Coordination and response.
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
the peripheral nervous system (PNS) consisting of the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord
NS function
coordination and regulation of body functions
3 types of neurones
sensory neurons - carry electrical impulses from sense organs to the CNS
relay neurons - connect both sensory and motor neurones
motor neurons - carry electrical impulses from the CNS to either muscles or glands (effectors)
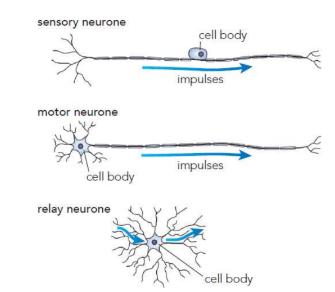
neuron adapation
Lots of mitochondria to release energy, for, transmission of impulse.
Long axons to transmit impulse over long distances
Many branches to connect to other neurons
Dendrites have large surface area for many receptors
reflex arc eg
The stimulus detected by the receptors and converted into an electrical impulse.
The EI travels along the sensory neuron. The SN sends the electrical impulse to the CNS (coordinator)
The electrical impulse is passed on to relay neurone in the spinal cord.
Relay neurone connects to motor neurone and passes the impulse on.
the motor neuron carries an electrical impulse to an effector
the effector carries out a response
reflex arc
a means of automatically and rapidly integrating and coordinating stimuli with the responses of effectors (muscles and glands)
vesicles - contain neurotransmitter molecules
synaptic gap
receptor proteins
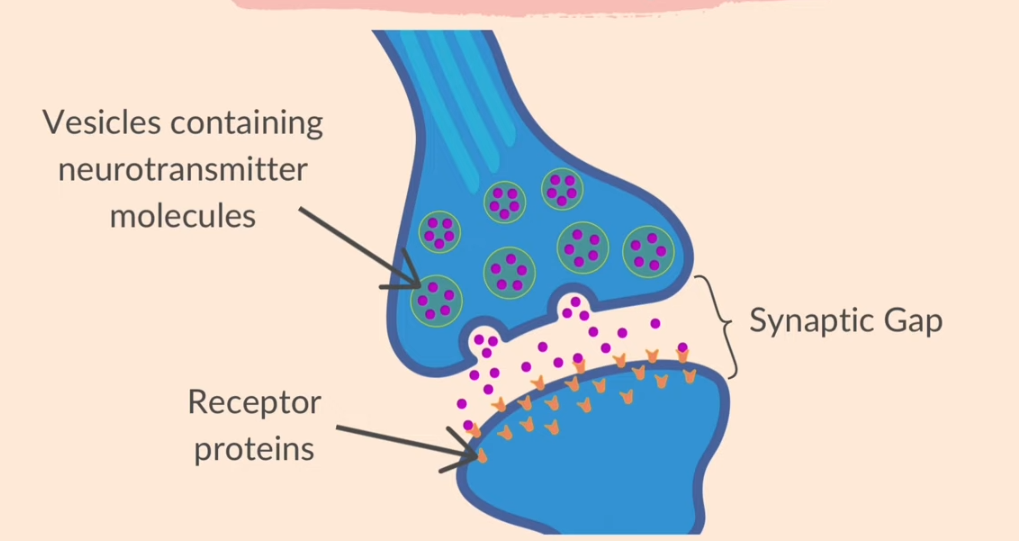
* the neurotransmitter mol diffuse across the gap
* neurotransmitter molecules bind with receptor proteins on the next neuron
* an impulse is then stimulated in the next neuron
sense organ
groups of receptor cells responding to specific stimuli
sound,
touch,
temperature
chemicals
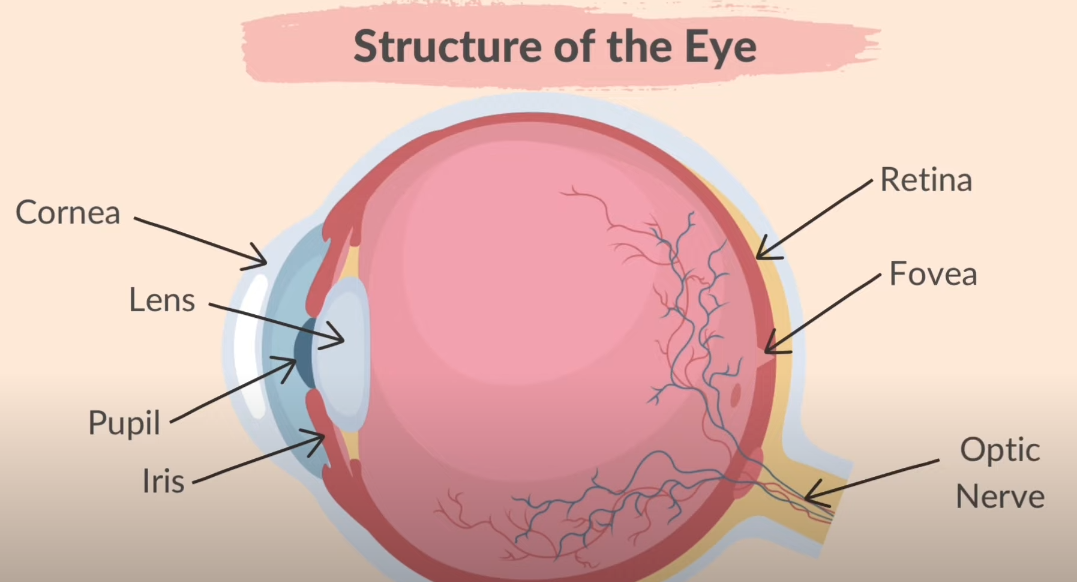
iris - controls how much light enters the pupil
lens - focuses light on the retina
retina - contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours
optic nerve - carries impulses to the brain
in bright light:
pupil diameter narrows
to allow less light in
to protect the retina from damage
\----------
in dark light:
pupil diameter dilates
to allow more light in
to improve vision and see better in the dark
antagonistic pupil reflex
bright light:
circular muscle of iris contract
radial muscle of iris relax
the pupil narrows/constricts
allowing less light in
-----------------------------
darkness:
radial muscles contract
circular muscles relax
the pupil dilates
allowing more light in
accomodation definition/
is the function of the eye that helps it view near and distant objects
accommodation
function of the eye that helps it view near or distant objects
near objs:
ciliary muscles contract
suspensory ligaments slacken and become less tait
lens becomes thicker
the lens refracts light rays more strongly to focus on the near obj
-------------
far objs:
ciliary muscles relax
suspensory ligaments are pulled tight and become taut
this pulls the lens and makes it thinner
the lens refracts light rays less strongly
