4. International trade (Exports and Imports)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Exports
When the world price is above equilibrium, the country will ____ the product, which is when we sell our products to other countries.
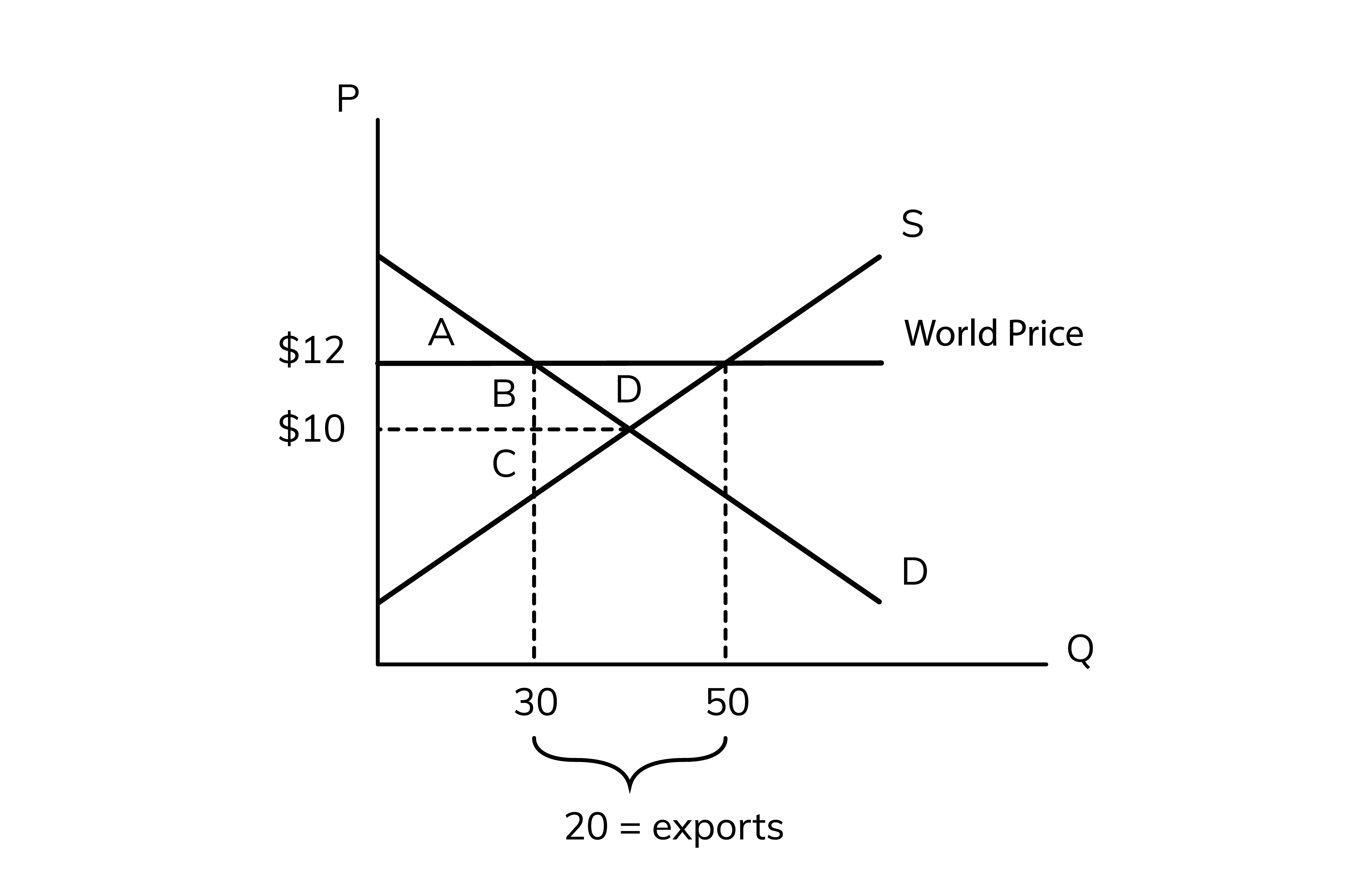
50, 30
In the diagram above, at the world price of $12, the domestic supply is __ units and the domestic demand is only ___ units so this country can export the difference between supply and demand to other countries
