yun
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:54 AM on 5/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
bonds
forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit
2
New cards
ionic bonds
transfer of electrons
3
New cards
covalent bonds
sharing of electrons
4
New cards
polar covalent bonds
unequal sharing of electrons that results in an unbalanced distribution of charge
5
New cards
electronegativity
the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself
6
New cards
shielding effect
the nucleus blocks valence shell electron attraction because of the presence of inner-shell electrons
7
New cards
Describe the periodic trends of shielding.
shielding increases down a group
8
New cards
this causes electronegativity values to decrease
9
New cards
greater than 1.7 EN difference value
ionic
10
New cards
between 0.3 and 1.7 EN difference value
polar covalent
11
New cards
0.3 and less EN difference value
non-polar covalent
12
New cards
greater than 50% ionic character \= ?
ionic
13
New cards
between 5% and 50% ionic character \= ?
polar covalent
14
New cards
less than 5% ionic character \= ?
covalent
15
New cards
What are the general rules for determining if a bond is ionic?
greater than 1.7 electronegativity difference
16
New cards
greater than 50% ionic character
ionic
17
New cards
What are the general rules for determining if a bond is polar covalent?
between 0.3 and 1.7 electronegativity difference
18
New cards
between 5% and 50% ionic character
polar covalent
19
New cards
What are the general rules for determining if a bond is covalent?
0.3 and less electronegativity difference
20
New cards
less than 5% ionic character
nonpolar covalent
21
New cards
molecule
a neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds
22
New cards
diatomic molecule
a molecule containing only two atoms
23
New cards
chemical formula
indicates the relative numbers of atoms of each kind of a chemical compound by using atomic symbols and numerical subscripts
24
New cards
molecular formula
shows the types and numbers of atoms combined in a single molecule of a molecular compound
25
New cards
non-polar covalent bonds
equal sharing of electrons
26
New cards
What are the 2 categories of covalent bonds?
non-polar covalent bonds
27
New cards
polar covalent bonds
unequal sharing of electrons that results in an unbalanced distribution of charge
28
New cards
What's the symbol for the difference in electronegativity?
delta
29
New cards
ΔEN
What's the symbol for the difference in electronegativity?
30
New cards
What happens when an ΔEN value is exactly 1.7?
2 nonmetals \= polar covalent
31
New cards
Only things held together by \_______ \_______ can be considered molecules.
covalent bonds
32
New cards
What are the 7 elements that form diatomic molecules?
bromium (Br)
33
New cards
What are the 7 elements that form diatomic molecules?
bromium (Br)
\
iodine (I)
\
nitrogen (N)
\
chlorine (Cl)
\
hydrogen (H)
\
oxygen (O)
\
fluorine (F)
\
iodine (I)
\
nitrogen (N)
\
chlorine (Cl)
\
hydrogen (H)
\
oxygen (O)
\
fluorine (F)
34
New cards
Where is BrINClHOF located on the periodic table?
7 shape starts at nitrogen (group 15)
35
New cards
bond energy
the energy required to break a bond
36
New cards
What does bond energy give us information about?
the strength of a bonding interaction
37
New cards
Where can bonds occur in electron dot notation?
on the single dots on each side
38
New cards
In nature, bonds want to occur how often?
as often as possible
39
New cards
the octet rule
chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom,
by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons, has an octet
of electrons in its highest occupied energy level
by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons, has an octet
of electrons in its highest occupied energy level
40
New cards
what are double bonds
two pairs of shared electrons
41
New cards
What's the difference between single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds?
double bonds have higher bond energy and shorter bond length than single bonds
42
New cards
triple bonds have higher bond energy and shorter bond length than single or double bonds (both)
double bonds have higher bond energy and shorter bond length than single bonds
triple bonds have higher bond energy and shorter bond length than single or double bonds (both)
triple bonds have higher bond energy and shorter bond length than single or double bonds (both)
43
New cards
triple bonds
three pairs of shared electrons
44
New cards
How do you find the "more negative" atom in a bond?
whichever has the highest EN value
45
New cards
How many possible arrangements are there when you have 1 central atom with 3 attached?
2
46
New cards
What are the possible arrangements when you have 1 central atom with 3 attached?
pyramidal, trigonal planar
47
New cards
How is the pyramidal molecular shape formed?
the lone pair of electrons cause the "bottom" atoms to push downward, which forms the pyramidal shape
48
New cards
If you only have 2 atoms, the only possible molecular shape is \_______.
linear
49
New cards
What's the bond angle for a linear molecular shape?
180 degrees
50
New cards
What's the bond angle for a bent molecular shape?
