Micro Bio Exam 2
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Antiseptic
kills microbe but safe for living tissue
Aseptic Technique
to not introduce new microbes
Bactericidal
kills bacteria
Bacteriostatic
inhibits new growth while its present
Degerm
get rid of microbes at a site
Disinfectant
kills but not safe for living tissue
Germicide
lower overall # of various microbes
Sterilant
kills everything including endospores
pasteurization
kills harmful organisms responsible for such diseases
most resistant to least microbes
endospores, protozoan cysts, mycobacteria (resistance to drying out and chemicals), pseudomonas (can use disinfectants as nutrients), naked viruses (nucleic acids surrounded by a protein shell), enveloped viruses, vegetative bacteria
d value
time required to kill 90% of the population of bacteria under specific conditions
critical items
direct contact with tissue, like a needle, needs to be sterile because it is going below the mucus membrane which is sterile
semi-critical
direct contact with mucous membranes, camera for colonoscopy
non-critical
contact with unbroken skin, blood pressure cuff
moist heat
denatures protein, examples include boiling and pasteurization, high temp. short time (HTST), ultra high temp. shorter time (UHT), autoclave which is faster because it is pressurized, not sterile but safe for consumption
filtration
pores need to be 0.2 micrometers for bacteria to be trapped, can’t catch viruses, used for heat sensitive liquids or gases
radiation as a physical germicide
use short energy waves to create ions (ionization) that chop up DNA
ultraviolet wave as a physical germicide
lead to mutations in microbes on the surface of objects
high-level disinfectants
all microbes except endospores
intermediate-level disinfectants
all vegetative microbes and most viruses
low-level disinfectants
