MCAT-physics
1/259
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
260 Terms
kilo
10^3 (k)
Mega
10^6 (M)
Giga
10^9 (G)
Tera
10^12 (T)
hecto
10^2(h)
deca
10^1 (da)
Deci
10^-1 (d)
centi
10^-2 (c)
milli
10^-3 (m)
Micro
10^-6 (μ)
nano
10^-9 (n)
Pico
10^-12 (p)
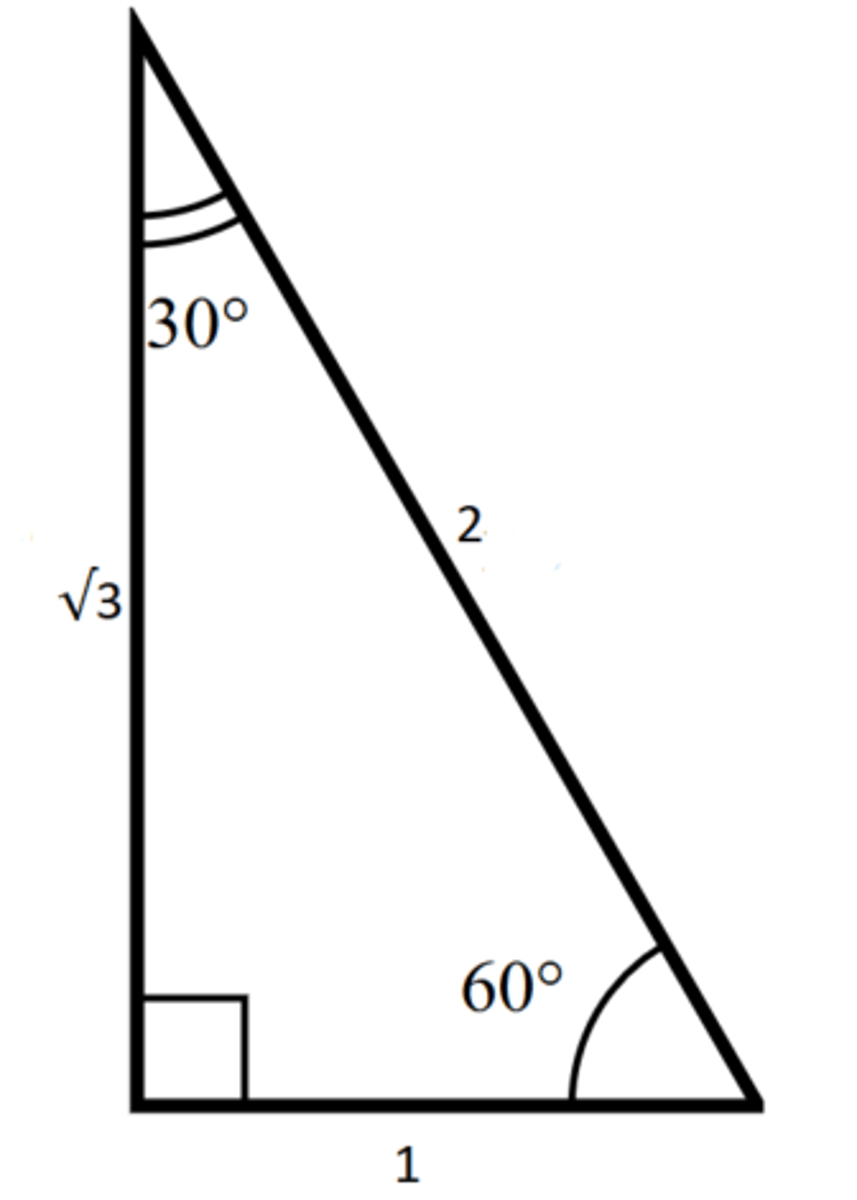
30-60-90 triangle
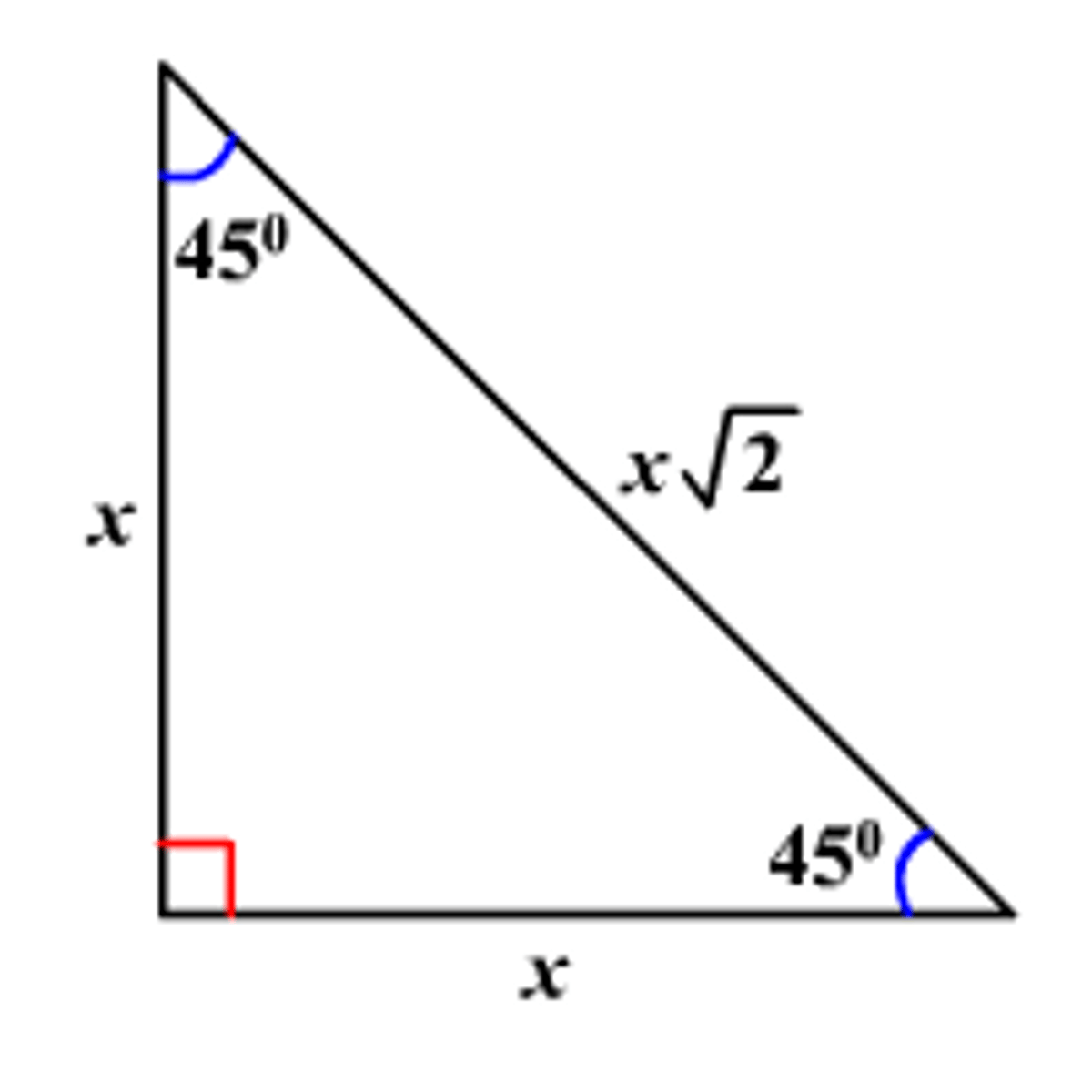
45 45 90 triangle
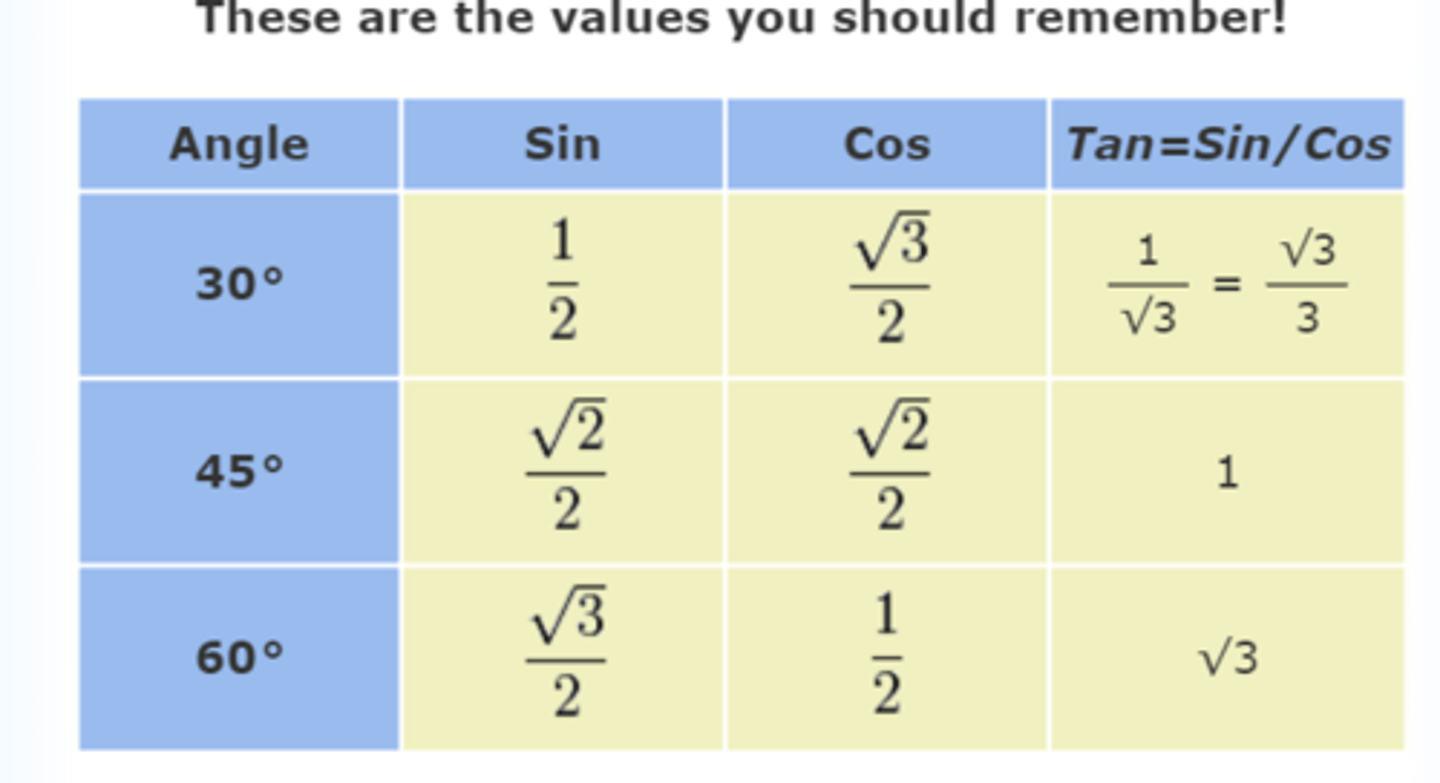
sin/cos values to remember
horizonal projectile motion=
cos
vf and vi formula with a and change in x
vf^2=vi^2+2achange in x
newton's laws:
1. objects at rest/motion will stay at rest/motion
2. F=ma
3. equal and opposite forces
4 fundamental forces
1. gravity
2. electromagnetic force
(dont need to know these)
3. strong nuclear force
4. weak nuclear force
center of mass
(x1m1+x2m2+x3m3)/(m1+m2+m3)
