Photosynthesis+ Respiration Word Wall Terms
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
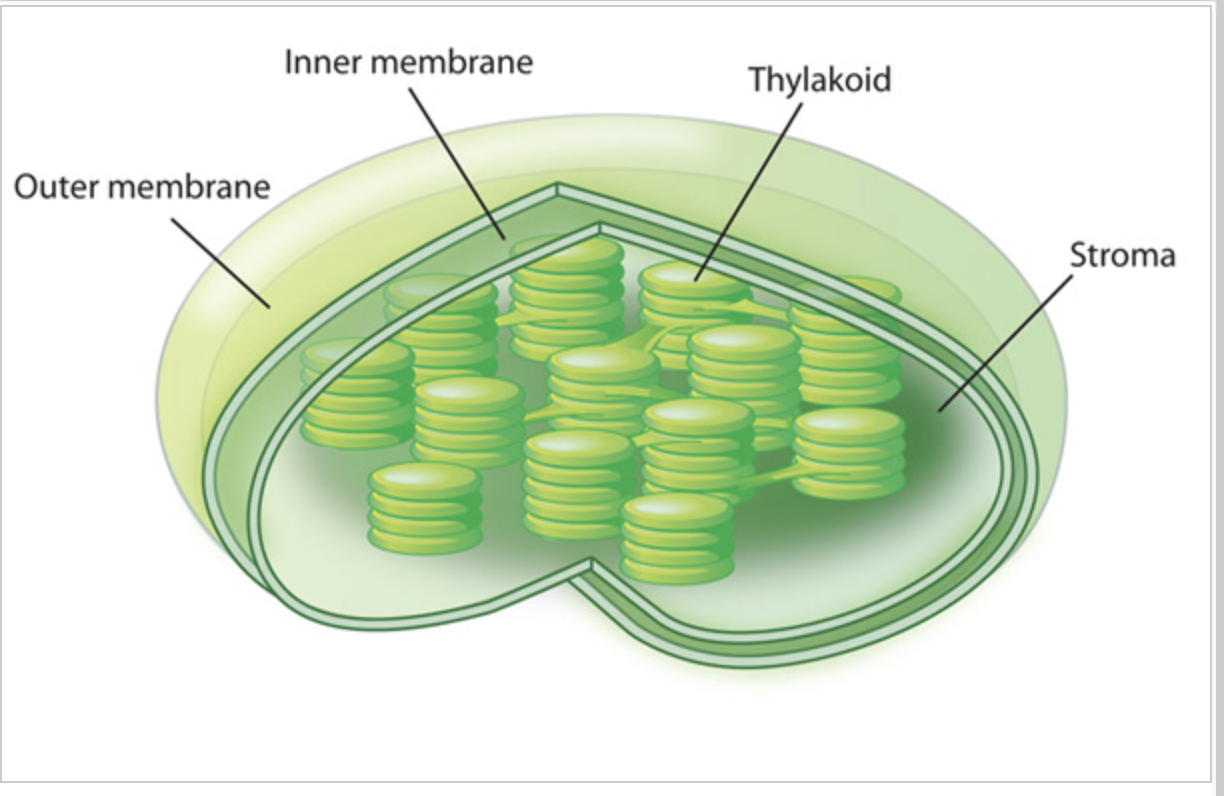
Chloroplast
Organelles in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs. They contain thylakoid membranes (site of light reactions) and stroma (site of the Calvin Cycle).
Chlorophyll (e⁻)
The green pigment that captures light energy. It excites electrons (e⁻) during the light-dependent reactions, which powers the production of ATP and NADPH.