fungi, vegetive bacteria except mycobacteria, enveloped viruses
factors affecting choice of a chemical
toxicity, does it get confused by other organic matter that is not dangerous, safe on the material being treated, residue that could still be toxic to tissue, cost and availability, storage, environmental risk
alcohols
antiseptics so its safe for tissue, dehydrate cells when more than 70%, dissolves membranes, does a little protein denaturing
aldehydes
disinfectant, sterilant, inactivates proteins and nucleic acids
halogens
oxidation (takes away electrons) of proteins so they are inactive, chlorine and iodine
ethylene oxide
sterilant used in chemiclave, stronger oxidizer of proteins
metal compounds as germicides
ions slowly leak out and attach to SH group on proteins to inactivate them, not safe to us
phenolics
disinfectant (not safe for tissue), destroy cell membrane and proteins, Lysol
biguanides
affects cellular proteins, chlorhexidine is the most effective, low toxicity, broad range of microbes affected
Quaternary ammonium compounds as germicides
positively charged detergents attracted to bacterial surface and destroy cell membrane, Pseudomonas are resistant
weak organic acids for preservation
benzoic, sorbic, propionic, used for bread, cheese, and juice, interfere with cell membrane of bacteria
nitrates and nitrites
in bacon, prevents endospore germination
lyophilization
freeze-drying, microbes can be revived when water is reintroduced
importance of studying metabolism
products can be useful to humans (ethanol from plants, antibiotics from viruses), can cause disease (products could be toxic), use different substrates making bacteria unique, target or antimicrobial therapies using bacteria specific pathways
catabolic pathways
breaking down “food” and harvesting its energy to make ATP, also produces precursor metabolic for biosynthesis
anabolism
