5. Molecular Basis of Inheritance
1/373
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Please read NCERT before doing this, at least once. This has almost everything from NCERT, but theory is something you have to be clear on before you try remembering all this. Anyway. Questions: Flashcards only. Answer mode: Answer with definition. Suitable for IAT, probably also NEET, NEST, etc. Good luck on your exams! Lmk if there's anything you'd like to add/change!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
374 Terms
Nucleic acids are polymers of ________.
Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides.
What is another name for nucleic acids?
polynucleotides.
What is the genetic material for the majority of organisms?
DNA
What are the two types of nucleic acids found in living systems?
DNA
RNA
What are the different functions that RNA can have?
messenger
genetic material
adapter
structural molecule
catalytic molecule (enzyme)
What are examples of organisms in which RNA is the genetic material?
viruses like corona virus, tobacco mosaic virus
The length of DNA is usually defined as number of ______ present in it.
The length of DNA is usually defined as number of nucleotides (or a pair of nucleotides referred to as base pairs) present in it.
The length of DNA is ______ in each organism.
(same / different)
different
a bacteriophage known as φ×174 has ______ nucleotides
(number of nucleotides)
a bacteriophage known as φ×174 has 5386 nucleotides
Bacteriophage lambda has ________ base pairs (bp).
(number of base pairs)
Bacteriophage lambda has 48502 base pairs (bp).
Escherichia coli has _______ bp.
(number of base pairs)
Escherichia coli has 4.6 × 106 bp.
Haploid content of human DNA is ________ bp.
Haploid content of human DNA is 3.3 × 109 bp.
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
Pentose Sugar
Nitrogenous Base
Phosphate group
What are the two components of a nucleoside?
Pentose Sugar
Nitrogenous Base
Which pentose sugar is present in RNA?
ribose
Which pentose sugar is present in DNA?
deoxyribose
What are the two types of phosphate groups?
Purines
Pyrimidines
What are the two purine phoshate groups?
Adenine
Guanine
What are the two pyrimidine phosphate groups?
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil
Which are bigger, purines or pyrimidines?
purines are bigger than pyrimidines
Which nitrogenous bases are present in DNA?
Adenine
Guanine
Cytosine
Thymine
Which nitrogenous bases are present in RNA?
Adenine
Guanine
Cytosine
Uracil
How many membered ring is a Purine?
9 membered ring (two rings)
How many membered ring is a Pyrimidine?
6 membered ring
In Purines, in which positions on the ring are Nitrogen atoms present?
the first, third, seventh, and ninth members are nitrogen

In Pyrimidines, in which positions on the ring are Nitrogen atoms present?
the first and third members are nitrogen

Nitrogenous bases are linked with pentose sugars with which sort of bond?
N-glycosidic bond
In polynucleotides, a nitrogenous base is linked to the OH of _____ C pentose sugar.
(which position carbon)
In polynucleotides, a nitrogenous base is linked to the OH of 1' C pentose sugar.
What are the two nucleosides that can form when Adenine is bonded with a pentose sugar?
Adenosine
Deoxyadenosine
What are the two nucleosides that can form when Guanine is bonded with a pentose sugar?
Guanosine
Deoxyguanosine
What are the two nucleosides that can form when Cytosine is bonded with a pentose sugar?
Cytidine
Deoxycytidine
What are the nucleosides that can form when Uracil is bonded with a pentose sugar?
Uridine
What are the nucleosides that can form when Thymine is bonded with a pentose sugar?
Deoxythymidine
In polynucleotides, a phosphate group is linked to OH of ____ C of a nucleoside.
(position of carbon)
In polynucleotides, a phosphate group is linked to OH of 5' C of a nucleoside.
A phosphate group is bonded with a nucleoside through which sort of bond?
Phosphoester linkage
Two nucleotides are linked through ______ phosphodiester linkage to form a dinucleotide.
(position of carbons)
Two nucleotides are linked through 3'-5' phosphodiester linkage to form a dinucleotide.
Two nucleotides are linked through 3'-5' ___________ to form a dinucleotide.
(type of bond)
Two nucleotides are linked through 3'-5' phosphodiester linkage to form a dinucleotide.
A number of nucleotides can be joined together to form a polynucleotide chain.
A polymer thus formed has at one end a free phosphate moiety at ____-end of sugar, which is referred to as ______-end of polynucleotide chain.
A number of nucleotides can be joined together to form a polynucleotide chain.
A polymer thus formed has at one end a free phosphate moiety at 5'-end of sugar, which is referred to as 5’-end of polynucleotide chain.
