CAFS Prelim
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Wellbeing Definition
State of personal satisfaction based on 5 factors
Wellbeing Factors
SPEECS - Social, Physical, Emotional, Economic, Cultural, Spiritual
Individual Wellbeing
directed impacted by SPEECS
Can influence a group and be influenced by Groups
Group Wellbeing
Influenced by the SPEECS of individuals within the group
Can be increased or decreased by individuals within the group
Needs Definition
Necessities of life which are essential to survival
Wants Definition
Personal preferences or desires not essential for survival
Specific Needs
HESEAS - Health, Education, Safety and Security, Employment, Adequate Standard of Living, Sense of Identity
Maslow’s Hierarchy diagram
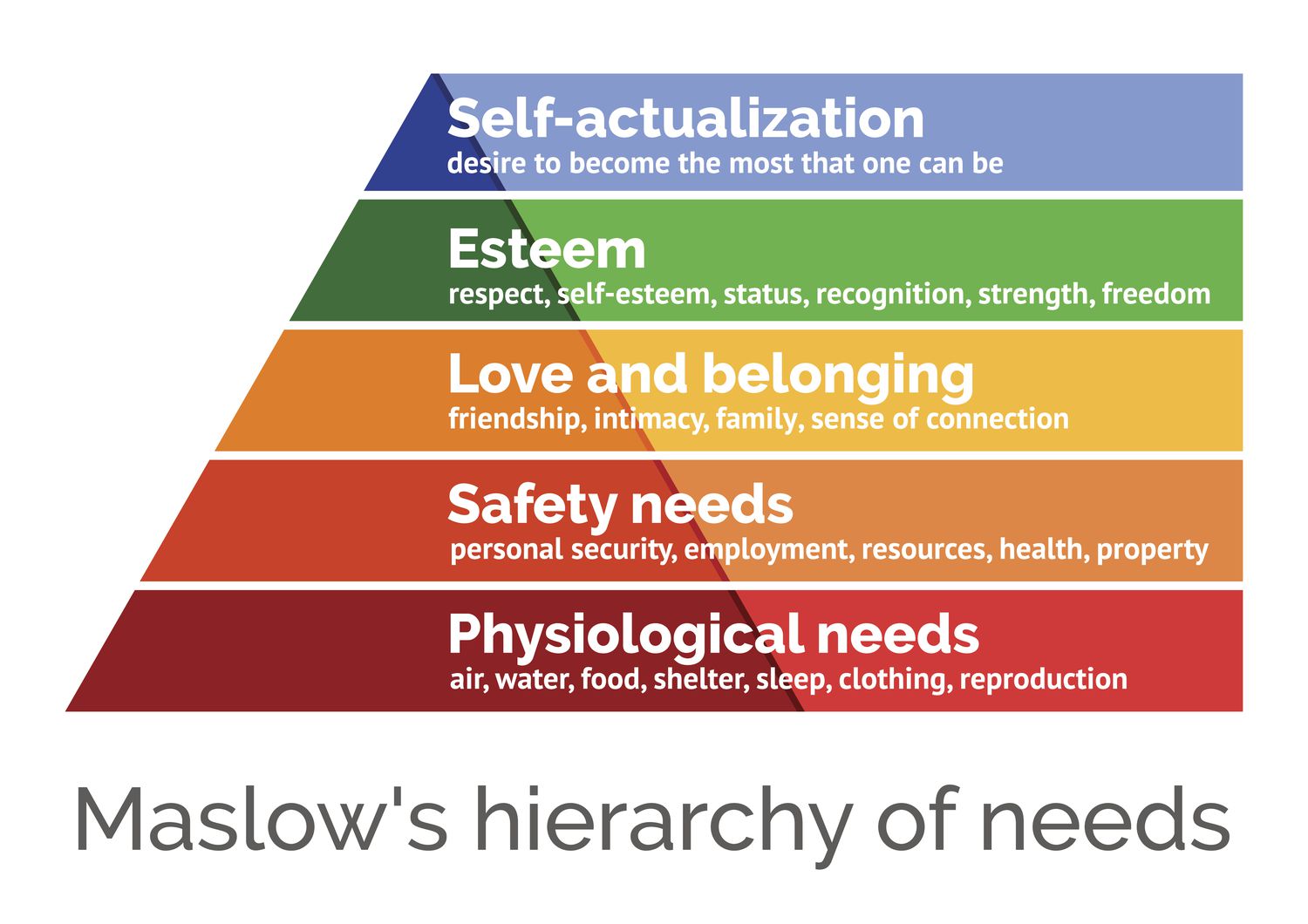
Maslow’s needs
Self Actualization, Esteem, Love and Belonging, Safety, Physiological
Self Actualization
Desire to become the best a person can be
Esteem
Self esteem (self-confidence) Gaining esteem (respect from others)
Love and Belonging
Social needs, feelings of acceptance, receiving affection
Safety
Physical and emotional safety - removal of fear, anxiety or chaos
Physiological
Food, Water, sleep/rest - most basic needs
Factors Influencing Satisfaction of needs and wants
Gender - Education - Economic Status - Culture - Geographical Location
Short Term Goals
Achieved Quickly hours to days e.g. making study flashcards
Medium Term Goals
More complex than short term, weeks to months e.g. getting a drivers license
Long Term Goals
Often reflect values may take years to achieve e.g. paying off a house
Value fo goal setting
provides guidance, motivation and organisation to help individuals complete tasks
Importance of Goal setting to wellbeing
Achieving a goal increases positive emotional wellbeing which provides motivation for other goals
Resources definition
Anything an individual uses to achieve a goal or complete a task
Benefits of resources
effective use and management of goals may assist obtaining desired quality of life, increase wealth, meet needs and wants, enhance wellbeing
Resources Impact on wellbeing
Access to various resources can potentially have both a negative and positive impact on our wellbeing
Resource Types
Human and Non Human
Human resources
Skills and abilities humans possess
Human resource examples
Energy, Knowledge, Intelligence, Sight, Language, Time, Skills, Motivation, Initiative , Creativity, Compassion etc
Non Human resources
Man made objects
Non human reosurces examples
Food, clothing, money, electricity, shelter, transport, technology, facilities etc
Interchangeability of resources
exchange of resources for goods or services
Interchangeability of resources example
Time → to make money → to buy food → to gain energy → to work → which uses time etc
Sustainability of resources
refers to effective and efficient use of resources to ensure best results and are available for future use
Strategies for sustainable non-human resources
recycling, up cycling, reusing resources, avoid waste, budget, plan resource usage
Sustainable resources examples
Energy, books, trees
Unsustainable resources examples
money, time, natural gas
Individual Management of resources
