cycle?
Regulates blood glucose levels and provides a mechanism to recycle lactate produced by muscles
Where are GLUT1 and GLUT2 transporters found?
hepatocytes (liver cells)
Where are GLUT3 transporters found?
Brain neurons
Where are GLUT4 transporters found?
skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, adipocytes
What do disaccharidases do?
break down disaccharides into monosaccharides