supply
The exports are equal to the excess
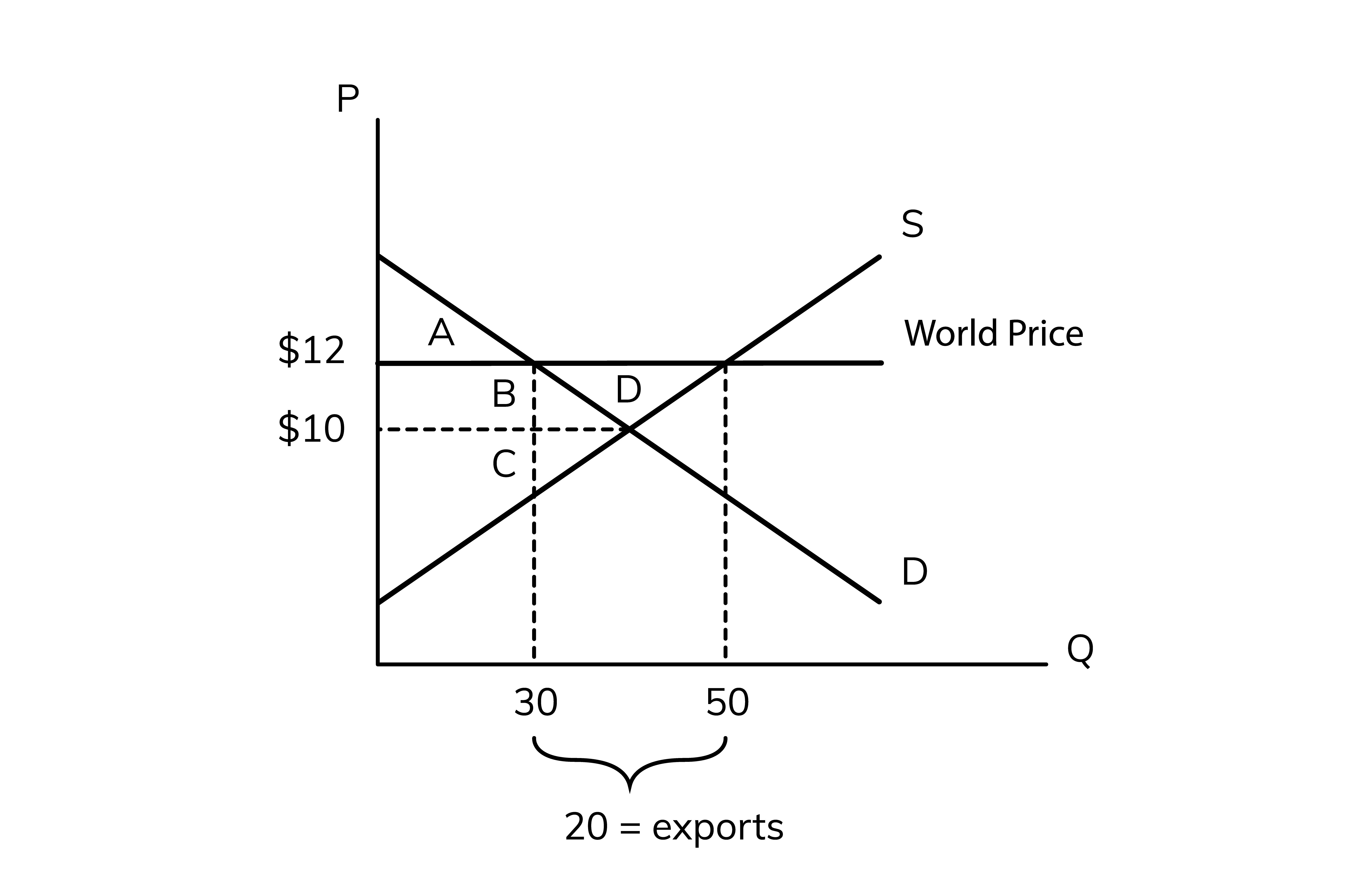
20
In the diagram above the exports =
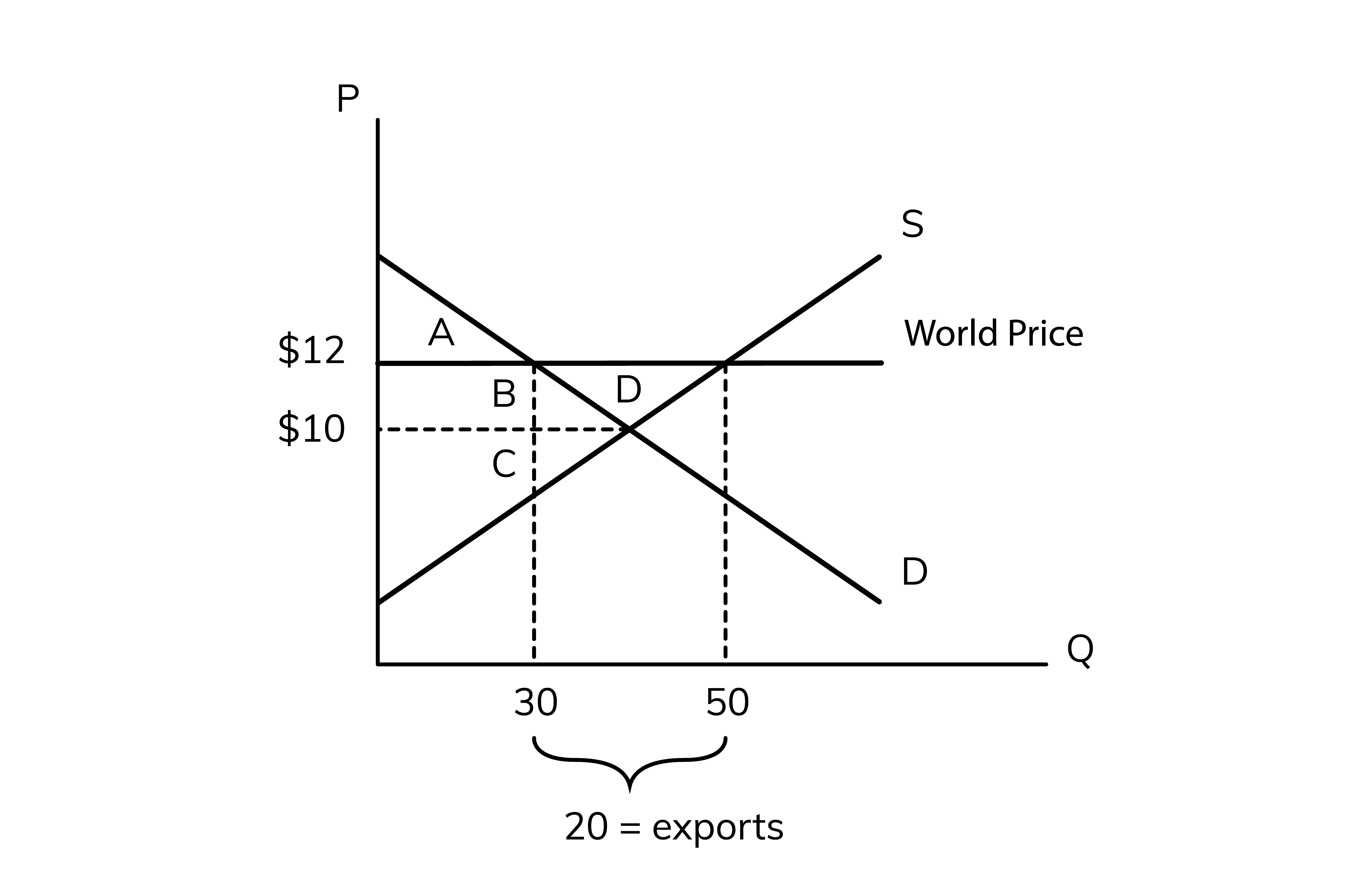
consumer surplus
the area above the price and below the demand.