Fstatic (the maximum it can be, but if less than max then it is opp of force applied to move the object)
(coefficient of friction)(normal force)
for gravity questions g=
m1m2/(r^2)
centripetal acceleration
v^2/r
Hooke's law: force needed to compress/stretch a string by x is
F=kx
torque
F(d)sin()
angle between force and lever arm
work=
F(d)cos()
angle between force and horizontal
unit=joules=1 N(m)= (kgxm^2)/s^2
mechanical advantage of ramps vs pulley
less force, same work
mechanical advantage= length of incline/height of incline
power
work/time
units: W=1 J/s
kg⋅m2⋅s−3
for projectile motion trig
angle formed with the x axis
vx=vcos()
vy=vsin()
velocity
area under a velocity v time graph is displacement
acceleration
area under an acceleration v velocity graph is change in velocity
kinematics equation missing acceleration
d=(vavg)t or d=((change in v)/2)t
kinematics equation missing displacement
vf=vi+at or (change in v)=at
kinematics equation missing final velocity
(change in x)=(vi)t+1/2at^2
kinematics equation missing time
vf^2=vi^2+2a(change in x)
motion on an inclined plane
g perpendicular= gcos()
g parallel=gsin()
Kinetic Energy (KE)
1/2mv^2
energy is proportional to
mass
energy and ____ are two ways of talking about the same thing
work
gravitational potential energy
mass x gravity x height
or
mgh
potential energy of a spring
1/2kx^2
when choosing between using kinematics or conservation of energy, remember that
time is not used in energy calculations
work
kinetic energy final-kinetic energy initial
pressure
force/area
units: 1 Pa or 1 N/m^2
work
pressure (change in volume)
think of the scenario in which a piston is moving in and out of a cylinder, changing the volume