use energy and percussor metabolites to synthetize polymers into cellular structures (macromolecules) needed to survive
metabolism
sum of total of all catabolic and anabolic reaction
radiant energy
sun energy harvested by plants and bacteria to synthesize organic compounds
chemical energy
energy in the form of organic compounds
enzymes
specific to each step in a pathway, turns one substate into one product (final or intermediate), proteins, forms or breaks bonds or transfers electrons between atoms by bending, can be reused because they are not altered when catalyzing a reaction
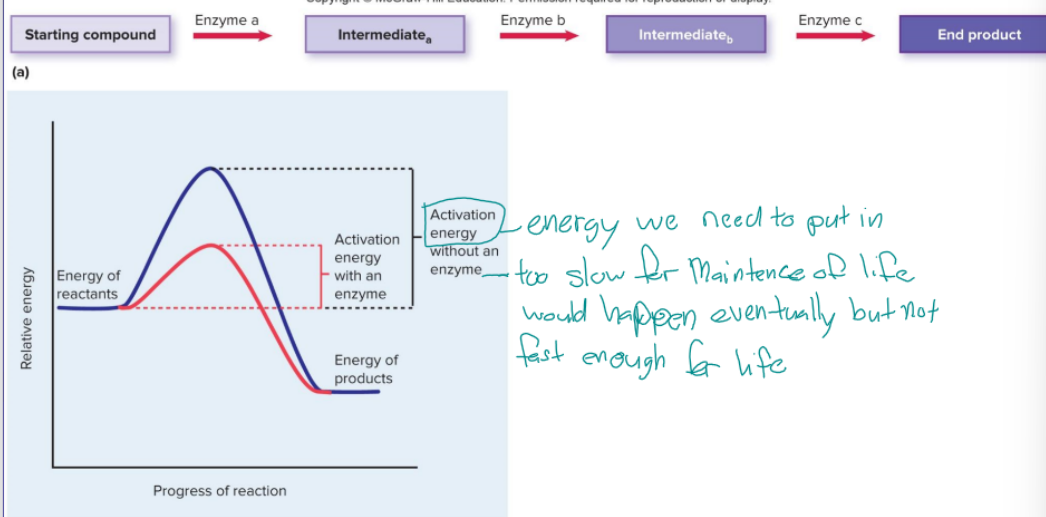
cofactors
non-protein component associated with the active site of the enzyme, promotes or facilitates enzyme function, metal ions such as magnesium which is needed for DNA and RNA polymerase
coenzyme
organic cofactor that acts as carriers of molecules or electrons, most are synthesized from vitamins
allosteric regulation of enzyme activity
positive and negative effectors that bind to the allosteric site, end product can be the inhibitor and detaches when concentrations are too low, allosteric inhibitor or activator changes the enzyme shape, the first enzyme in a pathway is usually affected
non-competitive inhibition
inhibitor that binds to a site that is not the active site, reversible includes allosteric inhibition, non-reversible (mercurochrome) forms a covalent bond between the inhibitor and enzyme that is non-reversable
competitive inhibition
competes with substrate for enzyme active site, plugs the active site because it looks like the substrate (structural analogs), sulfa drugs fill the active site so PABA can not attach and kills the bacteria
oxidative phosphorylation
glucose’s electrons are moved to the electron transport chain to make proton motive force making ATP via NAD and FAD, most used pathway to make ATP
