AP Psych Unit 1 2025
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
*NT(denotes terms that are associated with Neural Transmission) *I(Inhibitory NT) *E(Excitatory NT) *H(Hormone) GUYS THIS DOES NOT INCLUDE 1.6 WATCH THE AP DAILY FOR THAT
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Evolutionary perspective
A psychological viewpoint emphasizing how evolutionary processes shape behavior and mental processes. It suggests that traits and behaviors evolve to improve survival and reproduction, focusing on the impact of natural selection on psychological traits
Natural selection
A process where organisms better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more, driving evolution and gradual species change. Key factors are variation, competition, and inheritance.
Eugenics
A social philosophy promoting the enhancement of human genetic quality through selective breeding and sterilization. Popular in the early 20th century, it is now widely discredited due to ethical issues and its links to human rights abuses, such as forced sterilizations and genocide.
Nature v Nurture
Nature” means innate biological factors (namely genetics), while “nurture” can refer to upbringing or life experience more generally.
Twin studies
aims to reveal the importance of environmental and genetic influences for traits, phenotypes, and disorders
Central Nervous System (brain and spine)
This system comprises the brain and spinal cord, serving as the main control center for the body. It integrates sensory data, directs motor functions, and is crucial for reflex actions and higher cognitive processes.
Autonomic Nervous System
This system controls functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. It includes the sympathetic division, which prepares the body for stress, and the parasympathetic division, which promotes relaxation and recovery.
Sympathetic Nervous System
This system increases heart rate, dilates airways, and inhibits digestion. It is often referred to as the "fight or flight" system, activating during stress or emergencies to enhance physical performance and alertness.
Peripheral Nervous System
This system consists of nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord. It is responsible for transmitting sensory information to the central nervous system and carrying motor commands to the muscles. It is divided into the somatic and autonomic systems, facilitating voluntary and involuntary actions, respectively.
Somatic Nervous System
A part of the peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movements. It consists of motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to skeletal muscles, allowing for conscious control of actions. It also transmits sensory information from external stimuli to the central nervous system.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
job is usually to relax or reduce your body's activities, it carries, the rhyming phrases “rest and digest” or “feed and breed” are easy ways to remember what your parasympathetic nervous system does.
Neuron
A specialized cell that transmits electrical signals throughout the body. It consists of three main parts: the cell body, dendrites, and an axon.
Sensory Neurons
These neurons carry signals from sensory receptors (like those for touch, temperature, pain, and taste) to the brain and spinal cord, allowing the body to perceive and react to stimuli from the environment.
All-or-Nothing Principle*NT
neurons will either transmit an impulse over the synapse to the next neuron completely or not at all.
Action Potential*NT
occurs when a neuron transmits an electrical charge down its axon, which terminates in the release of chemical signals in the form of neurotransmitters.
Threshold*NT(firing threshold)
The level of stimulation required to trigger an action potential in neurons.
Excitatory Neurotransmitter
Describes a neurotransmitter that causes a postsynaptic neuron to propagate more action potentials.
inhibitory Neurotransmitter
Describes a neurotransmitter that causes a postsynaptic neuron to propagate fewer action potentials.
Dopamine*E & *I
A neurotransmitter involved in mood, movement, attention, and learning.
Serotonin
neurotransmitter that regulates sleep, mood, appetite, and body temperature.
Glutamate*E
an excitatory neurotransmitter that increases brain activity and plays a key role in learning and memory
Oxytocin*H
a hormone produced by the hypothalamus and released by the pituitary gland that plays a significant role in social bonding, sexual reproduction, childbirth, and the period after childbirth
Ghrelin*H
This hormone stimulates appetite, increases food intake and promotes fat storage. Its effects are counteracted by signals from the ventromedial hypothalamus.
Agonist Drugs
Drugs that mimic a particular neurotransmitter, activating the same receptors that it does
Antagonist Drugs
Drugs that block a particular neurotransmitter from activating its receptors
Stimulants
chemicals known to stimulate the nervous system
Depressants
one classification of drugs that reduce or slow our neural activity and body functions. A few depressants are alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates.
Marijuana
stimulates the release of dopamine, which stimulates the sensation of pleasure or euphoria. Feeling is short in duration.
Addiction
a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, continued use despite harmful consequences, and long-lasting changes in the brain
Glial Cells
non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system that support and protect neurons
Motor Neurons
the nerves responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system in order to initiate an action
Depolarization*NT
when there's a shift in a neuron's electrical charge that allows an action potential (nerve impulse) to occur.