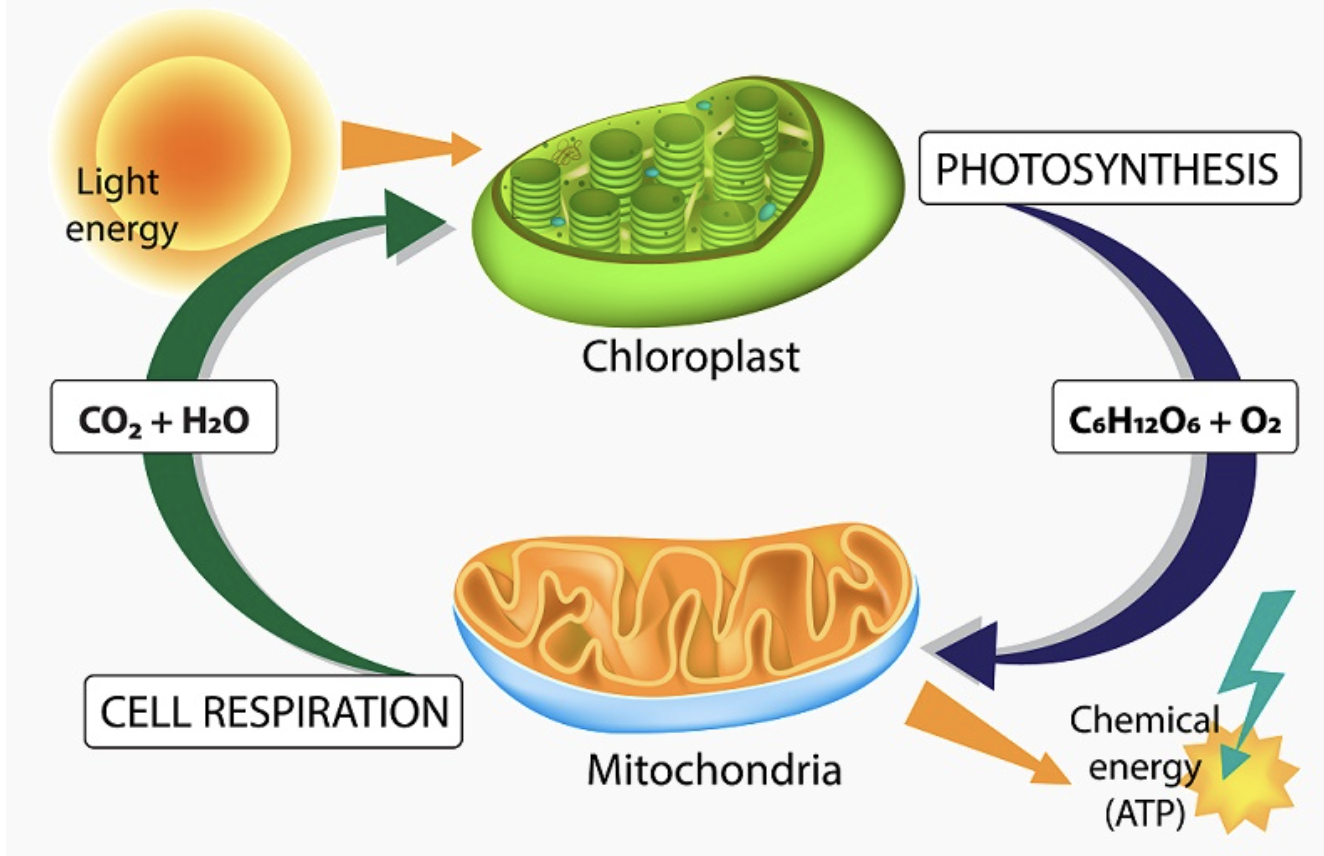
Energy Flow
Energy in photosynthesis flows from light (solar energy) to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) and is stored in glucose.
