Biol 200 Midterm
1/277
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
278 Terms
Direct interaction of template...
With incoming monomer (rNTP)
Allosteric effects
Binding of a ligand at one site of enzyme impacts a different ligand at a different active site of enzyme
Ex. Hsp70 (chaperone) ATP vs ADP affects the conformation of the substrate-binding domain, which changes interactions w the misfolded client protein
Kinase
an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a specified molecule.
phosphodiester bond
the type of bond that links the nucleotides in DNA or RNA. joins the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another nucleotide
isoelectric focusing
A specialized method of separating proteins by their isoelectric point using electrophoresis; the gel is modified to possess a pH gradient.
isoelectric point
Point at which a compound is electrically neutral. Determined by aa composition of each protein. Between cathode and anode
MS/MS
tandem mass spectrometry, recover ion, fragmenting it by high energy collision w an inert gas and doing mass spec on fragments
Chromatography
A technique that is used to separate the components of a mixture based on the tendency of each component to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material.
protein chromatography
Purifying specific proteins from a bulk pool of proteins, generally done in columns w a solid phase
gel filtration chromatography
a type of column chromatography that separates proteins based on their size using size-exclusion beads; also called size-exclusion chromatography
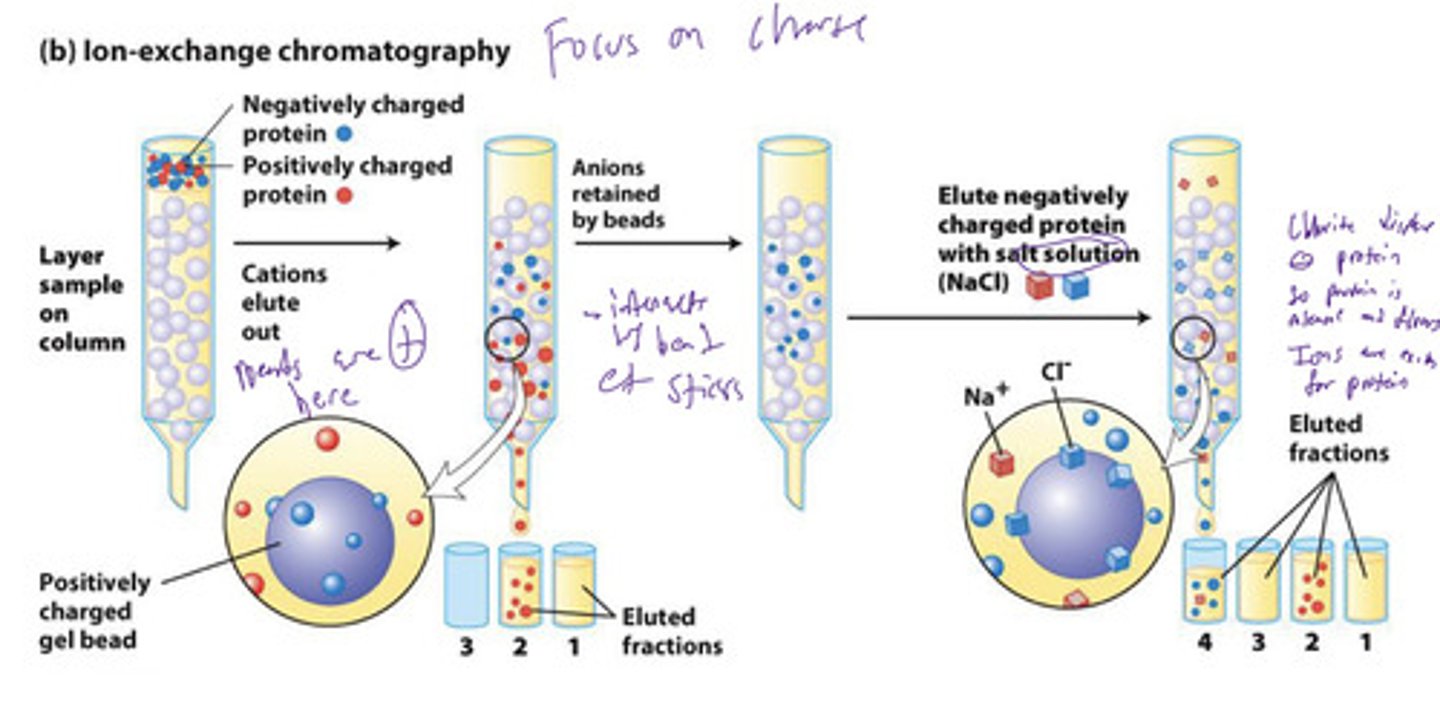
ion exchange chromatography
molecules separated based on net surface charge
speed of migration
Determined by the net charge/mass ratio m/z
Antibodies
It recognizes by highly-specific binding, a mc target, called an epitope, present on the antigen molecule against which the antibody was raised
ANtibodies bind to
Specific individual proteins even in complex mixture
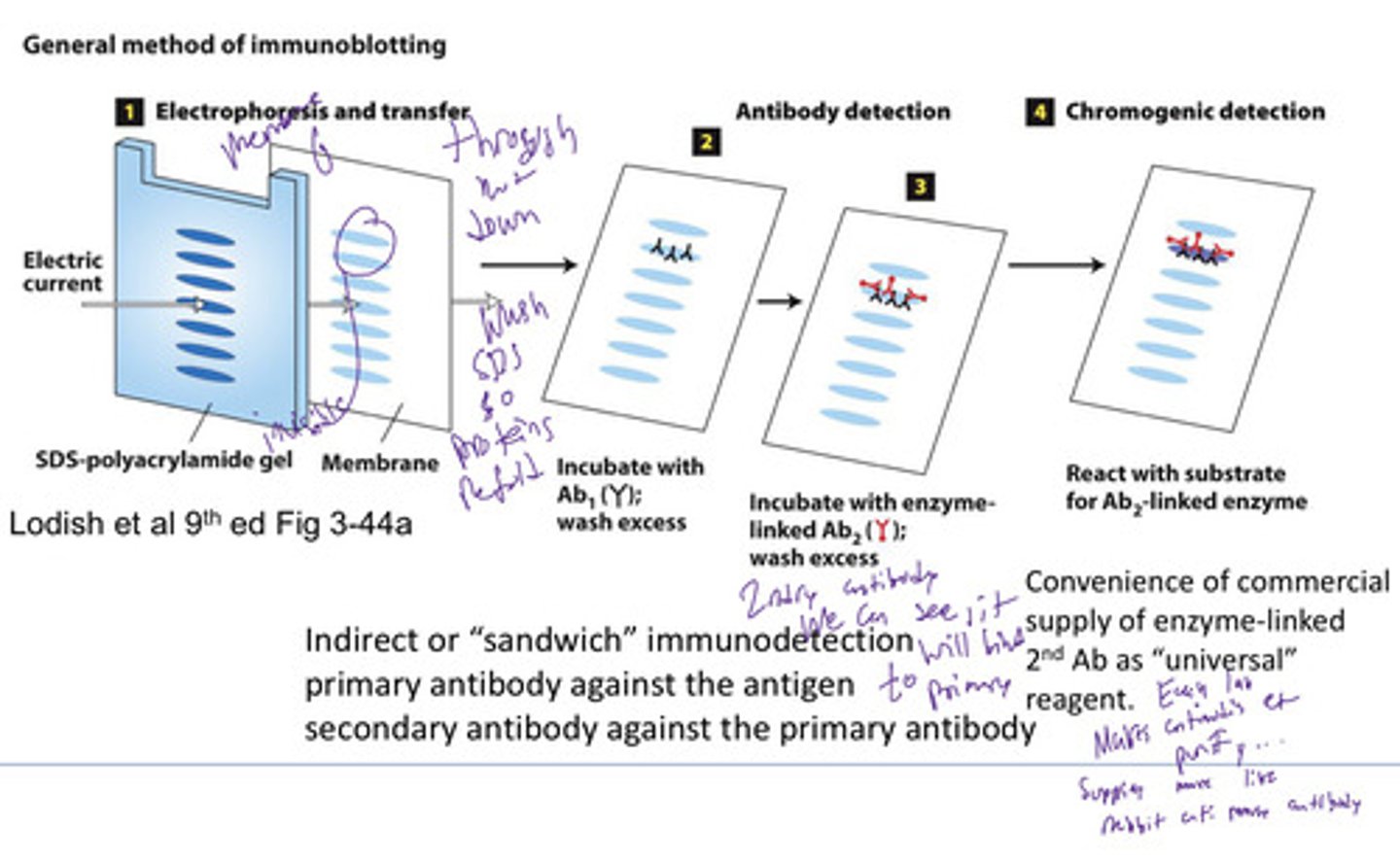
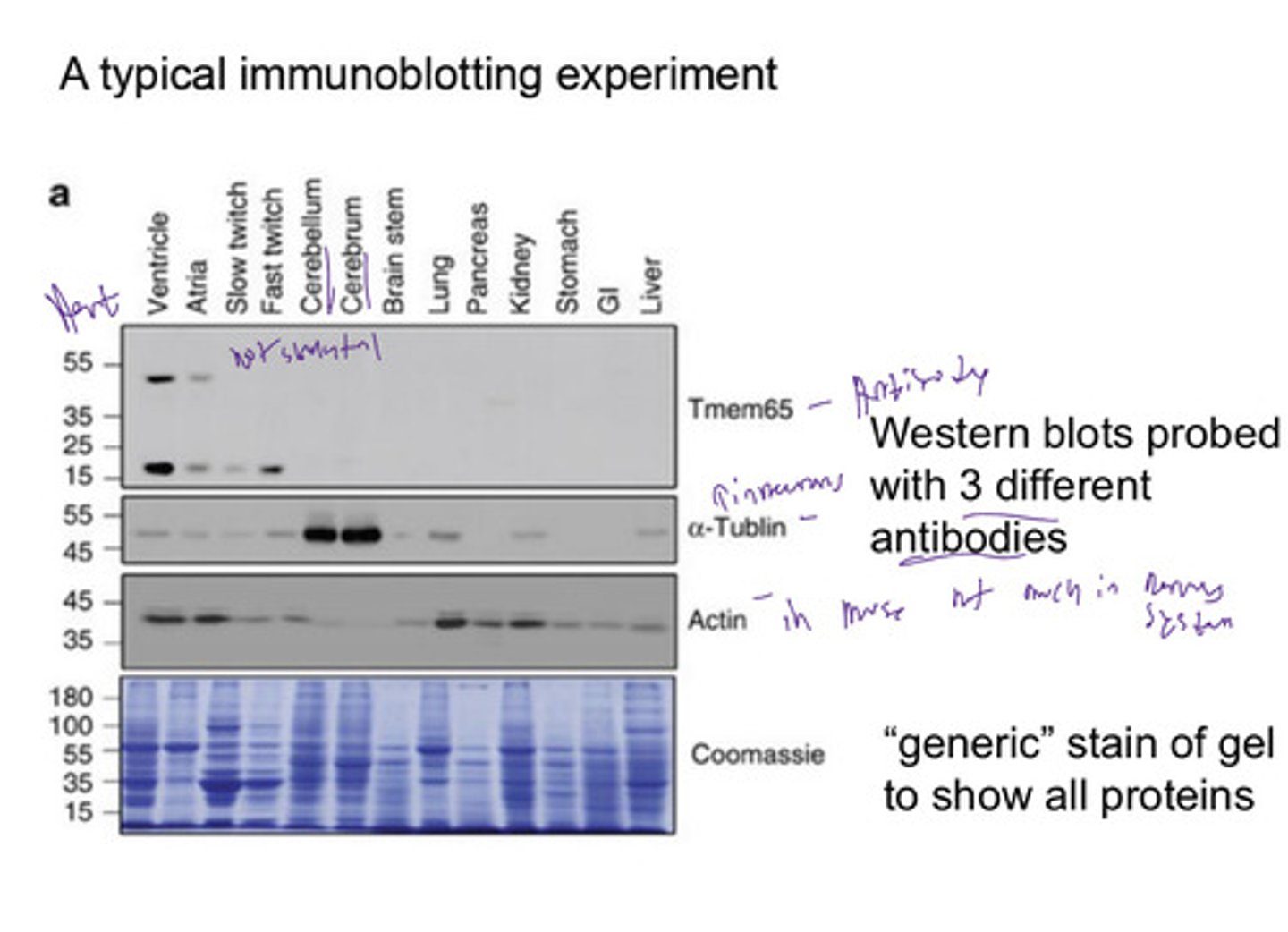
Immunoblot (Western blot)
Using antibodies to recognize individual protein species in a complex mixture of proteins separated by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
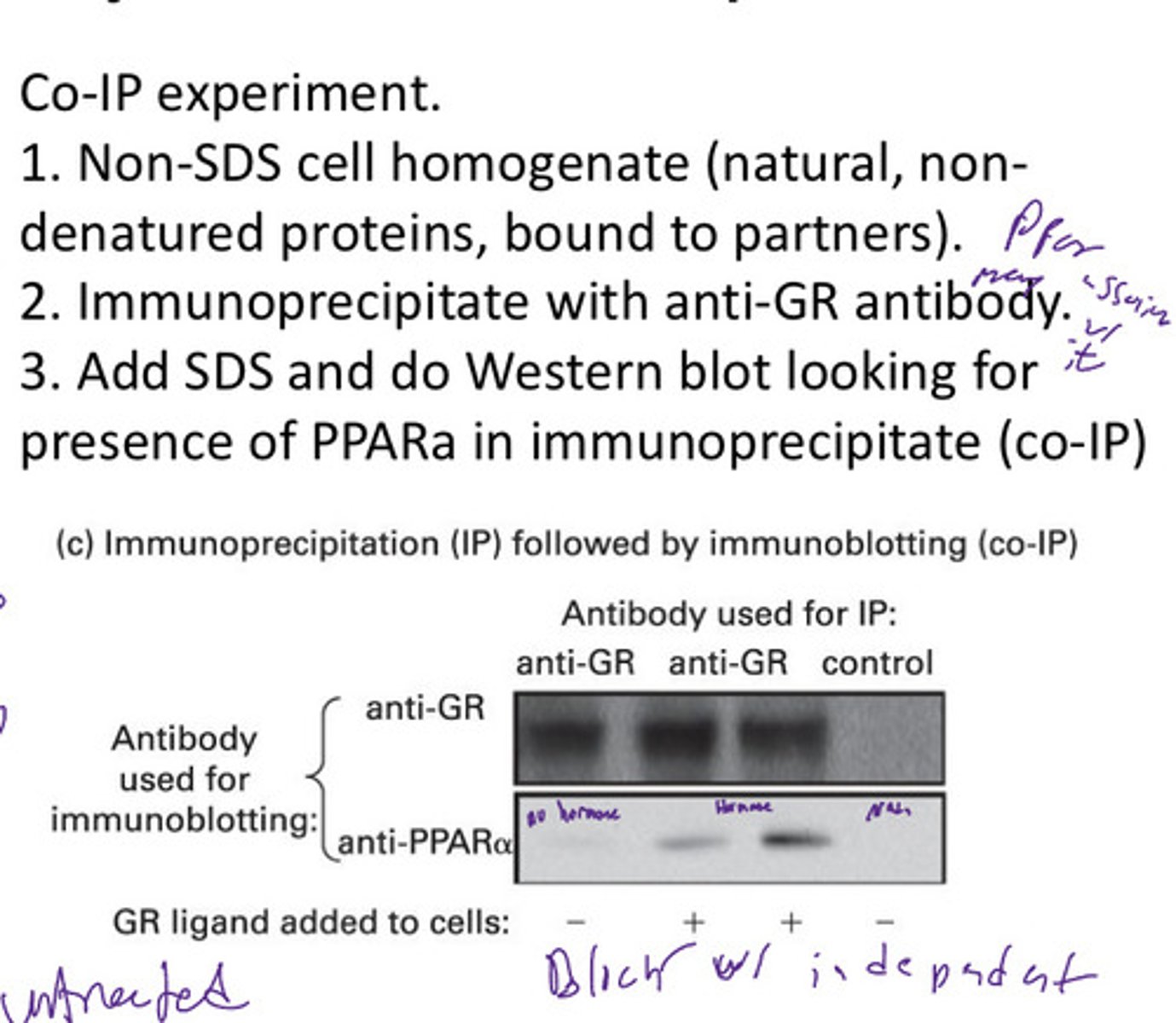
Immunopercipitate will contain the protein carrying the epitope recognized by antibody
Any partner proteins stably associated w that protein
Primary and secondary antibodies
Primary recognize epitope of interest
Secondary recognizes the primary antibody
Tm
Midpoint of temp where all dna is melted
scaffolding proteins
A type of large relay protein to which several other relay proteins are simultaneously attached to increase the efficiency of signal transduction.
deoxyribose vs ribose
Deoxyribose lacks an oxygen molecule when being compared to Ribose meaning it is missing an alcohol bond between one of the carbon molecules.