if a gas doing work to expand a balloon
then the gas has to cool because it is using energy
Fahrenheit =
2(degrees Celsius) + 32
first law of thermodynamics
0. Two bodies in thermal equilibrium are at the same T
1.Energy cannot be created or destroyed
2. The total entropy of a system must increase in every spontaneous reaction
3. The entropy of a pure, perfectly crystalline compound at absolute zero (0 K) is zero.
Change U=Q-W
first law of thermodynamics
-the total energy change of a system is equal to the transfer of energy into the system via heat minus the work performed BY the system on its surroundings
isolated system-
no exchange of energy or matter
closed system-
no exchange of matter, only exchange of energy
open system
exchange of matter and energy
system gaining energy (heat and work)
heat into system, work by system
system losing energy
heat out of system, work on system
second law of thermodynamics
two ways of saying:
1. if two objects are in thermal contact but not in thermal equilibrium, then heat energy will flow from object with higher temp to object of lower temp
2. the entropy of an isolated system will increase over time
heat
a mechanism of energy transfer and has unites of energy
temperature
static property proportional to kinetic energy
change in volume and change in length are proportional to change in temperature
change in length= (coefficient of thermal expansion constant specific to the substance)(length)(change in temperature)
PV=
NRT
zeroth law of thermodynamics
if one system (A) is in thermal equilibrium with two other systems (B and C), then systems B and C must also be in thermal equilibrium with eachother
lowest kelvin temp possible is
0 degrees (or absolute zero)
isochoric
volume remains constant
isobaric
constant pressure
isothermal
constant temp
adiabatic
process where no heat exchange takes place
density =
mass/volume
remember mass and _____ are not the same
weight
molarity
moles/liters
density of water (need to memorize)
1000 kg/m^3 or 1 kg/L or 1 g/mL or 1 g/cm^3
specific gravity
how dense something is compared to water (bc it is a proportion it does not have units)
pressure=
force/area
pressure on an object submerged in fluid=
(density of object)(g)(depth of submersion)
absolute pressure
hydrostatic prerssure of submerged object + pressure of atmosphere
the percentage of an object that will be submerged in water is proportional to its
specific gravity
buoyant force is equal to
the weight of the fluid displaced by the object
Pascal's Principle
The rule that when force is applied to a confined fluid, the increase in pressure is transmitted equally to all parts of the fluid.
watch video
higher velocity of a fluid
the more likely it is to become turbulent
the flow rate and the pressure drop are proportional to each other
aka a large pressure drop will cause flow rate to increase
poiseulle's law equation (describes flow of incompressible fluids through a cylinder)
know how variables relate to eachother, so if change one what the effect will be, memorize formula

Bernoulli's Law
Law stating that pressure in a moving fluid is less when the fluid is moving faster.