FAP - Factors affecting resource management (past experience, values, GASCD), Access to Support, Personal management skills
Values
Qualities that an individual believes to be desirable and important
Avaliability
Refers to the opportunity for families or individuals to obtain or use support networks
Accessibility
refers to the opportunity for families or individuals to reach support network
GASCD
Gender, Age, Socioeconomic status, Culture, Disability
Access to Support
assistance with gaining and using resources
Types of suppory
Formal and Informal
Formal Support
Organisations in the community
Formal Support examples
Government support e.g. Centrelink, Non-Gov e.g. Beyond Blue, Jigsaw etc
Informal Support
Support from the people closet to you
Informal support examples
Family - babysitting, Neighbours - putting your bins out when you’re not home etc
Personal Management Skills
Human resources - ability to achieve goals
Personal Management Skills Strategies
Priorities tasks, Communicate, Be Organised, Reduce your information, Use tools, Be innovated, resourceful and creative etc
Decision making
the process to making choices or reaching conclusions based on considering the alternatives
Forms of Decision Making
Intuitive - Rational - hesitant - Impulsive - Confident
Gender Expectations
Understanding that an individuals gender influences how society perspectives an individual,
Strategies for effective resource management
AAEDU - Using interchangeable resources, Adopting sustianble behaviours, Accessing support, Developing personal management skills, Engaging in education
Interview data
Qualitative
Structured Interviews
Most common, Formal - set questions about facts or content
Unstructures
Informal - discussion like, questions framed for follow ups and smooth nature
Advantages of an Interview
In-depth answers, observation of verbal cues to gain more information, Flexibility in questions
Disadvantages of an Interview
Answers can be difficult to compare, Time consuming, questions can be irrelevant, discussion taken off course, pressure on interviewee
Process to Conducting an interview
Choose Research idea, develop questions, decide on sampling method and sise, determine who to interview, conduct interview, collate results, analyse results
Family Definition
group of two or more persons related by birth, marriage, or adoption who live together; all such related persons are considered as members of one family.
Family Structures
Nuclear, Foster, Adoptive, Single Parent, Blended, Kinship, Communal, Same-sex, Childless, Defacto, Extended
Satisfying Needs
PBS - Promoting Wellbeing, Building Positive Relationships, Satisfying Needs (HESEAS)
Community Definition
a group of people with a common characteristic or interest living together within a larger society.
Levels of Community Organisation
Local, State, National, Global
Influences on decision making in communities
Legislation, Environmental factors, Lobbying and petitions, Protesting
Process of decision making
Arbitration, Consensus, Election, Voting, Referendum
Types of Change
External, Internal, Planned, Unplanned, Temporary, Permanent
Stages of a Lifespan
Infant, Child, Adolescence, Young Adult