Lect 20. NH3 uptake and aa synthesis
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
The α-amino and α-keto molecules can be converted to each other if the functional groups on the _____ are exchanged
α-carbons
What doe Transaminases do?
They catalyze the exchange of the functional groups on the α-carbon
An α-keto acid has a____ on the alpha carbon
A keto group (O=)
An α-amino acid has a____ on the alpha carbon
An amino group (H3N+)
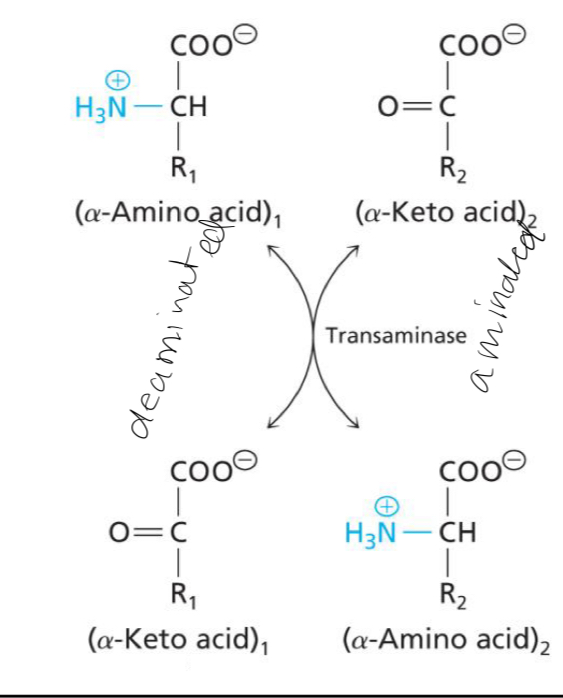
Deamination of α-amino and amination of α-keto acids
Transaminase enzymes catalyze the transfer of an amino group from the α-carbon on an amino acid to the α-carbon of an α-keto acid forming an α-amino acid.
The molecule that gains the amino group is ____
Aminated
The molecule that loses the amino group is
Deaminated
The transfer of amino groups for the formation of amino acids almost always uses ___ as the source of the amino group
glutamate
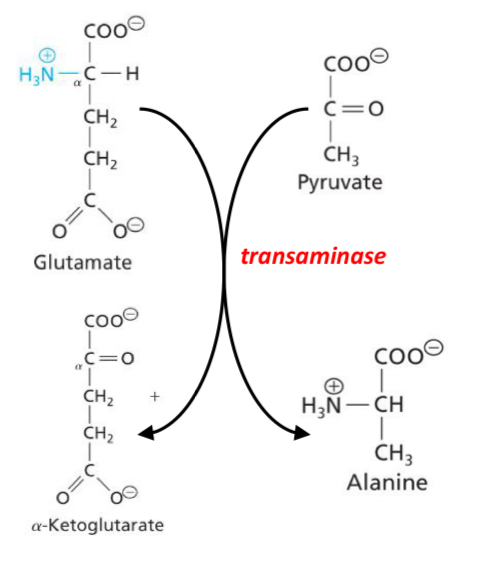
What does this picture show
Formation of Alanine from its α-keto acid counterpart
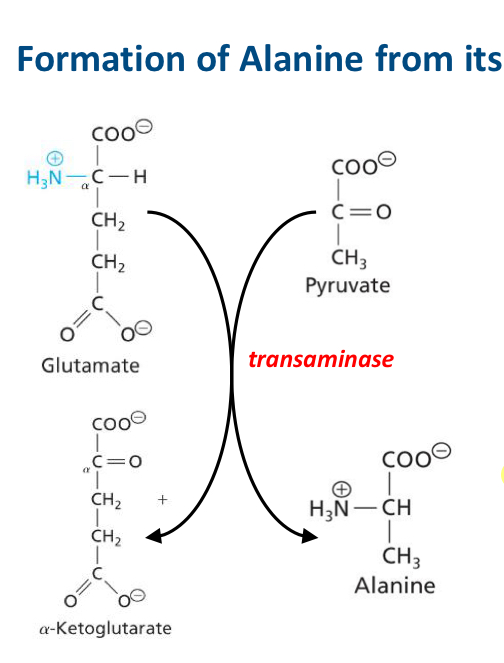
Explain what is happening here
The amino group on glutamate, (an α-amino acid), can be transferred to an accepting α-keto acid (pyruvate) forming alanine (an α-amino acid) and α-ketoglutarate (an α-keto acid).
How do special bacteria (not plants)keep a high level of glutamate to transfer amino groups into biological pathways
When the amino group on glutamate is used to form an amino acid in a transaminase reaction it regenerates α-ketoglutarate which can now pick up another ammonia thereby regenerating glutamate which can shuttle the amino group to another α-keto acid.