Repliosome
DNA pol III, DNA pol I, DNA helicase, DNA primase, SSBPs, DNA gyrate, DNA topoisomerase
a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA at rep fork
PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen)
in eukaryotes, clamps DNA pol delta and epsilon to DNA, increasing processivity
DNA polymerase alpha
contains primase activity and initiates nuclear DNA synthesis by synthesizing an RNA primer, followed by a short string of DNA nucleotides.
Polymerase alpha
in eukaryotes, this polymerase is complexed with a primase; initiates replication; lacks 3' to 5' exonuclease activity
Replication Factor C
clamp loader in eukaryotes
Ribonuclease
enzyme that breaks down RNA
Polymerase alpha
in eukaryotes, this polymerase is complexed with a primase; initiates replication; lacks 3' to 5' exonuclease activity... in okazaki
dimer
a molecule or molecular complex consisting of two identical molecules linked together.
homodimer
when two polypeptides encoded by the same gene bind to each other to form a dimer.
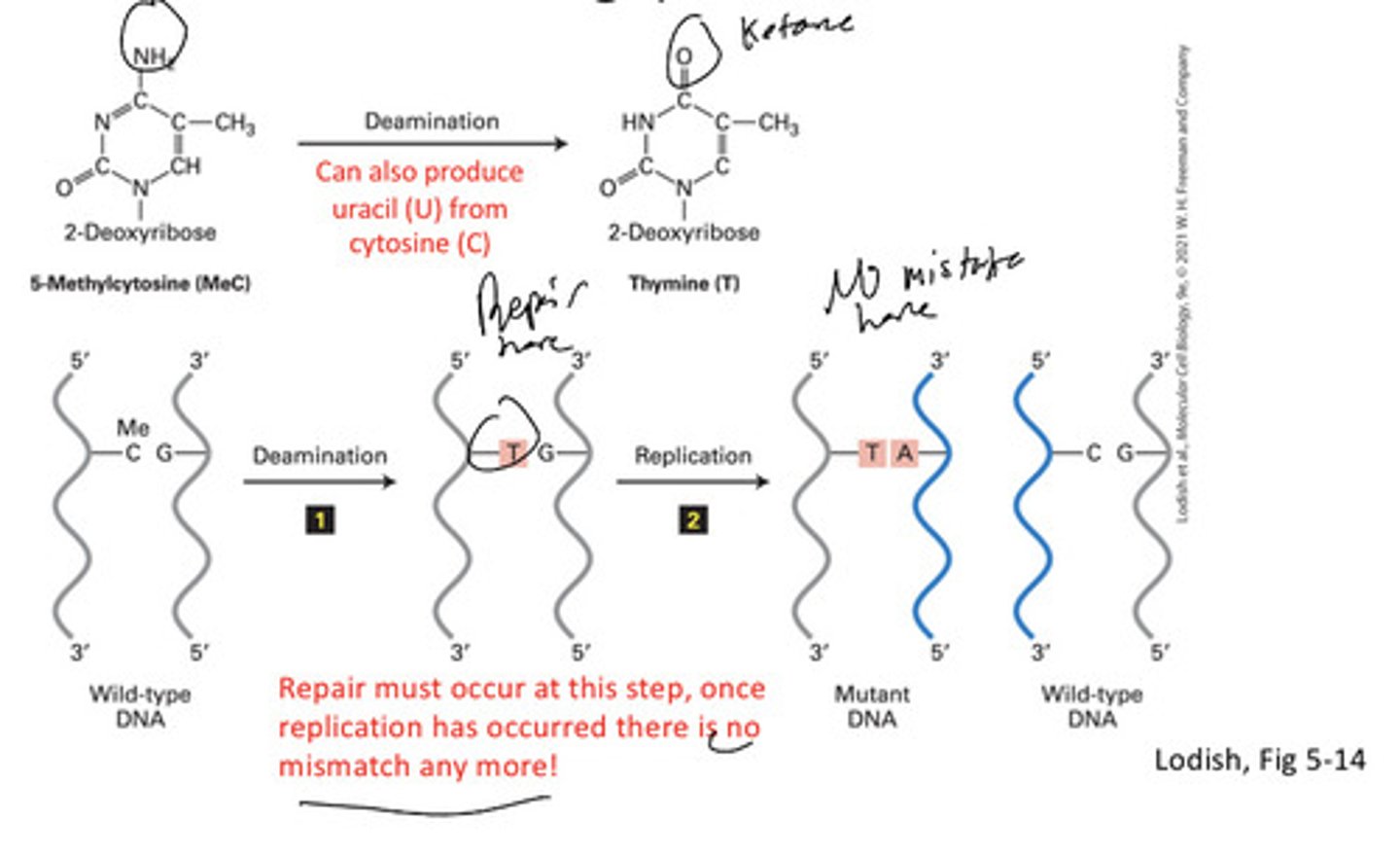
most common point mutation
Single base change c -> t or sometimes u
Deamination
the removal of an amino group from an organism, particularly from an amino acid
Repairs for base excision must happen after deamnination but before replication bc there will be no sign of anything wrong if correct pairing of wrong nucleotide in mutant dna
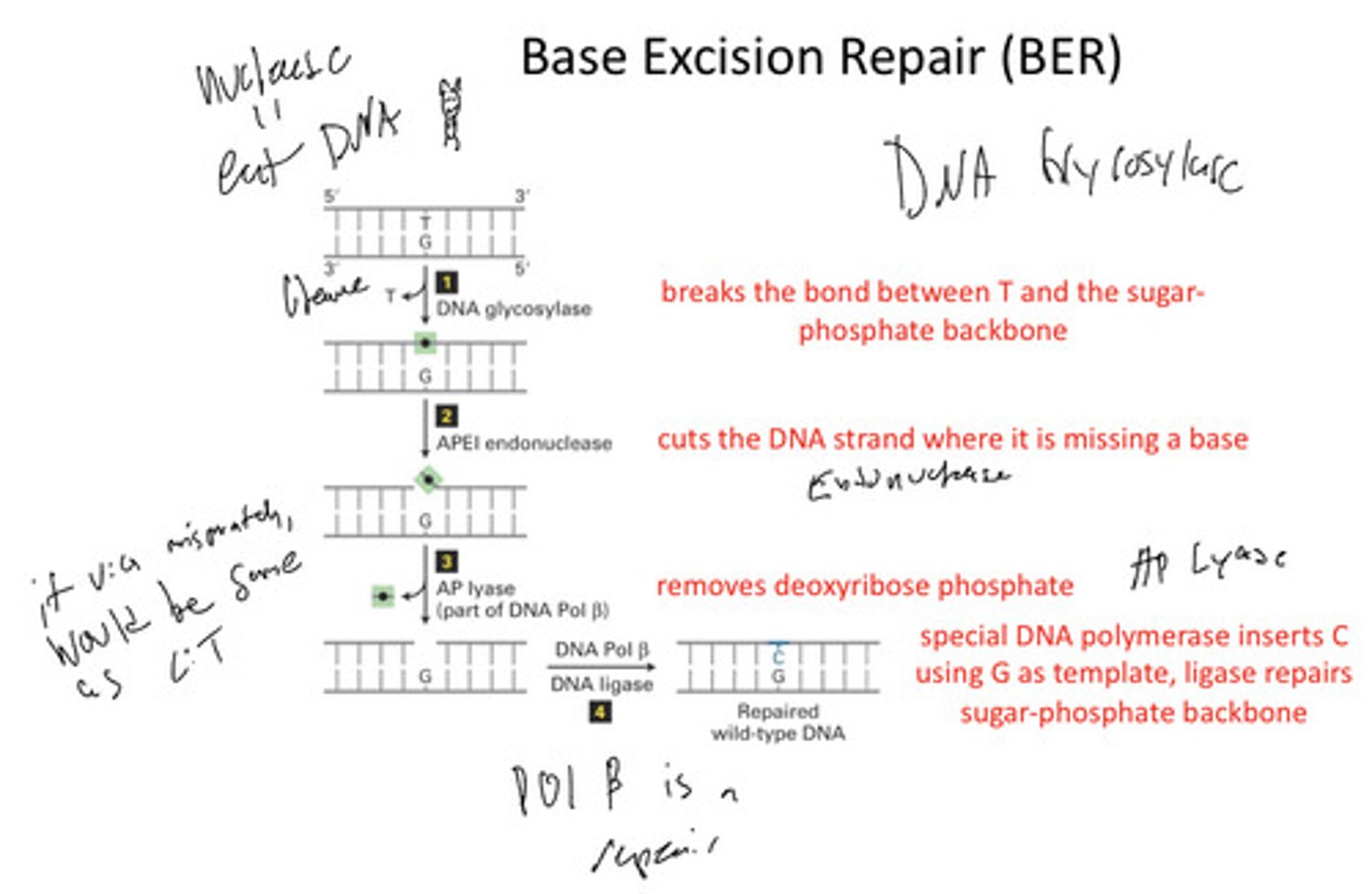
Base Excision Repair (BER) steps
1. Recognition by glycosylase
2. Removal of base from sugar creates an apyrimidinic or apurinic site (abasic)
3. APEI endonuclease nick on phosphodiester bond
4. Phosphodiesterase removes the deoxyribose sugar
5. DNA pol beta adds the new nucleotide