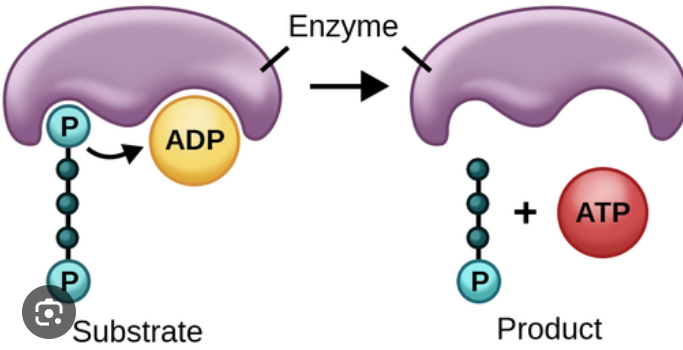
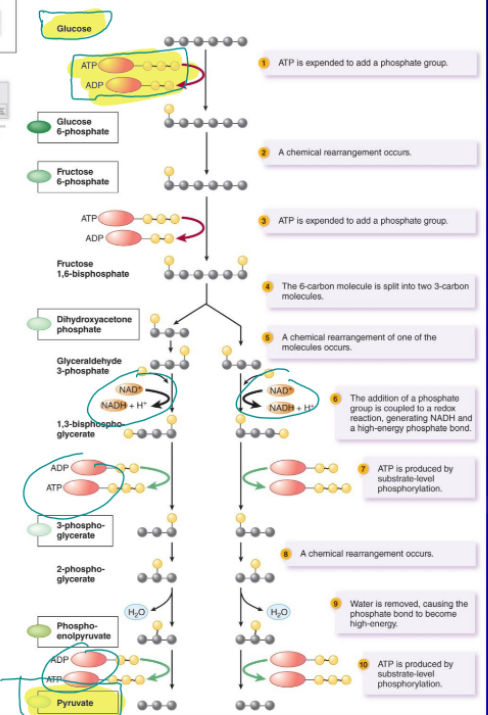
substrate level phosphorylation
ATP is made when an enzyme directly transfers a phosphate group onto ADP, occurs during glycolysis and Krebs cycle
photophosphorylation
producing ATP during photosynthesis from light energy using proton motive force
reduced state
has the electron to donate, reducing agent, NADH, FADH2, NADPH
oxidized state
doesn’t have the electron but is ready to accept one, oxidizing agent, NAD+, FAD+, and NADP+
glycolysis
produces lots of precursor metabolites
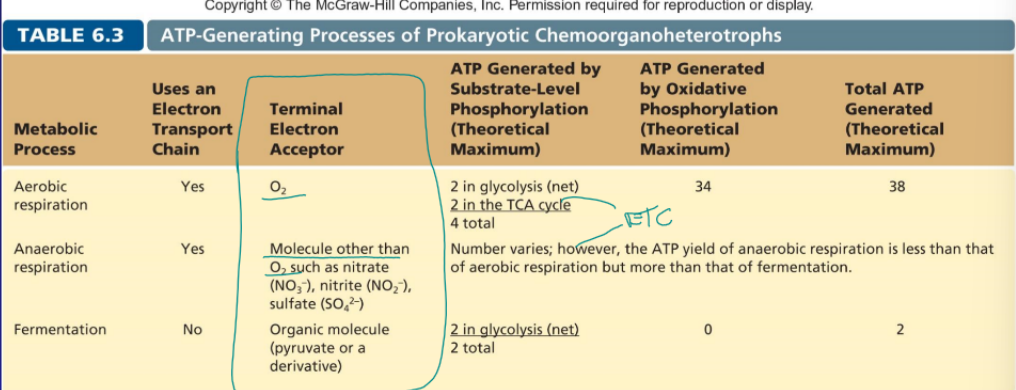
aerobic respiration
includes ETC, O2 is the terminal electron acceptor, 4 (2 from glycolysis and 2 from TCA) total ATP from substrate-level phosphorylation, 34 ATP from oxidative phosphorylation
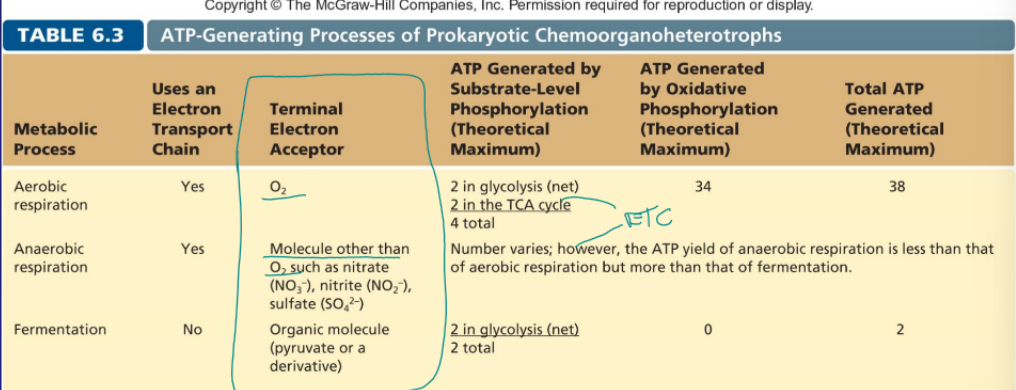
anaerobic respiration
molecular other than O2 is the terminal electron such as NO3- or SO4-2, ATP generated various but is more than fermentation but less the aerobic
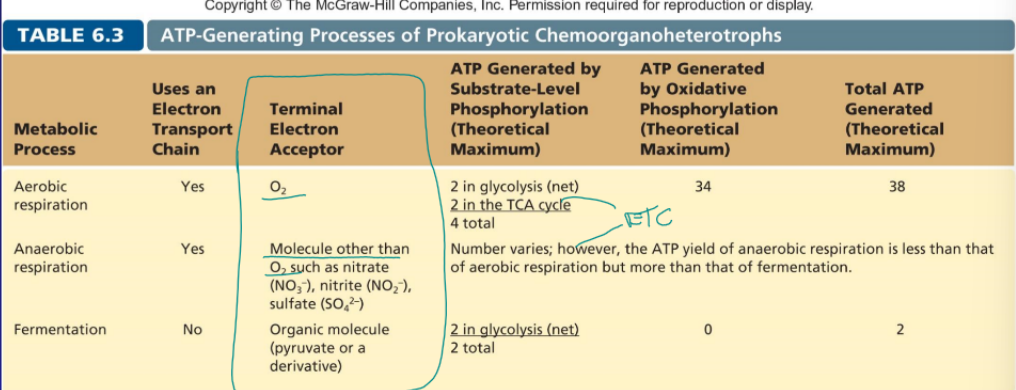
fermentation
no ETC, organic molecule such as pyruvate is the terminal electron acceptor, 2 ATP from glycolysis
amphibolic pathways
includes catabolic and anabolic processes, makes precursor metabolites
glycolysis
used in nearly all organisms to convert glucose (6 carbon molecule) to pyruvate, source of precursor metabolites, anaerobic, 2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
entner-doudoroff pathway
alternative to glycolysis used by some bacteria, only makes 1 ATP, 1NADH, 1 NADPH (needed for some anabolic pathways), and 2 pyruvates, aerobic
pentose phosphate pathway
use by many prokaryotes concurrently as glycolysis or E-D, starts with 3-7 carbon sugar to make precursor metabolites and some NADPH
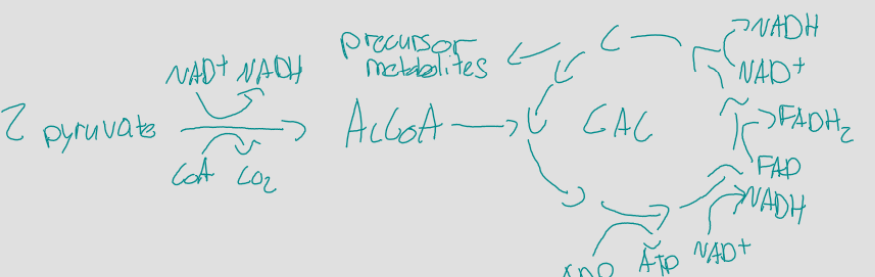
TCA, CAC, and Krebs cycle