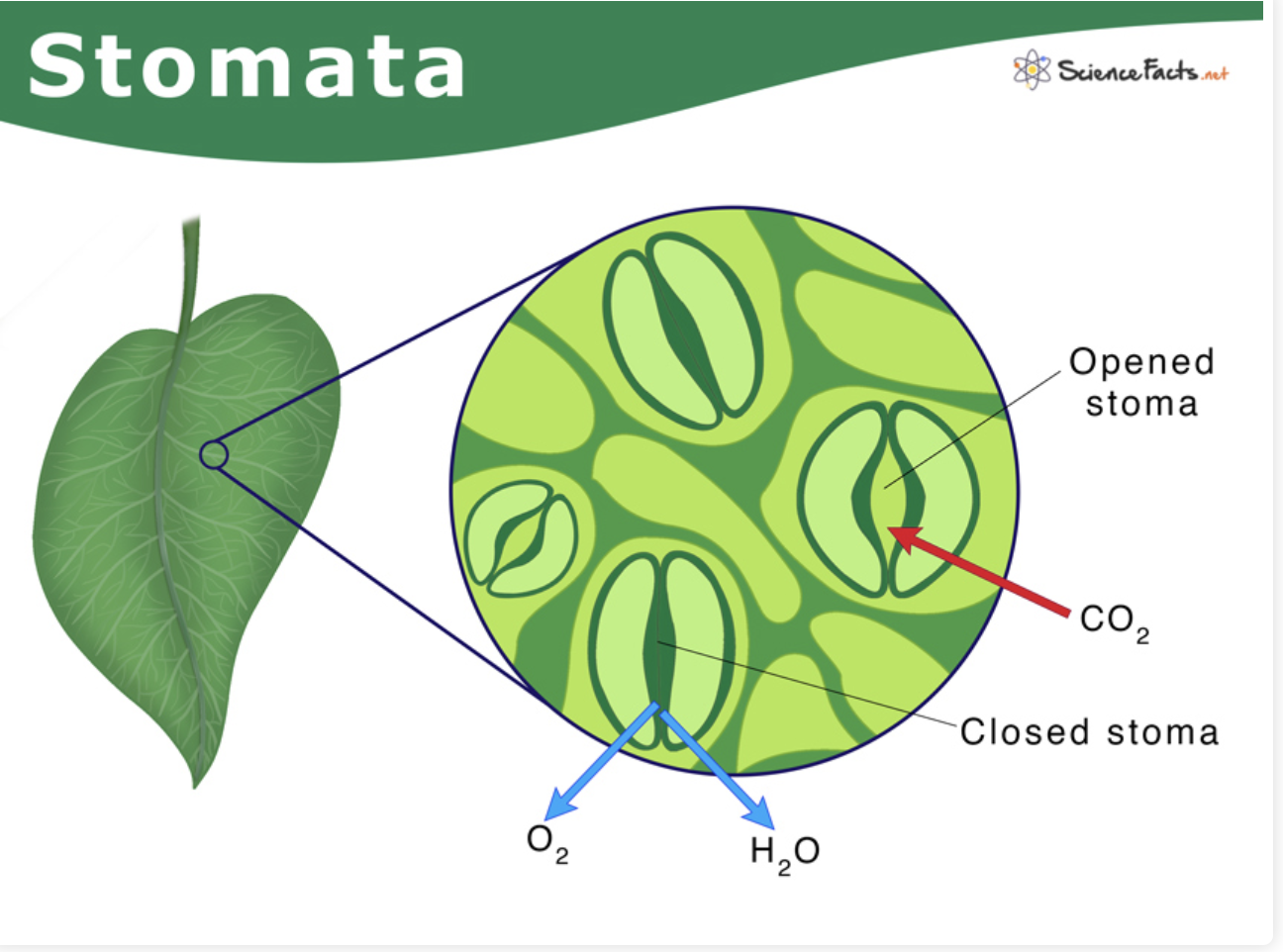
Stomata
Small openings on leaf surfaces that allow gas exchange (CO₂ in, O₂ out) and water vapor loss during transpiration.
Plant Water Balance
This refers to how plants manage water loss through transpiration while ensuring sufficient hydration for metabolic processes. Guard cells regulate stomata to balance water retention and gas exchange

Glucose
The sugar produced during photosynthesis, which serves as an energy source for plants and other organisms.
Cellulose
A polysaccharide made of glucose units. It forms the structural component of plant cell walls.
Oxygen Production
Oxygen is released as a by-product during the splitting of water molecules in the light-dependent reactions.
Light Energy
A form of energy that travels in waves and is emitted by sources like the sun or artificial light. It is used by plants in photosynthesis to convert solar energy into chemical energy.
Glucose
A form of stored energy in chemical bonds of molecules. It is released when these bonds are broken, such as in cellular respiration.
Flow of materials in plant
Water: Absorbed by roots, transported via xylem to leaves.
Sugars: Produced in leaves and transported via phloem to other parts of the plant.
Transpiration
The process by which plants lose water vapor through small pores called stomata, primarily on their leaves. This loss of water vapor helps regulate the plant's temperature and creates a vacuum that draws up water and nutrients from the roots through the plant.
Plant Adaptations
When C4 and CAM plants have alternative photosynthetic pathways to reduce water loss in arid conditions.