10, A + B
Without trade, the price is ___ so the consumer surplus is ____
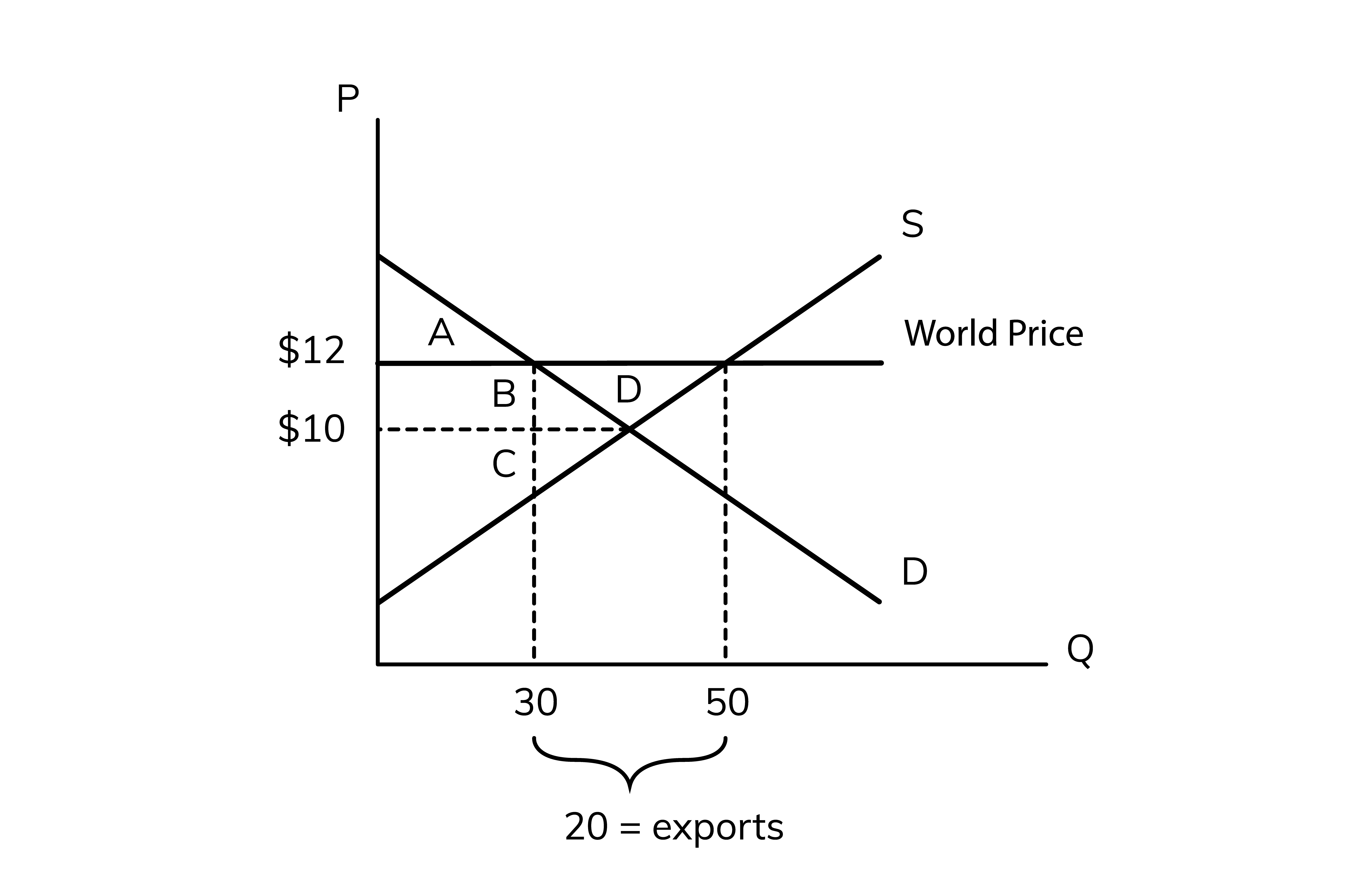
12, 30, A
with trade, the price is ___ and domestic consumers are buying a quantity of __ so consumer surplus is __
producer surplus
the area below the price but above the surplus
10, C
without trade, the price is __ so the producer surplus is __
12, 50, B + C + D