105 degrees
51
New cards
What's the difference between trigonal planar and pyramidal molecular shapes?
pyramidal has a lone pair
trigonal planar does NOT have a lone pair
trigonal planar does NOT have a lone pair
52
New cards
What elements can exceed the octet rule?
anything 3rd energy level and above
53
New cards
pyramidal (what are the properties?)
1 central atom with 3 attached
54
New cards
trigonal planar (what are the properties?)
1 central atom with 3 attached, but no lone pair
55
New cards
tetrahedral (what are the properties?)
4 atoms bonded to 1 central atom
56
New cards
Unshared pairs want the \_______ space away from each other.
maximum
57
New cards
bent molecular shape (what are the properties?)
variation of a tetrahedron
1 central atom and 2 attached
other 2 places are left vacant for the 2 lone pairs of electrons
1 central atom and 2 attached
other 2 places are left vacant for the 2 lone pairs of electrons
58
New cards
If your molecule has polar bonds, it may be a \_______ \_______.
polar molecule
59
New cards
What do polar molecules have?
slightly positive sides and slightly negative sides of the entire molecule
60
New cards
What do you need in order to determine if a molecule is entirely polar?
proper geometry to allow it (an axis that can divide positive vs negative)
polar bonds
polar bonds
61
New cards
dipoles
another word for polar molecules
62
New cards
Are polar molecules attracted to each other?
yes
63
New cards
partial symbol

64
New cards
axis
straight line
65
New cards
Not all atoms with polar bonds are \_______ \_______.
polar molecules
66
New cards
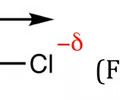
symbol to represent a polar bond
the arrow with a line on it
67
New cards
VSEPR theory
repulsion between the sets of valence-level electrons surrounding an atom causes these sets to be oriented as far apart as possible
68
New cards
In metals, the valence electrons are held \_____.
loosely
69
New cards
Do metal atoms lose their valence electrons in metallic bonding?
no, they release them into a sea of electrons
70
New cards
Do metallic bonds create compounds?
no, they're not called compounds
71
New cards
What are the 4 properties that result from a metallic bond?
malleable
ductile
conductivity
luster
ductile
conductivity
luster
72
New cards
luster
the narrow range of energy differences between orbitals allows electrons to be easily excited, and emit light upon returning to a lower energy level (shiny)
73
New cards
ductile
drawn into wires
74
New cards
conductivity
the flow of electrons
75
New cards
malleable
pounded/rolled into sheets
76
New cards
Why are metals malleable?
bonding is the same in all directions, so metals tend not to be brittle
77
New cards
lone pairs of electrons
shift the shape of a molecule
pairs of electrons that are not involved in a bond
pairs of electrons that are not involved in a bond
78
New cards
Do lone pairs of electrons occupy space?
yes
79
New cards
Why does repulsion occur in electrons?
due to negative-negative repulsion
80
New cards
hybridization
combining of two or more orbitals of nearly equal energy within the same atom into orbitals of equal energy
81
New cards
what shape is sp^3 hybridization
tetrahedral
82
New cards
The interactions between molecules are called \_______ \_______.
intermolecular forces
83
New cards
How do we tend to evaluate intermolecular forces?
boiling point
84
New cards
Intermolecular forces are generally \_______ (stronger/weaker) than bonds that join atoms in molecules.
weaker
85
New cards
Dipoles have \_______ (higher/lower) boiling points than non-polar molecules.
higher
86
New cards
dipole-dipole attractions
attraction between oppositely charged regions of neighboring molecules
87
New cards
What is the strongest intermolecular force?
hydrogen bonding
88
New cards
What is the middle-strongest intermolecular force?
dipole-dipole
89
New cards
How is hydrogen "bonding" represented?
dotted lines
90
New cards
When hydrogen is attracted to FON, it is extra \_______.
strong
91
New cards
What are the 3 highly electronegative atoms that hydrogen is bonded to in hydrogen bonding?
F O N
fluorine
oxygen
nitrogen
fluorine
oxygen
nitrogen
92
New cards
All molecules experience \_____ \_____.
London forces
93
New cards
What's the weakest intermolecular force?
London dispersion forces
94
New cards
What's the only intermolecular force among non-polar molecules?
London dispersion forces
95
New cards
formula unit
the simplest collection of atoms from which an ionic compound's formula can be established
96
New cards
Formation of ionic compounds is ALWAYS \_______.
exothermic
97
New cards
Creation of octets in polyatomic ions results in an \________________.
excess or deficit of electrons
98
New cards
Describe the melting point of ionic compounds.
high
99
New cards
Describe the conductivity of ionic compounds.
excellent conductors, molten and aqueaous
100
New cards
Describe the solubility of ionic compounds.
soluble