Bio Exam 3 - Meiosis and Mendelian Inheritance
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Meiosis
Cell division in which haploid cells are produced from diploid cells; takes place in germ cells in humans; produces sperm and egg cells (gametes); produces genetic variability
2 divisions of meiosis
Meiosis 1 - the reduction division, reduces number of chromosomes from 46 to 23, produces 2 cells, separates homologous pairs, Meiosis 2 - the equational division, produces 4 cells from the 2 produced in meiosis 1, separates sister chromatids; each division consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
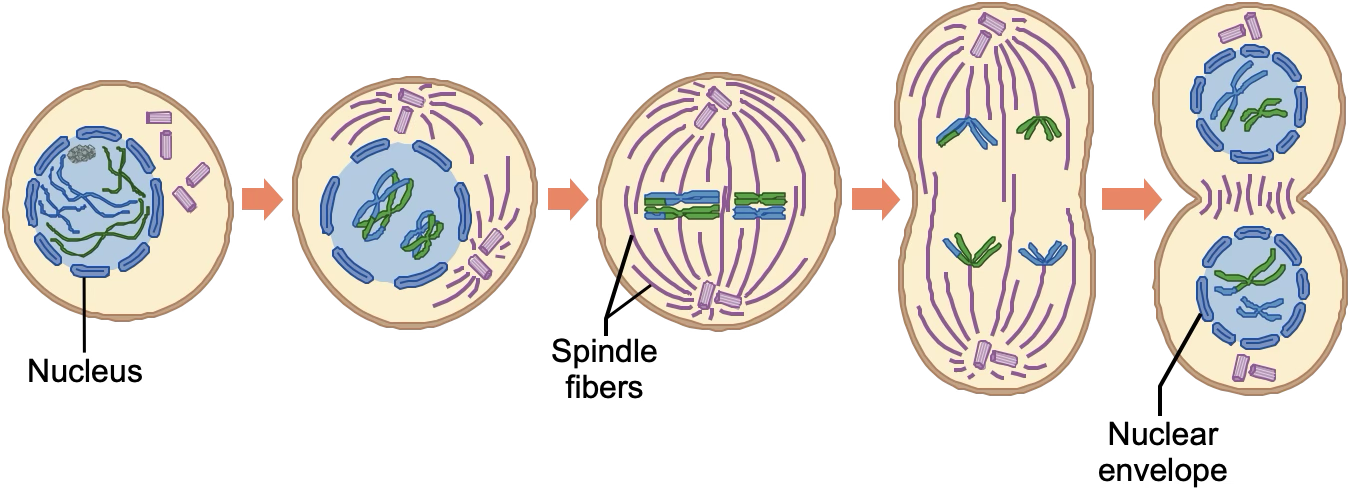
Meiosis 1
Mendel’s Law of Segregation
At the end of meiosis, each gamete carries one copy of an allele
Prophase 1
Homologs pair up and undergo crossing over; spindle forms, nuclear envelope breaks down
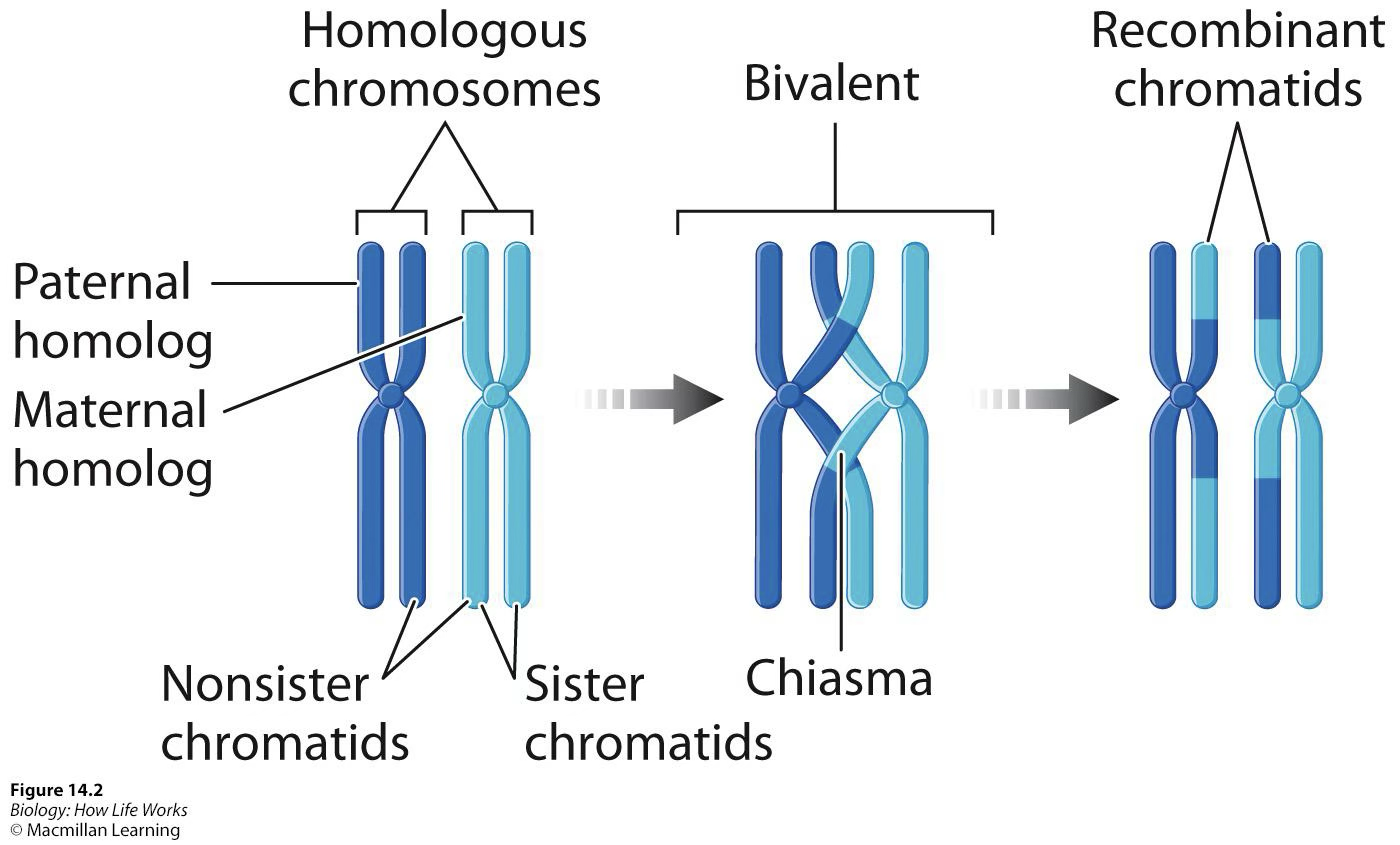