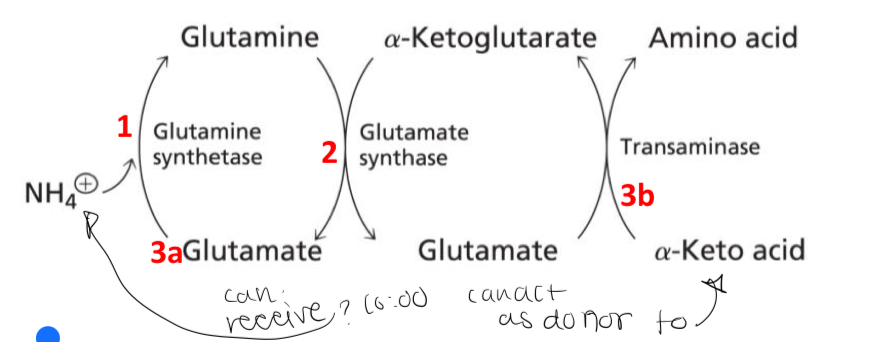
How are glutamate levels kept high to perform both of its NH3 assimilation functions in plants? Because if glutamate is used for incorporating NH3, it cannot be used to donate its amino group to α-keto acids
Reductive amination reaction that is catalyzed by Glutamate Synthase which transfers the amino nitrogen from glutamine to α-ketoglutarate to generate 2 molecules of glutamate
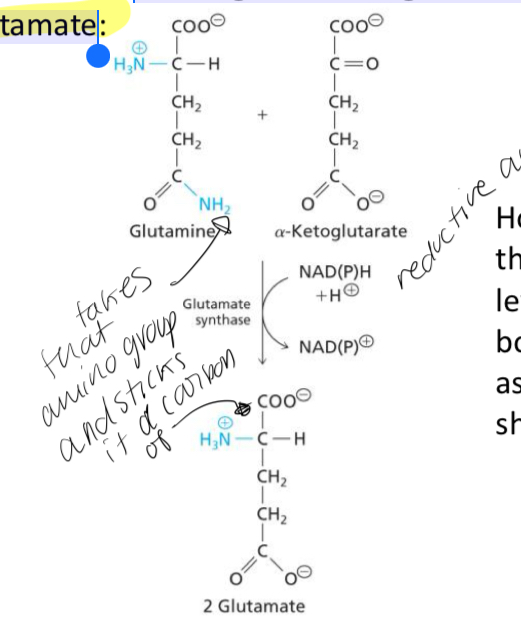
The reductive amination reaction catalyzed by Glutamate Synthase
How does the amination reaction catalyzed by Glutamate Synthase maintain high levels of glutamate for both of its ammonia assimilation functions
1. Glutamate assimilates ammonia to form glutamine.
2. Two glutamate molecules are formed from the reductive amido transfer between α-ketoglutarate and glutamine.
3a. Glutamate (a) can assimilate another ammonia
3b. Glutamate (b) can transfer an amino group to an α-keto acid to form a different amino acid which regenerates α-ketoglutarate.
How many of the amino acids can be derived from 2 TCA cycle intermediates?
The glycolysis intermediate 3-phosphoglycerate can synthesize ___
Serine and glycine
Steps to get 3-phosphoglycerate to serine
1. get rid of the hydroxyl on the α-carbon and replace it with an amino group,
2. remove the phosphoryl on carbon 3.
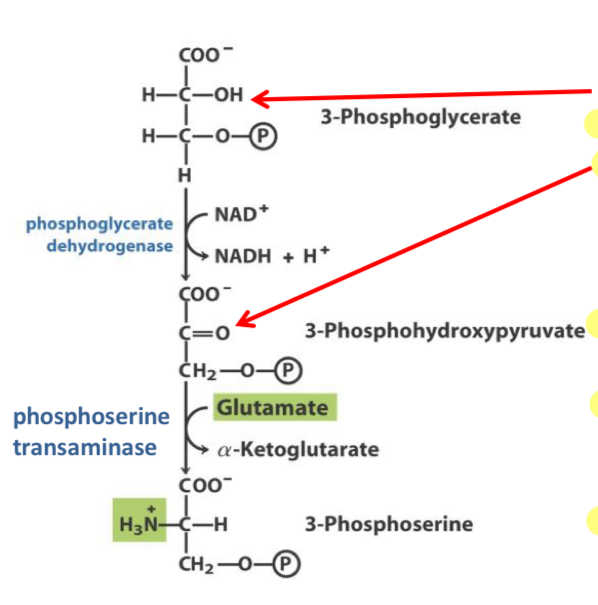
What does this photo show?