Resting Potential
the electrical potential difference between the inside and outside of a neuron.
Multiple Sclerosis
The loss of muscle control resulting from a deterioration of myelin sheaths.
Acetylcholine (ACh)*E
A neurotransmitter involved in learning, memory, and muscle contraction
Norepinephrine*I
a hormone and neurotransmitter involved in stress response; it increases heart rate, releases glucose from energy stores, and increases blood flow to skeletal muscle.
Adrenaline*H
a hormone that activates the sympathetic nervous system. This triggers our "fight or flight" response
Reuptake
the process by which neurotransmitter molecules that have been released at a synapse are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron that released them
Caffeine
a stimulant drug that blocks the action of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and relaxation
Hallucinogens
another classification of drugs that are known to distort perception and evoke sensory images without any actual sensory input
Alcohol
alcohol is actually a depressant. The liveliness comes from the fact that alcohol acts as a disinhibitor. This means it will act to slow down neural processing and brain activity responsible for judgment and inhibitions.
Opioids
Opiates, such as morphine and heroin, stop the production of endorphins.
Withdrawal
the term used to describe the symptoms that occur when a person ends the use of an addictive substance.
Reflex Arc
the sensory neuron sends a signal to the interneuron and activates it. The interneuron then relays that signal to the next neuron, a motor neuron. Motor neurons connect with interneurons in the spinal cord.
Interneurons
Interneurons connect sensory neurons to motor neurons
Refractory Period*NT
A period immediately after a neuronal firing during which no additional neuronal firings can be completed
Myasthenia Gravis
a chronic autoimmune disorder in which antibodies destroy the communication between nerves and muscle, resulting in weakness of the skeletal muscles.
Hormones
Chemical substances produced in your body that control and regulate the activity of certain cells or organs
Endorphines
are neurotransmitters linked to reduced pain and increased pleasure
GABA*I
GABA is known to be a major inhibitory neurotransmitter. GABA is observed to be most active in the brain during times of rest and sleep. In a sense, it inhibits being awake and it can reduce the occurance of tremors and seizures.
Melatonin*H
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.
Leptin*H
Signals the hypothalamus that the body has enough fat stored to function normally
Psychoactive drugs
substances that can alter perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior by changing the brain's neurochemistry
Cocaine
A powerful stimulant that increases alertness, feelings of well-being and euphoria, energy and motor activity while decreasing feelings of fatigue/hunger
Hallucinogens
another classification of drugs that are known to distort perception and evoke sensory images without any actual sensory input
Heroin
stop the production of endorphins
Tolerance
a diminished response to a drug
Dependence
the change in an emotional state after using a substance or engaging in a behavior for a long period of time
Brainstem
the lower part of the brain that connects it with the spinal cord. This includes the medula, the pons and the midbrain. Damage leads to death as it controls autonomic functions
Brain’s Reward Center
a complex network of neural circuits that help regulate motivation, reinforcement, and pleasure responses. It involves several interconnected regions such as the nucleus accumbens, VTA, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala.
Hypothalamus
regulates the autonomic nervous system by producing and releasing hormones.
Hippocampus
responsible for the formation of memory and processes explicit memories for storage
Lobes of the Cortex (Occipital, Temporal, Parietal, Frontal)
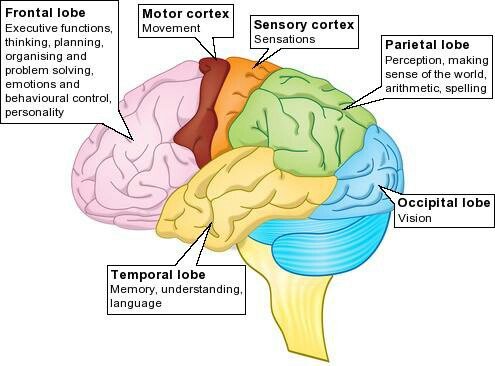
Split Brain Research
(experiments on people with a severed corpus callosum) has confirmed that in most people, the left hemisphere is the more verbal, and that the right hemisphere excels in visual perception and the recognition of emotion
Split brain Patient
an individual who has undergone a surgical procedure called corpus callosotomy, where the corpus callosum (the structure that connects the two hemispheres of the brain) is severed to some degree
electroencephalogram (EEG)
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain's surface; measured by electrodes placed on the scalp
functional MRI (fMRI)
a technique used for revealing blood flow, and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans; show brain functions as well as structure
Medulla
controls automatic (involuntary) functions of the body, such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. Helps with the regulation of a person’s cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Controls autonomic functions
Cerebellum
plays a role in motor control and movement including balance, subtle movement, and equilibrium.