2 types of receptor cells in the retina
rods - Provide night vision. Sensitive in dim light. provide black and white vision
cones - used for colour vision is bright light. three types of cones: which are sensitive to the colours light: red, green, and blue
---------
distribution:
rods: found all over the retina except blind spot and fovea
cones: concentrated at the fovea
has a high concentration of cone cells that are packed tightly together to give us sharp vision
why cant we see colours in the dark
cones are less sensitive in low/dim light
cones detect colour
rods sensitive in dim light, but cannot detect colour
voluntary vs involuntary action
voluntary:
slower. takes more time.
uses high centers of the brain
learnt
not automatic.
hormones
chemical substance produced by a gland and carried by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs
adrenaline
defined as the hormone secreted in ‘fight or flight’ situations
it:
increased heart rate - blood is pumped more quickly and efficiently. so more glucose and oxygen is delivered to vital muscle and organs. an increased heart rate allows carbon dioxide to be removed quickly from muscle cells
increased breathing rate - so more glucose and oxygen to the muscles and other vital organs. an increased rate of breathing allows carbon dioxide to be removed quickly from muscle cells.
increased pupil diameter - dilates pupil. allows more light into the eye. increase mental awareness.
metabolic effects of adrenalin
increasing the blood glucose concentration - stimulates , breakdown / conversion, of glycogen to glucose in liver. increase glucose concentration in the blood.
increasing heart rate - to provide more glucose and oxygen to the muscles for respiration
what happens if the blood glucose level is too low
pancreas detects and releases the hormones glucagon
in the liver glycogen is broken down into glucose
and releases into the bloodstream
what happens if the blood glucose level too high
pancreas detects this and releases insulin
this stimulates liver cells to take in more glucose
and convert glucose into glycogen for storage
comparison of nerves and hormones
speed of transmission
nerves - fast
hormones - slow
duration of effect:
nerves - short-term
hormones - longer lasting
hormonal coordination is only chemical, whilst nervous communication uses both chemicals and electrical impulses.
each hormone may have more than one target organ, whilst in nervous communication there is only one or specific target
negative feedback
(insert condition) is kept within narrow limits
change in body (eg skin temp)
acts as stimulus
to keep (insert condition at a set point) (eg keep temp at 37c)
corrective action done by the body
type 1 diabetes and the treatment
An autoimmune condition where the body fails to control blood glucose concentration. Due to insufficient insulin production by the pancreas. The immune system cells destroy beta cells in the pancreas, which produce insulin. As a result blood glucose concentrations are too high.