Light Reactions
Occur in the thylakoid membranes. They use light energy to split water, releasing oxygen, and produce ATP and NADPH.
Calvin Cycle
Occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. It uses ATP and NADPH from light reactions to convert CO₂ into glucose.
ATP
Energy currency of the cell, produced during light-dependent reactions.
Aerobic Processes
A biological process that requires oxygen to break down glucose (or other molecules) into energy, producing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
Anaerobic Processes
A biological process that occurs without oxygen, breaking down glucose into energy and producing byproducts like lactic acid (in animals) or ethanol and carbon dioxide (in yeast).
Cellular Respiration
A chemical process that occurs in cells to convert glucose and oxygen into energy (ATP), with carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. It happens at the cellular level and provides energy for biological functions.
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O
Breathing Respiration
A physical process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide. It occurs in the lungs (or similar organs) to exchange gases between the body and the environment, providing oxygen for cellular respiration.
Hemoglobin
A protein in red blood cells (RBCs) responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carrying carbon dioxide from tissues back to the lungs. Made of four protein subunits, each containing an iron-rich heme group that binds oxygen. Increases the blood’s capacity to carry oxygen efficiently. Gives blood its red color when bound to oxygen.
Red Blood Cells
Their primary function is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and organs and carry carbon dioxide, a waste product, from the tissues back to the lungs for exhalation. Red blood cells are specialized in this task due to their hemoglobin content, a protein that binds to oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Fermentation
A metabolic process where cells produce energy (ATP) without oxygen by breaking down glucose or other organic molecules.
Lactic Acid
A type of anaerobic fermentation that occurs in muscle cells and some bacteria, where glucose is broken down into lactic acid and energy (ATP) without the need for oxygen.
Process:
Glucose → 2 Lactic acid + 2 ATP.
Alcoholic Fermentation
A type of anaerobic fermentation that occurs in yeast and some microorganisms, where glucose is converted into ethanol (alcohol), carbon dioxide, and energy (ATP) without the use of oxygen.
Process:
Glucose → 2 Ethanol + 2 CO₂ + 2 ATP.
Mitochondria
Organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell because they generate most of the cell's energy in the form of ATP.
Function:
Cellular respiration: Convert nutrients (like glucose) into ATP through aerobic processes (glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation).
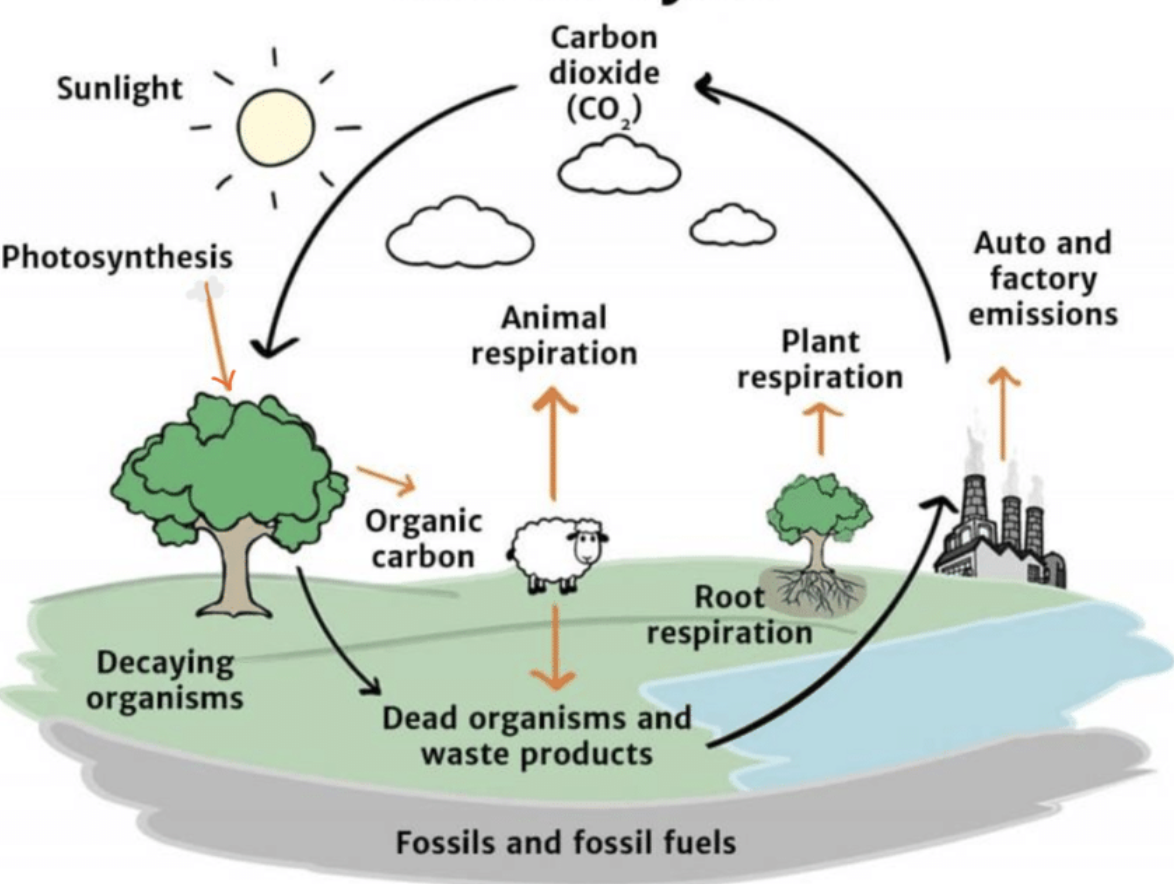
Carbon Cycle
The process by which carbon is exchanged between the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms, regulating Earth's climate and supporting life.
Transport Work
The movement of substances across cell membranes or within cells. This involves the active or passive transport of molecules like ions, nutrients, and waste products, often requiring energy (ATP) to move substances against a concentration gradient.