8 step cycle that oxidizes pyruvate (from glucose) using CoA to make acetyl-CoA, 2 turns, each turn makes 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, and precursor metabolites, in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes, pyruvate moves from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria of only eukaryotes, aerobic
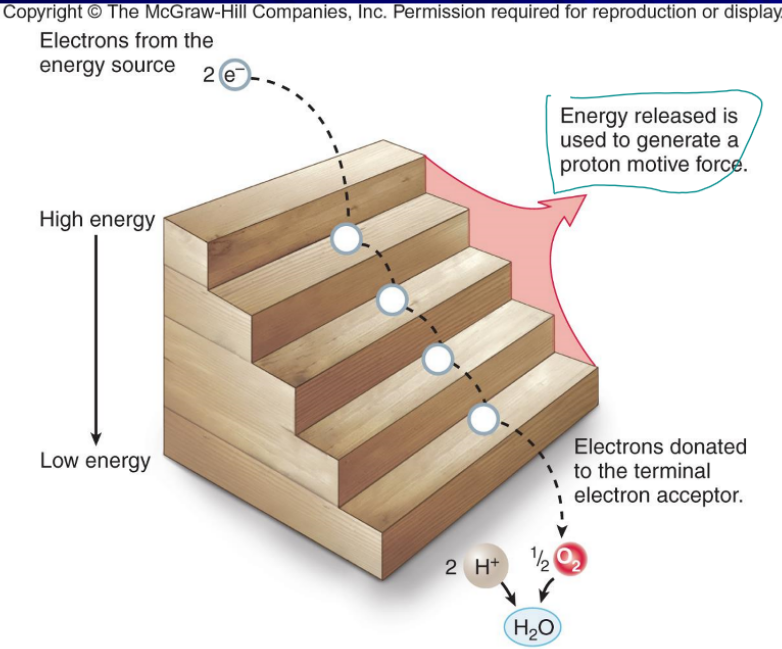
electron transport chain
only step to use oxygen, used to generate proton motive force, transmembrane proteins are reduced by NADH but is oxidized when the electron goes to the next protein, outside the cell membrane but in the cell wall in prokaryotes and between the mitochondria membranes in eukaryotes
ATP synthase
enzyme/transmembrane protein that uses energy from PMF to synthesize ATP by forming a channel that the H+ can go back with their concentration gradient
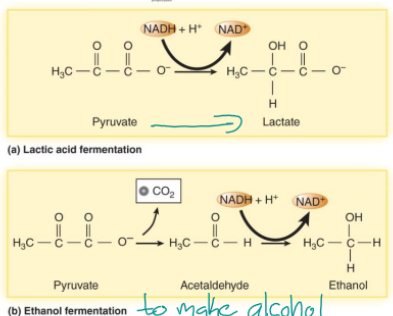
fermentation
keeps glycolysis going (so it can keep producing a few ATP) by emptying NADH to another electron acceptor (not ETC because there is no oxygen), makes acids or gases (lactic acid for food preservation, ethanol in alcohol, acetone)
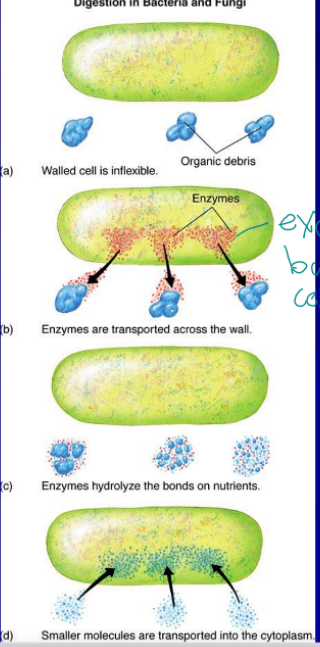
exoenzymes
enzymes that are created in the cell but their function is outside the cell, break up debris to monomers small enough for them to bring in through active transport
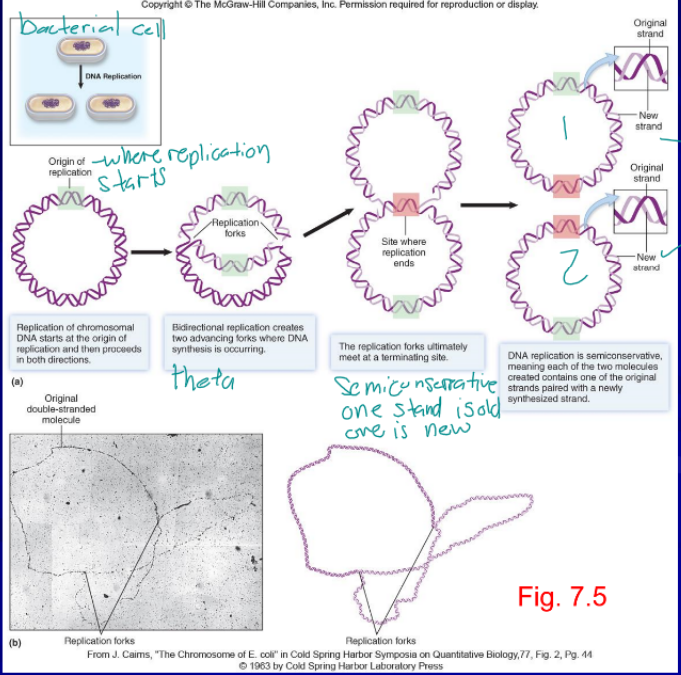
DNA replication
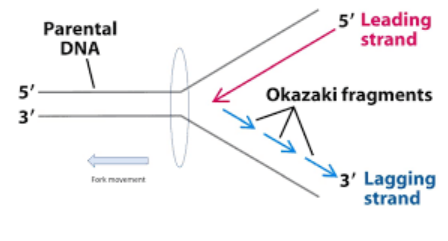
only happens when the cell is ready to divide, passing encoded information to the next generation, each replication fork had a leading and lagging strand(discontinuously synthesized as Okazaki fragments), from 5’ to 3’
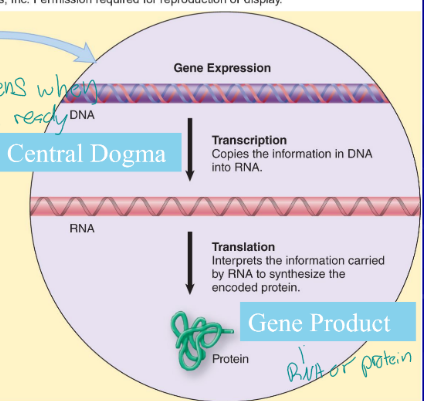
Central dogma
theory stating that genetic information flows only in one direction, from DNA, to RNA, to protein
characteristic of RNA
single-stranded polymer of nucleic acid, ribose sugar