with trade, the price is __ and domestic producers are selling a total quantity of __
A + B, A, -B
consumer surplus before trade, after trade, change
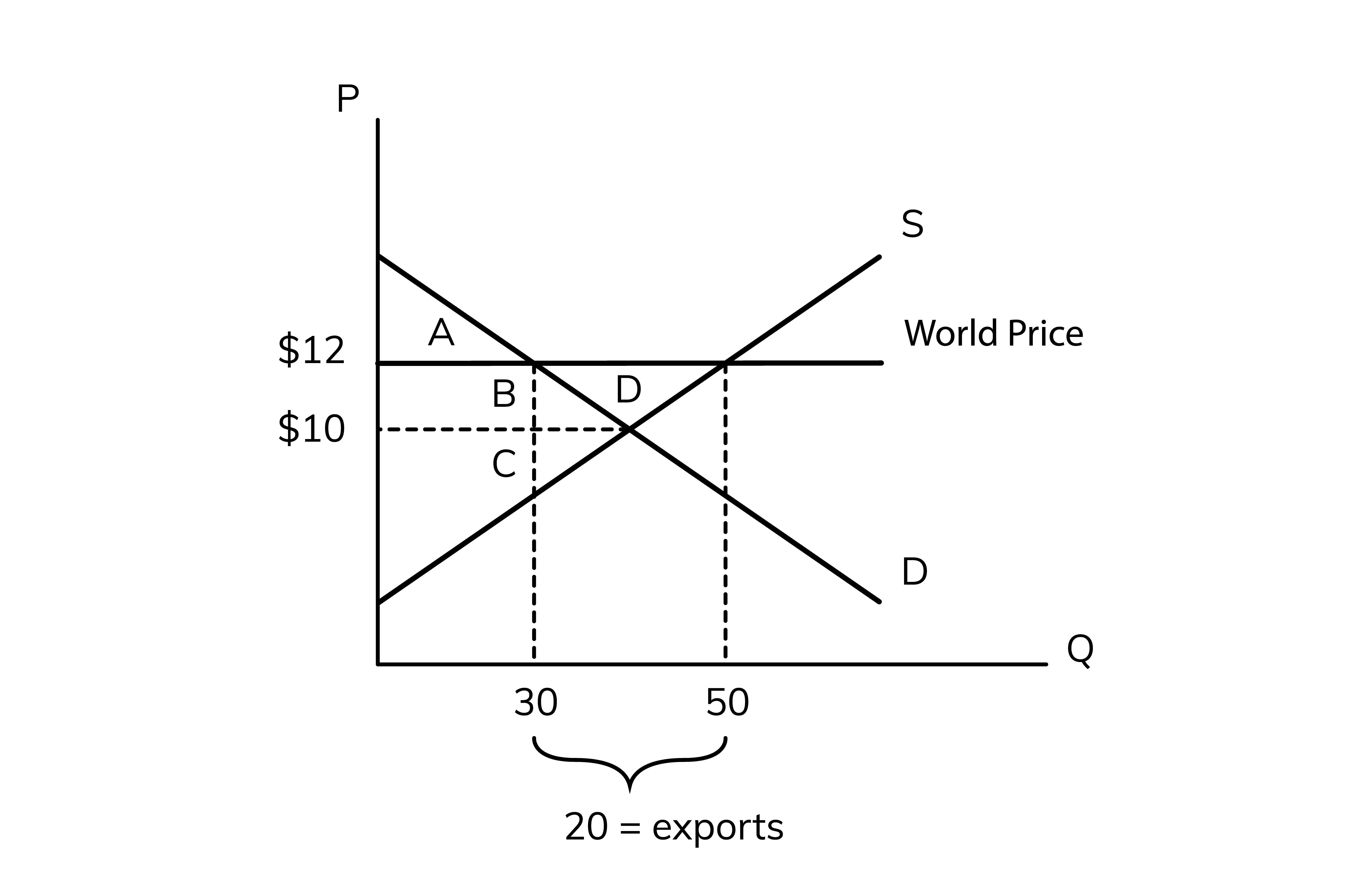
C, B + C + D, B +D
producer surplus before trade, after trade, change
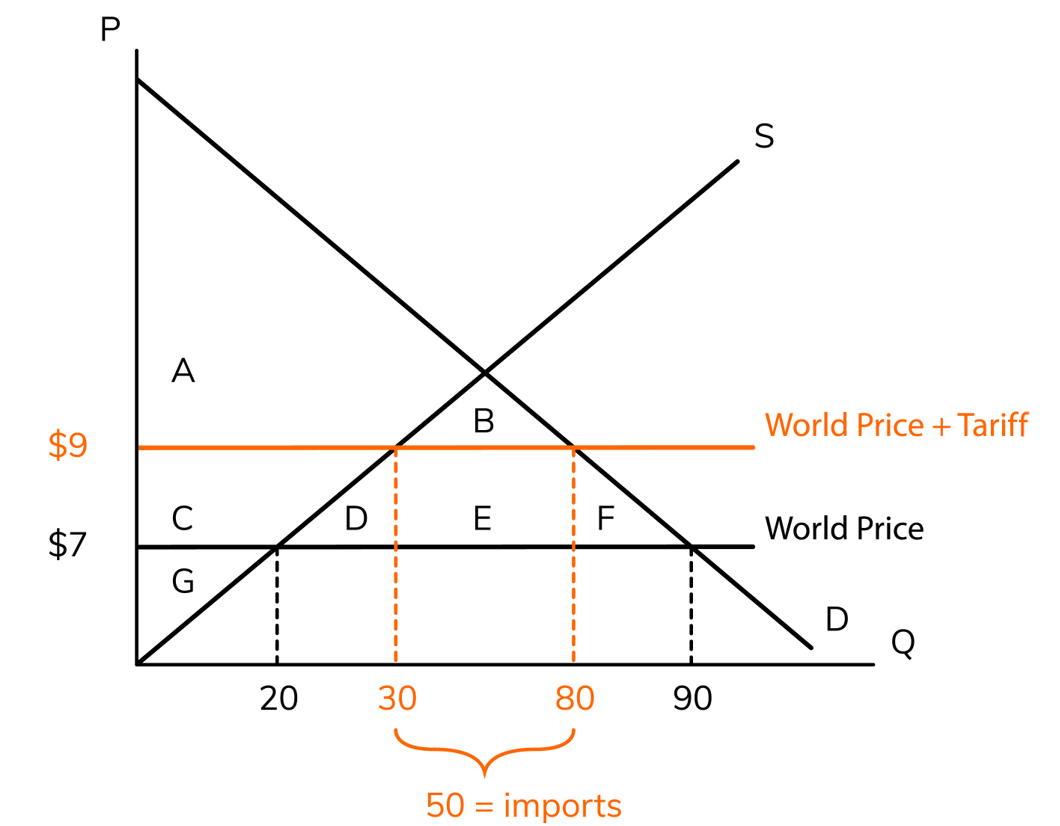
tariff
a __ is a tax on imports that is designed to help domestic businesses