Mechanical Work
The movement or physical change in a cell or organism, such as muscle contraction, movement of cilia or flagella, or the division of cells. It involves the use of energy to cause physical movement or shape changes in a cell or tissue.
Chemical Work
The process of building or breaking down chemical bonds in molecules, such as during biosynthesis or metabolism. This type of work is required for processes like DNA replication, protein synthesis, and cellular respiration, often requiring energy (ATP) to form or break bonds.
K Cal (1 Kcal=1000 cals)
A unit of energy used to measure the amount of energy food provides when consumed. One food calorie (kcal) is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of water by 1°C.
Body Temperature
Body Temperature: The measure of the body's ability to generate and get rid of heat. It is typically maintained around 37°C (98.6°F) in humans, though normal body temperature can range from 36.1°C (97°F) to 37.2°C (99°F) depending on factors like time of day, activity level, and individual variation.
Thermoregulation: The process by which the body maintains its internal temperature within a safe range, despite external temperature changes. This involves mechanisms like sweating, shivering, and adjusting blood flow to the skin.
Flow of materials in Human Body
The flow of oxygen into the lungs during inhalation and the expulsion of carbon dioxide during exhalation. This exchange is crucial for cellular respiration and maintaining body function.
ADP
It is produced when ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) loses one of its phosphate groups. It can be converted back into ATP through cellular processes, like in the mitochondria during cellular respiration, which allows for the storage and release of energy necessary for various cellular functions.
Glycolysis
The process by which glucose, a six-carbon sugar, is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. This occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and results in the production of ATP (energy) and NADH (an electron carrier). It does not require oxygen and is considered an anaerobic process. It is the first step in cellular respiration, providing energy for cells, especially when oxygen is scarce.
Krebs Cycle
A series of chemical reactions in the mitochondria that are part of cellular respiration. It takes place after glycolysis and is a key process for producing energy. The _______ generates ATP, NADH, FADH₂, and carbon dioxide (CO₂) as byproducts. These products are essential for the electron transport chain, which ultimately generates most of the cell’s ATP.
NADPH
A coenzyme that plays a key role in cellular reactions, particularly in photosynthesis. It acts as an electron carrier, helping to transfer energy and electrons in the process of reducing molecules. It is essential in anabolic reactions (building molecules), such as the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis, where it helps in the reduction of carbon dioxide to glucose.
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose (a sugar). It occurs mainly in the chloroplasts of plant cells. The general formula for photosynthesis is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