The first step to get from 3-phosphoglycerate to serine
What is the first step to get from 3-phosphoglycerate to serine
oxidize the α-carbon hydroxyl to a ketone.
Once we have the ketone on the α-carbon we have an α- keto acid to which we can add the amino group using a transaminase (phosphoserine transaminase).
The transaminase used to add the amino group to the α-carbon in the first step of Serine and Glycine synthesis
phosphoserine transaminase.
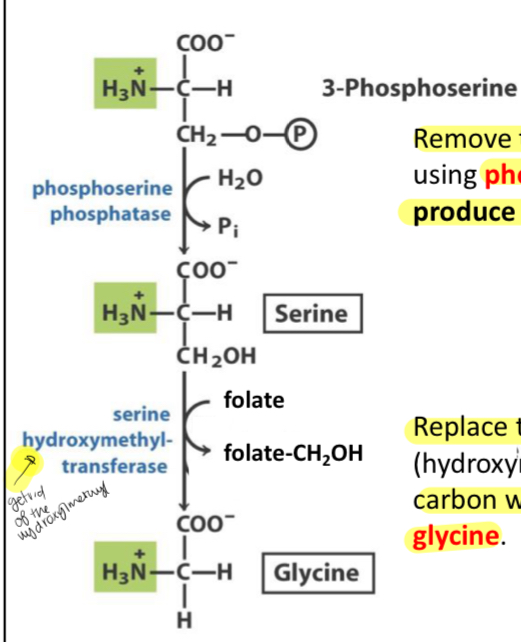
What does this reaction(s) show?
The second step to get from 3-phosphoglycerate to serine and Glycine
What occurs in the second step To get from 3-phosphoglycerate to serine to get from 3-phosphoglycerate to serine
The removal of the phosphate on carbon 3
Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction from 3-phosphoserine to serine and what is released?
Enzyme: Phosphoserine phosphatase
Released: H2O to Pi
How to get from serine to glycine
By replacing the methanol (hydroxymethyl) group on the α-carbon with a proton
Enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of serine to glycine
Serine hydroxymethyl-transferase
Takes folate and releases folate-CH2OH as a result
Which amino acids can be synthesized from oxaloacetate (a TCA intermediate)
Aspartate and Asparagine
Is oxaloacetate an α-keto acid or a α-anmino acid?
It is an α-keto acid
Which amino acid is the α-amino acid counterpart to oxaloacetate?
Aspartate
Which enzyme is used to catalyze the reaction of oxaloacetate to Aspartate
Aspartate transaminase
Uses glutamate (it is the amino donor to the α-keto) which is then turned to α-ketoglutarate as a result
What enzyme is used to convert Aspartate to asparagine?
Asparagine synthetase
-the energy from the hydrolysis of ATP to AMP + 2Pi is used by the enzyme to transfer an amido group from glutamine to Aspartate to form asparagine
The three different scenarios in animals that protein degradation occurs
1. protein-rich diet supplies amino acids in excess of protein synthesis requirements—amino acids are not stored;
2. normal cellular protein turnover—many of the proteins are only required for a brief period of time, therefore once a protein is no longer required, it is identified as requiring breakdown;
3. starvation—protein will be broken down into TCA intermediates to provide energy or precursors for gluconeogenesis. Regardless of the source, amino acids are generally sent to the liver for degradation.
What two pathways should you consider when breaking down amino acids
1. Fate of α-amino groups—they have to be removed and then collected for subsequent degradation and elimination;
2. Fate of carbon skeleton—which are α-keto acids.
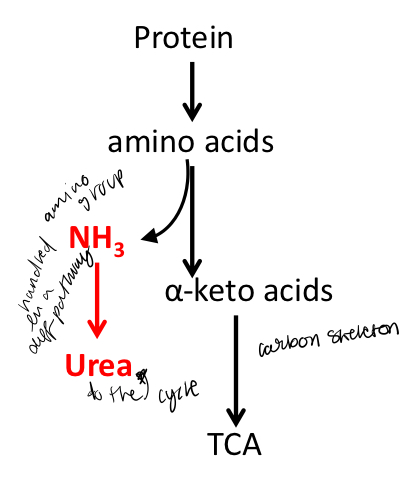
The first step of the breakdown of amino acids is to remove ____
the α-amino group from the α-carbon of the amino acid
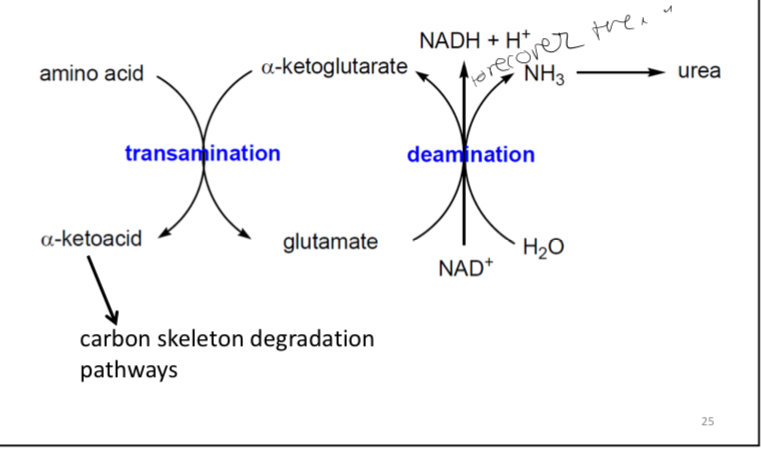
The two principal stages for the removal of amino groups
Transamination reactions
Delaminating of glutamate
Transamination reactions
these reactions function to collect amino groups into a pool of glutamate molecules.