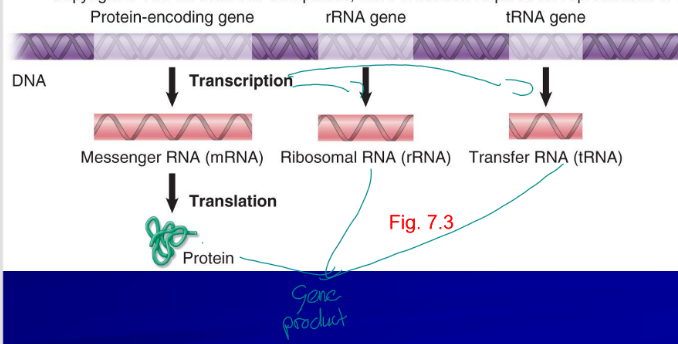
regulation of gene expression
depends on environment, low levels of transcription generates little gene product (protein or RNA)
DNA gyrase
enzyme that temporarily breaks DNA strands ahead of the helicase to prevent supercoiling
DNA ligase
enzyme that joins two DNA fragments by forming a covalent bond between the sugar and phosphate of adjacent nucleotides
DNA polymerase
enzyme that synthesizes DNA by using one strand as a template, adds nucleotides to the 3’ end, works in a 5’ to 3’ direction
helicase
enzyme the unwinds DNA that the replication fork, makes the double strand into a signal strand
Okazaki fragment
nucleic acid fragment produced during discontinuous synthesis of the lagging strand
origin of replication
distinct region of DNA molecule at which replication if initiated, can have multiple for large DNA strands
primase
enzyme that synthesizes small fragments of RNA to act as primers for DNA synthesis
primer
existing fragment of nucleic acid to which DNA polymerase can add nucleotides
replisome
complex of enzymes and other proteins that synthesize DNA
tanscription
first step in gene expression, produces RNA
- (template) strand
RNA is copied from this strand
+ (non-template) strand
strand not used for transcription
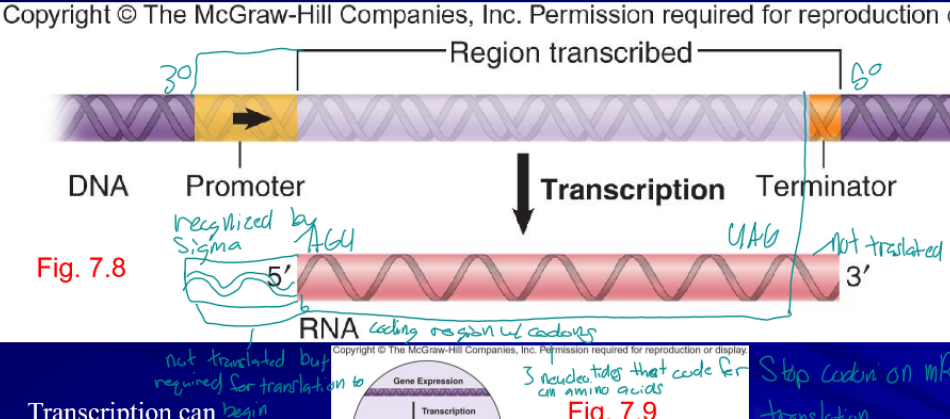
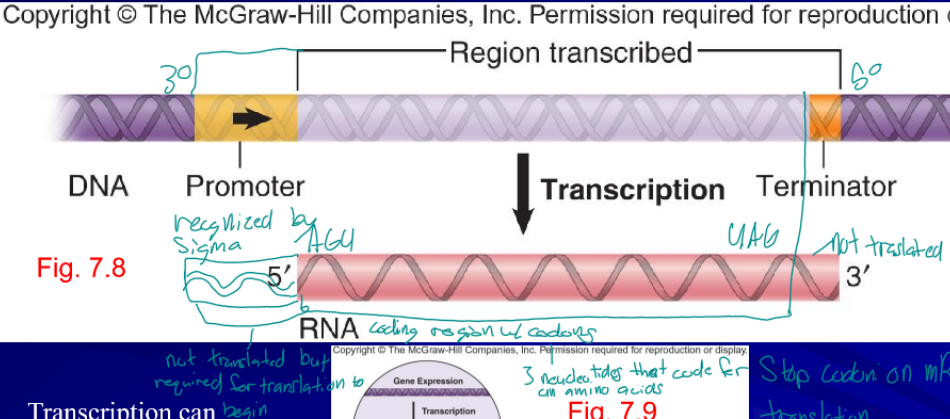
promoter
nucleotide sequence that RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription, not translated but required for translation to begin
RNA polymerase
enzyme the synthesizes RNA, always in the 5’ to 3’ direction
sigma (σ) factor
specific part of RNA polymerase the recognizes a specific promoter regions, allows the cell to transcribe specialized genes as need, only on to innate transcription
terminator
sequence at which RNA synthesis (transcription) stops, not translated, tells the polymerase to fall off the DNA and release the RNA