Crossing over
Homologous pairs interact and swap information; increases genetic variation
Metaphase 1
Homologous pairs align along the equator
Independent assortment (Mendel’s 2nd law)
Random alignment of chromosomes; maternal and paternal line up but it doesn’t matter what side
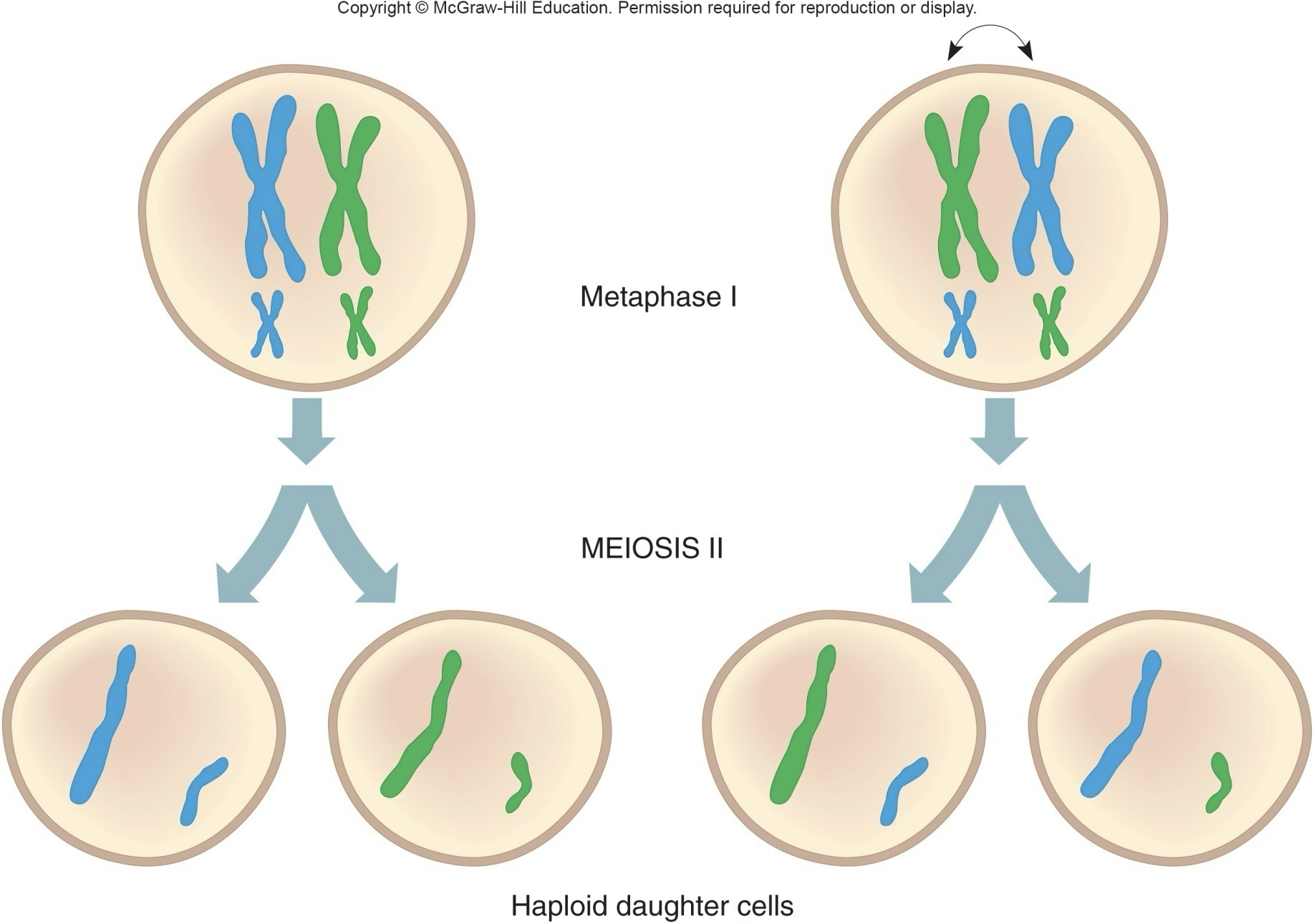
Anaphase 1 and Telophase 1
Homologs separate; move to opposite poles
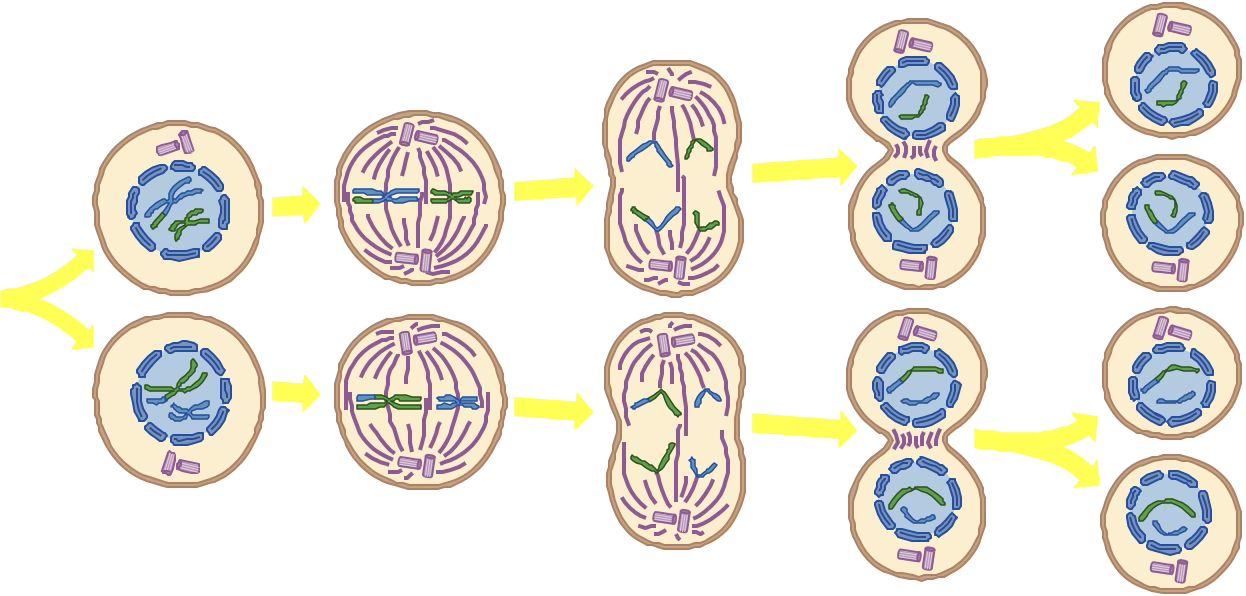
Meiosis 2
Meiosis 2
Same as meiosis 1, except sister chromatids line up and are separated
Mitosis - # of divisions, # of daughter cells, genetics, chromosome #, what kind of cells does it occur in, purpose
One division, two daughter cells per cycle, daughter cells genetically identical, chromosome number of daughter cells same as that of parent cell, occurs in somatic cells, used for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction
Meiosis - # of divisions, # of daughter cells, genetics, chromosome #, what kind of cells does it occur in, purpose
Two divisions, four daughter cells per cycle, daughter cells genetically different, chromosome number of daughter cells half that of parent cell, occurs in germline cells, used for sexual reproduction, producing new gene combinations
Cytoplasmic division in males vs females
Females - one oocyte and three polar bodies; males - cytoplasmic division is equal among the resulting cells
First and Second nondisjunction
First nondisjunction - homologous pairs don’t separate properly, all of the gametes have an incorrect number of chromosomes; second nondisjunction - sister chromatids don’t separate properly, two of the gametes have an incorrect number of chromosomes
Results of meiosis
4 haploid cells; each carry a new assortment of genes and chromosomes that hold one copy of the genome, diverse