Chem - Topic 6
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
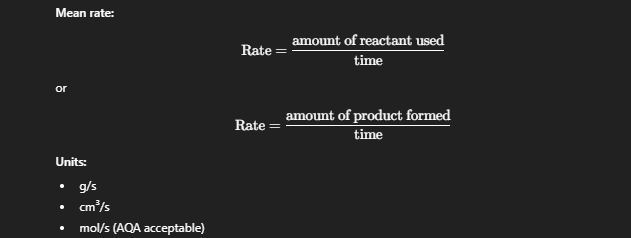
Rate of Reaction
Measure of how fast reactants are used up
Collision Theory
Particles must collide with enough energy to overcome the activation energy.
What does a rate of reaction depend on
The collision frequency of reacting particles. The more collisions there are the faster the reaction
The energu transferred during a collision, Particles must collide with enough energy.
Activation Energy
Minimum energy needed for reaction to occur
graphs and tangents and shii
How does increasing temperature increase the rate?
Particles move faster
So more frequent collisions, so increases the rate of reaction.
In addition, when particles move faster, the more energy they have. So more of the particles will have enough energy for reaction to occur.
How does increasing concentration increase the rate?
More particles in the same volume, (same with pressure).
So more frequent collisions.
How does increasing surface area increase the rate?
Breaking a solid into smaller pieces, increase the SA:V ratio.
So particles have more area to work, so more frequent collisions
How does increasing catalyst increase the rate?
Provides an alternative reaction pathway, to decrease the activation energy
So more particles have enough energy to react.
Reversible Reaction
A chemical reaction where products can react to re-form original reactants.
What happens to energy changes in reversible reactions?
In reversible reactions:
If the forward reaction is exothermic, the reverse is endothermic.
If the forward is endothermic, the reverse is exothermic.
Equilibrium
Equilibrium is reached when the rate of forward reaction equals the rate of backward reaction.
What are the conditions eeeded for Equilibrium
Equilibrium is only established in a closed system → no reactants or products can escape.
Le Chatelier’s Principle
If a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it shifts to oppose the change and restore a new equilibrium.
Effect of Temperature
• Increase temp → shifts to endothermic direction
• Decrease temp → shifts to exothermic direction
Effect of Pressure
• Increase pressure → shifts to side with fewer gas molecules
• Decrease pressure → shifts to side with more gas molecules
Effect of Concentration
• Increase reactant → shifts right (makes more products)
• Remove product → shifts right
• Increase product → shifts left (forms more reactants)