6. Last phosphodiester bond made by ligase
Mismatch Excision Repair (MER)
Recognize mismatch on daughter strand; triggers binding of endonuclease (dimeriszed w pms2) and cuts daughter; Helicase then unwinds and exonuclease digest multiple nucleotides; poly delta replaces w correct nucleotides and ligase repairs backbone
nucleotide excision repair
A repair system that removes and then correctly replaces a damaged segment of DNA using the undamaged strand as a guide. The dna helix is distorted at this time
NER 2
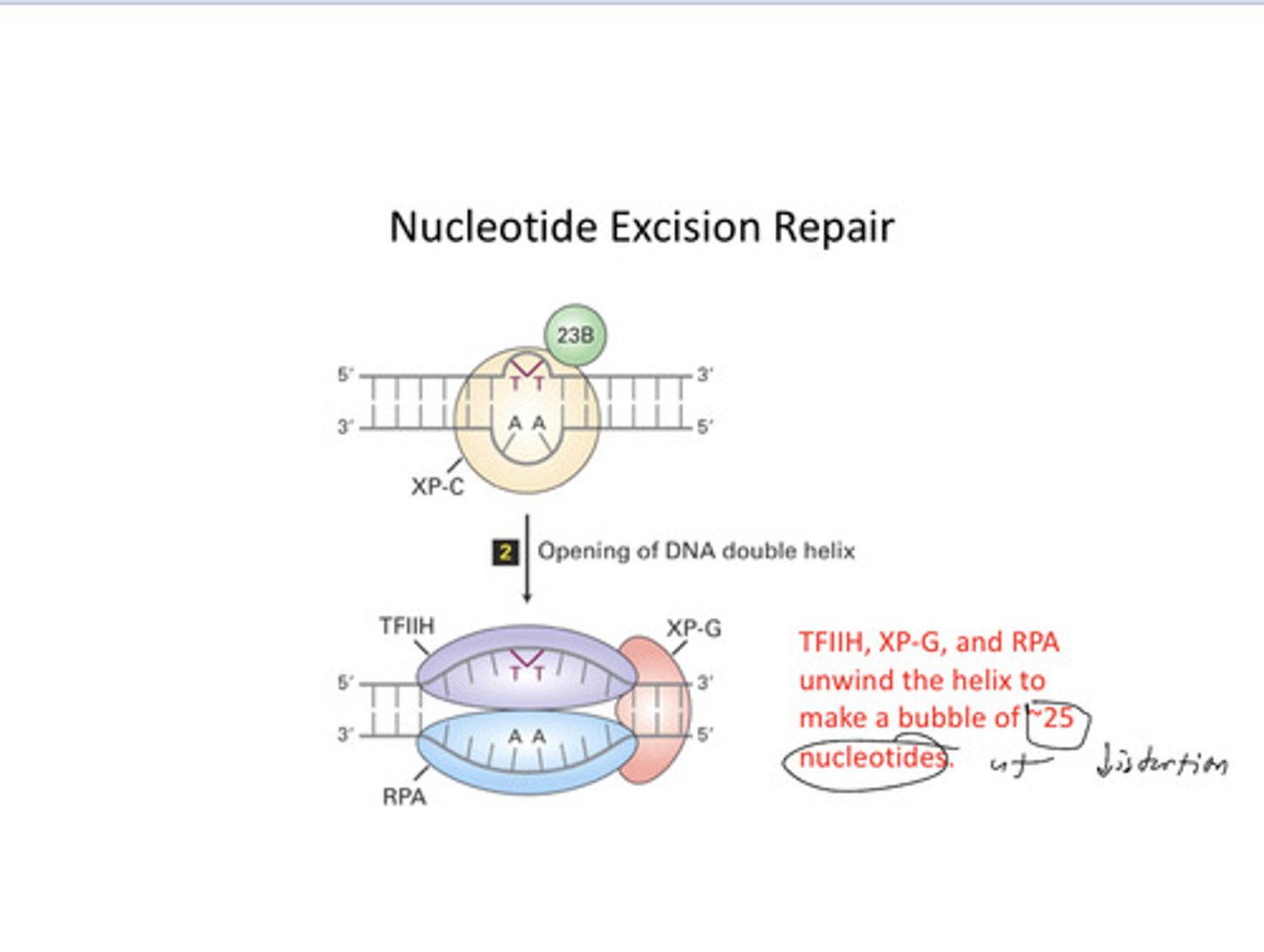
NER 3
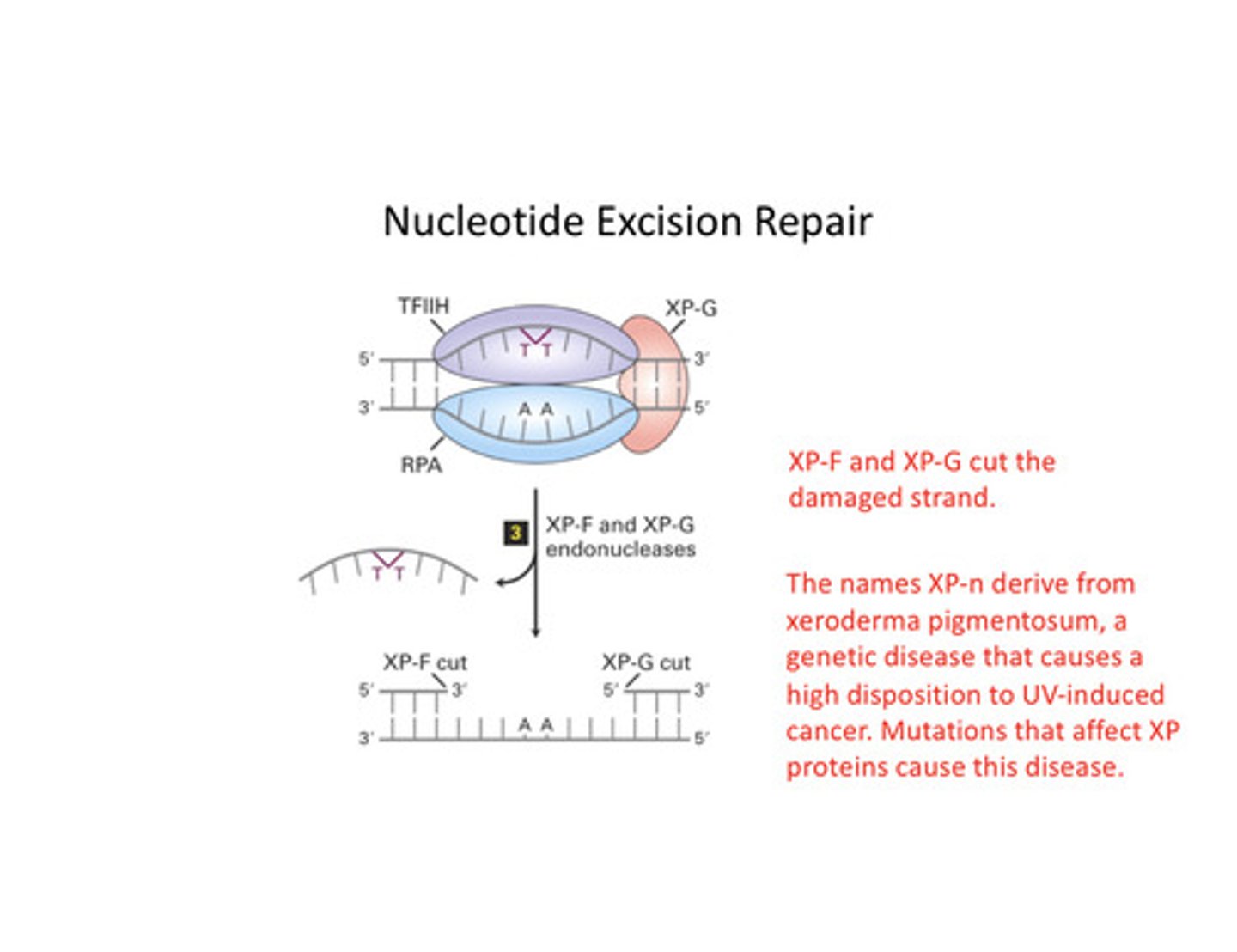
NER 4
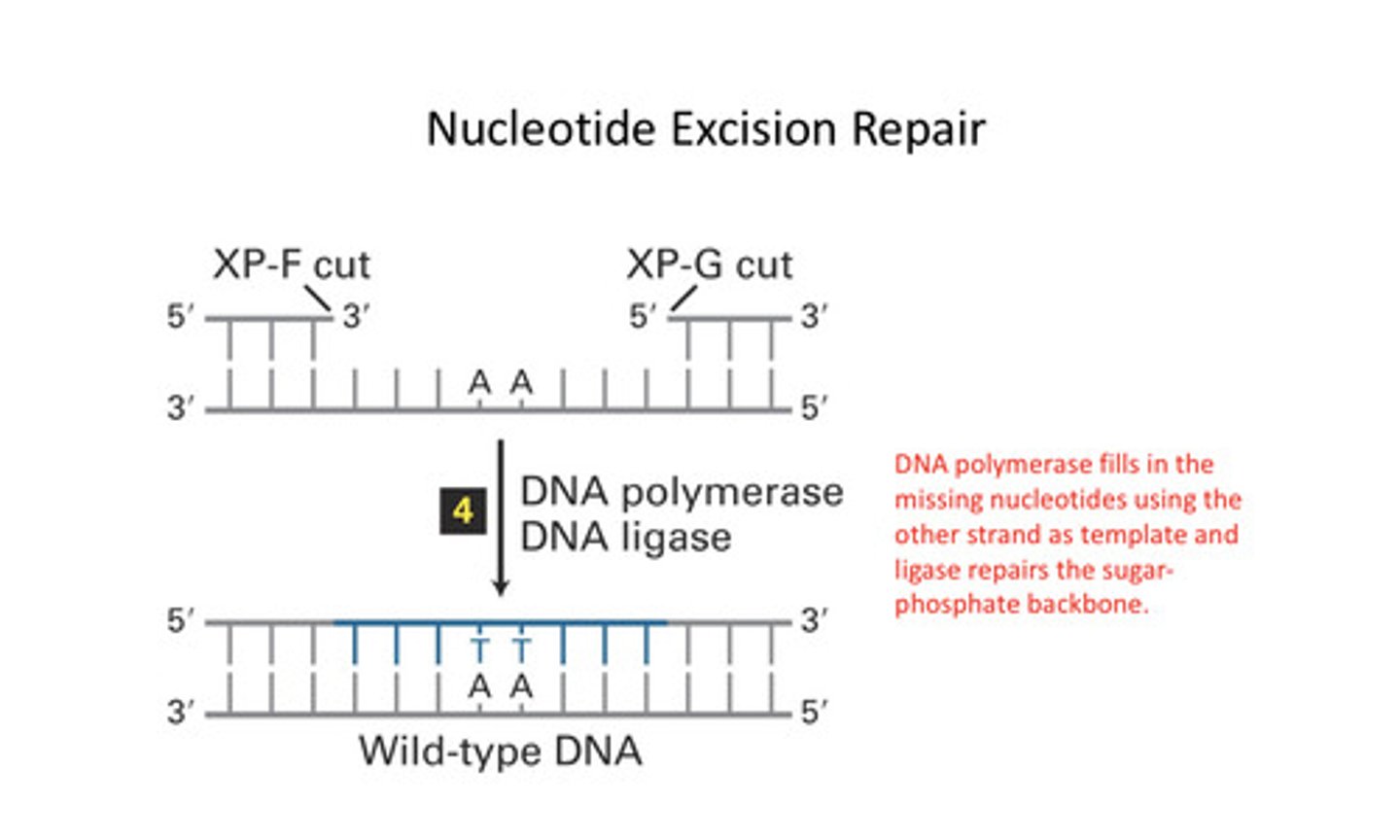
Double strand breaks are repaired by
Non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination
DNA polymerases delta and eta stall when
The reach a thymine-thiamine dimer
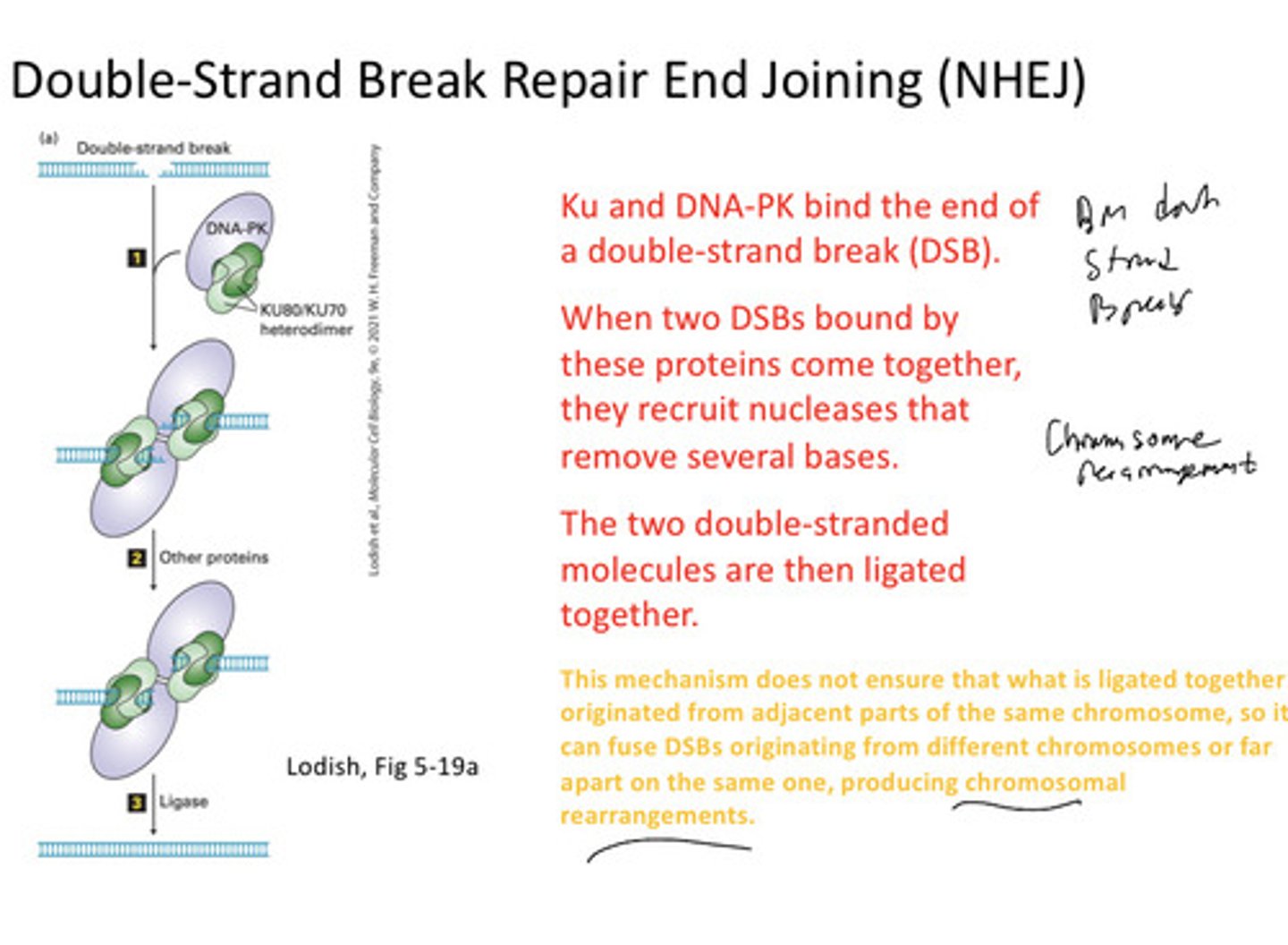
NHEJ steps
KU AND DNA-PK BIND TO THE end of a break; two DSBs bound by these proteins come together the recruit nu élevasses to cut bases; then two double strands are lighted. It ligands but it is not always the original that was present
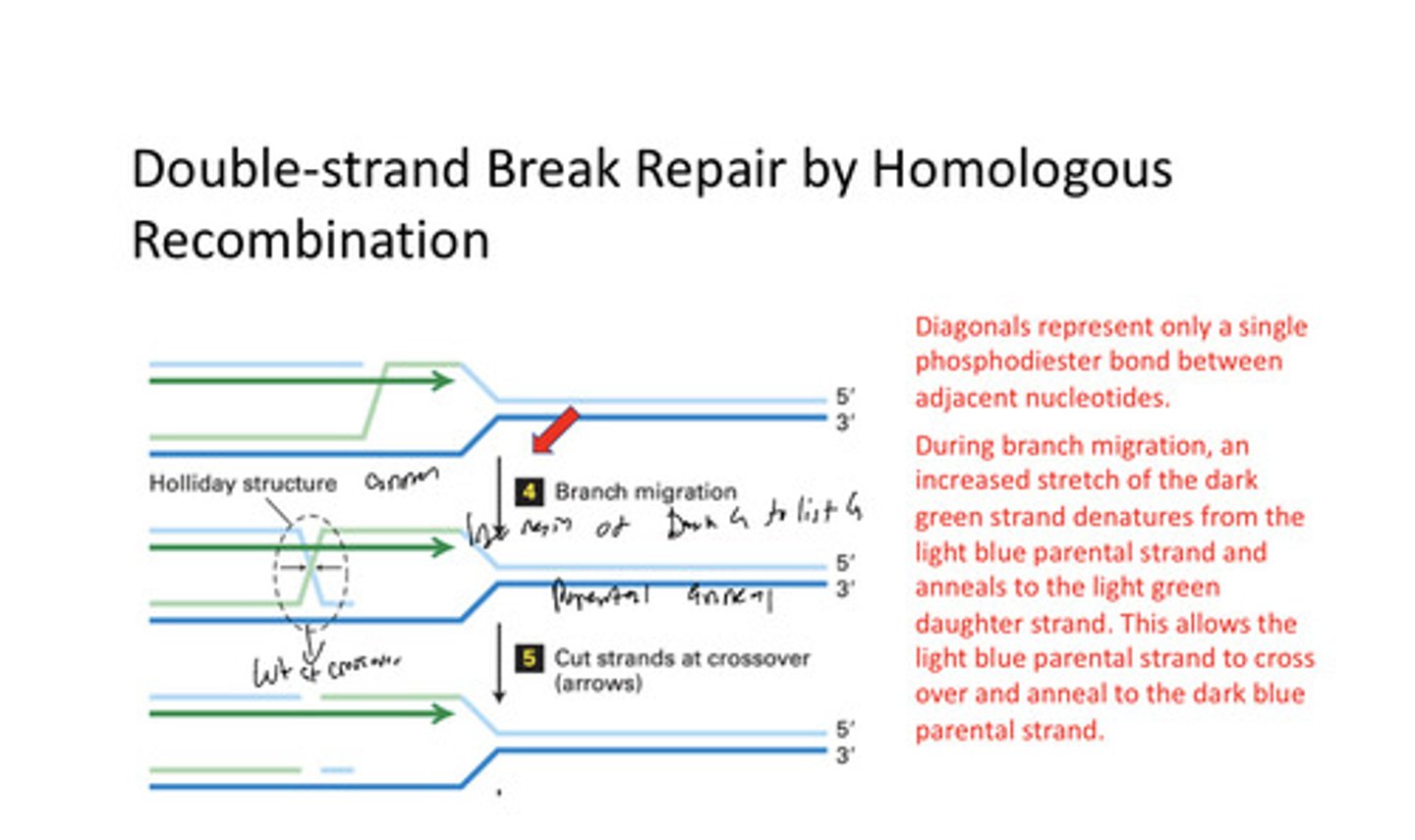
Double strand break repair by Homologus Recombonation
Replication fork collapse at break in phosphdiester backbone; 5' exonuclease cuts the parental strand while daughter of other parental strand is lighted/repaired; strand invasion occurs and daughter of other parental strand binds to the orig parental while orig daughter and 2nd parental un change; branch migration creates a Holliday structure; then there are cuts made at the crossover; ends are lighted; and rep fork is new
strand invasion