polycistronic message
many coding regions between the promoter and terminator on bacterial mRNA
cistron
coding region
stop codon
on mRNA and stops translation, signals the end of the protein because not tRNA recognize the codon
tRNA
reads the mRNA, carries a specific amino acid
anticodon
sequence of three nucleotides in the tRNA that is complementary and antiparallel to a particular mRNA codon, allow tRNA recognition and binding to the appropriate codon
codon: 5’ AUC 3’ anticodon: 3"‘ UAG 5’
mRNA
RNA that carries the genetic information that is deciphered during translation
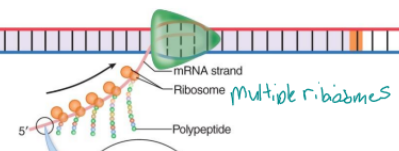
polyribosome (polysome)
multiple ribosome can attach to a single mRNA to make multiple proteins at once
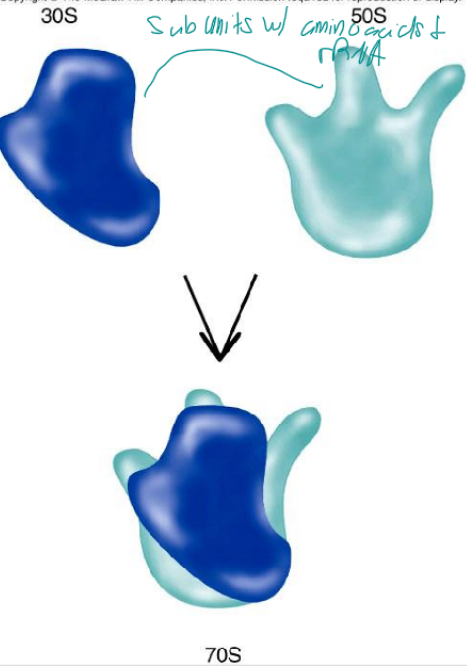
ribosome RNA
facilitates joining of amino acids, targeted by several antibacterial drugs
ribosome-binding site
sequence of nucleotides in mRNA that the ribosome first binds to, translation start after the start codon
rRNA
RNA in ribosomes
start codon
codon that initiates translation, first AUG after the ribosome-binding site
untranslated region (UTR)
promoter region, any codons between the ribosome-binding site and the start codon, codons after the stop codon
E-site
where the empty tRNA will exit once it’s amino acid has been connected
p-site
holds the tRNA that carries the protein (peptide) being built, amino acid from the a-site will be joined to the chain in this one by a peptide bond
a-site
where the new tRNA recognizes the next codon and with enter (accepted), the amino acid in this site will be attached to the one in the p-site by a peptide bond
mRNA processing before translation in eukaryotes
cap is added to the 5’ end and a poly A tail to the 3’ end, introns are removed by splicing, transported out of the nucleus to cytoplasm, monocistronic