Delaminating of glutamate
-functions to funnel the gathered amino groups into the urea cycle
-if the ammonia derived from the removal of amino groups is not required it must be excreted because ammonia is toxic to an organism (unless a specialized bacteria).
Stage 1 transaminase reactions
Transfer amino groups from amino acids to α-ketoglutarate forming a pool of glutamate.
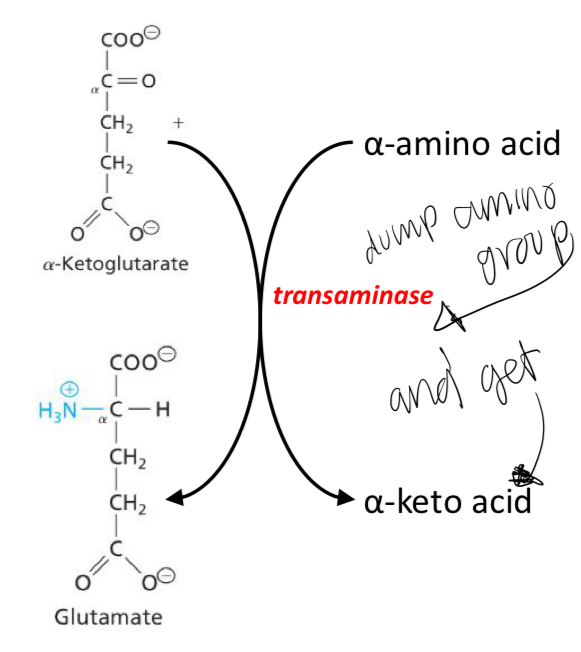
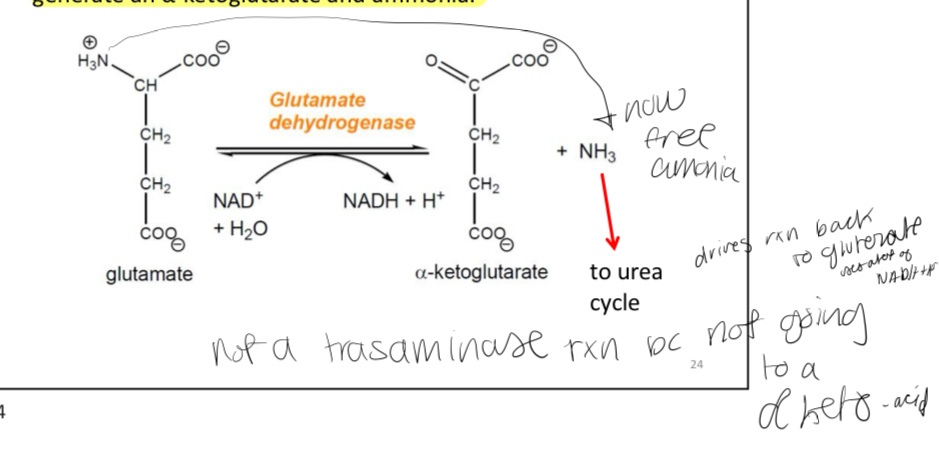
Stage 2: Delaminating of glutamate
Once we have the pool of glutamate molecules in the liver, the amino group can be removed by glutamate dehydrogenase to generate an α-ketoglutarate and ammonia.
Summary of flow of amino groups from amino acids to urea cycle
What happens to carbon skeletons
They are converted into molecules central to metabolism:
1. α-ketoglutarate
2. succinyl CoA
3. fumarate
4. oxaloacetate
5. pyruvate
6. acetyl CoA
The degradation of the majority of amino acids is ____ i.e they can directly supply guconeogenesis pathways
Glucogenic
The amino acid products that are ketogenic can be used to generate
Ketone bodies or acetyl CoA for energy production