During synthesis-dependent strand annealing and meiotic recombination, the entry of the 3' end of a displaced DNA into the intact sister chromatid.
branch migration
the lateral movement of a Holliday junction
Holliday structure
In DNA recombination, an intermediate stage seen in transmission electron microscope images as an X-shaped structure showing four single-stranded DNA regions.
DNA polymerase delta
completes replication on the lagging strand
RPA (replication protein A)
Keeps the DNA template in optimal conformation for transcription. (Template could fold otherwise).
PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen)
in eukaryotes, clamps DNA pol delta and epsilon to DNA, increasing processivity
Shows No correlation between isoelectric pt and its MW
indirect immunofluorescence
An immunofluorescent diagnostic technique in which the fluorochrome is not attached to the primary antibody that recognises the target antigen, but to a secondary antibody that binds the primary antibody.
Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
is a popular technique to identify physiologically relevant protein-protein interactions by using target protein-specific antibodies to indirectly capture proteins that are bound to a specific target protein
PCR steps
denaturation, annealing, extension
Oligonucleotides
short nucleotide sequences that are used in PCR and as complementary genetic probes to identify specific gene sequences...50 or less
after the PCR reaction, how do you actually visualize the DNA?
do agarose gel eletrophoresis to separate the different sizes of the PCR products (sizes id the the fragment)
dideoxy chain termination method (Sanger method)