treatment:
injecting insulin
monitor their blood glucose level regularly
take extra care of their diet, avoiding foods high in sugar
exercise regularly, which can lower blood glucose levels through increased muscle respiration
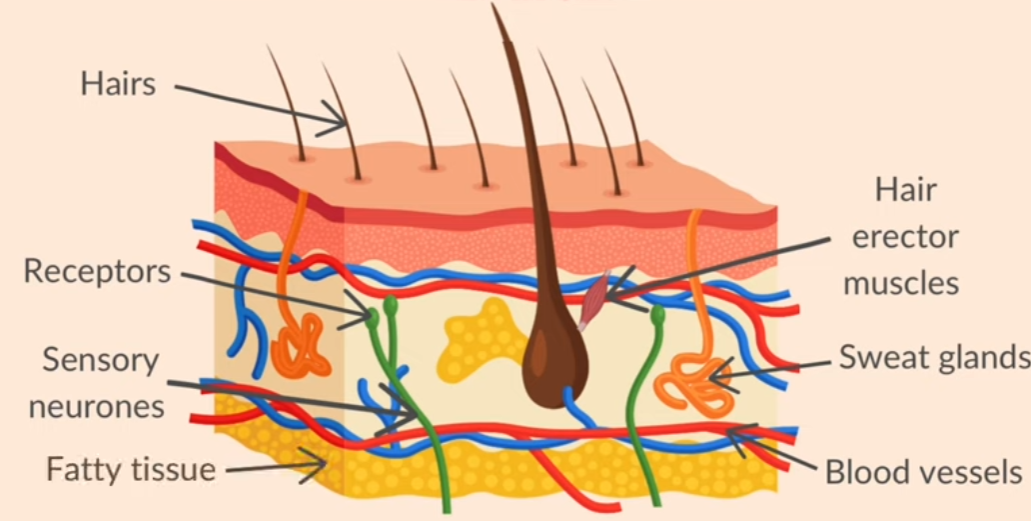
skin diagram 2
N is artery.
P is arteriole.
J is capillary.
L is shunt vessel, which redirects blood under the surface of the skin.
K is a venule.
M is vein.
temperature control when too cold
too cold:
fatty tissue in the skin act as an insulating layer that helps prevent excess heat loss from the body through the skin
when it is cold, the hair erector muscles contract causing the hairs to stand upright/erect. this is to trap a layer of air. air is a good insulator so it helps reduce heat loss.
the body shivers, the muscle contractions of shivering generate heat energy through respiration. this warms the body
muscle in arteriole wall contract. vasoconstriction occurs. less blood flows to skin capillaries. this helps reduce heat loss through the skin by radiation. Shunt vessels dilate/open. Blood is redirected away from the skin capillaries to minimize heat loss.
this is detected by thermoreceptors in the brain and skin.
temperature control when too hot
hair erector muscles relax, causing hairs to lie flat
allowing air circulation
which increases heat loss to the environment by radiation.
sweat glands secrete sweat. sweat evaporates off the skin, and the heat is lost to the surroundings. cooling the body.
vasodilation: muscles arteriole wall relax. vasodilation occurs. more blood flows to skin capillaries to increase the heat loss through the surface of the skin through radiation. shunt vessels constrict or close. Blood is redirected toward the skin capillaries
this is detected by thermoreceptors in the brain and skin.
phototropism - a response in which parts of a plant grow towards or away from the direction of the light source
role of auxin in controlling shoot growth
auxins are made in the shoot tip
auxins diffuse down the stem
auxins collect in the side in the dark
the auxins stimulates greater cell elongation on side in the dark
on this side, cells are stimulated to absorb more water, so that side of the plant grows more
this causes the plant to grow towards the light
Auxins accumulate on the lower side of the shoot, due to gravity.
Cells on the lower side grow more quickly
The shoot bends upwards.
This is called negative geotropism.
(If a shoot is placed horizontally in the absence of light:)
If a root is placed horizontally in the absence of light:
Auxins accumulate on the lower side of the root, due to gravity.
Auxin inhibits cell elongation.
Cells on the lower side grow more slowly
The root bends downwards.
This is called positive geotropism.
benefits of phototropism and gravitropism
more photosynthesis
more (light) energy, absorbed
more growth
(reach air for) carbon dioxide for photosynthesis ; (reach air for) oxygen for respiration ; idea that they grow tall so that flowers are exposed for, (wind / insect) pollination
roots grow downwards / towards (direction of) gravity ; to reach, water / ions or minerals ; to anchor plant in the soil ;