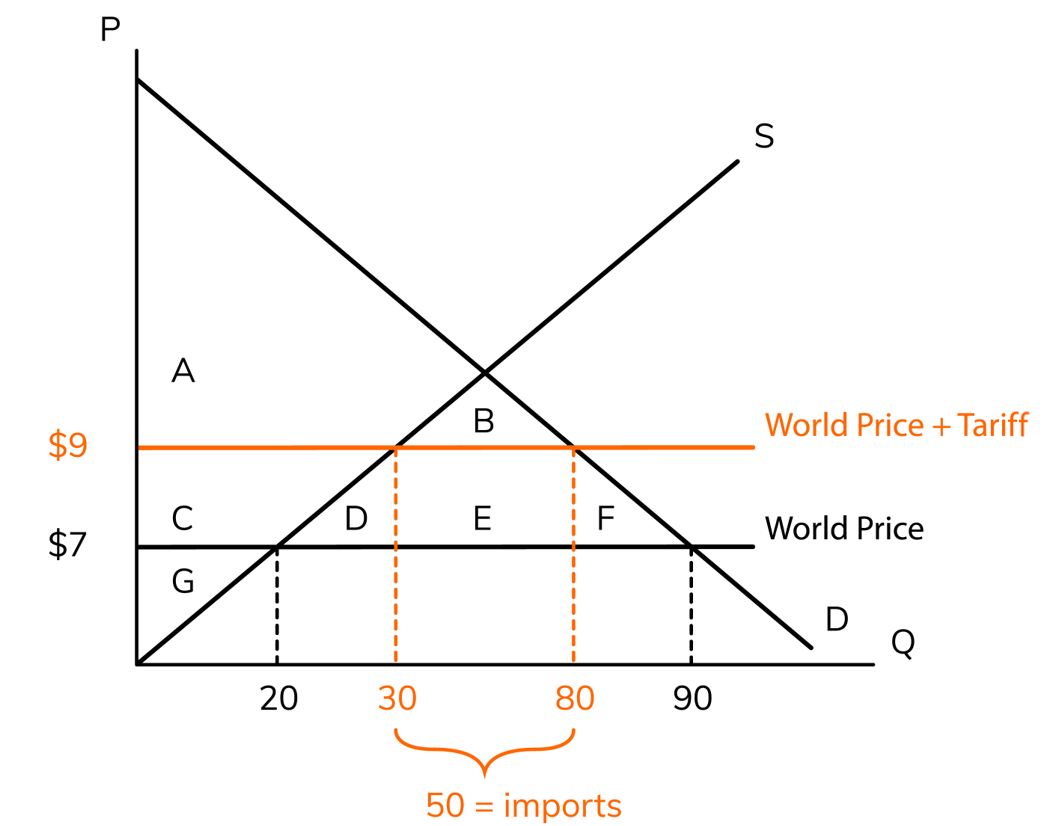
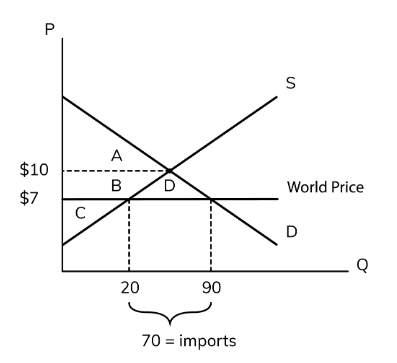
import
When the world price is below the equilibrium, the country will __ the product, which is when we buy goods from other countries.
100, E
The government tariff revenue is the tariff multiplied by the imports (because the government doesn't tax the domestic businesses). This would be __ which is the rectangle __
pro, increased variety of goods
when there is more than 1 type of good on the market
pro, Economies of Scale
when producing in bulk lowers your costs.
pro, Increased competition
good for consumers (we get better prices)
pro, Enhanced flow of ideas
we can learn from each other
con, jobs argument
free trade can hurt some domestic jobs.