a DNA sequencing method in which target DNA is denatured and annealed to an oligonucleotide primer, which is then extended by DNA polymerase using a mixture of deoxynucleotide triphosphates (normal dNTPs) and chain-terminating dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs)
dideoxynucleotide
individual monomer of DNA that is missing a hydroxyl group (-OH)...terminates replication (poly epsilon can't continue)
limits of sanger sequencing
300-500 nucleotides max, hard to tell differences between few nucleotide diffs 330 vs 335
Linkers
Parts of dna cut, linked to a linker then bound, then can color nucleotide bases and then the bases will match which shows what is in teh strand and then color is washed but a computer can recognize it
New sequences
Skip PCR
Nanopore sequencing
Method of sequencing DNA that involves drawing individual strands of DNA through tiny sub-microscopic holes called nanopores and reading the DNA sequence one base pair at a time...portable
homologus recombination repair
BRCA 1 involved, and there is a fixing of Honolulu's pairs done by recombi potentially Holliday structures
EcoRI and HindIII are
restriction endonucleases
Vector DNA molecule
a', bind to sticky ends
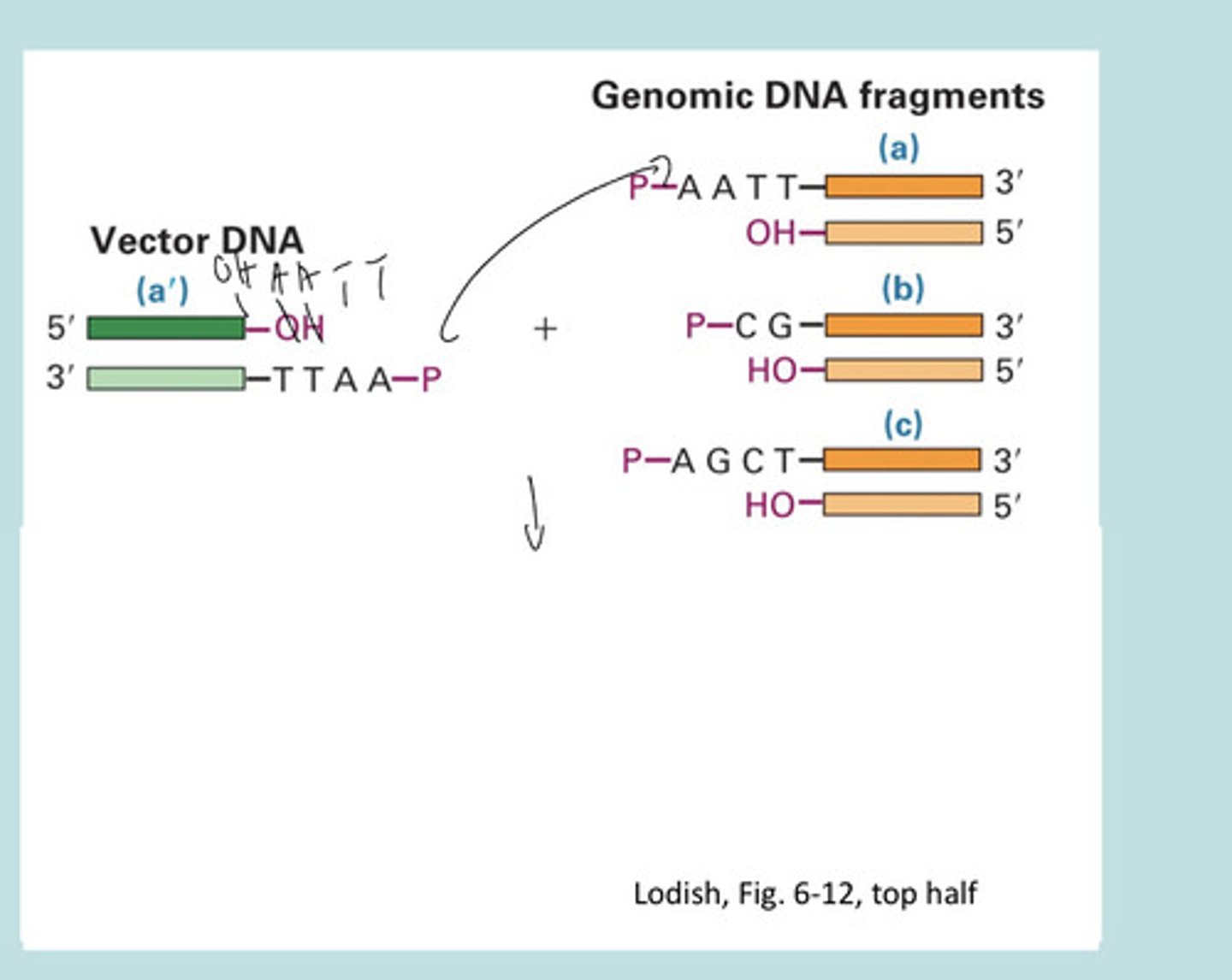
polylinker
synthetic DNA element in a cloning vector with unique restriction sites used for insertion of foreign DNA
Plasmid Vector + DNA Fragment ^enzymatically insert dna into plasmid vector —>
Recombinant plasmid 9circle w original sequence plus fragment)
Transformation
(genetics) modification of a cell or bacterium by the uptake and incorporation of exogenous DNA (can be synthetic or natural)
synthetic transformation
Heating up the membrane to break the membrane to allow for the plasmid to be absorbed by the cell
Cells that don't transform with plasmids...