Limbic System
a group of brain structures that regulate basic emotions such as fear and rage and drives such as hunger and sex
Thalamus
located between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain
Amygdala
he center of emotion and motivations
prefrontal cortex
controls executive functions or a set of abilities that are needed to control cognitive behaviors
motor cortex
regulates voluntary movements such as walking
Broca’s Area
located in the left hemisphere in the frontal lobe. This area is responsible for speech production and language comprehension
Aphasia
Aphasia is a language disorder that affects how you communicate.
Lesioning (Brain Surgical Procedure)
Lesioning involves intentionally damaging or removing specific areas of the brain to treat certain disorders. This procedure can help alleviate symptoms by disrupting abnormal neural pathways.
Reticular Activating System
responsible for sensation, consciousness, attention, and the sleep-wake cycle. The RAS transmits the sensory messages to different areas of the cerebral cortex through the thalamus.
Cerebral Cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
Thalamus
is located between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It is made up of nuclei that receive different sensory and motor inputs. The thalamus then relays these signals to various areas of the cerebral cortex.
Pituitary Gland
considered the "master gland" of the endocrine system. Hormones secreted from the pituitary gland help regulate growth, metabolism, and numerous other bodily functions and processes.
Corpus callosum
A large band of neural fibers connecting two hemispheres of brain allowing them to communicate with each other.
Somatosensory Cortex
Processes body touch and movement
Association areas
allow us to have higher mental functions, such as learning, remembering, thinking, problem-solving, and speaking by integrating information from other brain regions.
Wernicke’s Area
located in the back of the temporal lobe near the occipital lobe of the left cerebral hemisphere
Brain Plasticity
refers to the brain's ability to change and adapt as a result of experience. It can reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life.
Contralateral organization
the property that the hemispheres of the cerebrum and the thalamus represent mainly the contralateral side of the body.
Spinal Cord
This is what connects your brain to the rest of the body, lets your nerves send info to the brain and vice versa
Pons
The bridge between different areas of the nervous system. Connects the medulla to the cerebellum and helps to coordinate moevment
Midbrain
a part of the central nervous system located below the cerebral cortex and at the topmost part of the brainstem. Plays a role in auditory and visual processing
Consciousness
the state of being aware of and able to think and perceive one's surroundings, thoughts, and sensations.
Circadian Rhythm
A natural internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and other physiological processes on a roughly 24-hour cycle, influenced by factors such as light and darkness.
Types of consciousness (sleep/wake)
Refers to the different states of awareness and responsiveness that individuals experience, including wakefulness, REM sleep, and non-REM sleep, each characterized by distinct brain activity and physiological response
Jet lag - Disruption to circadian rhythm
A temporary sleep disorder that occurs when a person's internal body clock is out of sync with the time cues of a new time zone, often resulting in fatigue, insomnia, and difficulty concentrating.
NREM Stages 1-3
NREM Stages 1-3
Definition: NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) sleep consists of three stages, characterized by progressively deeper levels of sleep:
Stage 1 - Light sleep where one drifts in and out of sleep, can be awakened easily. Theta waves
Stage 2 - Onset of true sleep with decreased heart rate and body temperature. Beta waves
Stage 3 - Deep sleep, crucial for physical recovery and growth, difficult to wake from. Delta waves
Hypnogogic sensations
These are vivid sensory experiences that occur during the transition from wakefulness to sleep, often involving hallucinations or sensations such as falling, floating, or hearing sounds.
REM Sleep (Paradoxical Sleep)
A stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movement, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams. It is called 'paradoxical' because, despite the body's paralysis and low muscle tone, the brain exhibits activity levels similar to wakefulness, playing a crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional regulation.
REM Rebound
The phenomenon where individuals experience increased amounts of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep following a period of sleep deprivation or disrupted sleep, often resulting in more intense and vivid dreams.
Activation Synthesis dream theory
states that a dream is the cerebral cortex processing nerve impulses being sent from the body to the brain stem into something that makes sense.
Consolidation Dream Theory
dreaming is influenced by the consolidation of memory during sleep, dream happen to help consolidate memory