general ruled of ideal fluids:
narrower tube->higher velocity
narrower tube->lower pressure
higher velocity->lower pressure
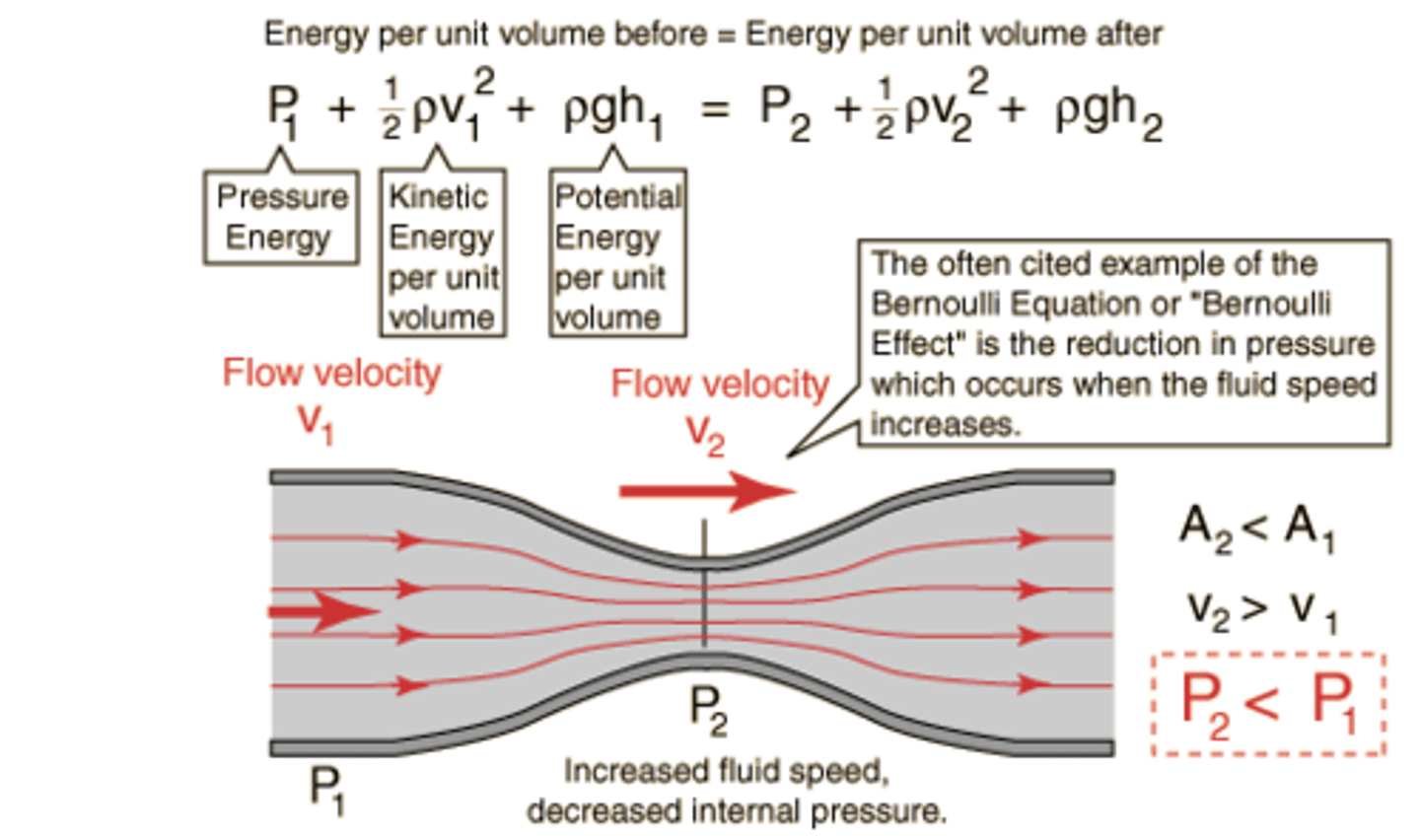
venturi effect
narrower tube-> lower pressure (venturi effect), higher velocity
higher velocity->lower pressure
laminar flow
a smooth pattern of flow
(opposite of turbulent)
relationship between fluid velocity and cross-sectional area of the pipe through which the fluid is travelling
v1A1=v2A2
so fluid velocity and cross-sectional area are inversely proportional
properties of ideal fluids
1. the fluid is incompressible
2. the fluid is not viscose
3. the fluid exhibits laminar flow
increased flow speed resulting from being forced through a confined space results in
a zone of low pressure
scalar quantities do not have
a direction
(but vector quantities do have direction)
E (magnitude of electric field)=
(kq)/r^2 or F/q
The SI units of the electric field are newtons per coulomb (N/C), or volts per meter (V/m)
Work (in an electric field)
W=(kQq)/r
potential energy of a chrarge
(kQq)/r
-same as work
V, electric potential
(kQ)/r
Conductivity
A material's ability to allow heat to flow
(sigma)(area/length)
-sigma is a constant that is the inverse of p
Resistivity
A material's opposition to the flow of electric current.
p(length/area)
-p is a constant
dimagnetic
no unpaired electrons
paramagnetic
Atom or substance containing unpaired electrons and is consequently attracted by a magnetic field
magnetic fields cannot be blocked
but, it can be rerouted with a material that conducts better than the materials around it, ie copper
electric field lines are drawn
from positive to neg charges
an insulator does not have free electrons, but when a charged object is brought near it...
polarization does occur at an atomic level
electric potential energy=
electric potential (charge)
electric potential=
k(Q/r)
1atm
= 101kPa = 760 mmHg