Cells that intake plasmids...
Die!
Replicate their plasmids!
Then the cell multiplies so they can be tested ( many diff # of plasmids within cell)
Genomic libraires
NO longer used, shows chromosomal DNA
reverse transcriptase (RT)
The enzyme possessed by retroviruses that carries out the reversion of RNA to DNA—a form of reverse transcription.
complementary DNA (cDNA)
a complementary, single-stranded, DNA molecule to another mRNA or DNA; composed by mRNA via reverse transcriptase
cDNA reps population of mRNA that was present in sample used
Microarray and in situ hybridization techniques
MRNA expression, co-regulation, and localization
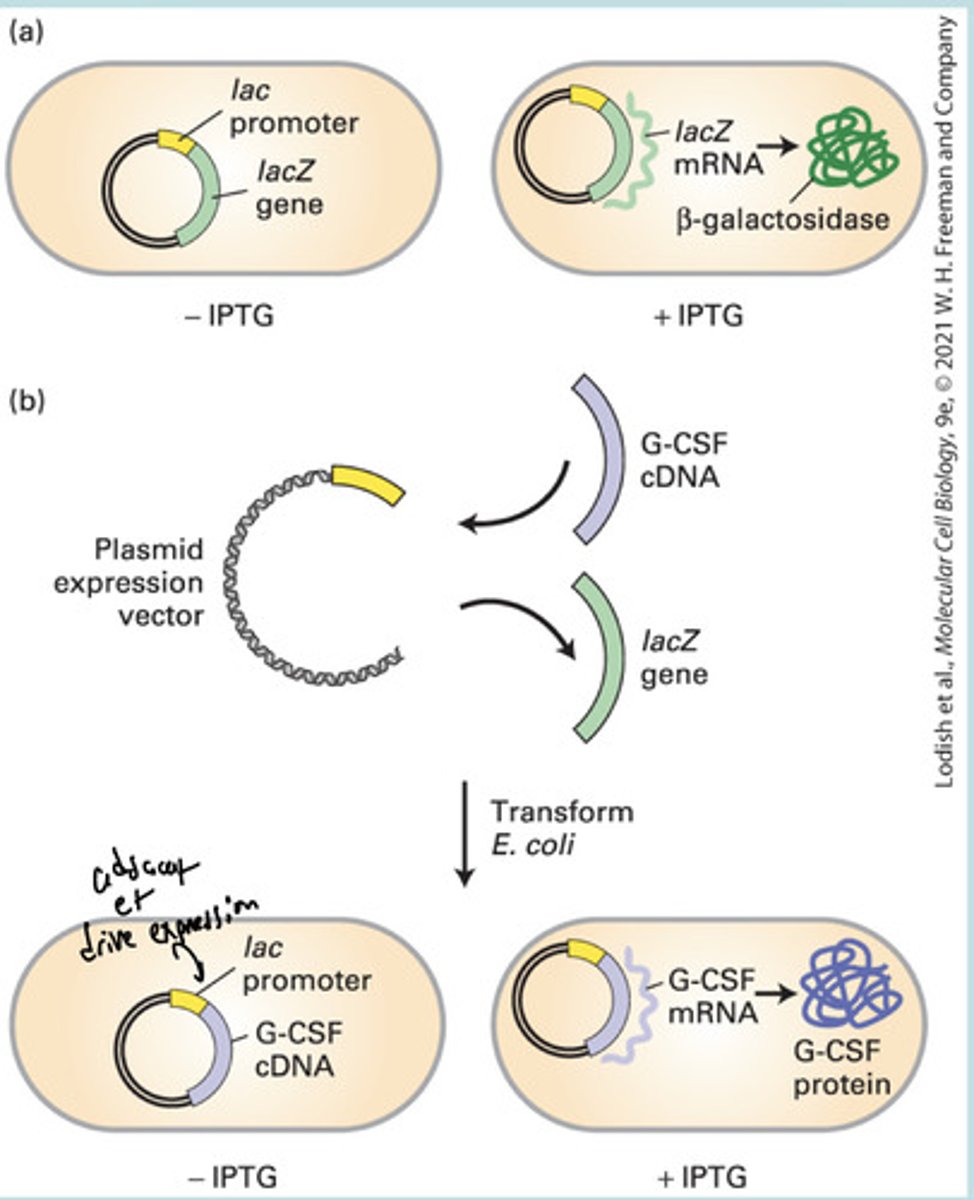
Recombinant Dna expression vectors enable...