A number of nucleotides can be joined together to form a polynucleotide chain.
A polymer thus formed has at one end a free phosphate moiety at 5'-end of sugar, which is referred to as 5’-end of polynucleotide chain.
Similarly, at the other end of the polymer the sugar has a free OH of ____ C group which is referred to as _____- end of the polynucleotide chain.
A number of nucleotides can be joined together to form a polynucleotide chain.
A polymer thus formed has at one end a free phosphate moiety at 5'-end of sugar, which is referred to as 5’-end of polynucleotide chain.
Similarly, at the other end of the polymer the sugar has a free OH of 3' C group which is referred to as 3'- end of the polynucleotide chain.
What is the backbone of a polynucleotide chain made of?
pentose sugars
phosphate groups
What is the structural difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
In RNA, every nucleotide residue has an additional –OH group present at 2' -position in the ribose.
What are the two structural differences between DNA and RNA?
In RNA, every nucleotide residue has an additional –OH group present at 2' -position in the ribose. Also, in RNA the uracil is found at the place of thymine (5-methyl uracil, another chemical name for thymine).
Why is Thymine also called 5-methyl uracil?
Because if you attach a methyl group to the fifth carbon in Uracil, you get Thymine.
DNA as an acidic substance present in nucleus was first identified by __________________ in 1869.
DNA as an acidic substance present in nucleus was first identified by Friedrich Meischer in 1869.
DNA as an acidic substance present in nucleus was first identified by Friedrich Meischer in 1869. What did he name it?
Nuclein
It was only in 1953 that James Watson and Francis Crick, based on the X-ray diffraction data produced by __________ and ___________, proposed a very simple but famous Double Helix model for the structure of DNA.
It was only in 1953 that James Watson and Francis Crick, based on the X-ray diffraction data produced by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin, proposed a very simple but famous Double Helix model for the structure of DNA.
It was only in 1953 that ________________ and ______________, based on the X-ray diffraction data produced by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin, proposed a very simple but famous Double Helix model for the structure of DNA.
It was only in 1953 that James Watson and Francis Crick, based on the X-ray diffraction data produced by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin, proposed a very simple but famous Double Helix model for the structure of DNA.
Who produced the Double Helix model for the structure of DNA?
James Watson and Francis Crick
Who named the acids found in the nucleus of cells “nuclein”?
Friedrich Meischer
Who made the observation that for a double stranded DNA, the ratios between Adenine and Thymine and Guanine and Cytosine are constant and equals one?
Erwin Chargaff
What did Erwin Chargaff do?
He made the observation that for a double stranded DNA, the ratios between Adenine and Thymine and Guanine and Cytosine are constant and equals one.
Why is it easy to predict the nitrogenous bases present on the second strand of dsDNA if the nitrogenous bases on the first strand are known?
Nitrogenous bases are always complementary.
How many hydrogen bonds form between Adenine and Thymine?
2
How many hydrogen bonds form between Cytosine and Guanine?
3
How many hydrogen bonds form between Cytosine and Guanine?
3
Which nitrogenous bases can pair with Adenine?
Thymine
Uracil
Which nitrogenous bases can pair with Thymine?
Adenine
Which nitrogenous bases can pair with Cytosine?
Guanine
Which nitrogenous bases can pair with Guanine?
Cytosine
What is the salient feature of DNA with regards to composition?
It is made of two polynucleotide chains, where the backbone is constituted by sugar-phosphate, and the bases project inside.
What is the salient feature of DNA with regards to chain polarity?
The two chains have anti-parallel polarity. It means, if one chain has the polarity 5' → 3', the other has 3' → 5' .
What is the salient feature of DNA with regards to base pairing?
The bases in two strands are paired through hydrogen bond (H-bonds) forming base pairs (bp). Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine from opposite strand and vice-versa. Similarly, Guanine is bonded with Cytosine with three H-bonds. As a result, always a purine comes opposite to a pyrimidine. This generates approximately uniform distance between the two strands of the helix.
What is the pitch of a helix of DNA?
3.4 nm
How many base pairs are in one 360 degree turn of a helix of DNA?
10
What is the distance between two nitrogenous base pairs in a DNA helix?
0.34 nm
The two strands of DNA in a helix are coiled in a _____-handed fashion.
(left / right)
The two strands of DNA in a helix are coiled in a right-handed fashion.
In nucleic acids, phosphate groups are linked by phosphodiester bond to which positions of carbons in the pentose sugars?
5’ and 3’
What is the most common form of DNA?
B-form of DNA
DNA is double-stranded where both strands are ____________ to each other.
( parallel / anti-parallel / perpendicular)
anti-parallel
What are the two ends of a double-strand of DNA called?
3’ end and 5’ end
How is the length of DNA in any cell calculated?
= distance between base pairs * total number of base pairs in the cell
What is the length of DNA in one human cell?
2.2 metres
DNA is _________-charged
(positively / negatively)
negatively
Why is DNA negatively charged?
Because of presence of phosphoric acid
Why does the distance between the two strands in a DNA double helix stay almost constant?
Because the nitrogenous base pairs are bonded purine to pyrimidine, and the structures of purines and pyrimidines are of similar size.
Who proposed the central dogma of molecular biology?
Francis Crick
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
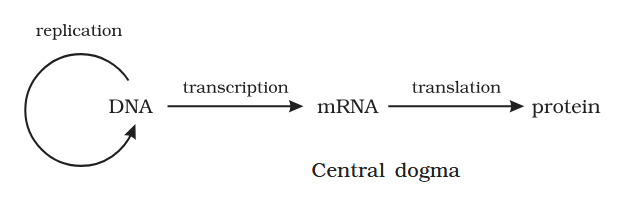
How is the central dogma different in some viruses?
In some viruses the flow of information is in reverse direction, that is, from RNA to DNA.
In some viruses the flow of information is in reverse direction, that is, from RNA to DNA.
What is this process called?
Reverse Transcription
How is DNA organised in prokaryotes such as E. coli ?
In prokaryotes, such as, E. coli, DNA is held with some proteins in a region termed as ‘nucleoid’. The DNA in nucleoid is organised in large loops held by proteins.
Depict a nucleosome.
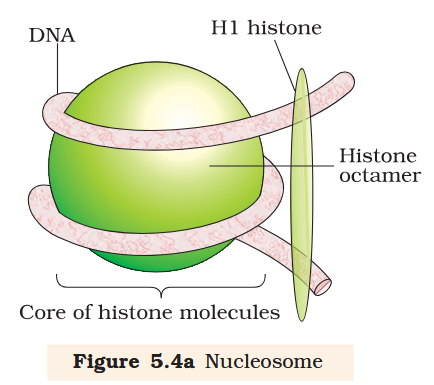
In eukaryotes, which proteins are present around DNA?
histones
How do histones acquire charge?
A protein acquires charge depending upon the abundance of amino acids residues with charged side chains.
Histones are _______-charged.
(positively / negatively)
positively
Why are histones positively charged?
Histones are rich in the basic amino acid residues lysine and arginine. Both the amino acid residues carry positive charges in their side chains.
Which amino acids are histones rich in?
Lysine
Arginine
Histones are organised to form a unit of eight molecules called __________________.
Histones are organised to form a unit of eight molecules called histone octamer.
What is a histone octamer?
Histones are organised to form a unit of eight molecules called histone octamer.
What is a nucleosome?
The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form a structure called nucleosome
A typical nucleosome contains how many base pairs of DNA?
200
Nucleosomes constitute the repeating unit of a structure in nucleus called ________.
Nucleosomes constitute the repeating unit of a structure in nucleus called chromatin.
What is the repeating structure of chromatin?
nucleosomes
What is chromatin?
thread-like stained (coloured) bodies seen in nucleus, consisting of repeating units of nucleosomes.
What is a “beads-on-string” structure?
The nucleosomes in chromatin are seen as ‘beads-on-string’ structure when viewed under electron microscope.
The beads-on-string structure in chromatin is packaged to form ____________________.
The beads-on-string structure in chromatin is packaged to form chromatin fibers.
What are chromatin fibres?
The beads-on-string structure in chromatin is packaged to form chromatin fibers.
The beads-on-string structure in chromatin is packaged to form chromatin fibers that are further coiled and condensed at metaphase stage of cell division to form ___________.
The beads-on-string structure in chromatin is packaged to form chromatin fibers that are further coiled and condensed at metaphase stage of cell division to form chromosomes.
What are chromosomes?
The beads-on-string structure in chromatin is packaged to form chromatin fibers that are further coiled and condensed at metaphase stage of cell division to form chromosomes.
The packaging of chromatin at higher level requires additional set of proteins that collectively are referred to as what?
Non-histone Chromosomal (NHC) proteins
What are Non-histone Chromosomal (NHC) proteins?
The packaging of chromatin at higher level requires additional set of proteins that collectively are referred to as Non-histone Chromosomal (NHC) proteins.