Regulated expression of exogenous genes and production of proteins in prokaryotic et eukaryotic cells
Microarray analysis
Simultaneously measures levels of many mRNAs
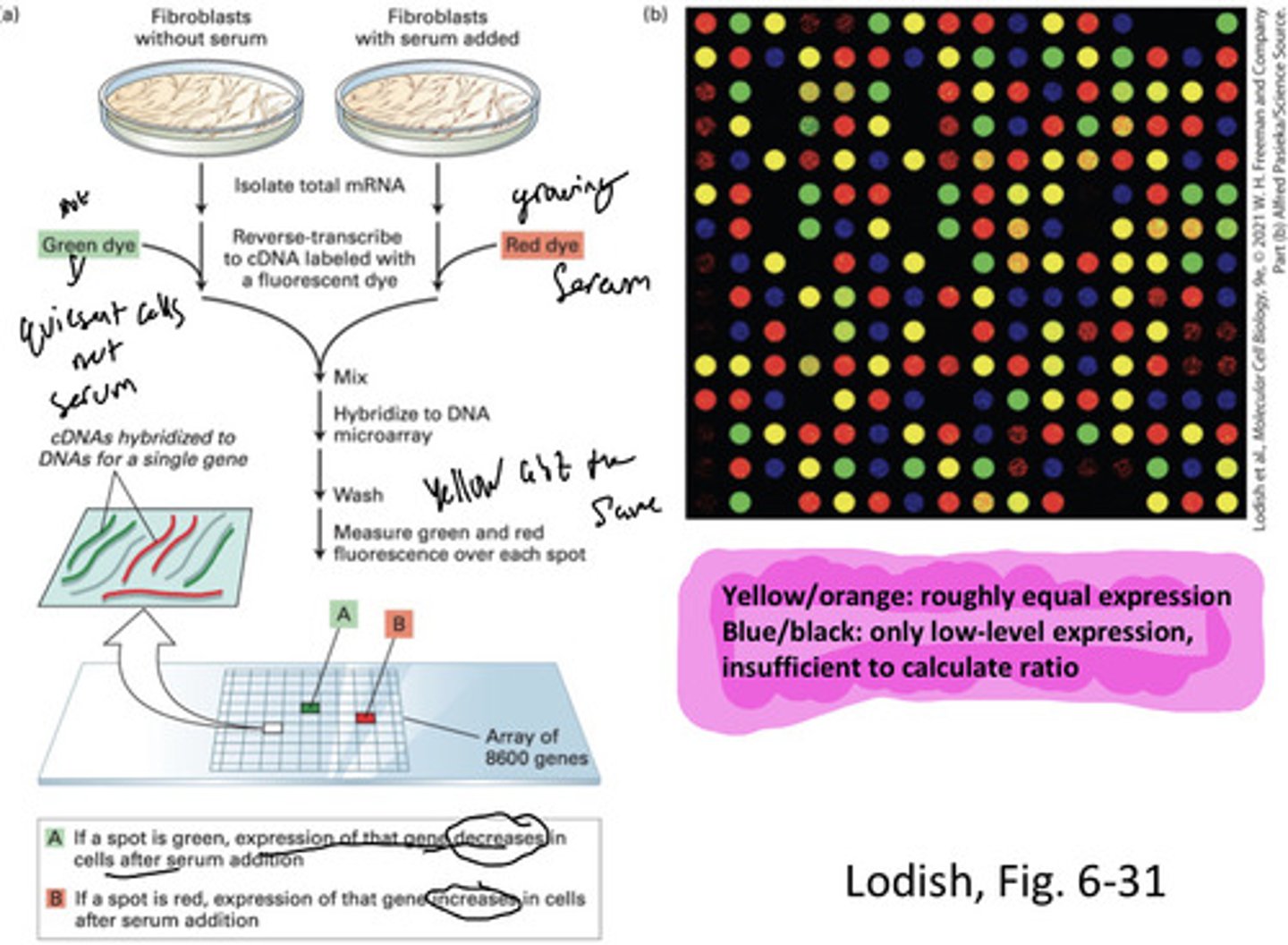
Cluster analysis can identify...
Coordinately regulated genes
inducible promoter
a promoter that functions only under special circumstances, responds to a signal (ex. Inducible alcohol promoter)
transient transfection
the introduction of DNA (plasmid) into cells for a short duration
stable transfection (transformation)
All are transfected; Called a cell-line; protein is expressed from cDNA integrated into the host chromosome; random insertion
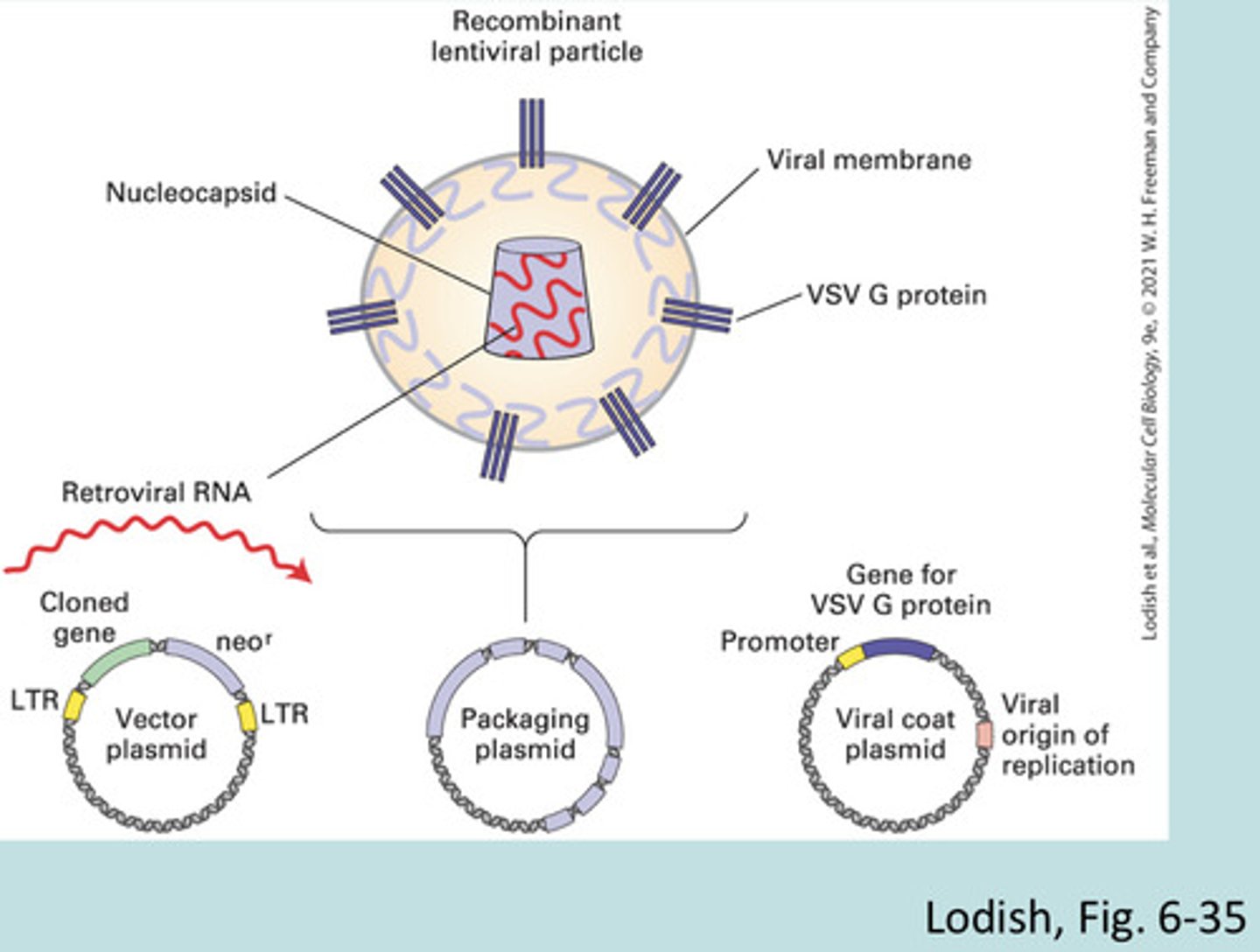
Retroviral vectors
integrate cloned genes into the DNA of the host cell
3278 species represents only around .2% of animals
Largest Sequenced genome is from the Australian lungfish Xiphophorus!! 43Gb, 14x human genome...many tarnsposable elements
transient transfection
the introduction of DNA (plasmid) into cells for a short duration, involves an origin of replication
stable transfection
Plasmid stably integrated into a chromosome is selected by drug resistance gene (genomic integration)
control region
Region of an operon which is composed of promotors and operators; upstream, don't end up in mRNA
Simple transcription unit
exons of gene, control regions, introns, splice sites, poly(A) site, Cap site
Poly A site
a site in the RNA transcript that is about 10-30 nucleotides downstream of the poly (A) consensus sequence AAUAAA
open reading frame (ORF)
AUG followed by a number of codons and a stop codon in the same reading frame
BLAST
Makes best possible alignment between two or more sequences (protein)
Difference in genome size
Comes from differing Amy's of non coding rna, many eukaryotes have similar numbers of proteins
gene density
In an organism's genome, the ratio of the number of genes to genome size in millions of base pairs.
Greater in lower euk than in more complex euks
Orthologs
homologous genes separated by a speciation event
Paralogs
homologous genes within a single species
solitary or single copy genes
25-50% of protein coding genes are represented once in the genome
Remainders
Occur qs duplicates or in multiple copies
Simple sequence repeats (SSRs)
1-10 base sequence repeated 15-100 times in tandem, in introns
Micro satellite DNA
Minsatellite dna
Short séquences can be generated by backward slippage
Become spathogenic
Mini satellite DNA
Repeat units 14 to 100 bp
20-50 tandem repeats
Arrays of 1 to 5 kb
Often in centromeres and telomeres
Determine paternity and can be used as evidence abt criminal
Retrotransposons
Transposable elements that move within a genome by means of an RNA intermediate, a transcript of the retrotransposon DNA.
DNA transposons
Mobile genetic elements that move without making an RNA intermediate.